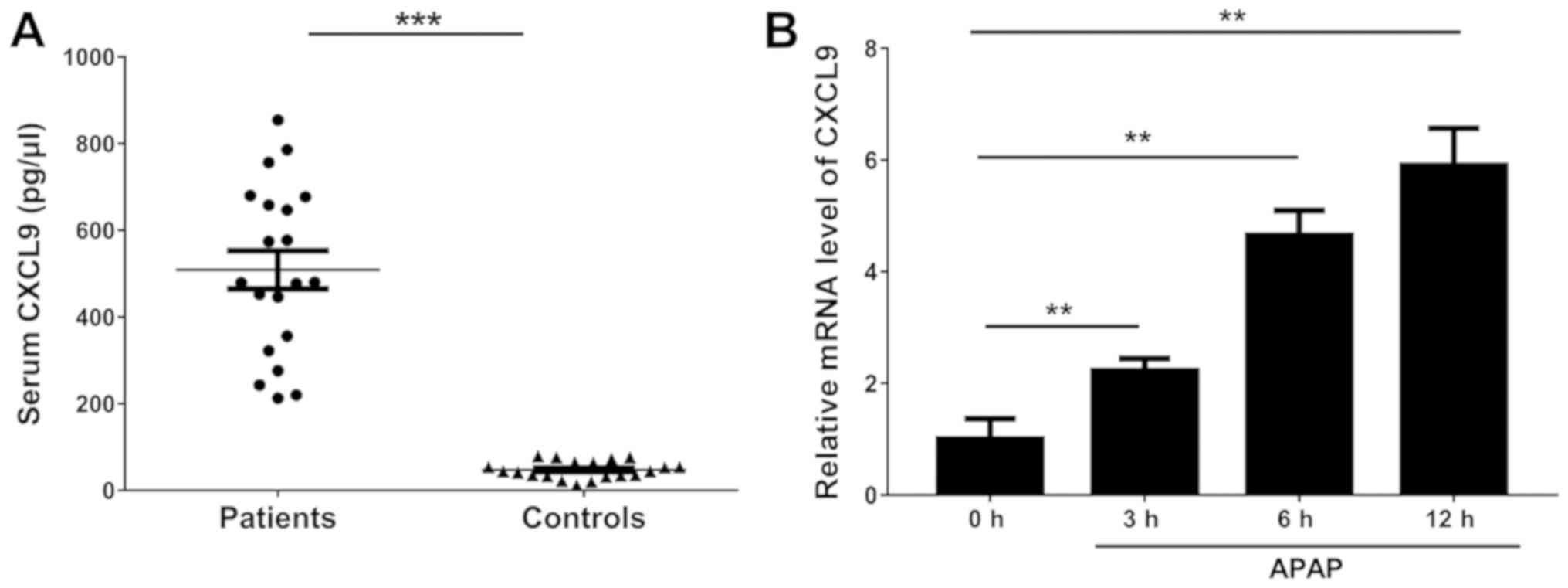
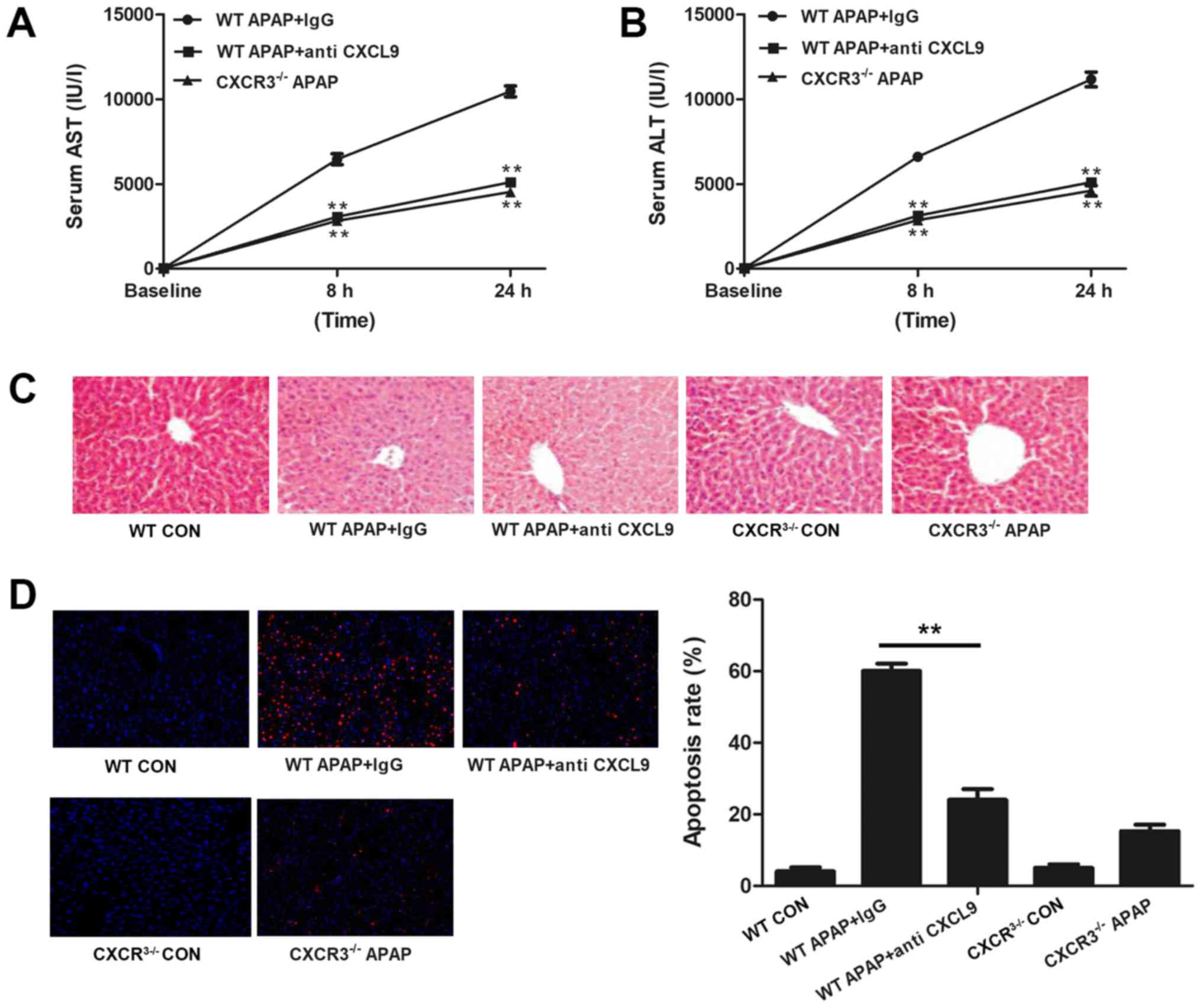
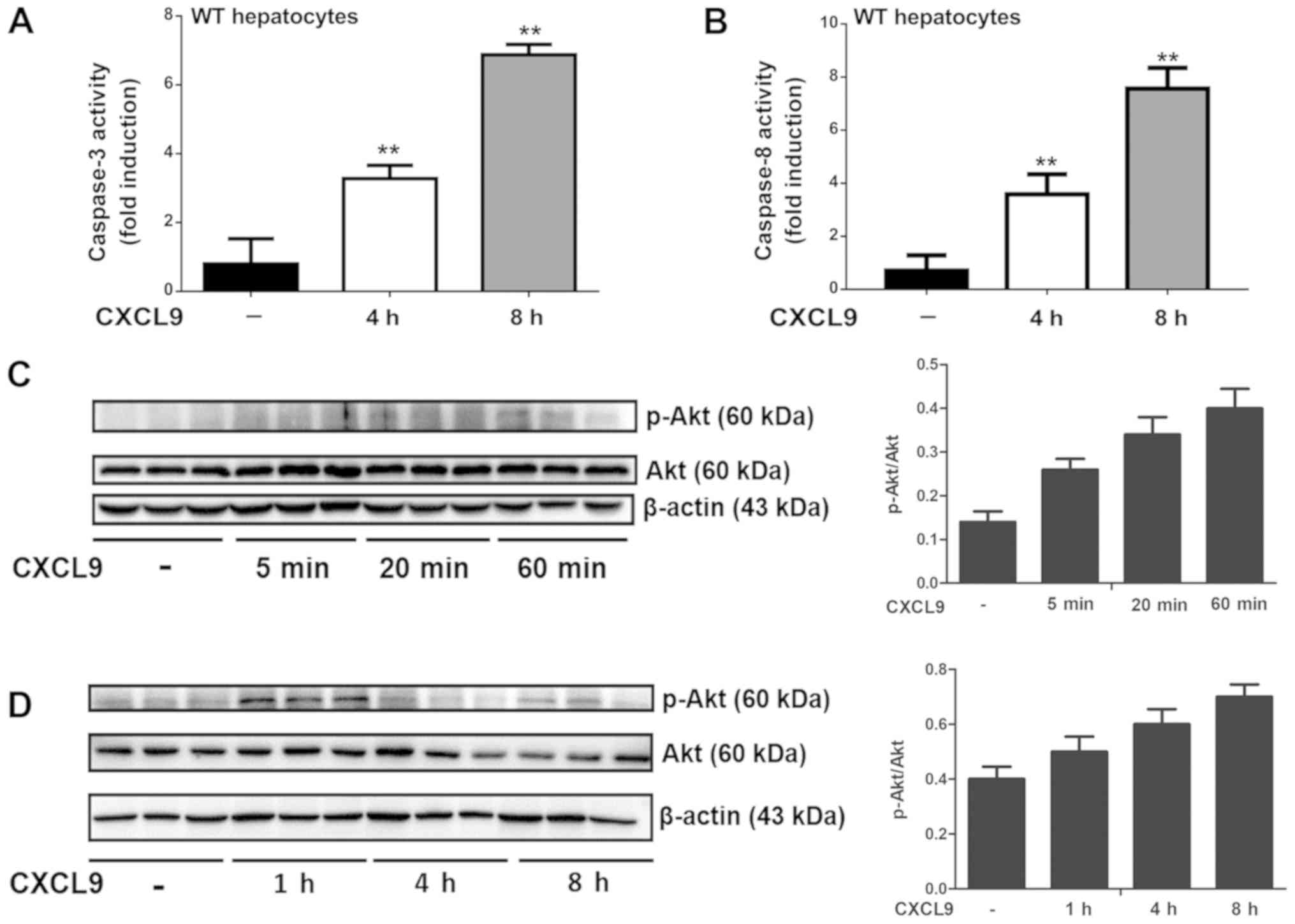
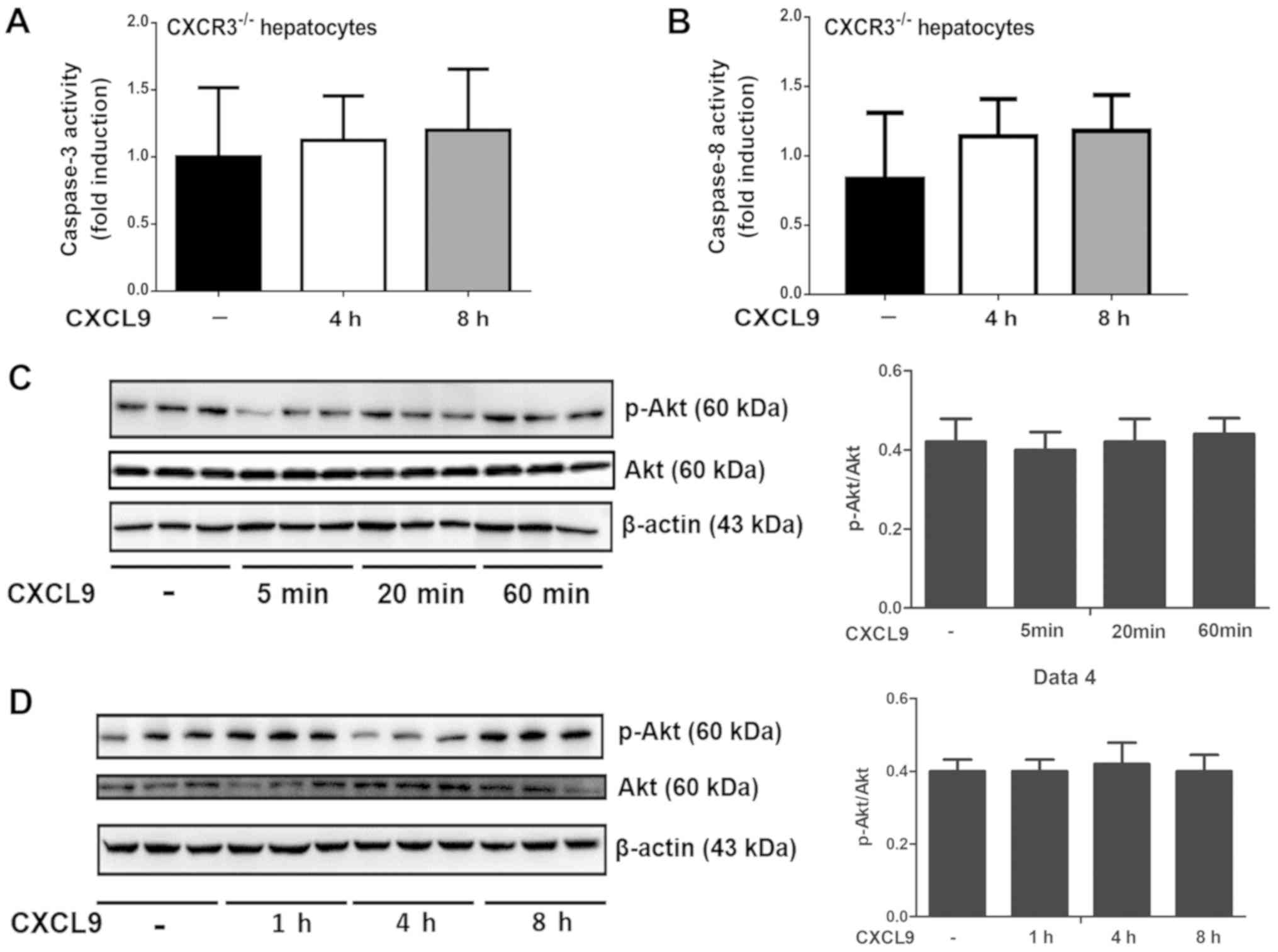
|
1
|
Larson AM, Polson J, Fontana RJ, Davern
TJ, Lalani E, Hynan LS, Reisch JS, Schiodt FV, Ostapowicz G, Shakil
AO, et al: Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: Results of a
united states multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology.
42:1364–1372. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Senior JR: Drug hepatotoxicity from a
