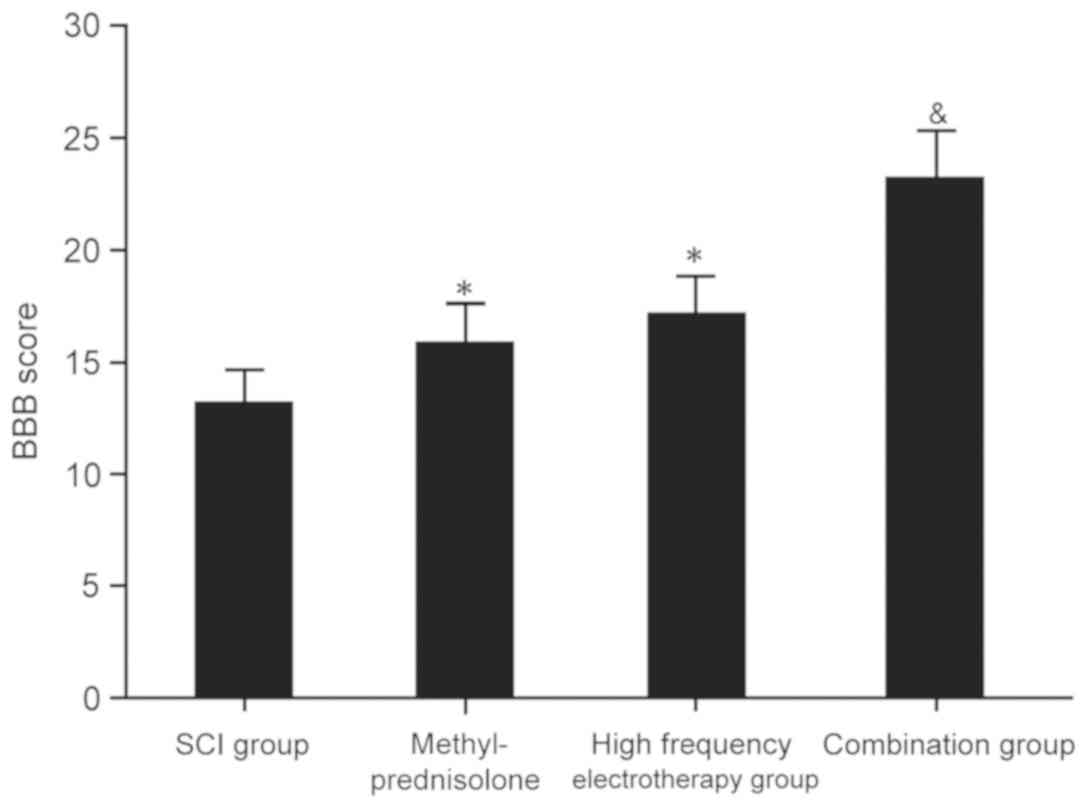
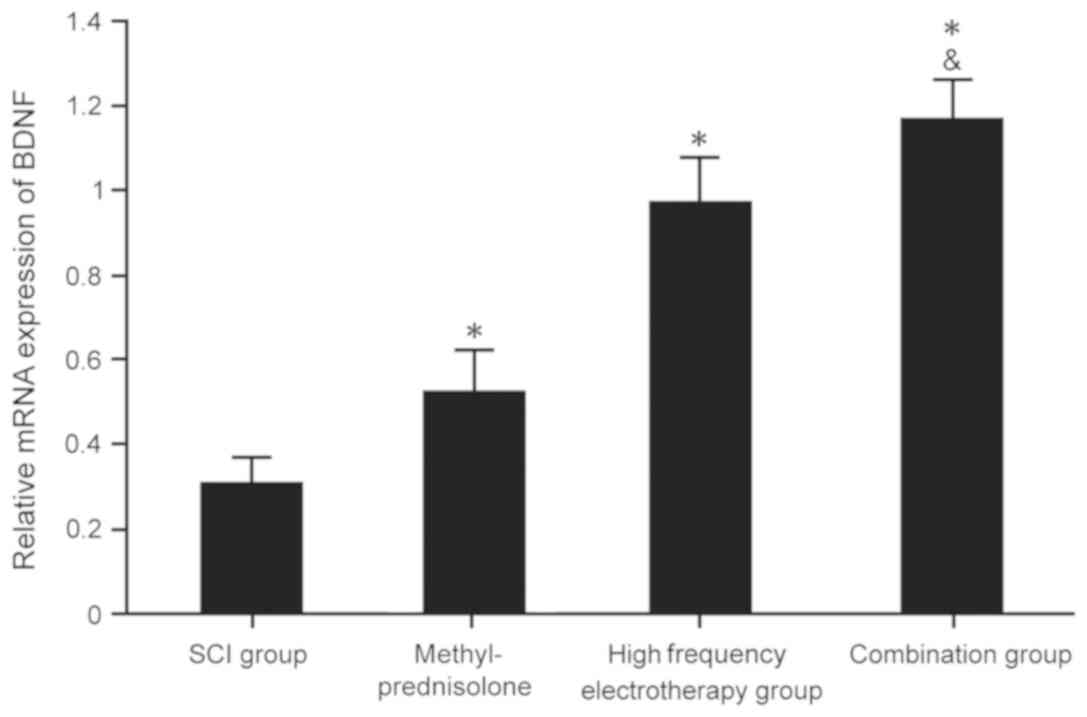
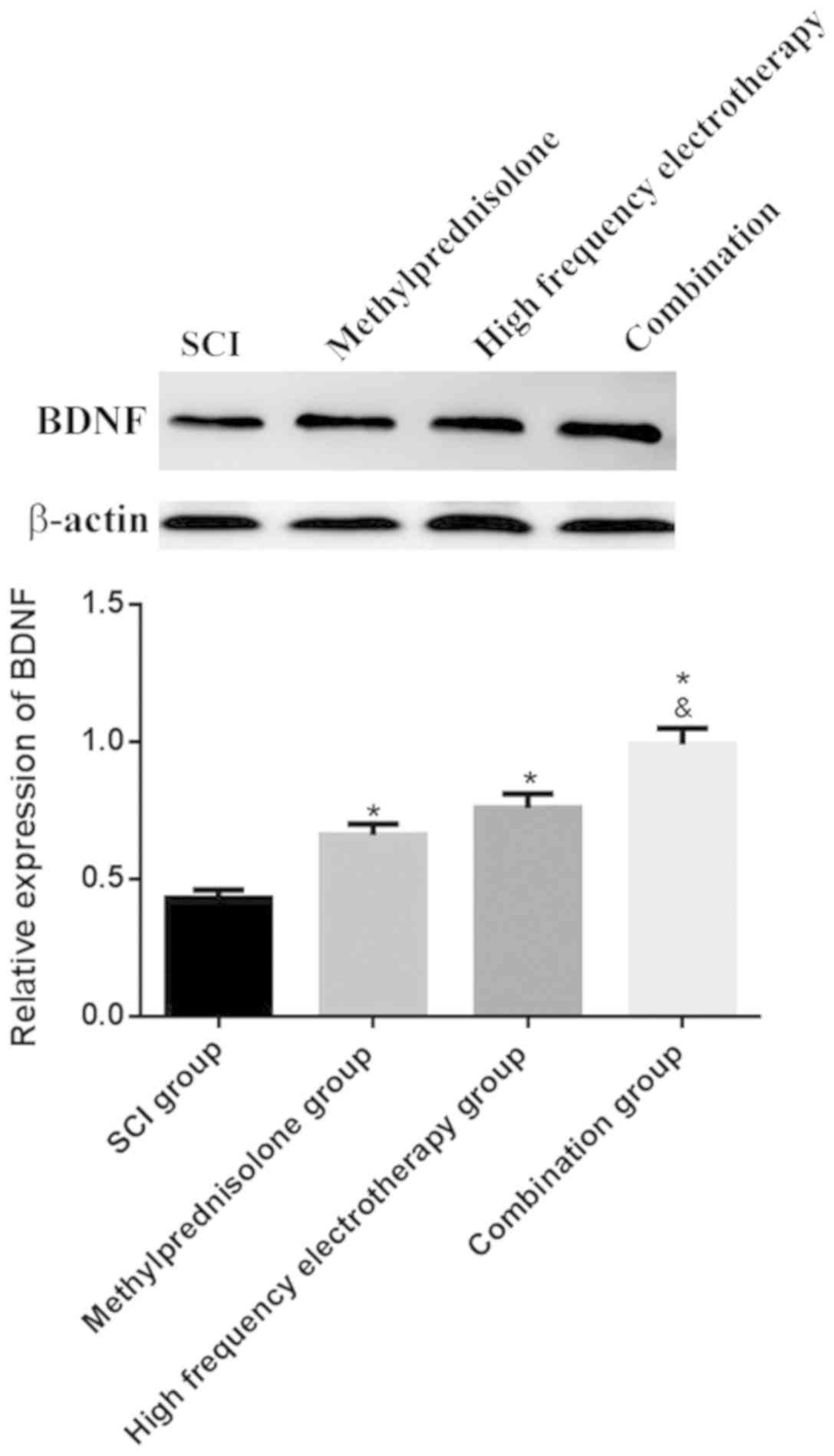
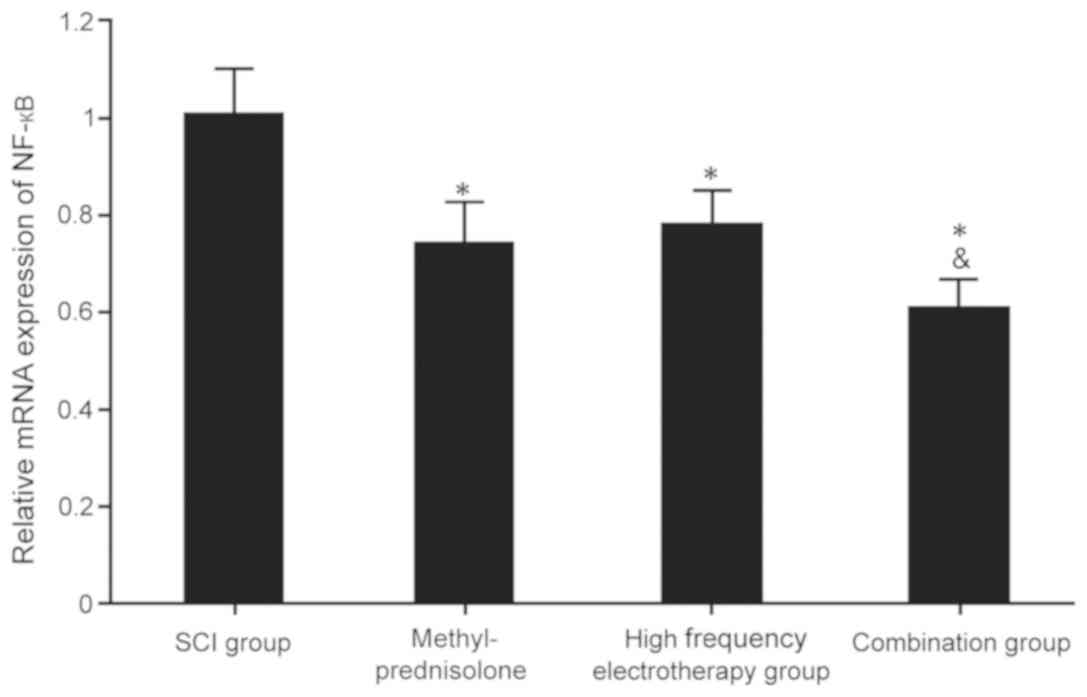
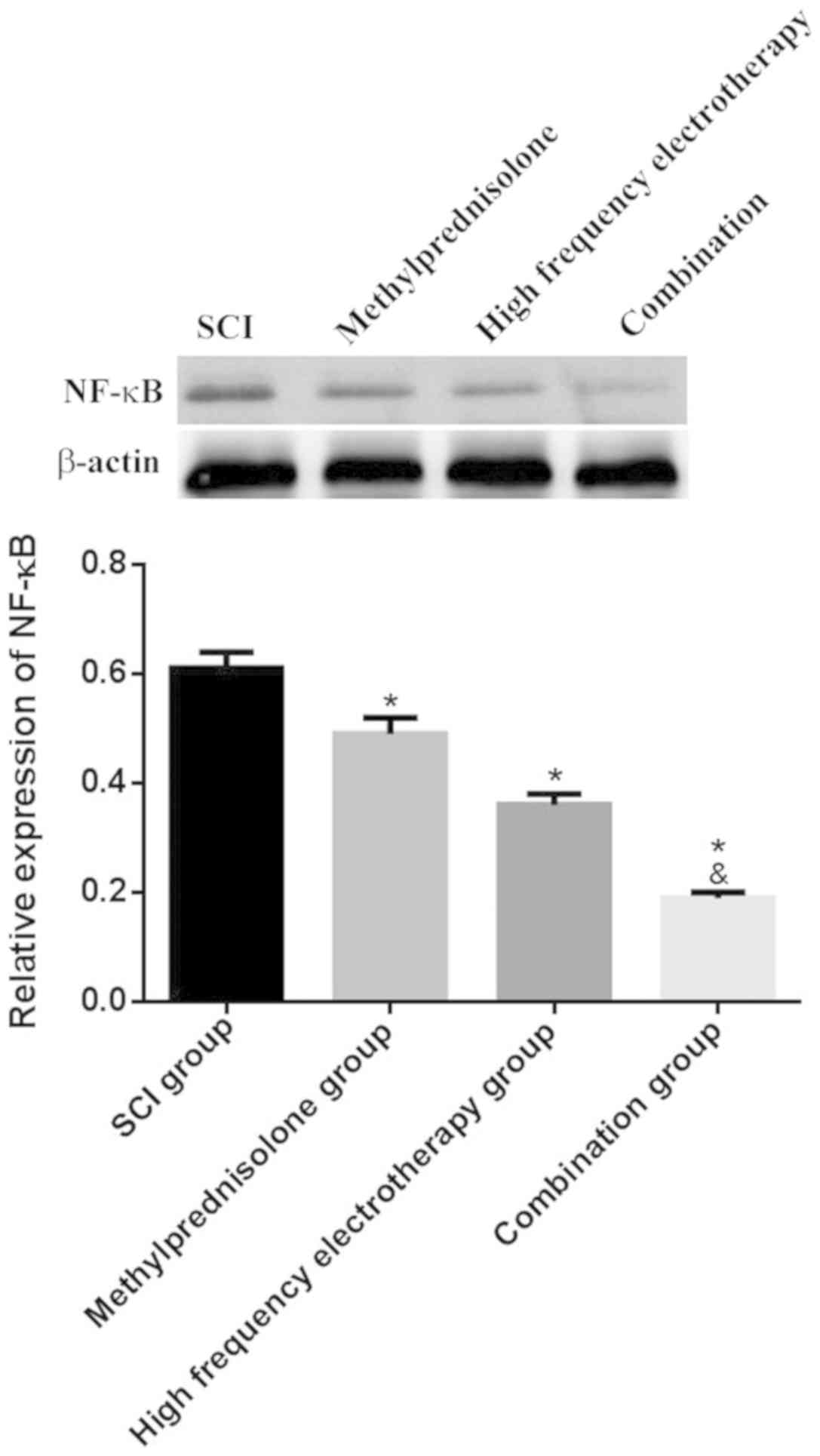
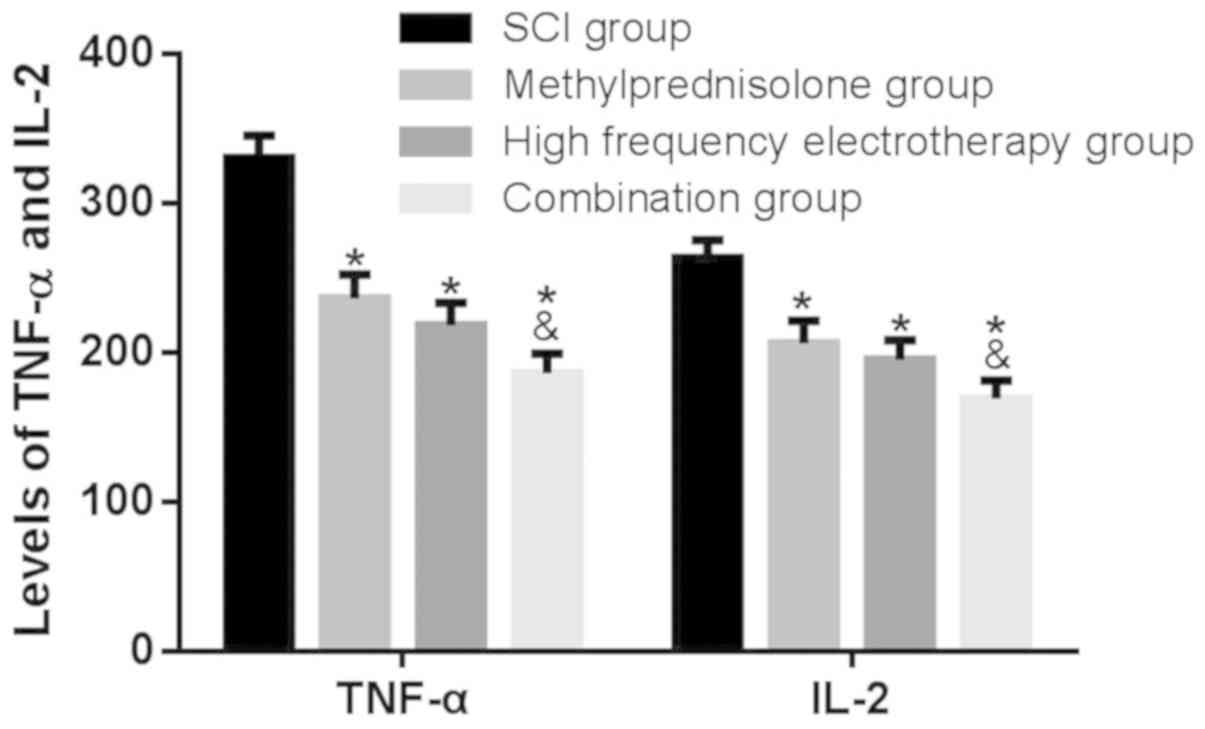
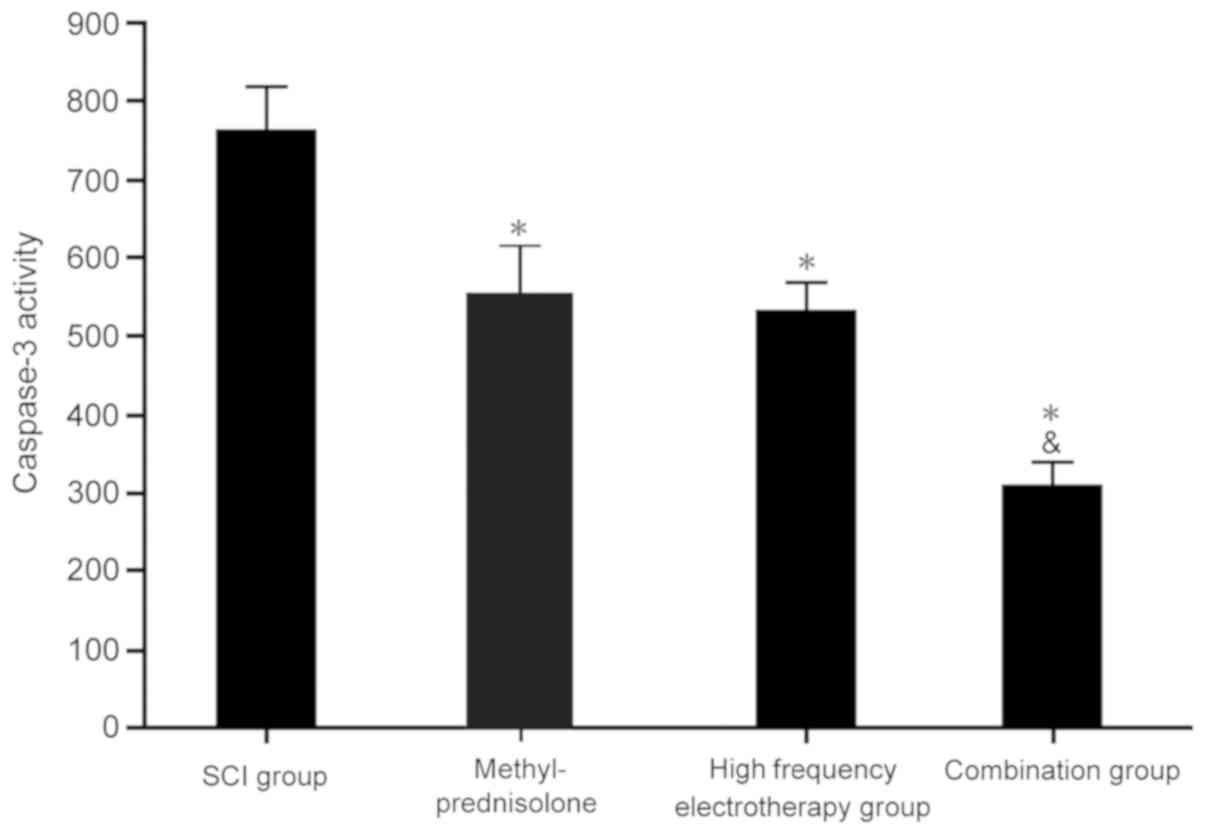
|
1
|
Burkovskiy I, Zhou J and Lehmann C:
Experimental cannabinoid 2 receptor inhibition in CNS
injury-induced immunodeficiency syndrome. Microcirculation.
23:283–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cheah M, Andrews MR, Chew DJ, Moloney EB,
Verhaagen J, Fässler R and Fawcett JW: Expression of an activated
integrin promotes long-distance sensory axon regeneration in the
spinal cord. J Neurosci. 36:7283–7297. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fang H, Zhang JC, Yang M, Li HF, Zhang JP,
Zhang FX, Wang QY, Wang RR and Liu J: Perfusion of gastrodin in
abdominal aorta for alleviating spinal cord ischemia reperfusion
