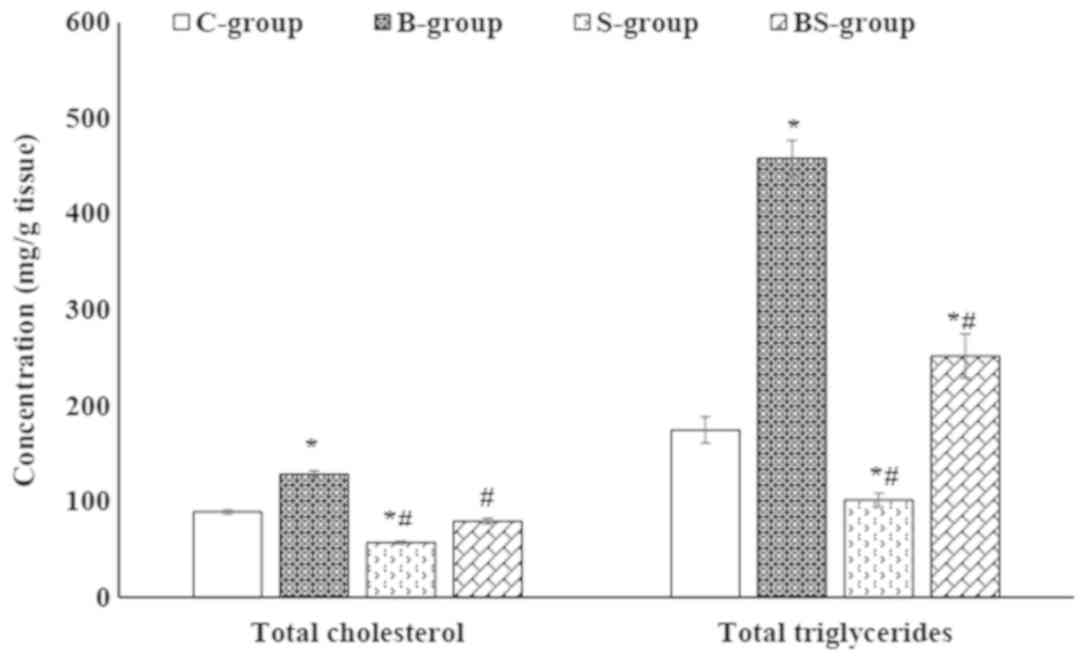
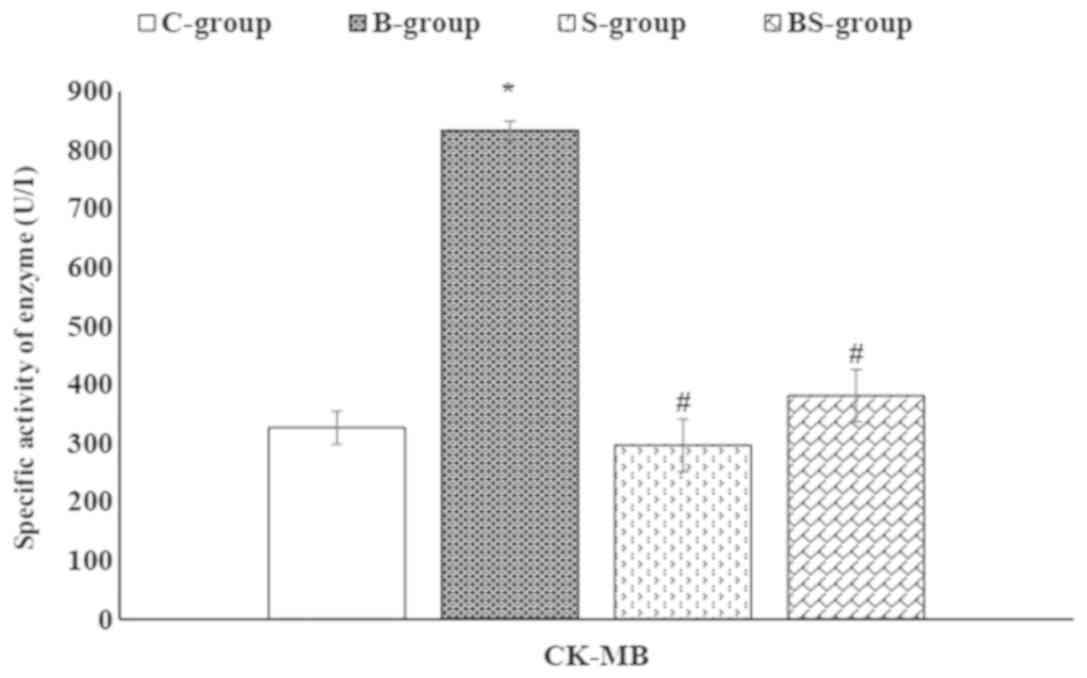
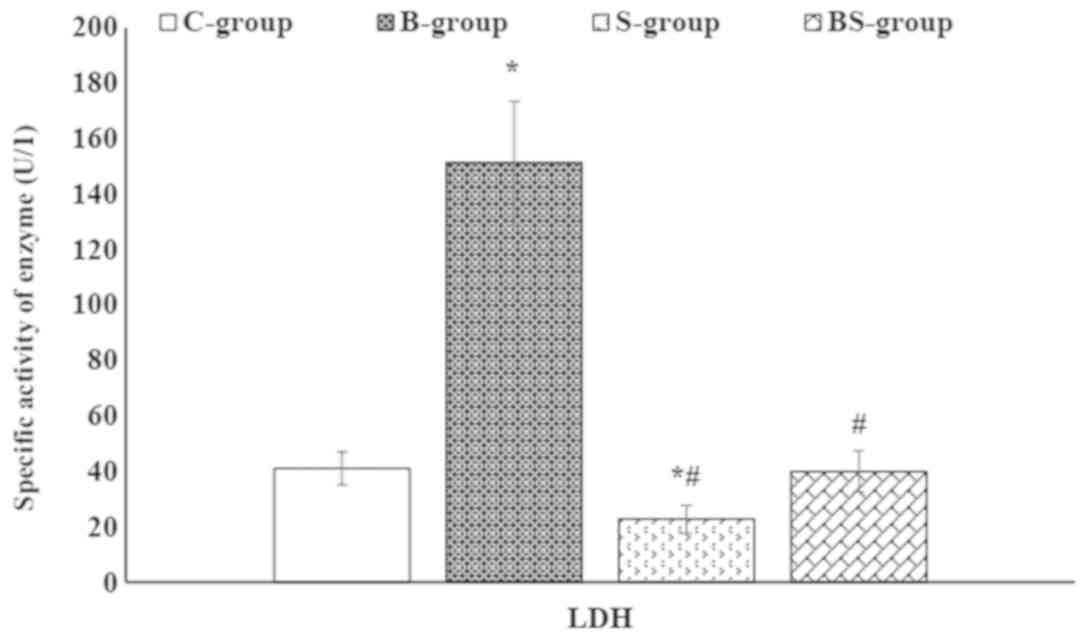
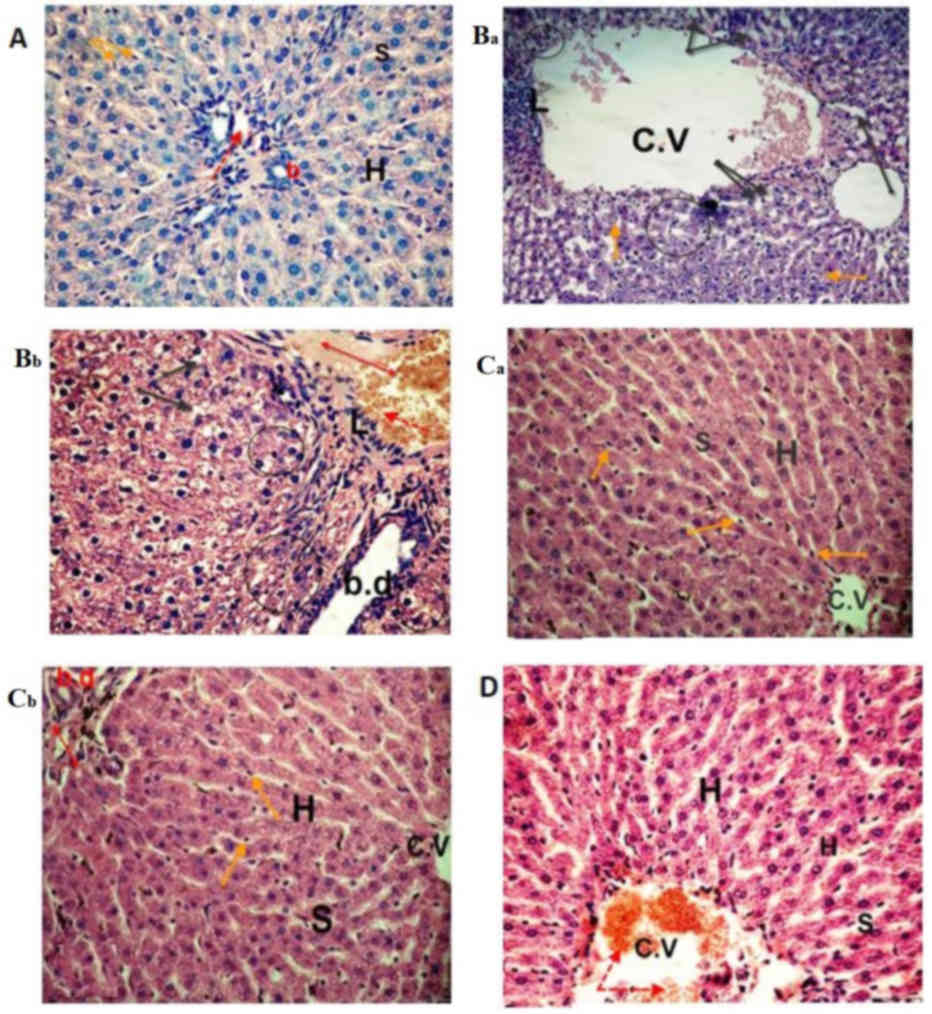
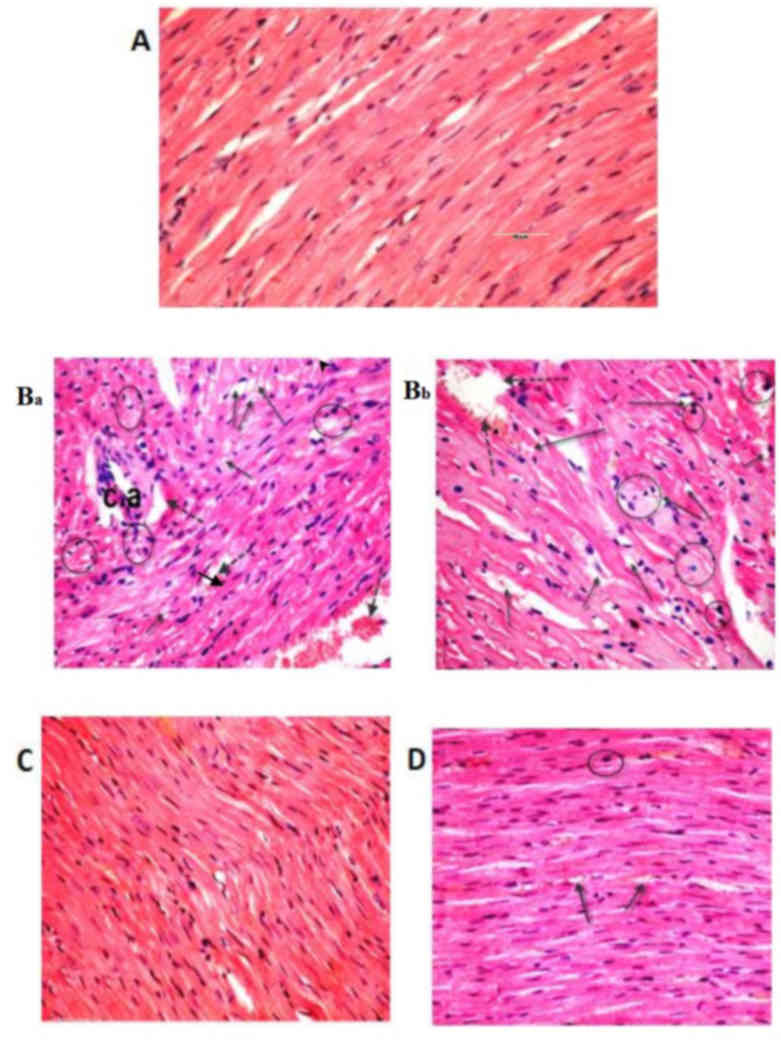
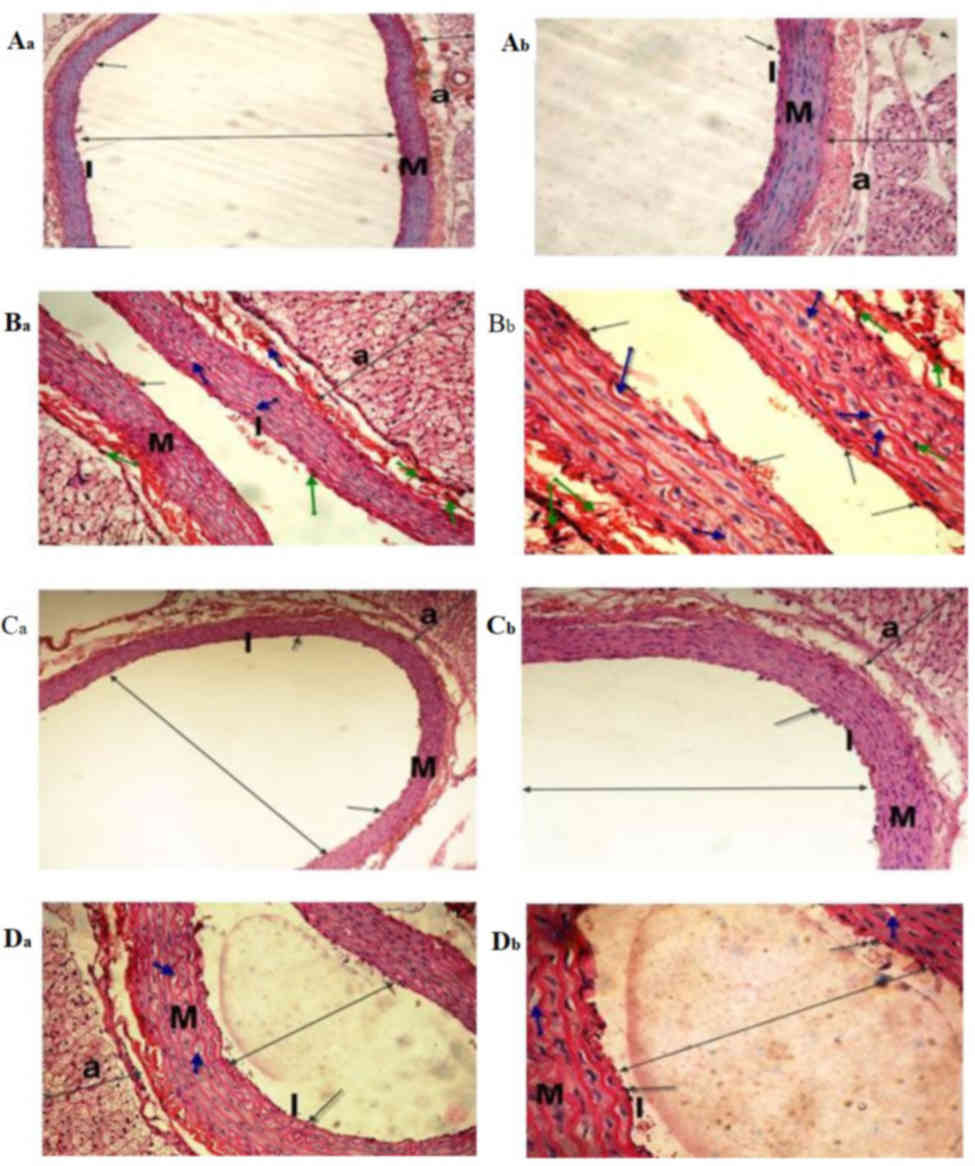
|
1
|
Vandenberg LN, Hauser R, Marcus M, Olea N
and Welshons WV: Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod
Toxicol. 24:139–177. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bushnik T, Haines D, Levallois P, Levesque
J, Van Oostdam J and Viau C: Lead and bisphenol A concentration in
the Canadian population. Health Rep. 21:7–18. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kang JH, Kondo F and Katayama Y: Human
