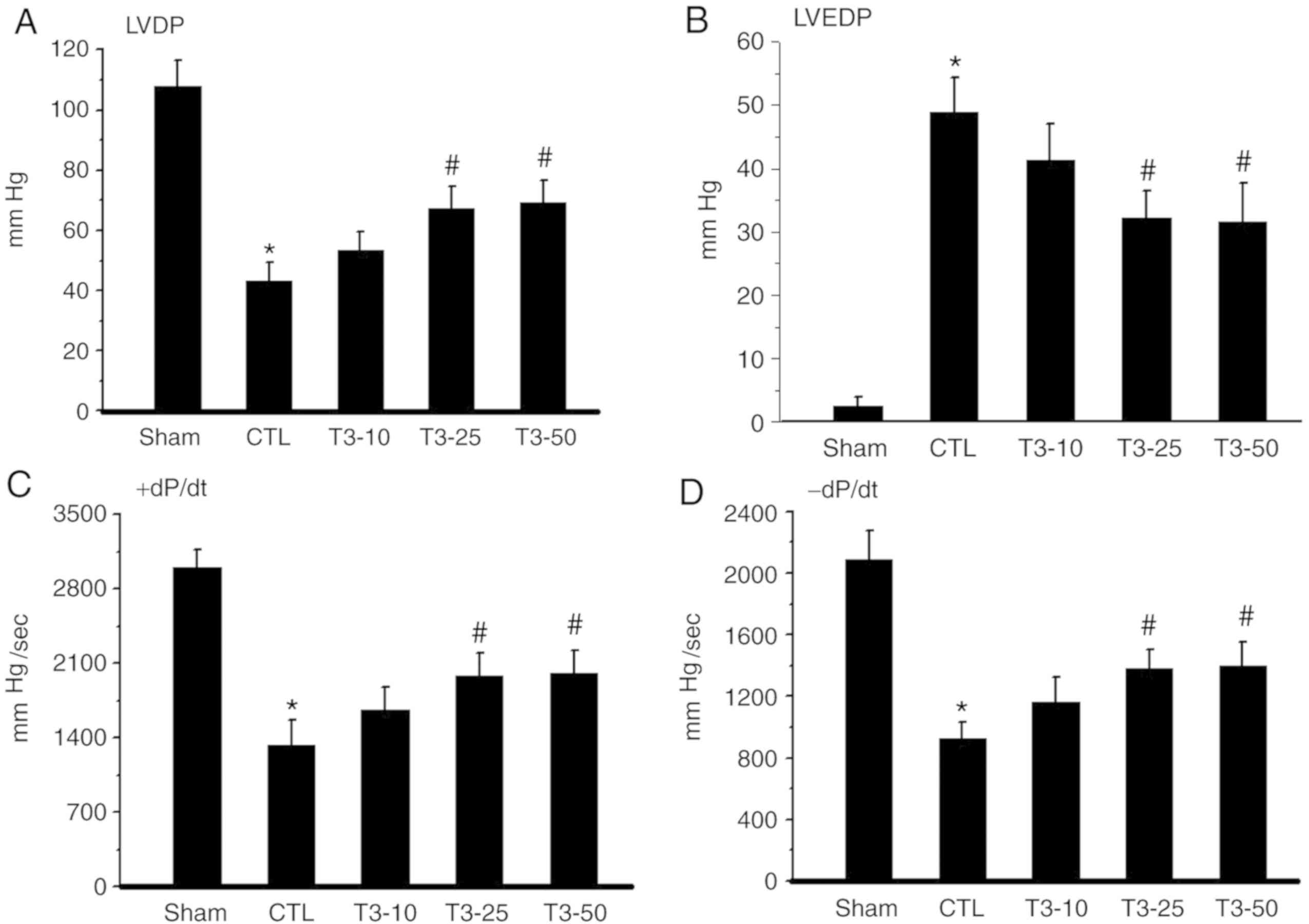
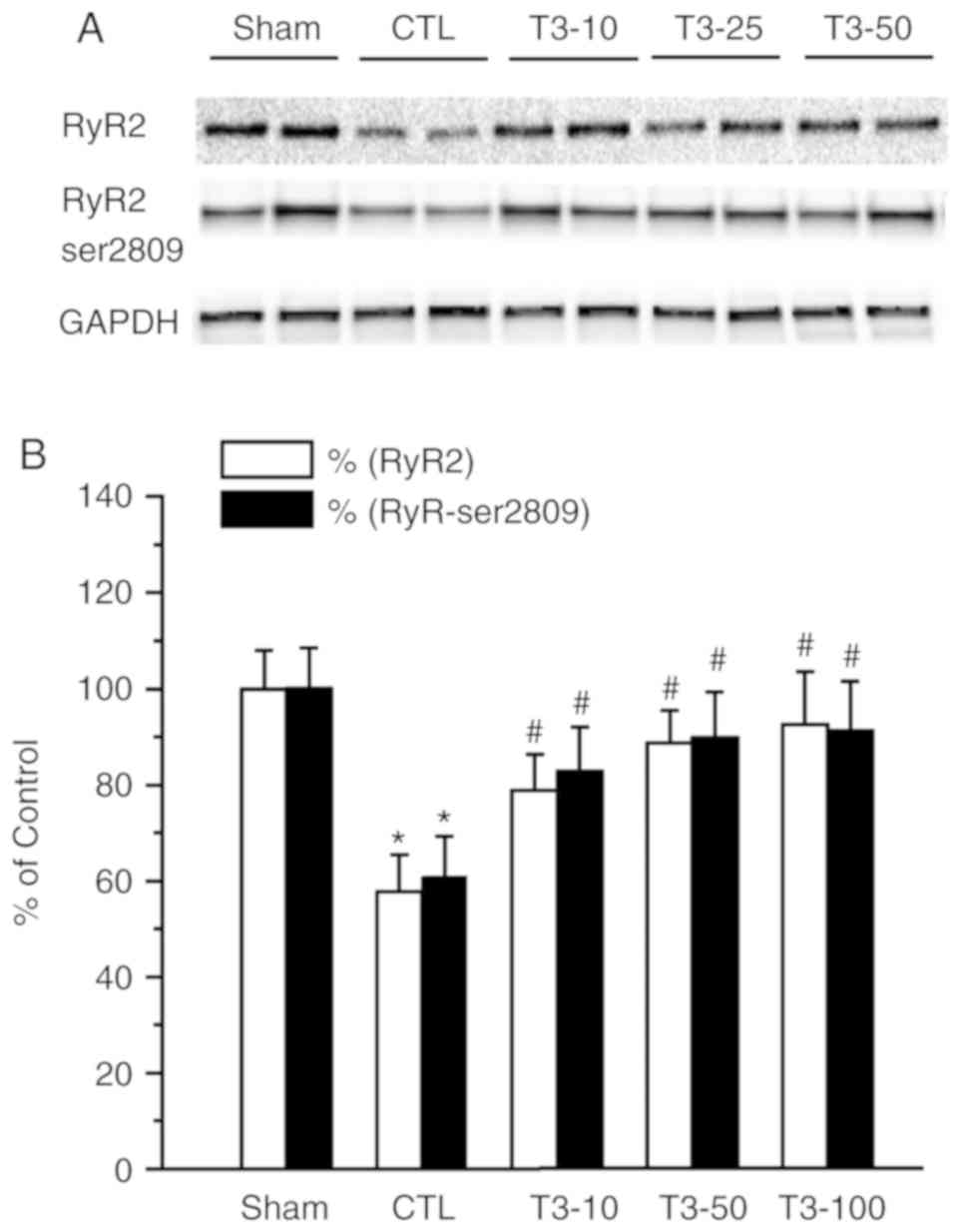
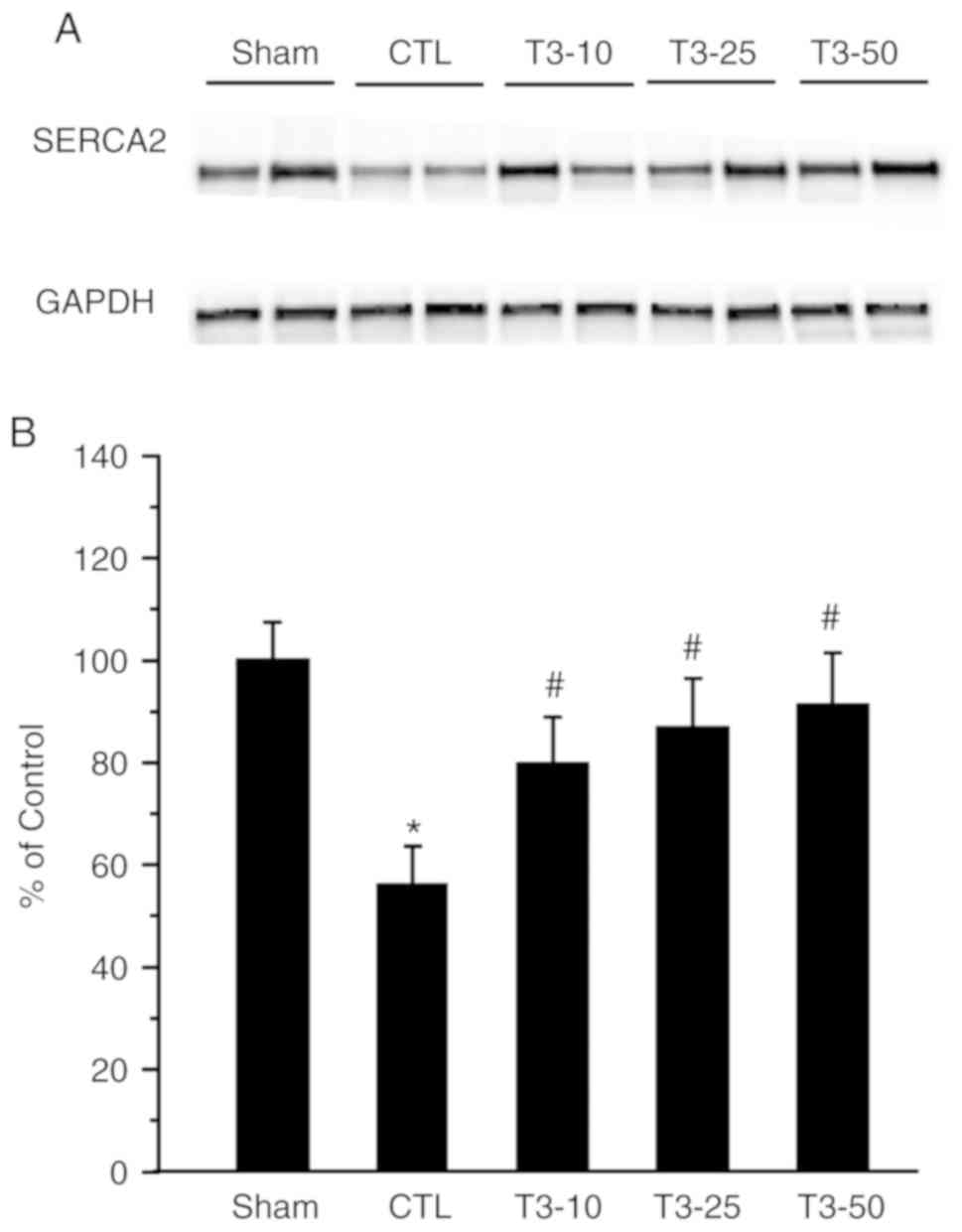
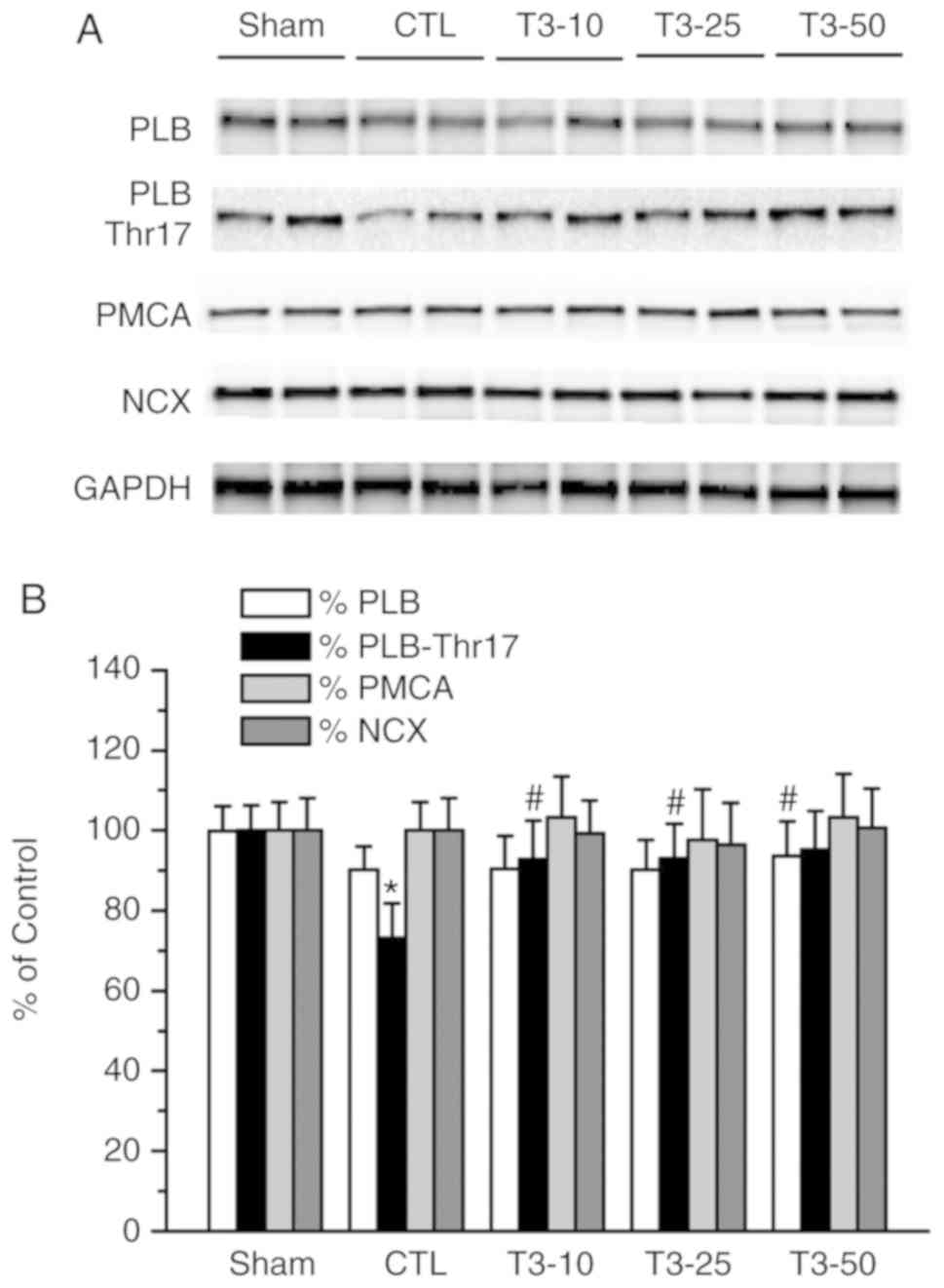
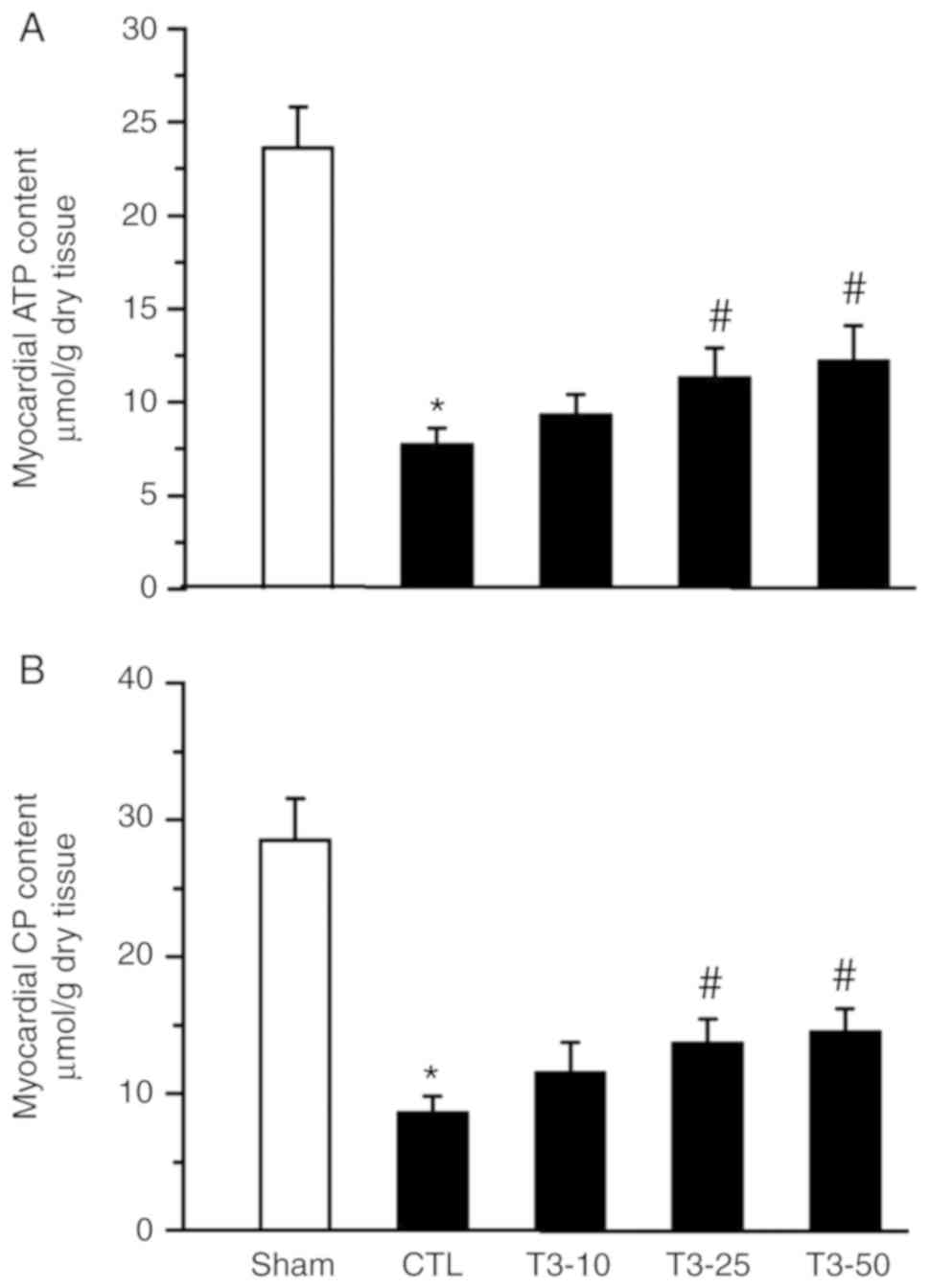
|
1
|
Li L, Guo CY, Yang J, Jia EZ, Zhu TB, Wang
LS, Cao KJ, Ma WZ and Yang ZJ: Negative association between free
triiodothyronine level and international normalized ratio in
euthyroid subjects with acute myocardial infarction. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 32:1351–1356. