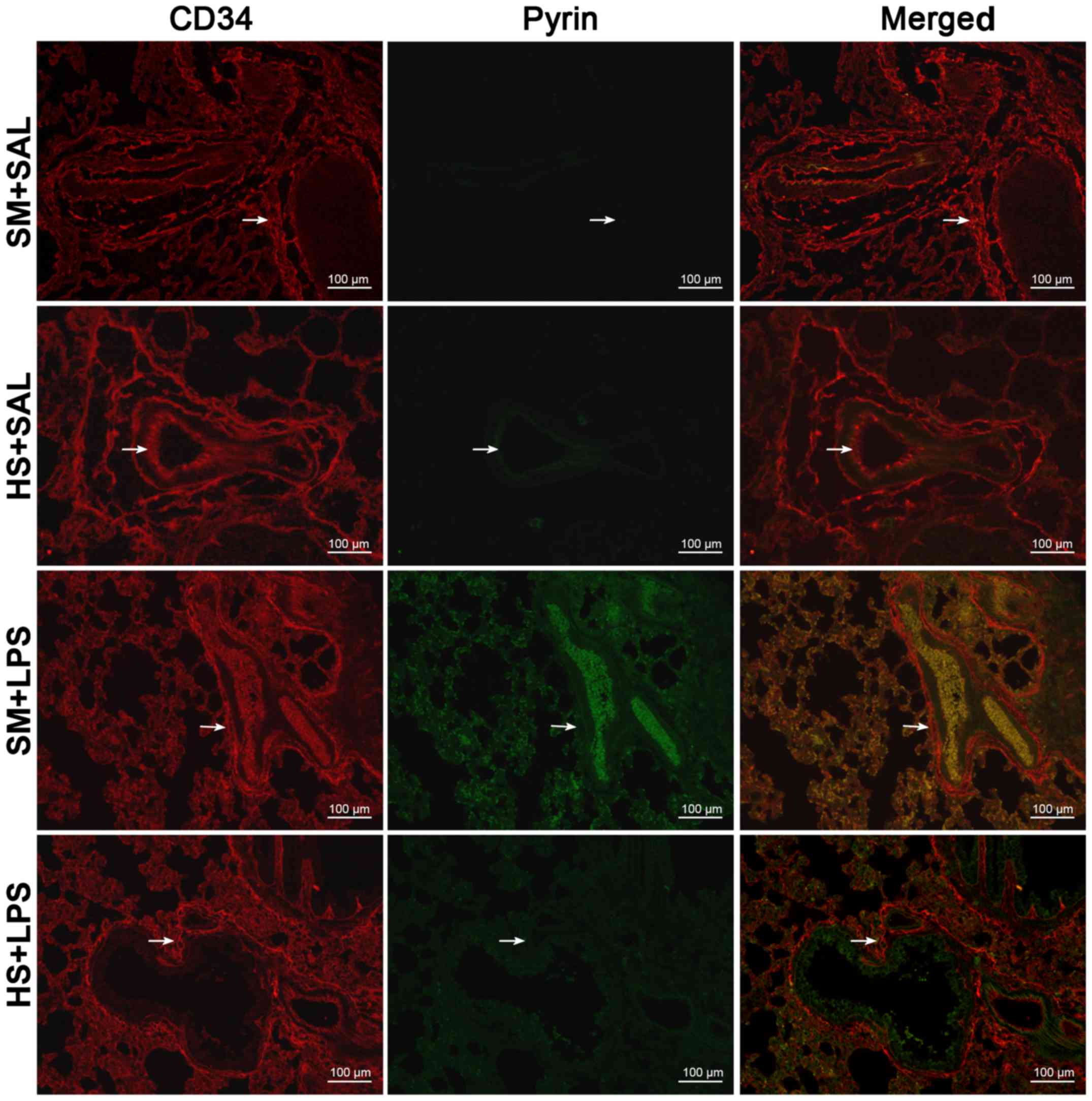
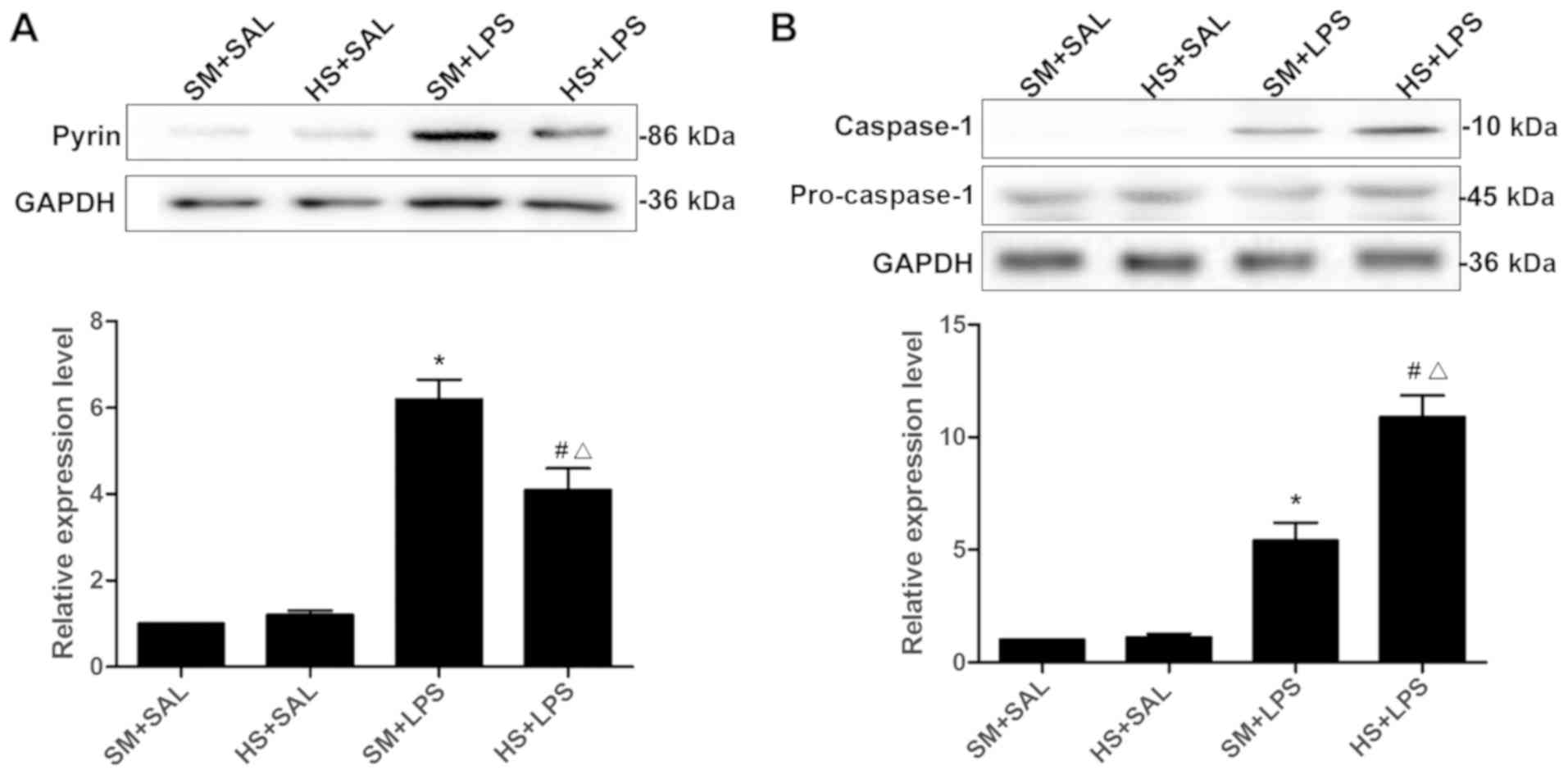
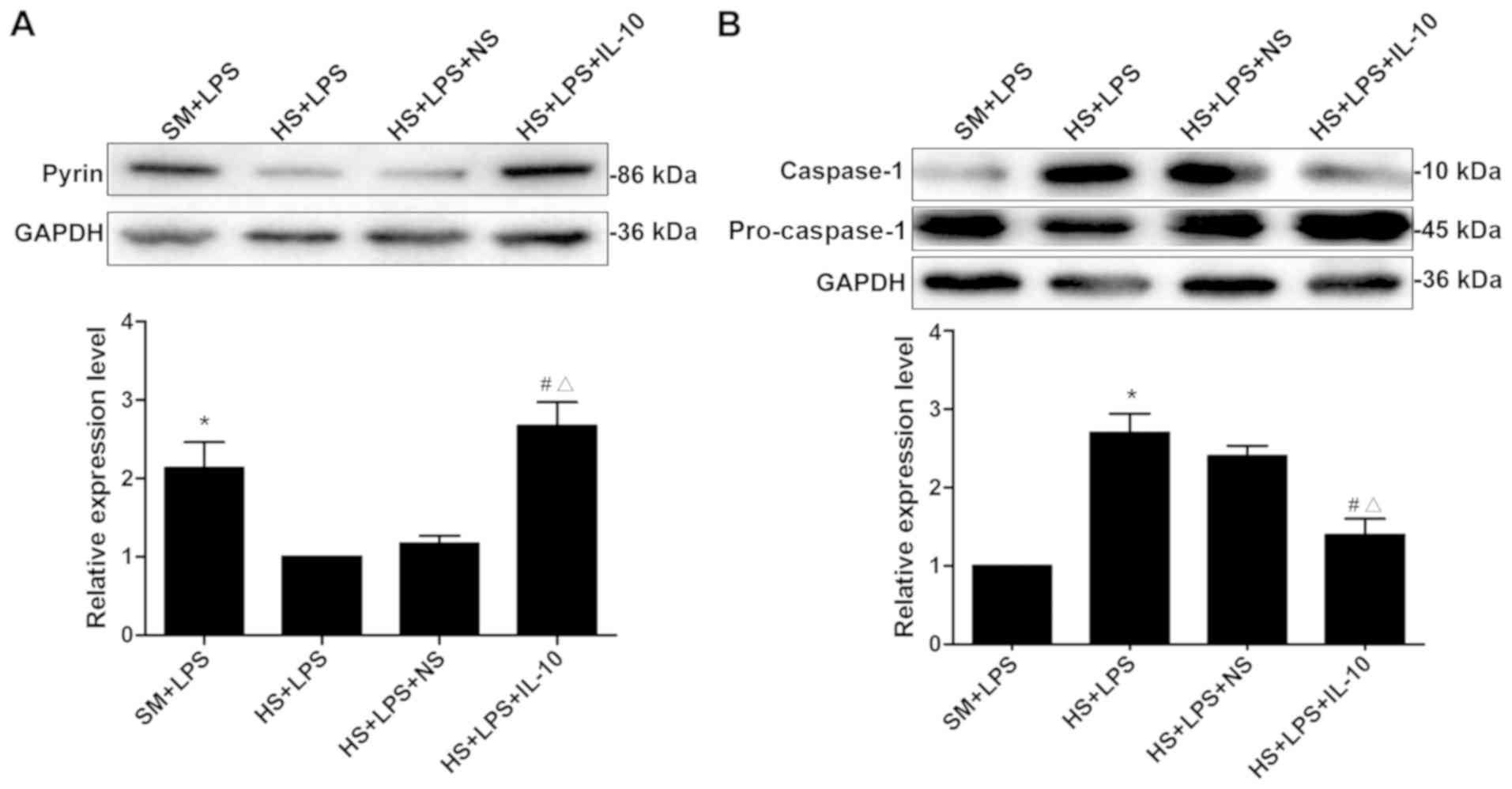
|
1
|
El-Menyar A, El-Thani A, El Rasheid Z,
Ahmad Z, Tuma M, AbdulRahman H, Parchani A, Peralta R and Latifi R:
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS): Is it preventable or
inevitable. Int J Clin Med. 3:722–730. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
van Wessem KJP and Leenen LPH: Reduction
in mortality rates of postinjury multiple organ dysfunction
syndrome: A shifting paradigm? A prospective population-based
cohort study. Shock. 49:33–38. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Anne Morrison C, Moran A, Patel S,
Vidaurre Mdel P, Carrick MM and Tweardy DJ: Increased apoptosis of
peripheral blood neutrophils is associated with reduced incidence
of infection in trauma patients with hemorrhagic shock. J Infect.
66:87–94. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moore FA, Sauaia A, Moore EE, Haenel JB,
