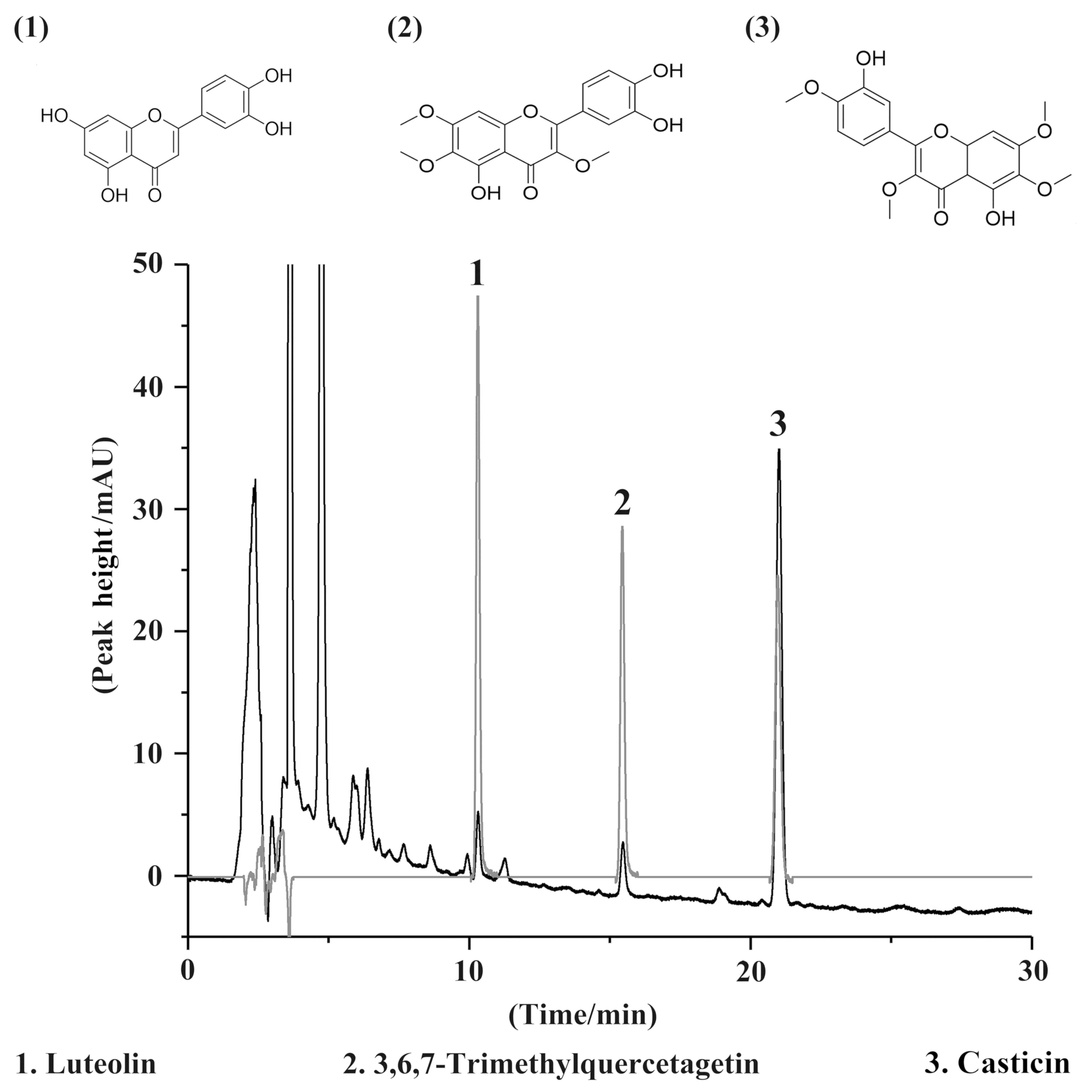