injury. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 9:688–693. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qin W, Li X, Peng Y, Harlow LM, Ren Y, Wu
Y, Li J, Qin Y, Sun J, Zheng S, et al: Sclerostin antibody
preserves the morphology and structure of osteocytes and blocks the
severe skeletal deterioration after motor-complete spinal cord
injury in rats. J Bone Miner Res. 31:14822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rao SN and Pearse DD: Pearse, regulating
axonal responses to injury: The intersection between signaling
pathways involved in axon myelination and the inhibition of axon
regeneration. Front Mol Neurosci. 9:332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Harsha KJ and Parameswaran K: Permanent
spinal cord injury during lumbar spinal anesthesia: A report of two
cases. Neurol India. 64:808–811. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nunnerley J, Gupta S, Snell D and King M:
Training wheelchair navigation in immersive virtual environments
for patients with spinal cord injury-end-user input to design an
effective system. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 12:417–423. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sachdeva R, Farrell K, McMullen MK, Twiss
JL and Houle JD: Dynamic changes in local protein synthetic
machinery in regenerating central nervous system axons after spinal
cord injury. Neural Plast. 2016:40872542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haik MN, Alburquerque-Sendín F, Moreira
RF, Pires ED and Camargo PR: Effectiveness of physical therapy
treatment of clearly defined subacromial pain: A systematic review
of randomised controlled trials. Br J Sports Med. 50:1124–1134.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Page MJ, Green S, Mrocki MA, Surace SJ,
Deitch J, McBain B, Lyttle N and Buchbinder R: Electrotherapy
