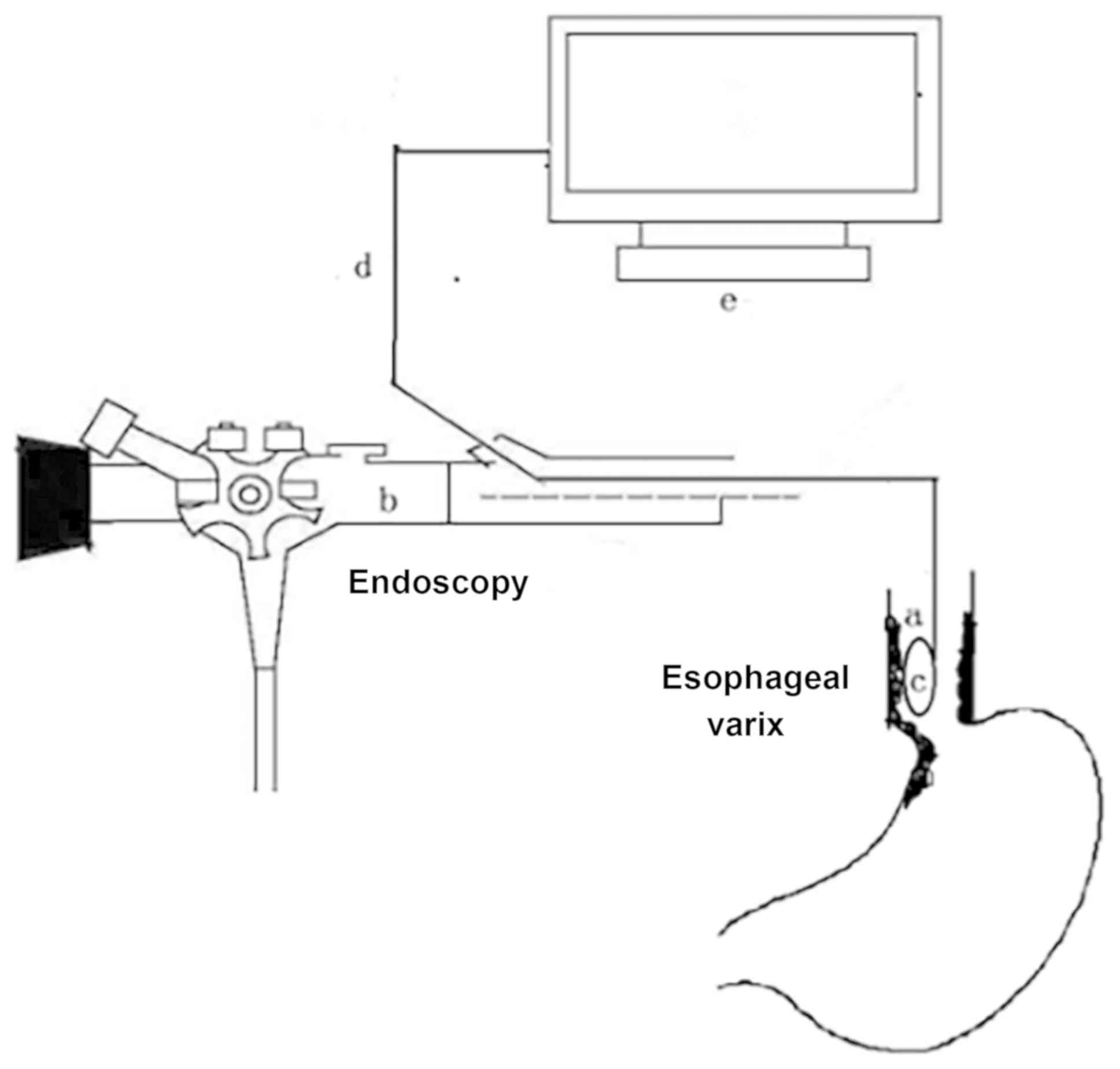
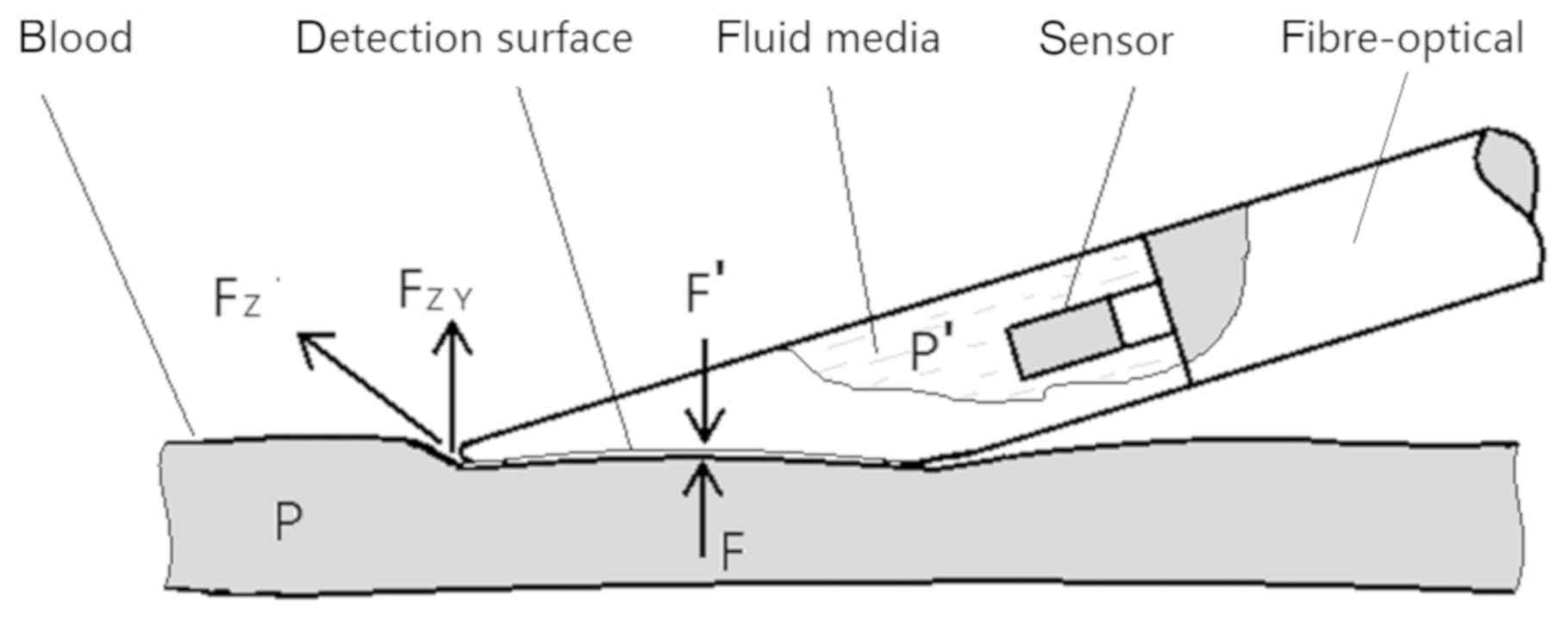
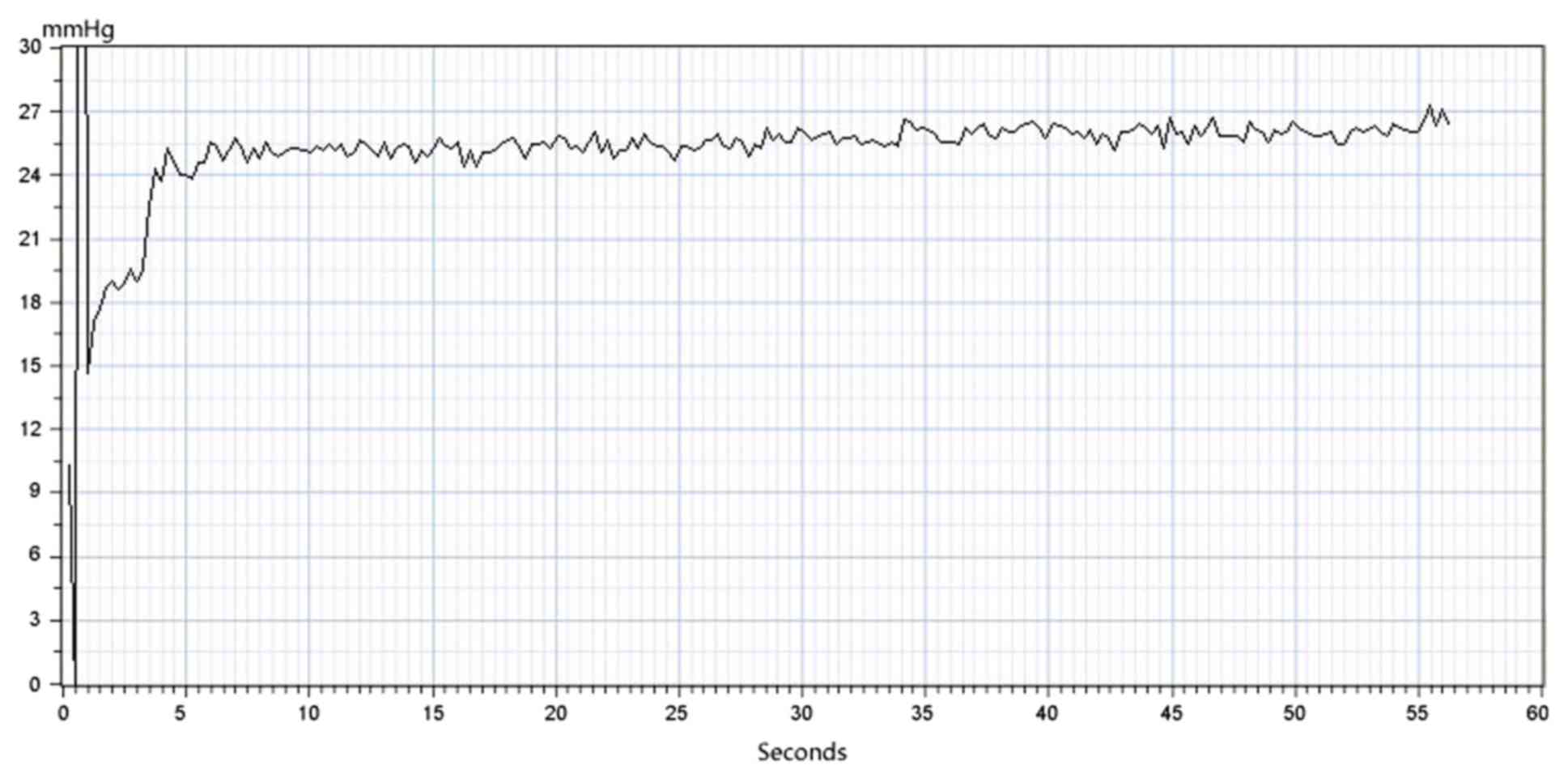