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ragone MI, Bonazzola P, Colareda GA and
Consolini AE: Cardioprotective effect of hyperthyroidism on the
stunned rat heart during ischaemia-reperfusion: Energetics and role
of mitochondria. Exp Physiol. 100:680–697. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Holland FW II, Brown PS Jr and Clark RE:
Acute severe postischemic myocardial depression reversed by
triiodothyronine. Ann Thorac Surg. 54:301–305. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Novitzky D and Cooper DK: Thyroid hormone
and the stunned myocardium. J Endocrinol. 223:R1–R8. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Velissaris T, Tang AT, Wood PJ, Hett DA
and Ohri SK: Thyroid function during coronary surgery with and
without cardiopulmonary bypass. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
36:148–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Priest JR, Slee A, Olson AK, Ledee D,
Morrish F and Portman MA: Triiodothyronine supplementation and
cytokines during cardiopulmonary bypass in infants and children. J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 144:938–943.e2. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Forini F, Lionetti V, Ardehali H, Pucci A,
Cecchetti F, Ghanefar M, Nicolini G, Ichikawa Y, Nannipieri M,
Recchia FA and Iervasi G: Early long-term L-T3 replacement rescues
mitochondria and prevents ischemic cardiac remodelling in rats. J
Cell Mol Med. 15:514–524. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pingitore A, Chen Y, Gerdes AM and Iervasi
G: Acute myocardial infarction and thyroid function: New
pathophysiological and therapeutic perspectives. Ann Med.
44:745–757. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Forini F, Kusmic C, Nicolini G, Mariani L,
Zucchi R, Matteucci M, Iervasi G and Pitto L: Triiodothyronine
prevents cardiac ischemia/reperfusion mitochondrial impairment and
cell loss by regulating miR30a/p53 axis. Endocrinology.