modalities for rotator cuff disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev
CD012225. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
D'Angelo R, Morreale A, Donadio V, Boriani
S, Maraldi N, Plazzi G and Liguori R: Neuropathic pain following
spinal cord injury: What we know about mechanisms, assessment and
management. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 17:3257–3261.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Braughler JM and Hall ED: Effects of
multi-dose methylprednisolone sodium succinate administration on
injured cat spinal cord neurofilament degradation and energy
metabolism. J Neurosurg. 61:290–295. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bi X, Lv H, Chen BL, Li X and Wang XQ:
Effects of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on pain in
patients with spinal cord injury: A randomized controlled trial. J
Phys Ther Sci. 27:23–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Phillips AA, Matin N, Frias B, Zheng MM,
Jia M, West C, Dorrance AM, Laher I and Krassioukov AV: Rigid and
remodelled: Cerebrovascular structure and function after
experimental high-thoracic spinal cord transection. J Physiol.
594:1677–1688. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rabchevsky AG, Fugaccia I, Sullivan PG,
Blades DA and Scheff SW: Efficacy of methylprednisolone therapy for
the injured rat spinal cord. J Neurosci Res. 68:7–18. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hextrum S and Bennett S: A Critical
examination of subgroup analyses: The national acute spinal cord
injury studies and beyond. Front Neurol. 9:112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abnoosian A and Maguire G: Case report of
an interaction of a vagal nerve stimulation system with a microwave
current from a body fat analyzer. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 20:229–230.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