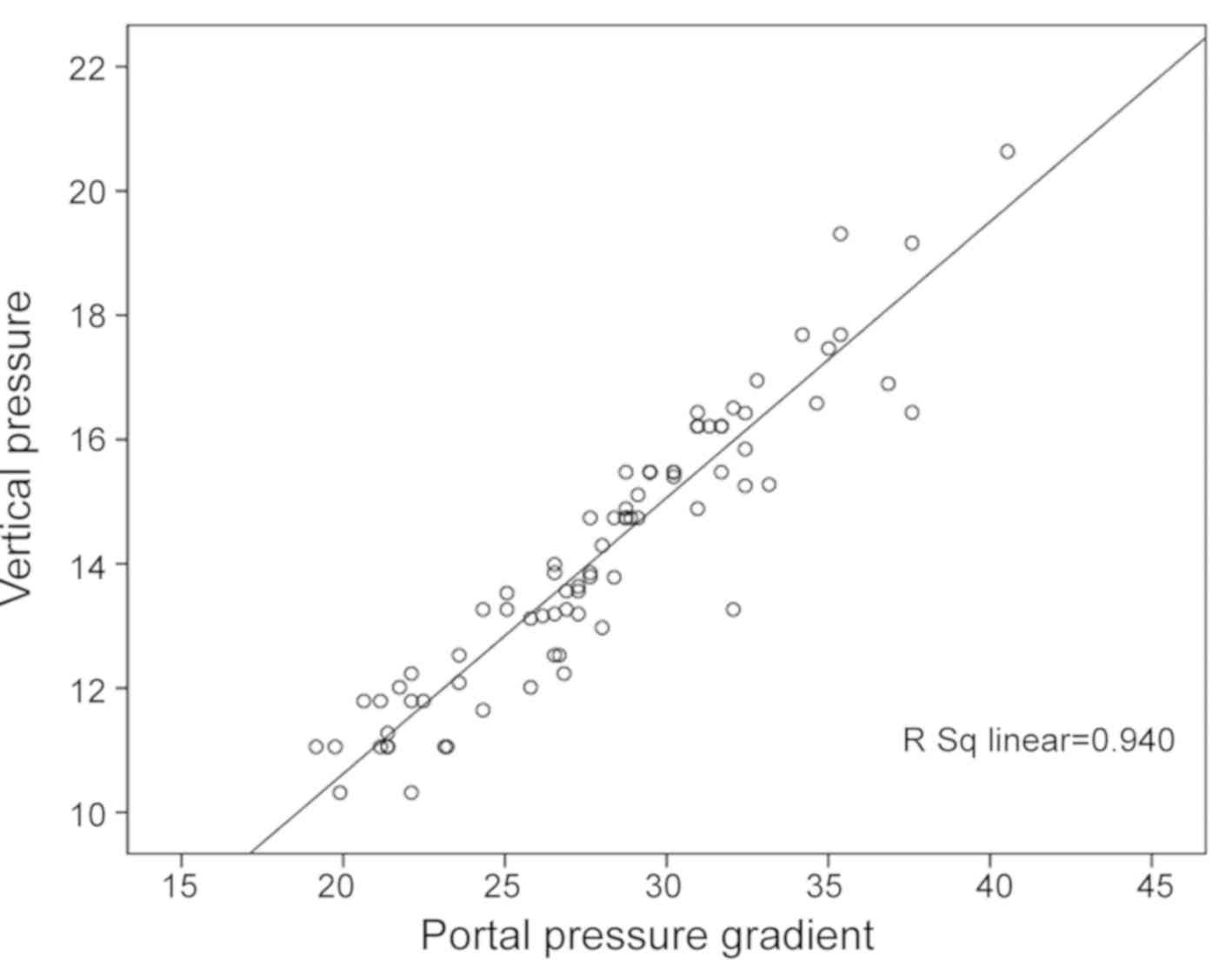
|
1
|
Scaglione S, Kliethermes S, Cao G, Shoham
D, Durazo R, Luke A and Volk ML: The epidemiology of cirrhosis in
the United States: A population-based study. J Clin Gastroenterol.