regulatory perspective. Clin Liver Dis. 11:507–524. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Atienzar FA, Blomme EA, Chen M, Hewitt P,
Kenna JG, Labbe G, Moulin F, Pognan F, Roth AB, Suter-Dick L, et
al: Key challenges and opportunities associated with the use of in
vitro models to detect human DILI: Integrated risk assessment and
mitigation plans. Biomed Res Int. 2016:97379202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou M, Wang M, Zhong RF, Liao XM, Deng
LL, Xu GB, He X, Li J, Li YJ, Liu T, et al: Discovery and
structure-activity relationship of auriculatone: A potent
hepatoprotective agent against acetaminophen-induced liver injury.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 27:3636–3642. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu XY, Hu JN, Liu Z, Zhang R, He YF, Hou
W, Wang ZQ, Yang G and Li W: Saponins (Ginsenosides) from the
leaves of Panax quinquefolius ameliorated
acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J Agric Food Chem.
65:3684–3692. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim M, Yun JW, Shin K, Cho Y, Yang M, Nam
KT and Lim KM: Expression levels of GABA-A receptor subunit alpha
3, gabra3 and lipoprotein lipase, lpl are associated with the
susceptibility to acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Biomol Ther
(Seoul). 25:112–121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Larson AM: Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity.