exposure to bisphenol A. Toxicology. 226:79–89. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vandenberg LN, Chahoud I, Heindel JJ,
Padmanabhan V, Paumgartten FJ and Schoenfelder G: Urinary,
circulating, and tissue biomonitoring studies indicate widespread
exposure to bisphenol A. Cien Saude Colet. 17:407–434. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zalko D, Jacques C, Duplan H, Bruel S and
Perdu E: Viable skin efficiently absorbs and metabolizes bisphenol
A. Chemosphere. 82:424–430. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Khalil N, Ebert JR, Wang L, Belcher S, Lee
M, Czerwinski SA and Kannan K: Bisphenol A and cardiometabolic risk
factors in obese children. Sci Total Environ. 470-471:726–732.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hassan ZK, Elobeid MA, Virk P, Omer SA,
ElAmin M, Daghestani MH and AlOlayan EM: Bisphenol A induces
hepatotoxicity through oxidative stress in rat model. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2012:1948292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim JH, Lee MR and Hong YC: Modification
of the association of bisphenol A with abnormal liver function by
polymorphisms of oxidative stress-related genes. Environ Res.
147:324–330. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Santangeli S, Maradonna F, Gioacchini G,
Cobellis G, Piccinetti CC, Dalla Valle L and Carnevali O:
BPA-induced deregulation of epigenetic patterns: Effects on female
zebrafish reproduction. Sci Rep. 6:219822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mohammed F, Abdulwali N, Guillaume D,
Tenyang N, Ponka R, Al-Gadabi K, Bchitou R, Abdullah AH and Naji
KM: Chemical composition and mineralogical residence of sesame oil
from plants grown in different Yemeni environments. Micochem J.
140:269–277. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hung WL, Lu CH, Liao CD and Hwang LS:
Safety evaluation of nano/sub-microsized lignin glycosides from
sesame meal [2013]. Food Control. 30:129–136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Khier MKSE, Ishag KEA and Yagoub AEGA:
Chemical composition and oil characteristics of sesame seed
cultivars grown in Sudan. J Agric Biol Sci. 4:761–766. 2008.
|
|
13
|
Hsu DZ, Chen KT, Chien SP, Li YH, Huang BM
and Chuang YC: Sesame oil attenuates acute iron-induced lipid
peroxidation-associated hepatic damage in mice. Shock. 26:625–630.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sankar D, Sambandam G, Ramakrishna Rao M
and Pugalendi KV: Modulation of blood pressure, lipid profiles and
redox status in hypertensive patients taking different edible oils.
