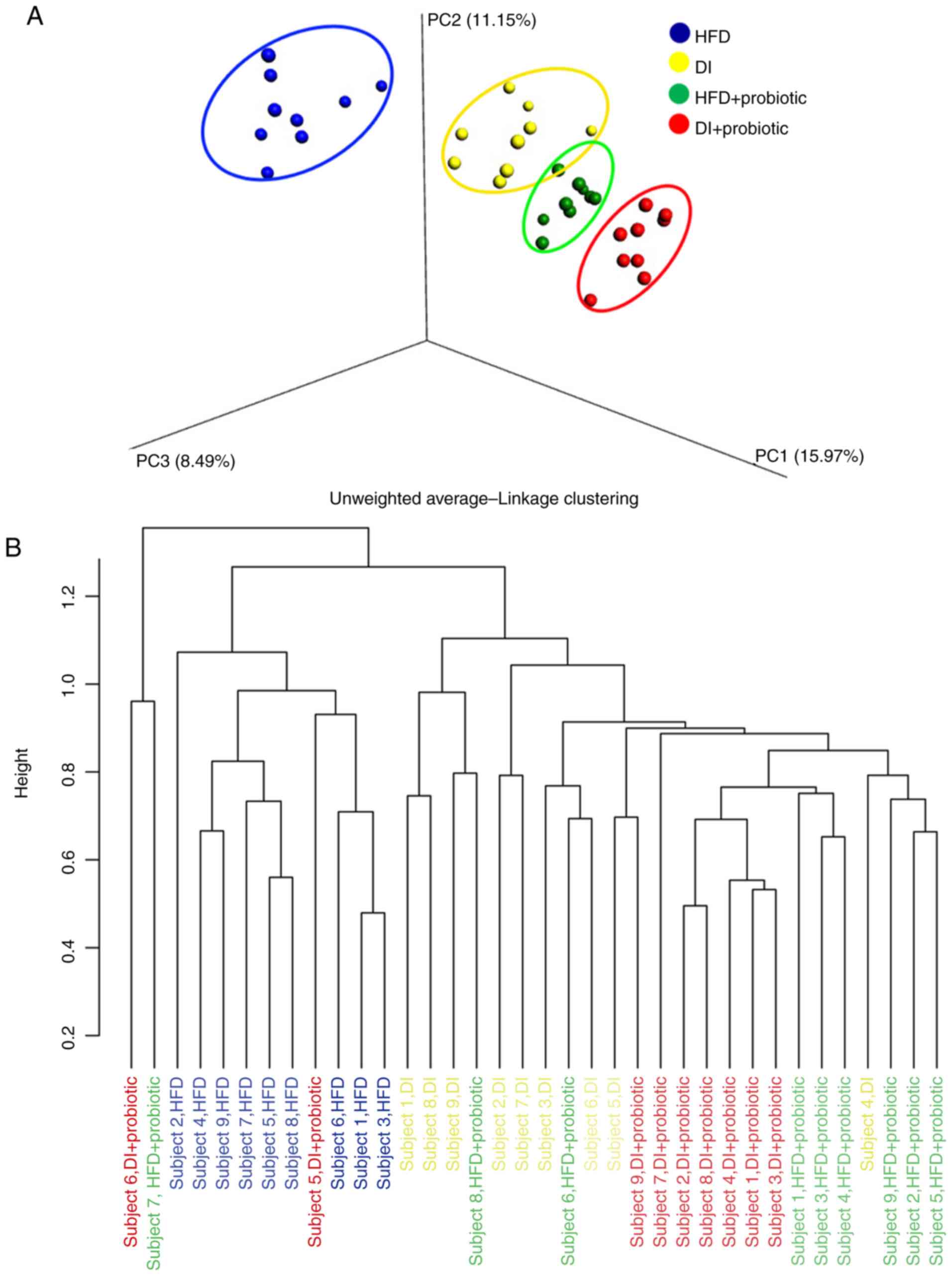
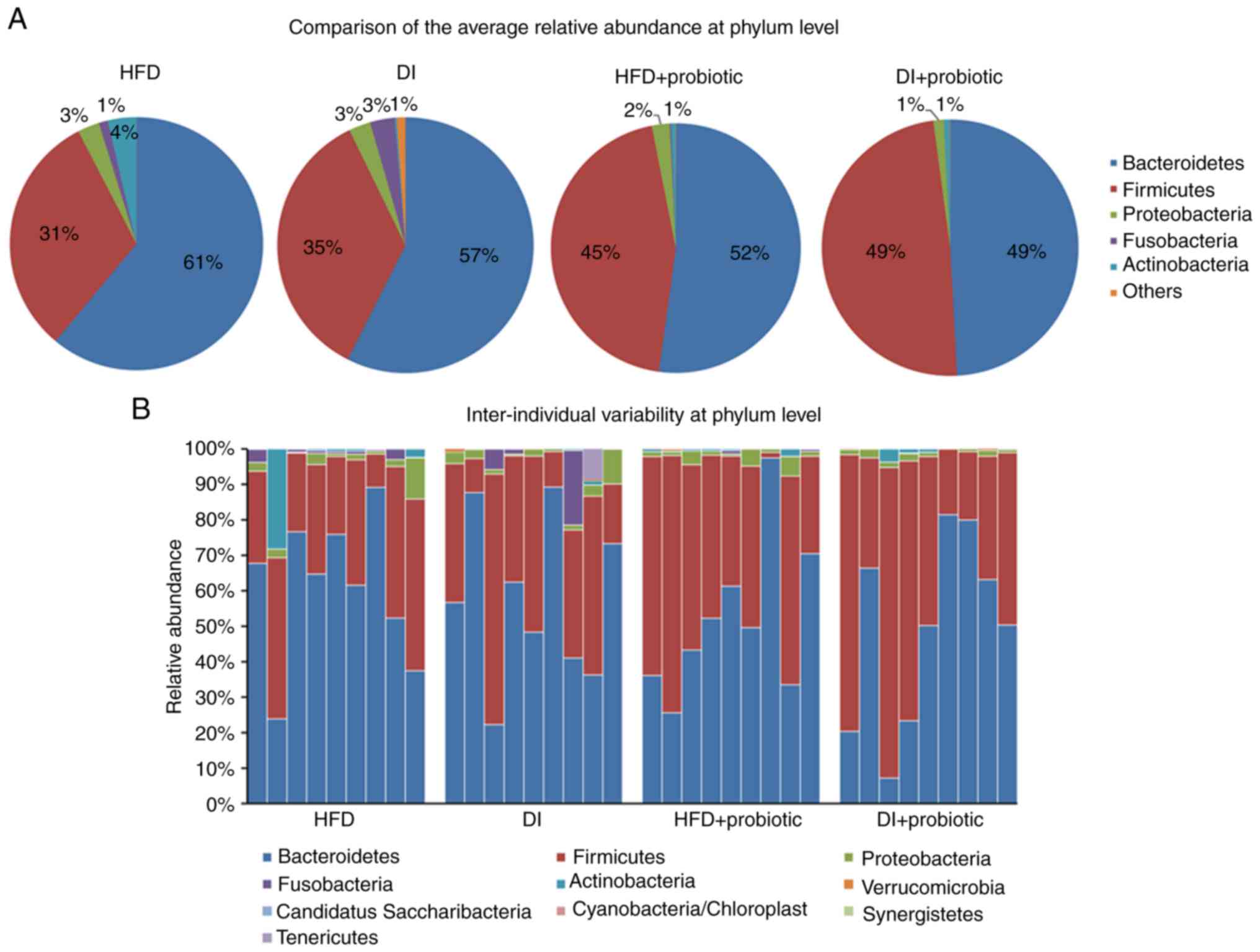
|
1
|
Zoetendal EG, Rajilic-Stojanovic M and de
Vos WM: High-throughput diversity and functionality analysis of the
gastrointestinal tract microbiota. Gut. 57:1605–1615. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zoetendal EG, Raes J, van den Bogert B,
Arumugam M, Booijink CC, Troost FJ, Bork P, Wels M, de Vos WM and
Kleerebezem M: The human small intestinal microbiota is driven by
rapid uptake and conversion of simple carbohydrates. ISME J.
