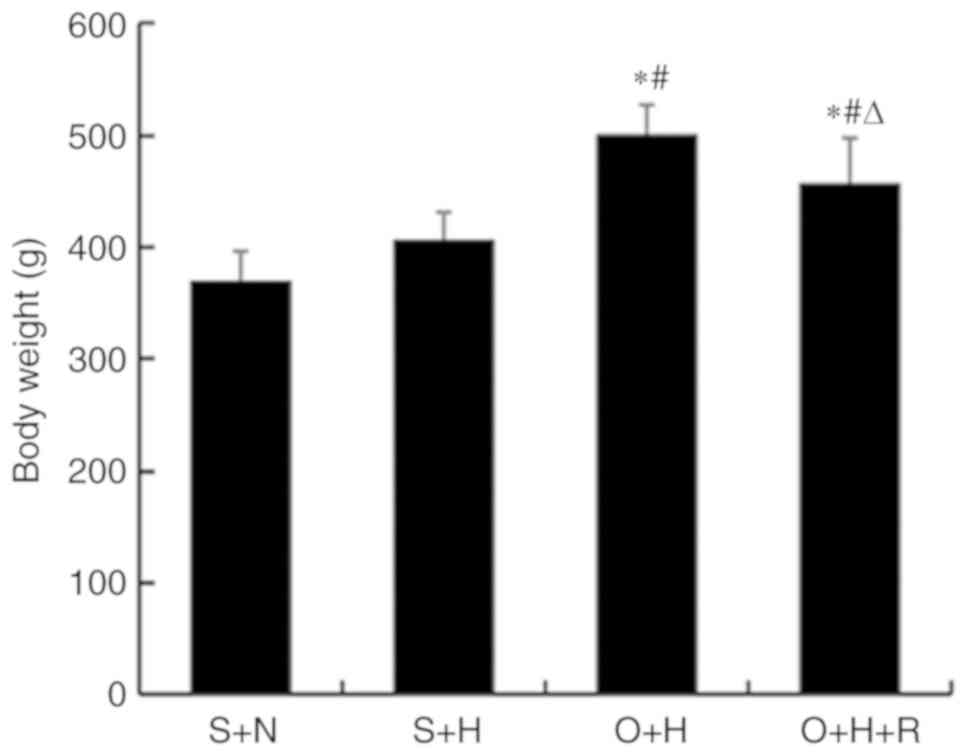
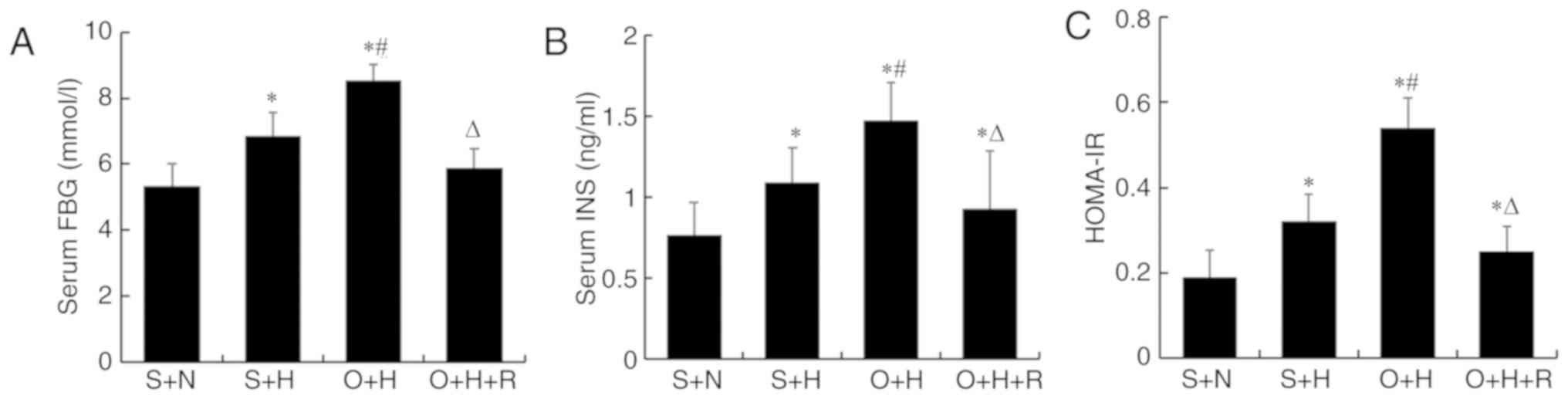
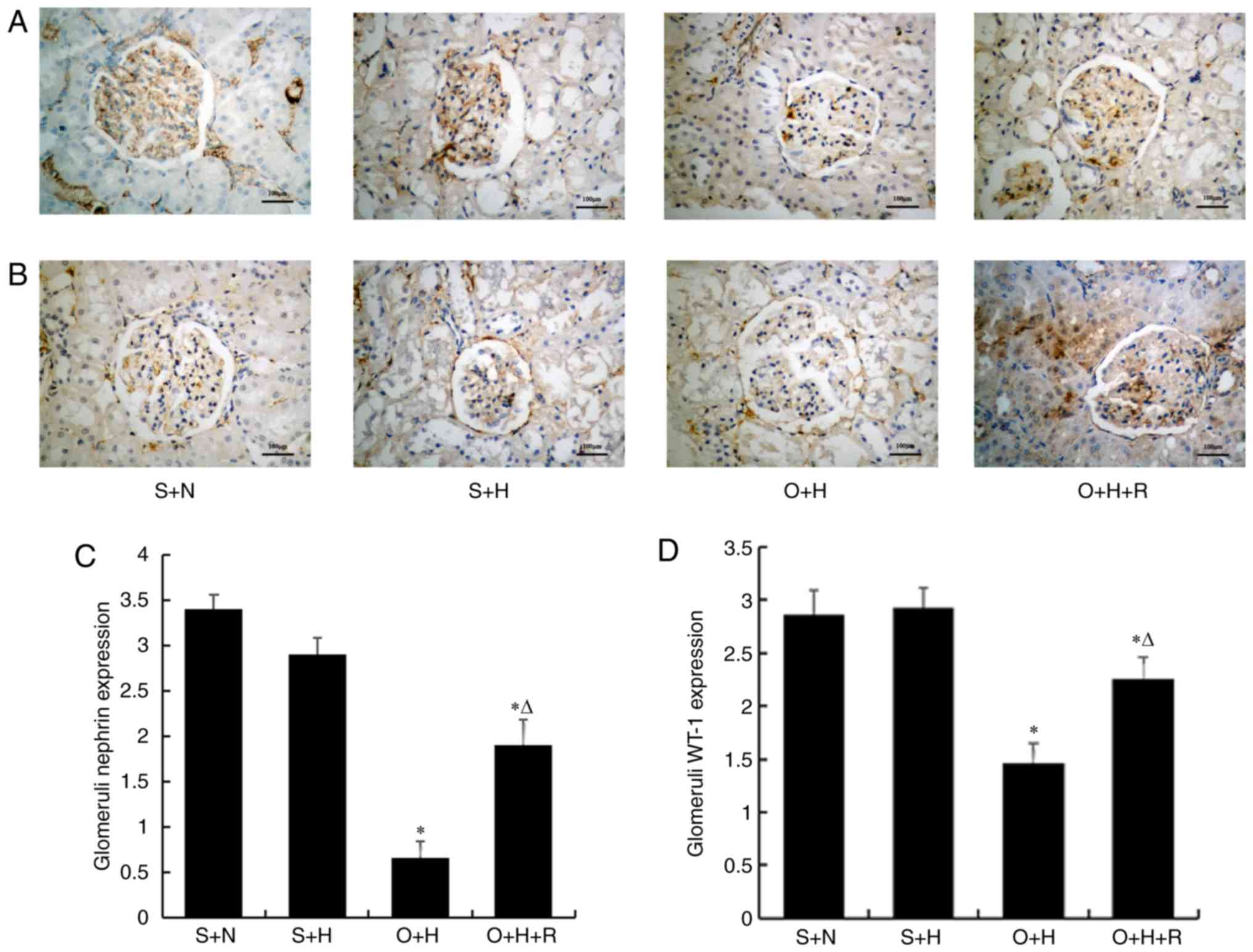
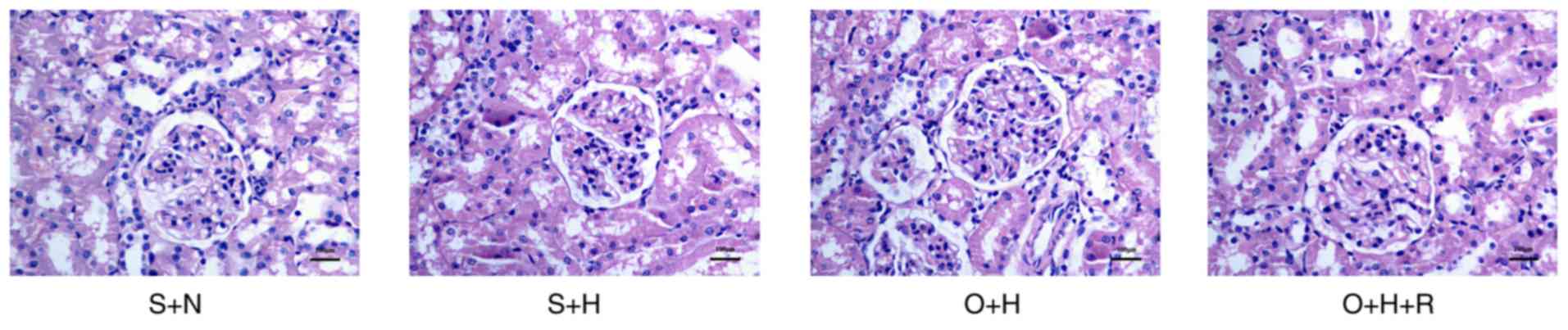
|
1
|
Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei
G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Gutierrez HR, Lu Y, Bahalim AN,
et al: National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index
since 1980: Systematic analysis of health examination surveys and
epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9·1 million
participants. Lancet. 377:578–586. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu H: Obesity and metabolic inflammation.
