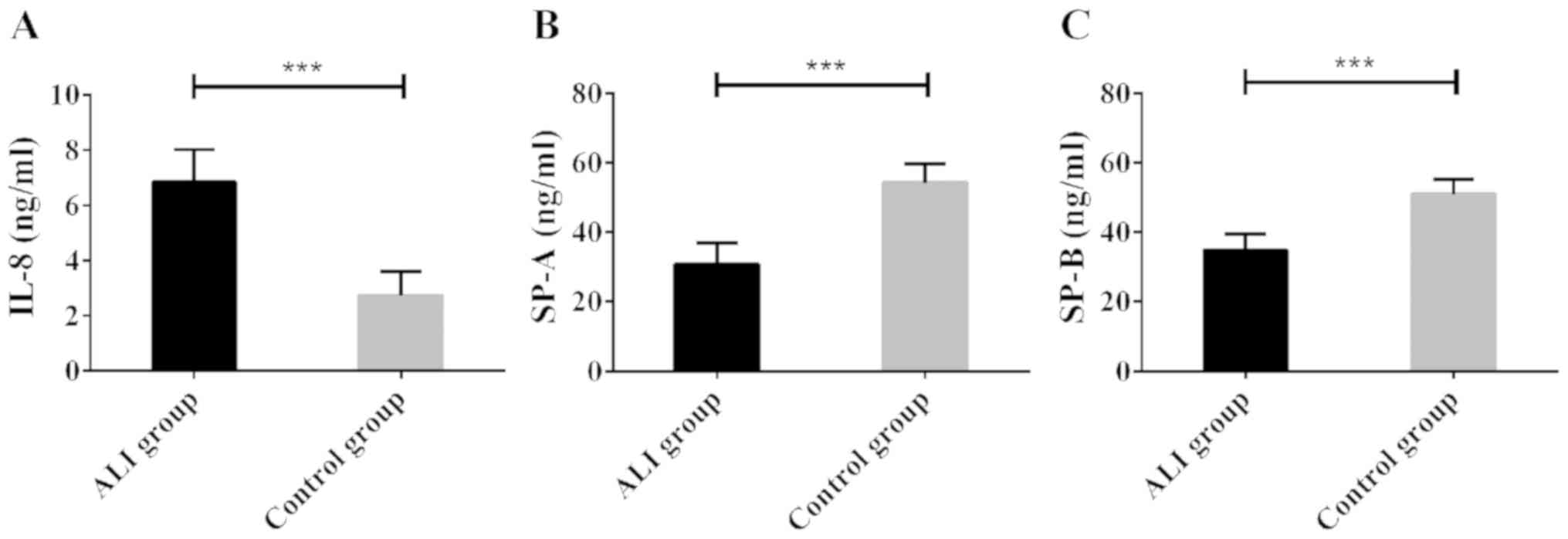
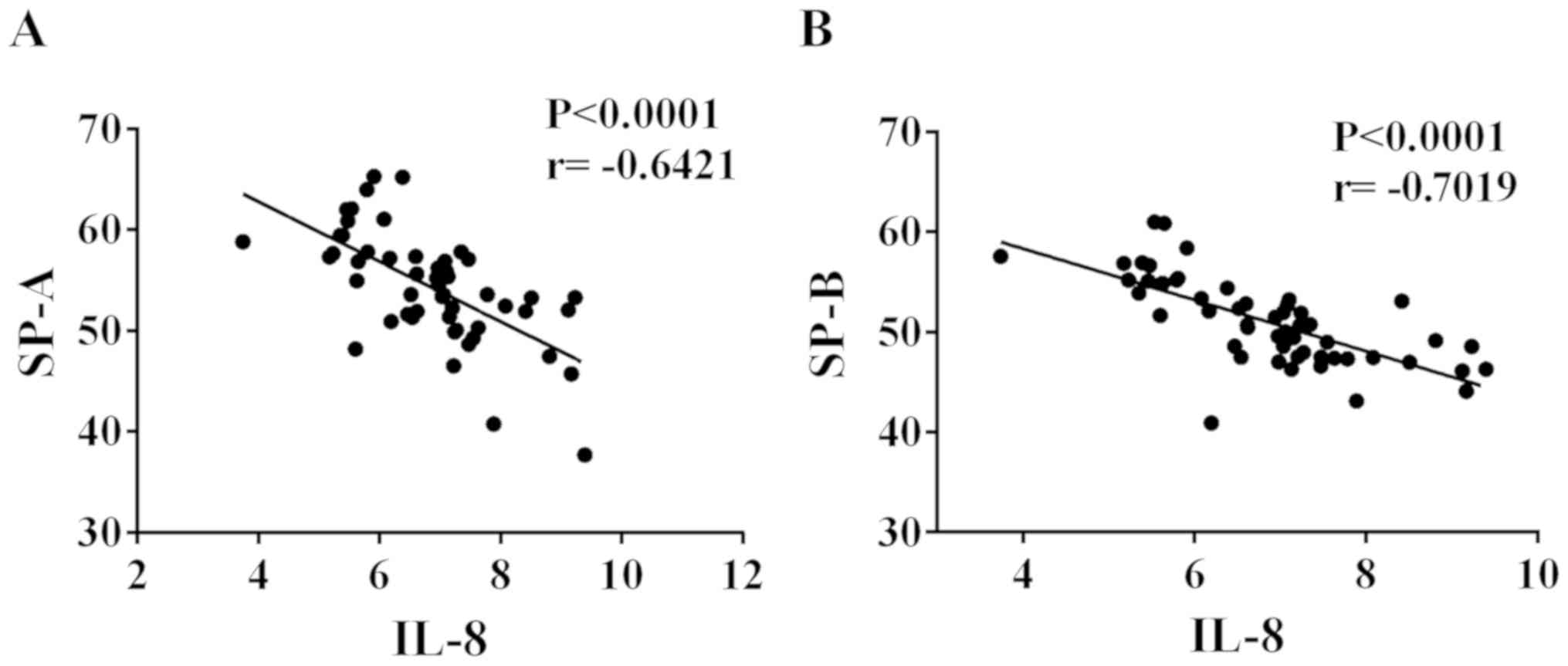
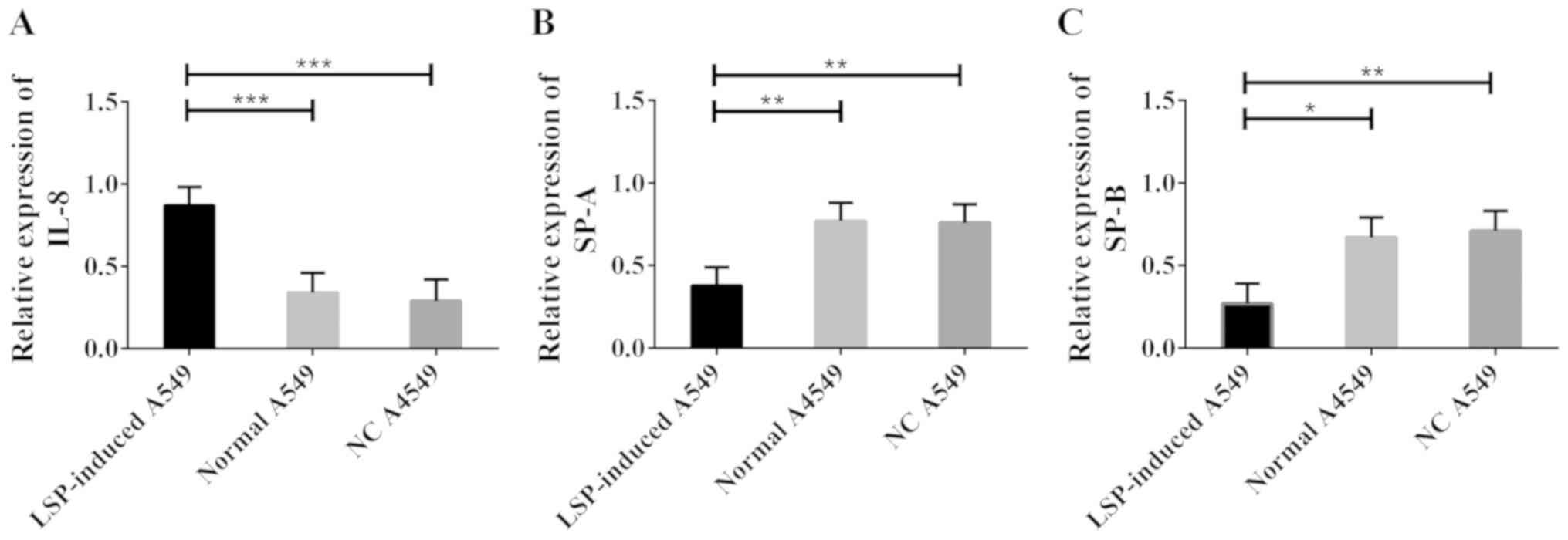
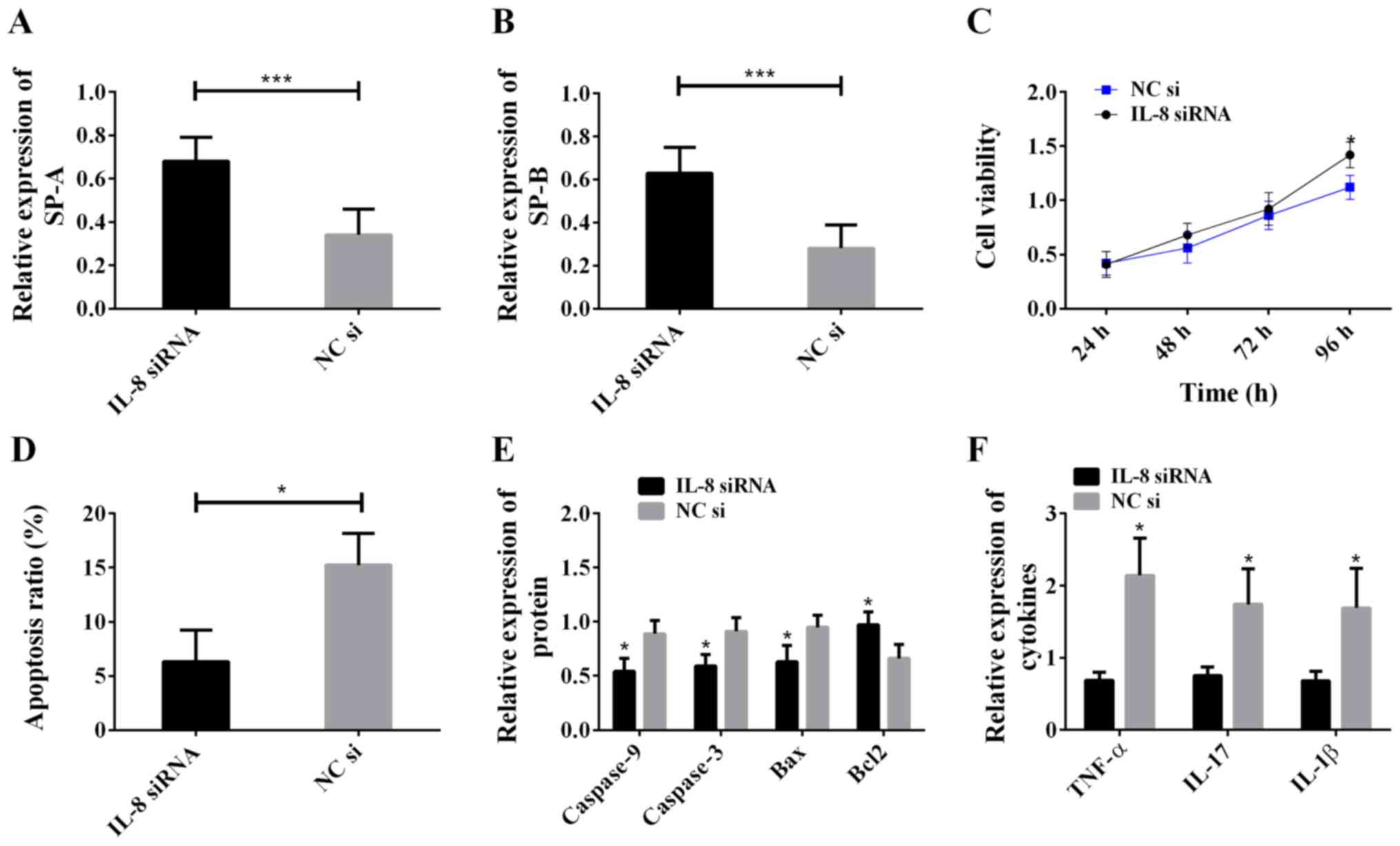
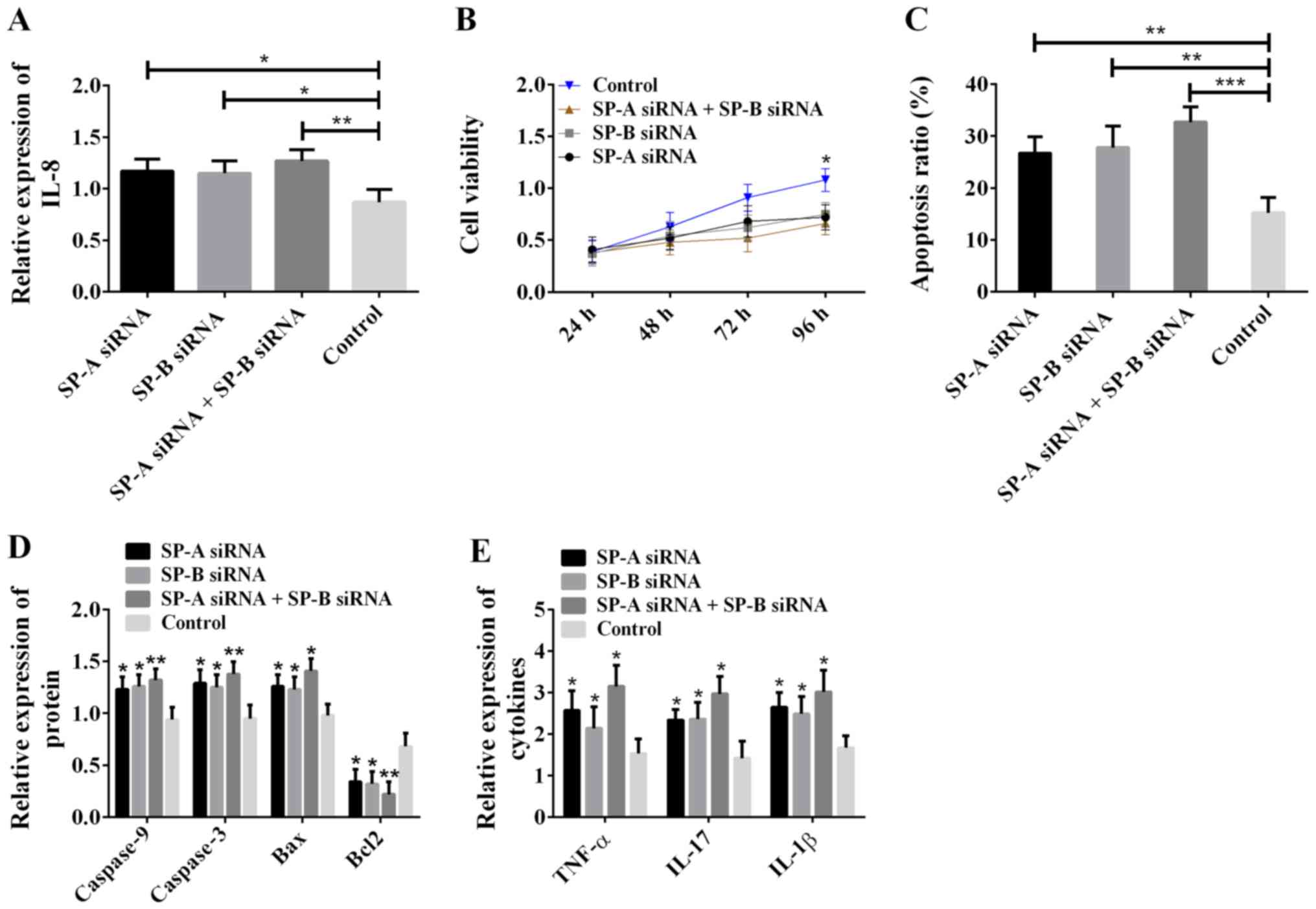
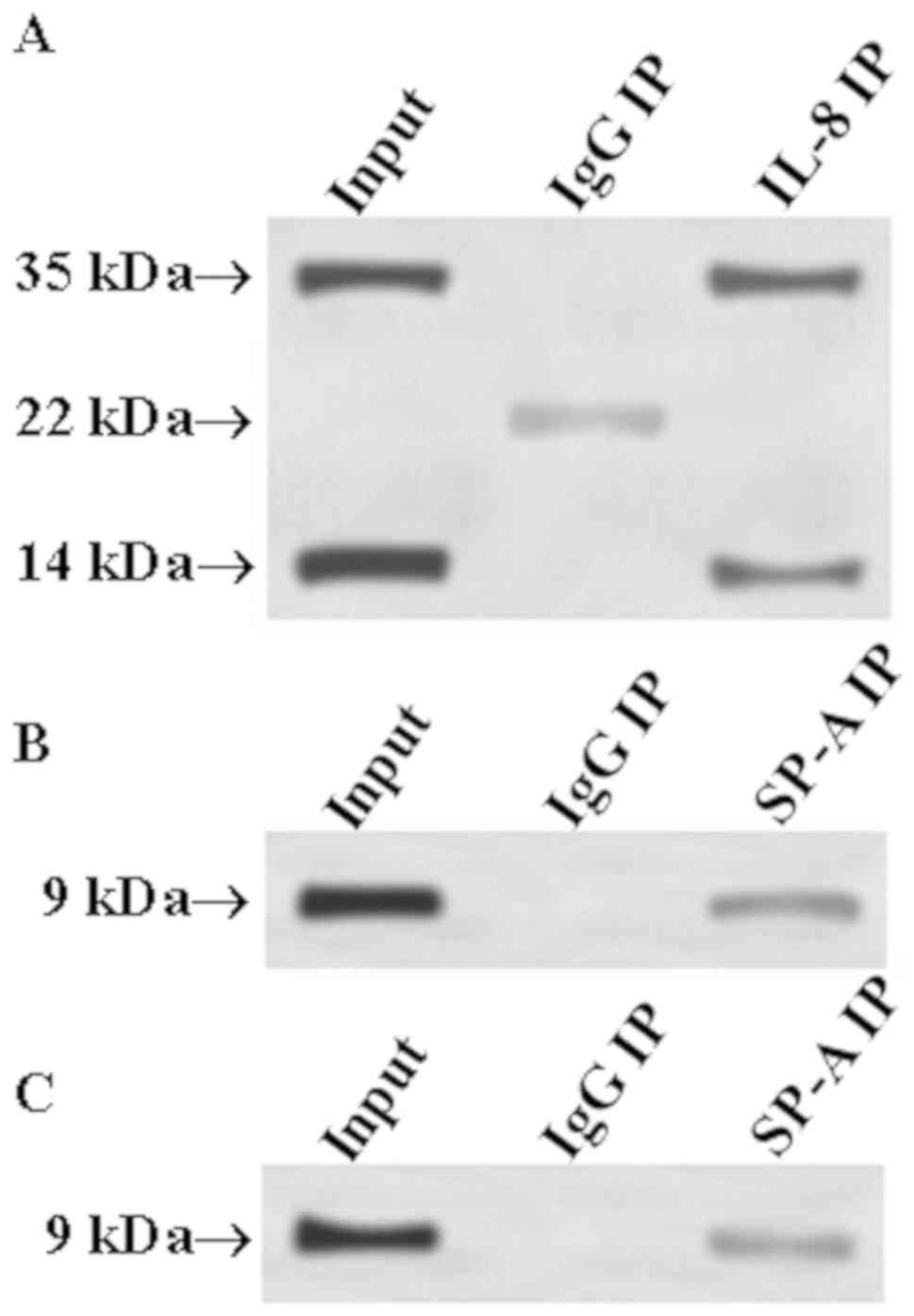
|
1
|
Lumb AB: Acute lung injuryNunn's Applied
Respiratory Physiology. 8th. Elsevier; pp. 439–449. 2017,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Butt Y, Kurdowska A and Allen TC: Acute
lung injury: A clinical and molecular review. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
140:345–350. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fanelli V and Ranieri VM: Mechanisms and
clinical consequences of acute lung injury. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 12
(Suppl 1):S3–S8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Terasaki Y, Suzuki T, Tonaki K, Terasaki
M, Kuwahara N, Ohsiro J, Iketani M, Takahashi M, Hamanoue M,
Kajimoto Y, et al: Molecular hydrogen attenuates gefitinib-induced
exacerbation of naphthalene-evoked acute lung injury through a
reduction in oxidative stress and inflammation. Lab Invest.
99:793–806. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kapur R, Kim M, Aslam R, McVey MJ, Tabuchi
A, Luo A, Liu J, Li Y, Shanmugabhavananthan S, Speck ER, et al: T
regulatory cells and dendritic cells protect against
transfusion-related acute lung injury via IL-10. Blood.