6:1415–1426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hooper LV, Midtvedt T and Gordon JI: How
host-microbial interactions shape the nutrient environment of the
mammalian intestine. Annu Rev Nutr. 22:283–307. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Backhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson
DA and Gordon JI: Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine.
Science. 307:1915–1920. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf
KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T, et al: A
human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic
sequencing. Nature. 464:59–65. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin CS, Chang CJ, Lu CC, Martel J, Ojcius
DM, Ko YF, Young JD and Lai HC: Impact of the gut microbiota,
prebiotics, and probiotics on human health and disease. Biomed J.
37:259–268. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brown K, DeCoffe D, Molcan E and Gibson
DL: Diet-induced dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota and the
effects on immunity and disease. Nutrients. 4:1095–1119. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abu-Shanab A and Quigley EM: The role of
the gut microbiota in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:691–701. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chiu CC, Ching YH, Li YP, Liu JY, Huang
YT, Huang YW, Yang SS, Huang WC and Chuang HL: Nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease is exacerbated in High-Fat Diet-Fed gnotobiotic mice
by colonization with the Gut Microbiota from patients with
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nutrients. 9:E12202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Federico A, Dallio M, Caprio GG, Ormando
VM and Loguercio C: Gut microbiota and the liver. Minerva
Gastroenterol Dietol. 63:385–398. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Budden KF, Gellatly SL, Wood DL, Cooper
MA, Morrison M, Hugenholtz P and Hansbro PM: Emerging pathogenic
links between microbiota and the gut-lung axis. Nat Rev Microbiol.
15:55–63. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bercik P: The microbiota-gut-brain axis:
Learning from intestinal bacteria? Gut. 60:288–289. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Collins SM and Bercik P: Gut microbiota:
Intestinal bacteria influence brain activity in healthy humans. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:326–327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bienenstock J, Kunze W and Forsythe P:
Microbiota and the gut-brain axis. Nutr Rev. 73 (Suppl 1):S28–S31.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dinan TG and Cryan JF: Gut-brain axis in
2016: Brain-gut-microbiota axis-mood, metabolism and behaviour. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:69–70. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Arumugam M, Raes J, Pelletier E, Le
Paslier D, Yamada T, Mende DR, Fernandes GR, Tap J, Bruls T, Batto
JM, et al: Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature.
473:174–180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K,
Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R,
et al: Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial
enterotypes. Science. 334:105–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bushman FD, Lewis JD and Wu GD: Diet, gut
enterotypes and health: Is there a link? Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop
Ser. 77:65–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim KA, Gu W, Lee IA, Joh EH and Kim DH:
High fat diet-induced gut microbiota exacerbates inflammation and
obesity in mice via the TLR4 signaling pathway. PLoS One.
7:e477132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN,
Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Varma Y,
Fischbach MA, et al: Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human
gut microbiome. Nature. 505:559–563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schulz MD, Atay C, Heringer J, Romrig FK,
Schwitalla S, Aydin B, Ziegler PK, Varga J, Reindl W, Pommerenke C,
et al: High-fat-diet-mediated dysbiosis promotes intestinal
carcinogenesis independently of obesity. Nature. 514:508–512. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ou JH, Ridlon JM, DeLany JP, Vipperla K,
Newton K and O'Keefe SJ: Obesity and colon cancer risk: Is it the
Fat? Gastroenterology. 142:S3132012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gerritsen J, Smidt H, Rijkers GT and de
Vos WM: Intestinal microbiota in human health and disease: The
impact of probiotics. Genes Nutr. 6:209–240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu X, Wang T, Li W, Jin F and Wang L:
Effects of NS Lactobacillus strains on lipid metabolism of rats fed
a high-cholesterol diet. Lipids Health Dis. 12:672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liboredo JC, Anastacio LR, Peluzio Mdo C,
Valente FX, Penido LC, Nicoli JR and Correia MI: Effect of
probiotics on the development of dimethylhydrazine-induced
preneoplastic lesions in the mice colon. Acta Cir Bras. 28:367–372.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bertkova I, Hijova E, Chmelarova A,
Mojzisova G, Petrasova D, Strojny L, Bomba A and Zitnan R: The
effect of probiotic microorganisms and bioactive compounds on
chemically induced carcinogenesis in rats. Neoplasma. 57:422–428.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang W, Shi LP, Shi L and Xu L: Efficacy
of probiotics on the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 57:101–106. 2018.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fan YJ, Chen SJ, Yu YC, Si JM and Liu B: A
probiotic treatment containing Lactobacillus, bifidobacterium and
enterococcus improves IBS symptoms in an open label trial. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 7:987–991. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang Y, Xia Y, Chen H, Hong L, Feng J,
Yang J, Yang Z, Shi C, Wu W, Gao R, et al: The effect of
perioperative probiotics treatment for colorectal cancer:
Short-term outcomes of a randomized controlled trial. Oncotarget.