Drug Discov Today Dis Mech. 10:e21–e25. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hsu CY, Iribarren C, McCulloch CE,
Darbinian J and Go AS: Risk factors for end-stage renal disease:
25-year follow-up. Arch Intern Med. 169:342–350. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Morandi A and Maffeis C: Urogenital
complications of obesity. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab.
27:209–218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kastarinen M, Juutilainen A, Kastarinen H,
Salomaa V, Karhapaa P, Tuomilehto J, Gronhagen-Riska C, Jousilahti
P and Finne P: Risk factors for end-stage renal disease in a
community-based population: 26-year follow-up of 25,821 men and
women in eastern Finland. J Intern Med. 267:612–620. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gambacciani M, Ciaponi M, Cappagli B,
Benussi C, De Simone L and Genazzani AR: Climacteric modifications
in body weight and fat tissue distribution. Climacteric. 2:37–44.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Burns KA and Korach KS: Estrogen receptors
and human disease: An update. Arch Toxicol. 86:1491–1504. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sayakhot P, Vincent A, Deeks A and Teede
H: Potential adverse impact of ovariectomy on physical and
psychological function of younger women with breast cancer.
Menopause. 18:786–793. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chedraui P, Escobar GS, Ramírez C,
Pérez-López FR, Hidalgo L, Mannella P, Genazzani A and Simoncini T:
Nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokine serum levels in
postmenopausal women with the metabolic syndrome. Gynecol
Endocrinol. 28:787–791. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mercantepe T, Unal D, Selli J, Mercantepe
F, Unal B and Karabiyik TN: Protective effects of estrogen and
bortezomib in kidney tissue of post-menopausal rats: An
ultrastructural study. Ren Fail. 38:1129–1135. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Amaral LS, Silva JA, Trindade TM, Ribas
WB, Macedo CL, Coimbra TM, Belo NO, Magalhaes AC and Soares TJ:
Renal changes in the early stages of diet-induced obesity in
ovariectomized rats. Physiol Res. 63:723–732. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meydani M and Hasan HS: Dietary
polyphenols and obesity. Nutrients. 2:737–751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nagao K, Jinnouchi T, Kai S and Yanagita
T: Effect of dietary resveratrol on the metabolic profile of
nutrients in obese OLETF rats. Lipids Health Dis. 12:1–6. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen DQ, Hu HH, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G
and Zhao YY: Natural products for the prevention and treatment of
kidney disease. Phytomedicine. 50:50–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen DQ, Feng YL, Cao G and Zhao YY:
Natural products as a source for antifibrosis therapy. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 39:937–952. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G,
Vaziri ND and Zhao YY: New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in
tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 292:76–83. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang M, Chen DQ, Chen L, Cao G, Zhao H,
Liu D, Vaziri ND, Guo Y and Zhao YY: Novel inhibitors of the
cellular renin-angiotensin system components, poricoic acids,
target Smad3 phosphorylation and Wnt/β-catenin pathway against
renal fibrosis. Br J Pharmacol. 175:2689–2708. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Feng YL, Chen DQ, Vaziri ND, Guo Y and
Zhao YY: Small molecule inhibitors of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition for the treatment of cancer and fibrosis. Med Res Rev.
2019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen L, Yang T, Lu DW, Zhao H, Feng YL,
Chen H, Chen DQ, Vaziri ND and Zhao YY: Central role of
dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad in CKD progression and potential
targets of its treatment. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:670–681. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
de la Lastra CA and Villegas I:
Resveratrol as an anti-inflammatory and anti-aging agent:
Mechanisms and clinical implications. Mol Nutr Food Res.