129:2557–2569. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Martin TR, Nakamura M and Matute-Bello G:
The role of apoptosis in acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 31
(Suppl):S184–S188. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oppenheim JJ, Zachariae COC, Mukaida N and
Matsushima K: Properties of the novel proinflammatory supergene
‘intercrine’ cytokine family. Annu Rev Immunol. 9:617–648. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krupa A, Kato H, Matthay MA and Kurdowska
AK: Proinflammatory activity of anti-IL-8 autoantibody: IL-8
complexes in alveolar edema fluid from patients with acute lung
injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 286:L1105–L1113. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu XW, Ma T, Cai Q, Wang L, Song HW and
Liu Z: Elevation of serum PARK7 and IL-8 levels is associated with
acute lung injury in patients with severe sepsis/septic shock. J
Intensive Care Med. 34:662–668. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Selman M, Lin HM, Montaño M, Jenkins AL,
Estrada A, Lin Z, Wang G, DiAngelo SL, Guo X, Umstead TM, et al:
Surfactant protein A and B genetic variants predispose to
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Hum Genet. 113:542–550. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Goto H, Ledford JG, Mukherjee S, Noble PW,
Williams KL and Wright JR: The role of surfactant protein A in
bleomycin-induced acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
181:1336–1344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng G, Ueda T, Nakajima H, Nakajima A,
Arima M, Kinjyo S and Fukuda T: Surfactant protein A exhibits
inhibitory effect on eosinophils IL-8 production. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 270:831–835. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schagat TL, Wofford JA and Wright JR:
Surfactant protein A enhances alveolar macrophage phagocytosis of
apoptotic neutrophils. J Immunol. 166:2727–2733. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ingenito EP, Mora R, Cullivan M, Marzan Y,
Haley K, Mark L and Sonna LA: Decreased surfactant protein-B
expression and surfactant dysfunction in a murine model of acute
lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 25:35–44. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Martínez-Calle M, Olmeda B, Dietl P, Frick
M and Pérez-Gil J: Pulmonary surfactant protein SP-B promotes
exocytosis of lamellar bodies in alveolar type II cells. FASEB J.
32:4600–4611. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ramana CV: Insights into the signal
transduction pathways of mouse lung type II cells revealed by
transcription factor profiling in the transcriptome. Genomics
Inform. 17:e82019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han B, Lodyga M and Liu M:
Ventilator-induced lung injury: Role of protein-protein interaction
in mechanosensation. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2:181–187. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Decuypere JP, Parys JB and Bultynck G:
Regulation of the autophagic bcl-2/beclin 1 interaction. Cells.
1:284–312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao X, Yu Z, Lv Z, Meng L, Xu J, Yuan S
and Fu Z: Activation of alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
(α7nAchR) promotes the protective autophagy in LPS-induced acute
lung injury (ALI) in vitro and in vivo. Inflammation. Sep
14–2019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hough RF, Islam MN, Gusarova GA, Jin G,
Das S and Bhattacharya J: Endothelial mitochondria determine rapid
barrier failure in chemical lung injury. JCI Insight. 4:42019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang NN, Zhang Y, Wang L, Xia JG, Liang
ST, Wang Y, Wang ZZ, Huang X, Li M, Zeng H, et al: Expression
profiling analysis of long noncoding RNAs in a mouse model of
ventilator-induced lung injury indicating potential roles in
inflammation. J Cell Biochem. 120:11660–11679. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li T, Zhao B, Wang C, Wang H, Liu Z, Li W,
Jin H, Tang C and Du J: Regulatory effects of hydrogen sulfide on
IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10 levels in the plasma and pulmonary tissue of
rats with acute lung injury. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 233:1081–1087.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harrod KS, Trapnell BC, Otake K, Korfhagen
TR and Whitsett JA: SP-A enhances viral clearance and inhibits
inflammation after pulmonary adenoviral infection. Am J Physiol.
277:L580–L588. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arias-Diaz J, Garcia-Verdugo I, Casals C,
Sanchez-Rico N, Vara E and Balibrea JL: Effect of surfactant
protein A (SP-A) on the production of cytokines by human pulmonary
macrophages. Shock. 14:300–306. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Epaud R, Ikegami M, Whitsett JA, Jobe AH,
Weaver TE and Akinbi HT: Surfactant protein B inhibits
endotoxin-induced lung inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
28:373–378. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|