Burch JM and Lezotte DC: Postinjury multiple organ failure: A
bimodal phenomenon. J Trauma. 40:501–512. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Minei JP, Cuschieri J, Sperry J, Moore EE,
West MA, Harbrecht BG, O'Keefe GE, Cohen MJ, Moldawer LL, Tompkins
RG, et al: The changing pattern and implications of multiple organ
failure after blunt injury with hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med.
40:1129–1135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Xiang M, Yuan Y, Xiao G, Zhang J,
Jiang Y, Vodovotz Y, Billiar TR, Wilson MA and Fan J: Hemorrhagic
shock augments lung endothelial cell activation: Role of temporal
alterations of TLR4 and TLR2. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp
Physiol. 297:R1670–R1680. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chae JJ, Wood G, Richard K, Jaffe H,
Colburn NT, Masters SL, Gumucio DL, Shoham NG and Kastner DL: The
familial Mediterranean fever protein, pyrin, is cleaved by
caspase-1 and activates NF-kappaB through its N-terminal fragment.
Blood. 112:1794–1803. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chae JJ, Komarow HD, Cheng J, Wood G,
Raben N, Liu PP and Kastner DL: Targeted disruption of pyrin, the
FMF protein, causes heightened sensitivity to endotoxin and a
defect in macrophage apoptosis. Mol Cell. 11:591–604. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He X, Qian Y, Li Z, Fan EK, Li Y, Wu L,
Billiar TR, Wilson MA, Shi X and Fan J: TLR4-upregulated IL-1β and
IL-1RI promote alveolar macrophage pyroptosis and lung inflammation
through an autocrine mechanism. Sci Rep. 6:316632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martinon F, Burns K and Tschopp J: The
inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of
inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell.