7:8432–8440. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang S, Xu L, Zhang D and Wu Z: Effect of
probiotics on small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients
with gastric and colorectal cancer. Turk J Gastroenterol.
27:227–232. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Knights D, Ward TL, McKinlay CE, Miller H,
Gonzalez A, McDonald D and Knight R: Rethinking ‘enterotypes’. Cell
Host Microbe. 16:433–437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xia F, Chen J, Fung WK and Li H: A
logistic normal multinomial regression model for microbiome
compositional data analysis. Biometrics. 69:1053–1063. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qian L, Gao R, Hong L, Pan C, Li H, Huang
J and Qin H: Association analysis of dietary habits with gut
microbiota of a native Chinese community. Exp Ther Med. 16:856–866.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wan Y, Wang F, Yuan J, Li J, Jiang D,
Zhang J, Huang T, Zheng J, Mann J and Li D: Effects of
macronutrient distribution on weight and related cardiometabolic
profile in healthy non-obese Chinese: A 6-month, randomized
controlled-feeding trial. Ebiomedicine. 22:200–207. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li W and Godzik A: Cd-hit: A fast program
for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide
sequences. Bioinformatics. 22:1658–1659. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Deng W, Wang Y, Liu Z, Cheng H and Xue Y:
HemI: A toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PLoS One. 9:e1119882014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Weichselbaum E: Potential benefits of
probiotics-main findings of an in-depth review. Br J Community
Nurs. 15(110): 112–114. 2010.
|
|
38
|
Iannitti T and Palmieri B: Therapeutical
use of probiotic formulations in clinical practice. Clin Nutr.
29:701–725. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gareau MG, Sherman PM and Walker WA:
Probiotics and the gut microbiota in intestinal health and disease.
Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:503–514. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chan YK, Brar MS, Kirjavainen PV, Chen Y,
Peng J, Li D, Leung FC and El-Nezami H: High fat diet induced
atherosclerosis is accompanied with low colonic bacterial diversity
and altered abundances that correlates with plaque size, plasma
A-FABP and cholesterol: A pilot study of high fat diet and its
intervention with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) or telmisartan
in ApoE(−/-) mice. BMC Microbiol. 16:2642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kato-Kataoka A, Nishida K, Takada M, Kawai
M, Kikuchi-Hayakawa H, Suda K, Ishikawa H, Gondo Y, Shimizu K,
Matsuki T, et al: Fermented milk containing Lactobacillus casei
strain shirota preserves the diversity of the gut microbiota and
relieves abdominal dysfunction in healthy medical students exposed
to academic stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 82:3649–3658. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lisko DJ, Johnston GP and Johnston CG:
Effects of dietary yogurt on the healthy human gastrointestinal
(GI) microbiome. Microorganisms. 5:E62017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kristensen NB, Bryrup T, Allin KH, Nielsen
T, Hansen TH and Pedersen O: Alterations in fecal microbiota
composition by probiotic supplementation in healthy adults: A
systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Genome Med.
8:522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang J, Wang L, Guo Z, Sun Z, Gesudu Q,
Kwok L, Menghebilige and Zhang H: 454 pyrosequencing reveals
changes in the faecal microbiota of adults consuming Lactobacillus
casei Zhang. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 88:612–622. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Park DY, Ahn YT, Park SH, Huh CS, Yoo SR,
Yu R, Sung MK, McGregor RA and Choi MS: Supplementation of
Lactobacillus curvatus HY7601 and Lactobacillus plantarum KY1032 in
diet-induced obese mice is associated with gut microbial changes
and reduction in obesity. PLoS One. 8:e594702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Backhed F, Fraser CM, Ringel Y, Sanders
ME, Sartor RB, Sherman PM, Versalovic J, Young V and Finlay BB:
Defining a healthy human gut microbiome: Current concepts, future
directions, and clinical applications. Cell Host Microbe.