155:4581–4590. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nicolini G, Forini F, Kusmic C, Pitto L,
Mariani L and Iervasi G: Early and short-term triiodothyronine
supplementation prevents adverse postischemic cardiac remodeling:
Role of transforming growth factor-β1 and antifibrotic miRNA
signaling. Mol Med. 21:900–911. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bi W, Jia J, Pang R, Nie C, Han J, Ding Z,
Liu B, Sheng R, Xu J and Zhang J: Thyroid hormone postconditioning
protects hearts from ischemia/reperfusion through reinforcing
mitophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 118:1092202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Forini F, Paolicchi A, Pizzorusso T, Ratto
GM, Saviozzi M, Vanini V and Iervasi G: 3,5,3′-Triiodothyronine
deprivation affects phenotype and intracellular [Ca2+]i of human
cardiomyocytes in culture. Cardiovasc Res. 51:322–330. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
An J, Rhodes SS, Jiang MT, Bosnjak ZJ,
Tian M and Stowe DF: Anesthetic preconditioning enhances Ca2+
handling and mechanical and metabolic function elicited by Na+-Ca2+
exchange inhibition in isolated hearts. Anesthesiology.
105:541–549. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pantos C, Mourouzis I, Saranteas T, Clavé
G, Ligeret H, Noack-Fraissignes P, Renard PY, Massonneau M,
Perimenis P, Spanou D, et al: Thyroid hormone improves
postischaemic recovery of function while limiting apoptosis: A new
therapeutic approach to support hemodynamics in the setting of
ischaemia-reperfusion? Basic Res Cardiol. 104:69–77. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
An J, Bosnjak ZJ and Jiang MT: Myocardial
protection by isoflurane preconditioning preserves Ca2+ cycling
proteins independent of sarcolemmal and mitochondrial KATP
channels. Anesth Analg. 105:1207–1213. 2007.table of contents.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sasamori J, Abe Y, Marunouchi T, Manome Y,
Uchibori T and Tanonaka K: Effects of 2-octynyladenosine (YT-146)
on mitochondrial function in ischemic/reperfused rat hearts. Biol
Pharm Bull. 38:1946–1953. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ranasinghe AM, Quinn DW, Pagano D, Edwards
N, Faroqui M, Graham TR, Keogh BE, Mascaro J, Riddington DW, Rooney
SJ, et al: Glucose-insulin-potassium and tri-iodothyronine
individually improve hemodynamic performance and are associated
with reduced troponin I release after on-pump coronary artery
bypass grafting. Circulation. 114 (1 Suppl):I245–I250. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Klemperer JD, Zelano J, Helm RE, Berman K,
Ojamaa K, Klein I, Isom OW and Krieger K: Triiodothyronine improves
left ventricular function without oxygen wasting effects after
global hypothermic ischemia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 109:457–465.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dyke CM, Yeh T Jr, Lehman JD, Abd-Elfattah
A, Ding M, Wechsler AS and Salter DR: Triiodothyronine-enhanced
left ventricular function after ischemic injury. Ann Thorac Surg.
52:14–19. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Umeda PK, Darling DS, Kennedy JM, Jakovcic
S and Zak R: Control of myosin heavy chain expression in cardiac
hypertrophy. Am J Cardiol. 59:49A–55A. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Accorroni A, Saponaro F and Zucchi R:
Tissue thyroid hormones and thyronamines. Heart Fail Rev.
21:373–390. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Singh RB, Chohan PK, Dhalla NS and
Netticadan T: The sarcoplasmic reticulum proteins are targets for
calpain action in the ischemic-reperfused heart. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 37:101–110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eisner DA, Caldwell JL, Kistamás K and
Trafford AW: Calcium and excitation-contraction coupling in the
heart. Circ Res. 121:181–195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mourouzis I, Mantzouratou P, Galanopoulos
G, Kostakou E, Roukounakis N, Kokkinos AD, Cokkinos DV and Pantos
C: Dose-dependent effects of thyroid hormone on post-ischemic
cardiac performance: Potential involvement of Akt and ERK
signalings. Mol Cell Biochem. 363:235–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
del Monte F, Harding SE, Dec GW, Gwathmey
JK and Hajjar RJ: Targeting phospholamban by gene transfer in human
heart failure. Circulation. 105:904–907. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pantos C, Mourouzis I, Saranteas T, Brozou
V, Galanopoulos G, Kostopanagiotou G and Cokkinos DV: Acute T3
treatment protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury
via TRalpha1 receptor. Mol Cell Biochem. 353:235–241. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Temsah RM, Kawabata K, Chapman D and
Dhalla NS: Preconditioning prevents alterations in cardiac SR gene
expression due to ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 282:H1461–H1466. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sterling K, Brenner MA and Sakurada T:
Rapid effect of triiodothyronine on the mitochondrial pathway in
rat liver in vivo. Science. 210:340–342. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|