10:417–426. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suzuki T, Franchi L, Toma C, Ashida H,
Ogawa M, Yoshikawa Y, Mimuro H, Inohara N, Sasakawa C and Nuñez G:
Differential regulation of caspase-1 activation, pyroptosis, and
autophagy via Ipaf and ASC in Shigella-infected macrophages. PLoS
Pathog. 3:e1112007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Welborn BM III, Moldawer LL, Seeger JM,
Minter RM and Huber TS: Role of endogenous interleukin-10 in local
and distant organ injury after visceral ischemia-reperfusion.
Shock. 20:35–40. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Molthen RC: A simple, inexpensive, and
effective light-carrying laryngoscopic blade for orotracheal
intubation of rats. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 45:88–93.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu X, Hu H, Li Z, Lin R, Mao J and Chen
L: Gua Lou Gui Zhi decoction attenuates post-stroke spasticity via
the modulation of GABAB receptors. Mol Med Rep. 12:5957–5962. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou R, Hu DY, Liu LM and Zhou XW:
Protective effects of apocynin on ‘two-hit’ injury induced by
hemorrhagic shock and lipopolysaccharide. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
23:1023–1028. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ulich TR, Fann MJ, Patterson PH, Williams
JH, Samal B, Del CJ, Yin S, Guo K and Renick DG: Intratracheal
injection of LPS and cytokines. V. LPS induces expression of LIF
and LIF inhibits acute inflammation. Am J Physiol. 267:L442–L446.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tawadros PS, Powers KA, Yang I, Becker DA,
Ginsberg MD, Szaszi K, Kapus A and Rotstein OD: Stilbazulenyl
nitrone decreases oxidative stress and reduces lung injury after
hemorrhagic shock/resuscitation and LPS. Antioxid Redox Signal.
9:1971–1977. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Testa JE, Chrastina A, Oh P, Li Y,
Witkiewicz H, Czarny M, Buss T and Schnitzer JE: Immunotargeting
and cloning of two CD34 variants exhibiting restricted expression
in adult rat endothelia in vivo. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 297:L251–L262. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feldmeyer L, Keller M, Niklaus G, Hohl D,
Werner S and Beer HD: The inflammasome mediates UVB-induced
activation and secretion of interleukin-1beta by keratinocytes.
Curr Biol. 17:1140–1145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Martinon F, Hofmann K and Tschopp J: The
pyrin domain: A possible member of the death domain-fold family
implicated in apoptosis and inflammation. Curr Biol. 11:R118–R120.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chae J, Cho YH, Lee GS, Cheng J, Liu PP,
Feigenbaum L, Katz SI and Kastner DL: Gain-of-function Pyrin
mutations induce NLRP3 protein-independent interleukin-1β
activation and severe autoinflammation in mice. Immunity.
34:755–768. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Iyer SS and Cheng G: Role of interleukin
10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune
disease. Crit Rev Immunol. 32:23–63. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lo C, Fu M and Cryer HG: Interleukin 10
inhibits alveolar macrophage production of inflammatory mediators
involved in adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Surg Res.
79:179–184. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Armstrong L and Millar AB: Relative
production of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 10 in
adult respiratory distress syndrome. Thorax. 52:442–446. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Khadaroo RG, Fan J, Powers KA, Fann B,
Kapus A and Rotstein OD: Impaired induction of IL-10 expression in
the lung following hemorrhagic shock. Shock. 22:333–339. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yeh FL, Shen HD and Fang RH: Deficient
transforming growth factor beta and interleukin-10 responses
contribute to the septic death of burned patients. Burns.
28:631–637. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kusske AM, Rongione AJ, Ashley SW,
McFadden DW and Reber HA: Interleukin-10 prevents death in lethal
necrotizing pancreatitis in mice. Surgery. 120:284–289. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cruz CM, Rinna A, Forman HJ, Ventura AL,
Persechini PM and Ojcius DM: ATP activates a reactive oxygen
species-dependent oxidative stress response and secretion of
proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages. J Biol Chem.
282:2871–2879. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Halle A, Hornung V, Petzold GC, Stewart
CR, Monks BG, Reinheckel T, Fitzgerald KA, Latz E, Moore KJ and
Golenbock DT: The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate
immune response to amyloid-beta. Nat Immunol. 9:857–865. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Watanabe H, Gaide O, Pétrilli V, Martinon
F, Contassot E, Roques S, Kummer JA, Tschopp J and French LE:
Activation of the IL-1beta-processing inflammasome is involved in
contact hypersensitivity. J Invest Dermatol. 127:1956–1963. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|