Clin Chim Acta. 355:97–104. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu CT and Liu MY: Daily sesame oil
supplementation attenuates local renin-angiotensin system via
inhibiting MAPK activation and oxidative stress in cardiac
hypertrophy. J Nutr Biochem. 42:108–116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wan Y, Li H, Fu G, Chen X, Chen F and Xie
M: The relationship of antioxidant components and antioxidant
activity of sesame seed oil. J Sci Food Agric. 95:2571–2578. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dar AA and Arumugam N: Lignans of sesame:
Purification methods, biological activities and biosynthesis-A
review. Bioorg Chem. 50:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Park SH, Ryu SN, Bu Y, Kim H, Simon JE and
Kim KS: Antioxidant components as potential neuroprotective agents
in sesame (sesamum indicam L). Food Rev Int. 26:103–121.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Grougnet R, Magiatis P, Laborie H, Lazarou
D, Papadopoulos A and Skaltsounis AL: Sesamolinol glucoside,
disaminyl ether, and other lignans from sesame seeds. J Agric Food
Chem. 60:108–111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Periasamy S, Liu CT, Chien SP, Chen YC and
Liu MY: Daily sesame oil supplementation mitigates
ketoconazole-induced oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis and
hepatic injury. J Nutr Biochem. 37:67–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang H and Tsao R: Dietary polyphenols,
oxidative stress and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Curr Opin Food Sci. 8:33–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yashaswini PS, Sadashivaiah B, Ramaprasad
TR and Singh SA: In vivo modulation of LPS induced leukotrienes
generation and oxidative stress by sesame lignans. J Nutr Biochem.
41:151–157. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reshma MV, Balachandran C, Arumughan C,
Sunderasan A, Sukumaran D, Thomas S and Saritha SS: Extraction,
separation and characterisation of sesame oil lignan for
nutraceutical applications. Food Chem. 120:1041–1046. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Morgan AM, El-Ballal SS, El-Bialy BE and
EL-Borai NB: Studies on the potential protective effect of cinnamon
against bisphenol A- and octylphenol-induced oxidative stress in
male albino rats. Toxicol Rep. 1:92–101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Baluchnejadmojarad T, Roghani M, Jalali
Nadoushan MR, Vaez Mahdavi MR, Kalalian-Moghaddam H,
Roghani-Dehkordi F, Dariani S and Raoufi S: The sesame lignin
sesamin attenuates vascular dysfunction in streptozotocin diabetic
rats: Involvement of nitric oxide and oxidative stress. Eur J
Pharmacol. 698:316–321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Folch J, Lees M and Sloane GH: A simple
method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from
animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 226:497–509. 1957.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bergmeyer HU, Herder M and Red R: Approved
recommendation (1985) on IFCC methods for the measurement of
catalytic concentration of enzymes. Part3. FCC method of alanine
aminotransferase. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 24:481–489.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jendrassik L and Gróf P: Vereinfachte
photometrische. Methoden zur Bestimmung des Blutbilirubins.
Biochemische Zeitschrift. 297:82–89. 1938.
|
|
29
|
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N and Yagi K: Assay for
lipid peroxides in animal tissue by thiobarbituric acid reaction.
Anal Biochem. 95:351–358. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Griffith OW: Determination of glutathione
and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinyl
pyridine. Anal Biochem. 106:207–212. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Smith JK, Vierheller TL and Thorne CA:
Assay of glutathione reductase in crude tissue homogenate using 5–5
dithio bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid). Anal Biochem. 175:408–413. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Paglia E and Valentine N: Studies on the
quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte
glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med. 70:158–169. 1967.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Marklund S and Marklund G: Involvement of
superoxide anion radical in auto-oxidation of pyrogallol and
convenient assay for SOD. Eur J Biochem. 47:469–474. 1974.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
IFCC methods for the measurement of
catalytic concentration of enzymes. Part 7, . IFCC method for
creatine kinase. JIFCC. 1:130–139. 1989.
|
|
35
|
Dito WR: Lactate dehydrogenase: A brief
reviewClinical Enzymology. Griffiths JC: Masson Publishing USA; New
York: pp. pp181979
|
|
36
|
Friedewald WT, Levy RI and Fredrickson DS:
Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein
cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative
ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 18:499–502. 1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Drury RAB and Wallington EA: Carleton's
histological techniqueOxford University Press; New York: 1981
|
|
38
|
Maćczak A, Cyrkler M, Bukowska B and
Michałowicz J: Bisphenol A, bisphenol S, bisphenol F and bisphenol
AF induce different oxidative stress and damage in human red blood
cells (in vitro study). Toxicol In Vitro. 41:143–149. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Abdel-Wahab WM: Thymoquinone attenuates
toxicity and oxidative stress induced by bisphenol A in liver of
male rats. Pak J Biol Sci. 17:1152–1160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bukowska B: Glutathione: Its biosynthesis,
induction agents and concentrations in selected diseases. Med Pr.