Clin Liver Dis. 11:525–548. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
James LP, Mayeux PR and Hinson JA:
Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Dispos.
31:1499–1506. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Granger DN, Vowinkel T and Petnehazy T:
Modulation of the inflammatory response in cardiovascular disease.
Hypertension. 43:924–931. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu H, Zhang G, Huang L, Pang H, Zhang N,
Chen Y and Wang G: Hepatoprotective effect of polyphenol-enriched
fraction from folium microcos on oxidative stress and apoptosis in
acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:36315652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan XT, Sun YS, Ren S, Zhao LC, Liu WC,
Chen C, Wang Z and Li W: Dietary α-mangostin provides protective
effects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via
Akt/mTOR-mediated inhibition of autophagy and apoptosis. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:E13352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sahin H, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Do ON,
Berres ML, Kaldenbach M, Schmitz P, Weiskirchen R, Liedtke C,
Streetz KL, Maedler K, et al: Proapoptotic effects of the
chemokine, CXCL 10 are mediated by the noncognate receptor TLR4 in
hepatocytes. Hepatology. 57:797–805. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han X, Wu Z, Di J, Pan Y, Zhang H, Du Y,
Cheng Z, Jin Z, Wang Z, Zheng Q, et al: CXCL9 attenuated
chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis by inhibiting
proliferation and reducing apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother.
65:547–554. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tokunaga R, Zhang W, Naseem M, Puccini A,
Berger MD, Soni S, McSkane M, Baba H and Lenz HJ: CXCL9, CXCL10,
CXCL11/CXCR3 axis for immune activation-a target for novel cancer
therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 63:40–47. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Muller M, Carter S, Hofer MJ and Campbell
IL: Review: The chemokine receptor CXCR3 and its ligands CXCL9,
CXCL10 and CXCL11 in neuroimmunity-a tale of conflict and
conundrum. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 36:368–387. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu W, Ren HY, Dong YJ, Wang LH, Yin Y, Li
Y, Qiu ZX, Cen XN and Shi YJ: Bortezomib regulates the chemotactic
characteristics of T cells through downregulation of CXCR3/CXCL9
expression and induction of apoptosis. Int J Hematol. 96:764–772.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cassim S, Raymond VA, Lapierre P and
Bilodeau M: From in vivo to in vitro: Major metabolic alterations
take place in hepatocytes during and following isolation. PLoS One.
12:e1903662017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Henderson NC, Pollock KJ, Frew J,
Mackinnon AC, Flavell RA, Davis RJ, Sethi T and Simpson KJ:
Critical role of c-jun (NH2) terminal kinase in paracetamol-induced
acute liver failure. Gut. 56:982–990. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu J, Wu H, Liu ZY, Zhu Q, Shan C and
Zhang KQ: Advanced glycation end products induce the apoptosis of
and inflammation in mouse podocytes through CXCL9-mediated
JAK2/STAT3 pathway activation. Int J Mol Med. 40:1185–1193. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakamoto N, Ebinuma H, Kanai T, Chu PS,
Ono Y, Mikami Y, Ojiro K, Lipp M, Love PE, Saito H and Hibi T:
CCR9+ macrophages are required for acute liver inflammation in
mouse models of hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 142:366–376. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schumann J, Wolf D, Pahl A, Brune K,
Papadopoulos T, van Rooijen N and Tiegs G: Importance of kupffer
cells for T-cell-dependent liver injury in mice. Am J Pathol.
157:1671–1683. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakashima H, Kinoshita M, Nakashima M,
Habu Y, Shono S, Uchida T, Shinomiya N and Seki S: Superoxide
produced by Kupffer cells is an essential effector in concanavalin
A-induced hepatitis in mice. Hepatology. 48:1979–1988. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bonder CS, Ajuebor MN, Zbytnuik LD, Kubes
P and Swain MG: Essential role for neutrophil recruitment to the
liver in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. J Immunol. 172:45–53.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|