von Bary C, Mazzitelli D, Voss B, Kübler
F, Schmeller ML, Ndrepepa G and Zrenner B: Evaluation of epicardial
microwave lesions in the pig model using an electroanatomic mapping
system. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 22:5–11. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Man L, Lv X, Du XD, Yin G, Zhu X, Zhang Y,
Soares JC, Yang XN, Chen X and Zhang XY: Cognitive impairments and
low BDNF serum levels in first-episode drug-naive patients with
schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 263:1–6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sapkota S and Dixon RA: A network of
genetic effects on non-demented cognitive aging: Alzheimer's
genetic risk (CLU + CR1 + PICALM) intensifies cognitive aging
genetic risk (COMT + BDNF) selectively for APOe4 carriers. J
Alzheimers Dis. 62:887–900. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen BH, Park JH, Lee TK, Song M, Kim H,
Lee JC, Kim YM, Lee CH, Hwang IK, Kang IJ, et al: Melatonin
attenuates scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment via protecting
against demyelination through BDNF-TrkB signaling in the mouse
dentate gyrus. Chem Biol Interact. 285:8–13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hanada M, Tsutsumi K, Arima H, Shinjo R,
Sugiura Y, Imagama S, Ishiguro N and Matsuyama Y: Evaluation of the
effect of tranilast on rats with spinal cord injury. J Neurol Sci.
346:209–215. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu YH, Liu GH, Mei JJ and Wang J: The
preventive effects of hyperoside on lung cancer in vitro by
inducing apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation through caspase-3
and P53 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 83:381–391. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|