49:405–430. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xia N, Daiber A, Forstermann U and Li H:
Antioxidant effects of resveratrol in the cardiovascular system. Br
J Pharmacol. 174:1633–1646. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu Y, Feng B, He S, Su Z and Zheng G:
Resveratrol combined with total flavones of hawthorn alleviate the
endothelial cells injury after coronary bypass graft surgery.
Phytomedicine. 40:20–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huo X, Zhang T, Meng Q, Li C and You B:
Resveratrol effects on a diabetic rat model with coronary heart
disease. Med Sci Monit. 25:540–546. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fulda S: Resveratrol and derivatives for
the prevention and treatment of cancer. Drug Discov Today.
15:757–765. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jeon BT, Jeong EA, Shin HJ, Lee Y, Lee DH,
Kim HJ, Kang SS, Cho GJ, Choi WS and Roh GS: Resveratrol attenuates
obesity-associated peripheral and central inflammation and improves
memory deficit in mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetes. 61:1444–1454.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsai CC, Tey SL, Lee MC, Liu CW, Su YT and
Huang SC: Mechanism of resveratrol-induced relaxation of the guinea
pig fundus. Phytomedicine. 43:55–59. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim S, Jin Y, Choi Y and Park T:
Resveratrol exerts anti-obesity effects via mechanisms involving
down-regulation of adipogenic and inflammatory processes in mice.
Biochem Pharmacol. 81:1343–1351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tou JC: Resveratrol supplementation
affects bone acquisition and osteoporosis: Pre-clinical evidence
toward translational diet therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:1186–1194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alberdi G, Rodríguez VM, Miranda J,
Macarulla MT, Arias N, Andrés-Lacueva C and Portillo MP: Changes in
white adipose tissue metabolism induced by resveratrol in rats.
Nutr Metab (Lond). 8:292011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pan QR, Ren YL, Zhu JJ, Hu YJ, Zheng JS,
Fan H, Xu Y, Wang G and Liu WX: Resveratrol increases nephrin and
podocin expression and alleviates renal damage in rats fed a
high-fat diet. Nutrients. 6:2619–2631. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kato T and Mizuno S: Nephron, Wilms'
tumor-1 (WT1), and synaptopodin expression in developingpodocytes
of mice. Exp Anim. 66:183–189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zagotta I, Dimova EY, Debatin KM, Wabitsch
M, Kietzmann T and Fischer-Posovszky P: Obesity and inflammation:
Reduced cytokine expression due to resveratrol in a human in vitro
model of inflamed adipose tissue. Front Pharmacol. 6:792015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sharma R, Sharma NK and Thungapathra M:
Resveratrol regulates body weight in healthy and ovariectomized
rats. Nutr Metab (Lond). 14:302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tang J, Yan H and Zhuang S: Inflammation
and oxidative stress in obesity-related glomerulopathy. Int J
Nephrol. 2012:6083972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Abu-Taha M, Rius C, Hermenegildo C,
Noguera I, Cerda-Nicolas JM, Issekutz AC, Jose PJ, Cortijo J,
Morcillo EJ and Sanz MJ: Menopause and ovariectomy cause a low
grade of systemic inflammation that may be prevented by chronic
treatment with low doses of estrogen or losartan. J Immunol.
183:1393–1402. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brunskill EW and Potter SS: Changes in the
gene expression programs of renal mesangial cells during diabetic
nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 13:702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Batlle D, Wysocki J, Soler MJ and
Ranganath K: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Enhancing the
degradation of angiotensin II as a potential therapy for diabetic
nephropathy. Kidney Int. 81:520–528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kalani A, Mohan A, Godbole MM, Bhatia E,
Gupta A, Sharma RK and Tiwari S: Wilm's tumor-1 protein levels in
urinary exosomes from diabetic patients with or without
proteinuria. PLoS One. 8:e601772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Matoba K, Kawanami D, Ishizawa S, Kanazawa
Y, Yokota T and Utsunomiya K: Rho-kinase mediates TNF-α-induced
MCP-1 expression via p38 MAPK signaling pathway in mesangial cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 402:725–730. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li L, Xiao N, Yang X, Gao J, Ding J, Wang
T, Hu G and Xiao M: A high cholesterol diet ameliorates
hippocampus-related cognitive and pathological deficits in
ovariectomized mice. Behav Brain Res. 230:251–258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huang SS, Ding DF, Chen S, Dong CL, Ye XL,
Yuan YG, Feng YM, You N, Xu JR, Miao H, et al: Resveratrol protects
podocytes against apoptosis via stimulation of autophagy in a mouse
model of diabetic nephropathy. Sci Rep. 7:456922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|