49:690–696. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tandon RK and Saikia N: Measuring
intravariceal pressure. Gastrointest Endosc. 70:414–416. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Palmer ED: On correlations between portal
venous pressure and the size and extent of esophageal varices in
portal cirrhosis. Ann Surg. 138:741–744. 1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rigau J, Bosch J, Bordas JM, Navasa M,
Mastai R, Kravetz D, Bruix J, Feu F and Rodés J: Endoscopic
measurement of variceal pressure in cirrhosis: Correlation with
portal pressure and variceal hemorrhage. Gastroenterology.
96:873–880. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gertsch PH and Meister JJ: Pressure
measurement in oesophageal varices: Preliminary report on a new
non-invasive method. Gut. 28:1162–1165. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Miller ES, Kim JK, Gandehok J, Hara M, Dai
Q, Malik A, Miller A and Miller L: A new device for measuring
esophageal variceal pressure. Gastrointest Endosc. 56:284–291.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miller LS, Dai Q, Thomas A, Chung CY, Park
J, Irizarry S, Nguyen T, Thangada V, Miller ES and Kim JK: A new
ultrasound-guided esophageal variceal pressure-measuring device. Am
J Gastroenterol. 99:1267–1273. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vegesna AK, Chung CY, Bajaj A, Tiwana MI,
Rishikesh R, Hamid I, Kalra A, Korimilli A, Patel S, Mamoon R, et
al: Minimally invasive measurement of esophageal variceal pressure
and wall tension (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 70:407–413.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kong DR, Xu JM, Zhang L, Zhang C, Fu ZQ,
He BB, Sun B and Xie Y: Computerized endoscopic balloon manometry
to detect esophageal variceal pressure. Endoscopy. 41:415–420.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kong DR, He BB, Wu AJ, Wang JG, Yu FF and
Xu JM: Fiberoptic sensor for noninvasive measurement of variceal
pressure. Endoscopy 45 Suppl 2 UCTN. E55–E56. 2013.
|
|
11
|
Tajiri T, Yoshida H, Obara K, Onji M, Kage
M, Kitano S, Kokudo N, Kokubu S, Sakaida I, Sata M, et al: General
rules for recording endoscopic findings of esophagogastric varices
(2nd edition). Dig Endosc. 22:1–9. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A
and Bosch J: Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk
stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance
by the American Association for the study of liver diseases.
Hepatology. 65:310–335. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Watari A, Miyata K, Kanazawa H and
Kobayashi M: Comparison of portal pressure with intravascular
esophageal variceal pressure (IEVP) directly measured with a
flexible indwelling needle. Gastroenterol Jpn. 28:631–637. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gertsch P, Fischer G, Kleber G, Wheatley
AM, Geigenberger G and Sauerbruch T: Manometry of esophageal
varices: Comparison of an endoscopic balloon technique with needle
puncture. Gastroenterology. 105:1159–1166. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bosch J, Bordas JM, Rigan J, Viola C,
Mastai R, Kravetz D, Navasa M and Rodés J: Noninvasive measurement
of the pressure of esophageal varices using an endoscopic gauge:
Comparison with measurements by variceal puncture in patients
undergoing endoscopic sclerotherapy. Gastroenterology. 6:667–672.
1986.
|
|
16
|
Polio J, Hanson J, Sikuler E, Vogel G,
Gusberg R, Fisher R and Groszmann RJ: Critical evaluation of a
pressure-sensitive capsule for measurement of esophageal varix
pressure. Studies in vitro and in canine mesenteric vessels.
Gastroenterology. 92:1109–1115. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Puckett JL, Liu J, Bhalla V, Kravetz D,
Krinsky ML, Hassanein T and Mittal RK: Ultrasound system to measure
esophageal varix pressure: An in vitro validation study. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 288:G914–G919. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|