12:611–622. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hanifi A, Culpepper T, Mai V, Anand A,
Ford AL, Ukhanova M, Christman M, Tompkins TA and Dahl WJ:
Evaluation of bacillus subtilis R0179 on gastrointestinal viability
and general wellness: A randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial in healthy adults. Benef Microbes.
6:19–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hildebrandt MA, Hoffmann C, Sherrill-Mix
SA, Keilbaugh SA, Hamady M, Chen YY, Knight R, Ahima RS, Bushman F
and Wu GD: High-fat diet determines the composition of the murine
gut microbiome independently of obesity. Gastroenterology.
137:1716–1724.e1-2. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Heinsen FA, Fangmann D, Muller N, Schulte
DM, Ruehlemann MC, Turk K, Settgast U, Lieb W, Baines JF, Schreiber
S, et al: Beneficial effects of a dietary weight loss intervention
on human gut microbiome diversity and metabolism are not sustained
during weight maintenance. Obes Facts. 9:379–391. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bell DS: Changes seen in gut bacteria
content and distribution with obesity: Causation or association?
Postgrad Med. 127:863–868. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shang Y, Khafipour E, Derakhshani H, Sarna
LK, Woo CW, Siow YL and O K: Short term high fat diet induces
Obesity-Enhancing changes in mouse gut microbiota that are
partially reversed by cessation of the high fat diet. Lipids.
52:499–511. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Schwiertz A, Taras D, Schafer K, Beijer S,
Bos NA, Donus C and Hardt PD: Microbiota and SCFA in lean and
overweight healthy subjects. Obesity (Silver Spring). 18:190–195.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Duncan SH, Lobley GE, Holtrop G, Ince J,
Johnstone AM, Louis P and Flint HJ: Human colonic microbiota
associated with diet, obesity and weight loss. Int J Obes (Lond).
32:1720–1724. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Human Microbiome Project Consortium:
Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome.
Nature. 486:207–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang J, Guo Z, Xue Z, Sun Z, Zhang M,
Wang L, Wang G, Wang F, Xu J, Cao H, et al: A phylo-functional core
of gut microbiota in healthy young Chinese cohorts across
lifestyles, geography and ethnicities. ISME J. 9:1979–1990. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mariat D, Firmesse O, Levenez F, Guimaraes
V, Sokol H, Dore J, Corthier G and Furet JP: The
Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with
age. BMC Microbiol. 9:1232009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kang C, Wang B, Kaliannan K, Wang X, Lang
H, Hui S, Huang L, Zhang Y, Zhou M, Chen M and Mi M: Gut microbiota
mediates the protective effects of dietary capsaicin against
chronic low-grade inflammation and associated obesity induced by
high-fat diet. MBio. 8:e00470–e00417. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ferrario C, Taverniti V, Milani C, Fiore
W, Laureati M, De Noni I, Stuknyte M, Chouaia B, Riso P and
Guglielmetti S: Modulation of fecal clostridiales bacteria and
butyrate by probiotic intervention with Lactobacillus paracasei DG
varies among healthy adults. J Nutr. 144:1787–1796. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Song JJ, Tian WJ, Kwok LY, Wang YL, Shang
YN, Menghe B and Wang JG: Effects of microencapsulated
Lactobacillus plantarum LIP-1 on the gut microbiota of
hyperlipidaemic rats. Brit J Nutr. 118:481–492. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Eeckhaut V, Machiels K, Perrier C, Romero
C, Maes S, Flahou B, Steppe M, Haesebrouck F, Sas B, Ducatelle R,
et al: Butyricicoccus pullicaecorum in inflammatory bowel disease.
Gut. 62:1745–1752. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Devriese S, Eeckhaut V, Geirnaert A, Van
den Bossche L, Hindryckx P, Van de Wiele T, Van Immerseel F,
Ducatelle R, De Vos M and Laukens D: Reduced Mucosa-associated
butyricicoccus activity in patients with ulcerative colitis
correlates with aberrant claudin-1 expression. J Crohns Colitis.