55:501–509. 2004.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Guéraud F, Atalay M, Bresgen N, Cipak A,
Eckl PM, Huc L, Jouanin I, Siems W and Uchida K: Chemistry and
biochemistry of lipid peroxidation products. Free Radic Res.
44:1098–1124. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wojnar W, Zych M and Kaczmarczyk-Sedlak I:
Antioxidative effect of flavonoid naringenin in the lenses of type
1 diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:974–984. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Soumya R and Vani R: Vitamin C as a
modulator of oxidative stress in erythrocytes of stored blood. Acta
Haematologica Polonica. 48:350–356. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Vahdati Hassani F, Abnous K, Mehri S,
Jafarian A, Birner-Gruenberger R, Yazdian Robati R and Hosseinzadeh
H: Proteomics and phosphoproteomics analysis of liver in male rats
exposed to bisphenol A: Mechanism of hepatotoxicity and biomarker
discovery. Food Chem Toxicol. 112:26–38. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ke C, Liu X, Zuo H, Zhao J, Yang X and
Yuan J: The oxidative damage of bisphenol A on the organs of the
mice. Sci Res. 5:1190–1194. 2013.
|
|
46
|
Lin Y, Ding D, Huang Q, Liu Q, Lu H, Lu Y,
Chi Y, Sun X, Ye G, Zhu H, et al: Downregulation of miR-192 Causes
Hepatic Steatosis and Lipid Accumulation by Inducing SREBF1: Novel
mechanism for bisphenol A-triggered non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 1862:869–882.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Marmugi A, Ducheix S, Lasserre F, Polizzi
A, Paris A, Priymenko N, Bertrand-Michel J, Pineau T, Guillou H,
Martin PG and Mselli-Lakhal L: Low doses of bisphenol A induce gene
expression related to lipid synthesis and trigger triglyceride
accumulation in adult mouse liver. Hepatology. 55:395–407. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Marmugi A, Lasserre F, Beuzelin D, Ducheix
S, Huc L, Polizzi A, Chetivaux M, Pineau T, Martin P, Guillou H and
Mselli-Lakhal L: Adverse effects of longterm exposure to bisphenol
A during adulthood leading to hyperglycaemia and
hypercholesterolemia in mice. Toxicology. 325:133–143. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rönn M, Kullberg J, Karlsson H, Berglund
J, Malmberg F, Orberg J, Lind L, Ahlström H and Lind MP: Bisphenol
A exposure increases liver fat in juvenile fructose-fed Fischer 344
rats. Toxicology. 303:125–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Korkmaz A, Ahbab MA, Kolankaya D and
Barlas N: Influence of vitamin C on bisphenol A, nonylphenol and
octylphenol induced oxidative damages in liver of male rats. Food
Chem Toxicol. 48:2865–2871. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nicolucci C, Errico S, Federico A, Dallio
M, Loguercio C and Diano N: Human exposure to Bisphenol A and liver
health status: Quantification of urinary and circulating levels by
LC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 140:105–112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Periasamy S, Chien SP, Chang PC, Hsu DZ
and Liu MY: Sesame oil mitigates nutritional steatohepatitis via
attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation: A tale of two-hit
hypothesis. J Nutr Biochem. 25:232–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ljunggrena SA, Igglandb M, Rönnc M, Lindd
L, Lindc PM and Karlsson H: Altered heart proteome in fructose-fed
Fisher 344 rats exposed to bisphenol A. Toxicology. 347-349:6–16.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Aboul Ezz A, Khadrawy Y and Mourad I: The
effect of bisphenol A on some oxidative stress parameters and
acetylcholinesterase activity in the heart of male albino rats.
Cytotechnol. 67:145–155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Suthar H, Verma RJ, Patel S and Jasrai YT:
Green tea potentially ameliorates bisphenol A-induced oxidative
stress: An in vitro and in silico study. Biochem Res Inter.
2014:2597632014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Helal EG, Badawi MM, Soliman G, Abdel-Kawi
AN, Fadel EA and Abozaid GM: Physiological and Histopathological
studies on Bisphenol-A compound as xenoestrogen in male albino
rats. Egypt J Hospit Med. 50:127–136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Ma JQ, Ding J, Zhang L and Liu CM:
Hepatoprotective properties of sesamin against CCl4
induced oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in mice via JNK
pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 64:41–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Makni M, Fetoui H, Garoui EM, Gargouri NK,
Jaber H, Makni J, Boudawara T and Zeghal N: Hypolipidemic and
hepatoprotective seeds mixture diet rich in omega-3 and omega-6
fatty acids. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:2239–2246. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Suwimol S, Wiroj J, Kewalin W, Natchapon
J, Pathamaporn H and Auranun S: Effects of sesame seeds consumption
on serum cholesterol and oxidative status in hypercholesterolemia.
Food Public Health. 2:193–196. 2012.
|
|
60
|
Asgary S, Kopaei RM, Najafi S, Heidarian E
and Sahebkar A: Antihyperlipidemic effects of Sesamum
indicum L. in rabbits fed a high-fat diet.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2013:3658922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim M, Woo M, Noh JS, Choe E and Song YO:
Sesame oil lignans inhibit hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress and
apoptosis in high-fat diet-fed mice. J Functional Foods.
37:658–665. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Penalvo JL, Hopia A and Adlercreutz H:
Effect of sesamin on serum cholesterol and triglycerides levels in
LDL receptor-deficient mice. Eur J Nutr. 45:439–444. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kushiro M, Masaokab T, Hageshitab S,
Takahashia Y, Idea T and Suganoc M: Comparative effect of sesamin
and episesamin on the activity and gene expression of enzymes in
fatty acid oxidation and synthesis in rat liver. J Nutr Biochem.
13:289–295. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ide T, Kushiro M, Takahashi Y, Shinohara
K, Fukuda N and Yasumoto S: Sesamin, a sesame lignan, as a potent
serum lipid-lowering food component. JARQ. 37:151–158. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Fernández-Formoso G, Pérez-Sieira S,
González-Touceda D, Dieguez C and Tovar S: Leptin, 20 years of
searching for glucose homeostasis. Life Sci. 140:4–9. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chavali SR, Zhong WW and Forse RA: Dietary
alpha-linolenic acid increases TNF-alpha, and decreases IL-6, IL-10
in response to LPS: Effects of sesamin on the delta-5 desaturation
of omega6 and omega3 fatty acids in mice. Prostaglandins Leukot
Essent Fatty Acids. 58:185–191. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Haider DG, Leuchten N, Schaller G, Gouya
G, Kolodjaschna J, Schmetterer L, Kapiotis S and Wolzt M:
C-reactive protein is expressed and secreted by peripheral blood
mononuclear cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 146:533–539. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Saleem MT, Chetty MC and Kavimani S:
Sesame oil enhances endogenous antioxidants in ischemic myocardium
of rat. Brazilian J Pharmacogn. 22:669–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Conti V, Izzo V, Corbi G, Russomanno G,
Manzo V, De Lise F, Donato A and Filippelli A: Antioxidant
supplementation in the treatment of aging-associated diseases.
Front Pharmacol. 7:242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ragavendran P, Sophia D, Arulraj A and
Gopalakrishnan VK: Cardioprotective effect of aqueous, ethanol and
aqueous ethanol extract of Aerva lanata (Linn.) against
doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in rats. Asian Pac J Trop
Biomed. 2 (Suppl):S212–S218. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Li WX, Kong X, Zhanga JX and Yang JR:
Long-term intake of sesamin improves left ventricular remodelling
in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Funct. 4:453–460. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|