11:229–236. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Walker AW, Ince J, Duncan SH, Webster LM,
Holtrop G, Ze X, Brown D, Stares MD, Scott P, Bergerat A, et al:
Dominant and diet-responsive groups of bacteria within the human
colonic microbiota. ISME J. 5:220–230. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
An C, Kuda T, Yazaki T, Takahashi H and
Kimura B: Caecal fermentation, putrefaction and microbiotas in rats
fed milk casein, soy protein or fish meal. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 98:2779–2787. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Park S, Ji Y, Jung HY, Park H, Kang J,
Choi SH, Shin H, Hyun CK, Kim KT and Holzapfel WH: Lactobacillus
plantarum HAC01 regulates gut microbiota and adipose tissue
accumulation in a diet-induced obesity murine model. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 101:1605–1614. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Saitoh S, Noda S, Aiba Y, Takagi A,
Sakamoto M, Benno Y and Koga Y: Bacteroides ovatus as the
predominant commensal intestinal microbe causing a systemic
antibody response in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Diagn Lab
Immunol. 9:54–59. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Dicksved J, Halfvarson J, Rosenquist M,
Jarnerot G, Tysk C, Apajalahti J, Engstrand L and Jansson JK:
Molecular analysis of the gut microbiota of identical twins with
Crohn's disease. ISME J. 2:716–727. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
El Hage R, Hernandez-Sanabria E and Van de
Wiele T: Emerging trends in ‘Smart Probiotics’: Functional
consideration for the development of novel health and industrial
applications. Front Microbiol. 8:18892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Winter J, Moore LH, Dowell VR Jr and
Bokkenheuser VD: C-ring cleavage of flavonoids by human intestinal
bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 55:1203–1208. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kasai C, Sugimoto K, Moritani I, Tanaka J,
Oya Y, Inoue H, Tameda M, Shiraki K, Ito M, Takei Y and Takase K:
Comparison of the gut microbiota composition between obese and
non-obese individuals in a Japanese population, as analyzed by
terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism and
next-generation sequencing. BMC Gastroenterol. 15:1002015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Fang D, Shi D, Lv L, Gu S, Wu W, Chen Y,
Chen Y, Guo J, Li A, Xinjun Hu, et al: Bifidobacterium
pseudocatenulatum LI09 and Bifidobacterium catenulatum LI10
attenuate D-galactosamine-induced liver injury by modifying the gut
microbiota. Sci Rep. 7:87702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Toscano M, De Grandi R, Miniello VL,
Mattina R and Drago L: Ability of Lactobacillus kefiri LKF01
(DSM32079) to colonize the intestinal environment and modify the
gut microbiota composition of healthy individuals. Dig Liver Dis.
49:261–267. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Jimenez MB: Treatment of irritable bowel
syndrome with probiotics. An etiopathogenic approach at last? Rev
Esp Enferm Dig. 101:553–564. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
van den Bogert B, Meijerink M, Zoetendal
EG, Wells JM and Kleerebezem M: Immunomodulatory properties of
Streptococcus and Veillonella isolates from the human small
intestine microbiota. PLoS One. 9:e1142772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Garrido D, Suau A, Pochart P, Cruchet S
and Gotteland M: Modulation of the fecal microbiota by the intake
of a Lactobacillus johnsonii La1-containing product in human
volunteers. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 248:249–256. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhu Q, Jin Z, Wu W, Gao R, Guo B, Gao Z,
Yang Y and Qin H: Analysis of the intestinal lumen microbiota in an
animal model of colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 9:e908492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hibberd AA, Lyra A, Ouwehand AC, Rolny P,
Lindegren H, Cedgard L and Wettergren Y: Intestinal microbiota is
altered in patients with colon cancer and modified by probiotic
intervention. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 4:e0001452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wong SH, Kwong TNY, Chow TC, Luk AKC, Dai
RZW, Nakatsu G, Lam TYT, Zhang L, Wu JCY, Chan FKL, et al:
Quantitation of faecal Fusobacterium improves faecal immunochemical
test in detecting advanced colorectal neoplasia. Gut. 66:1441–1418.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|