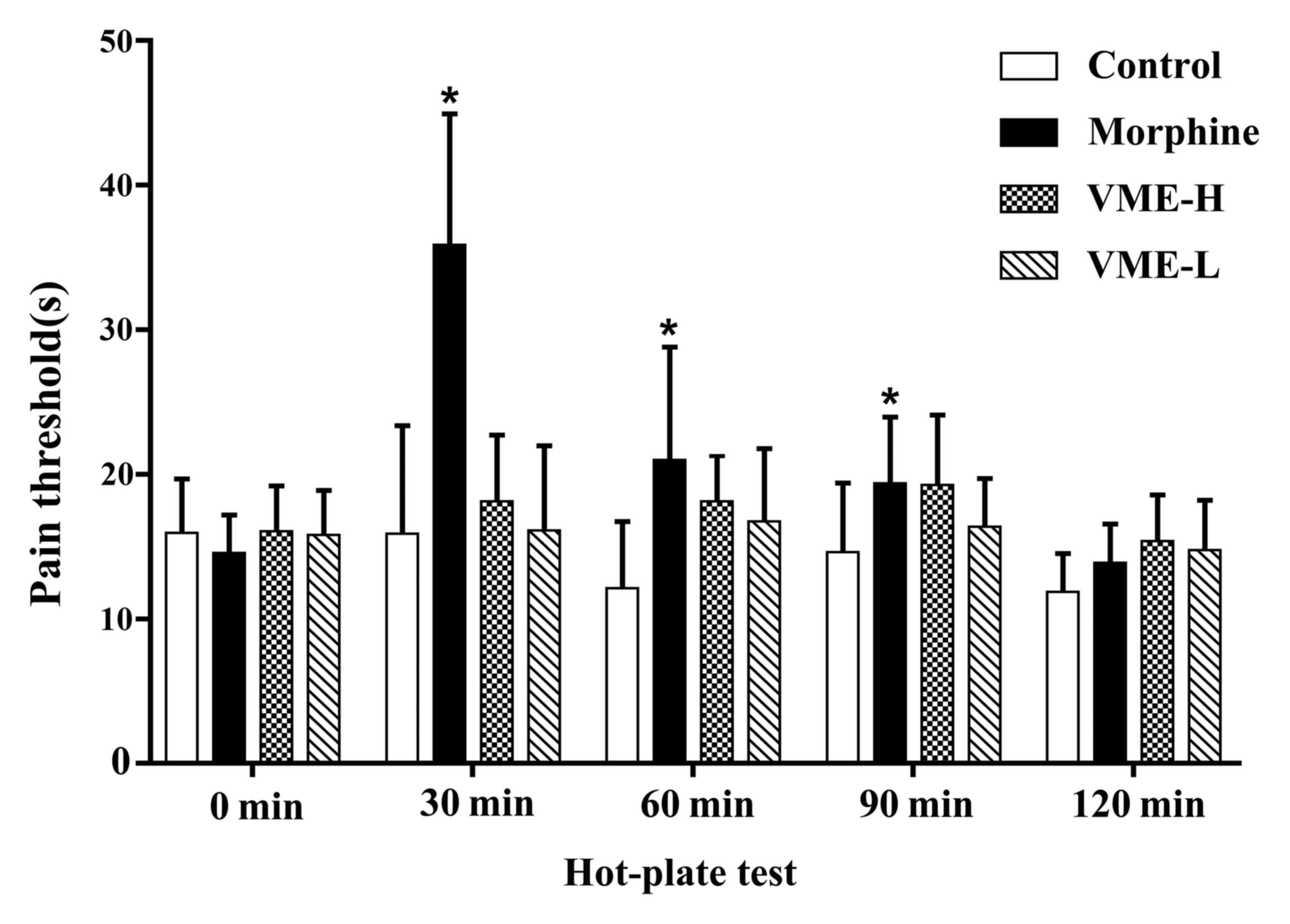
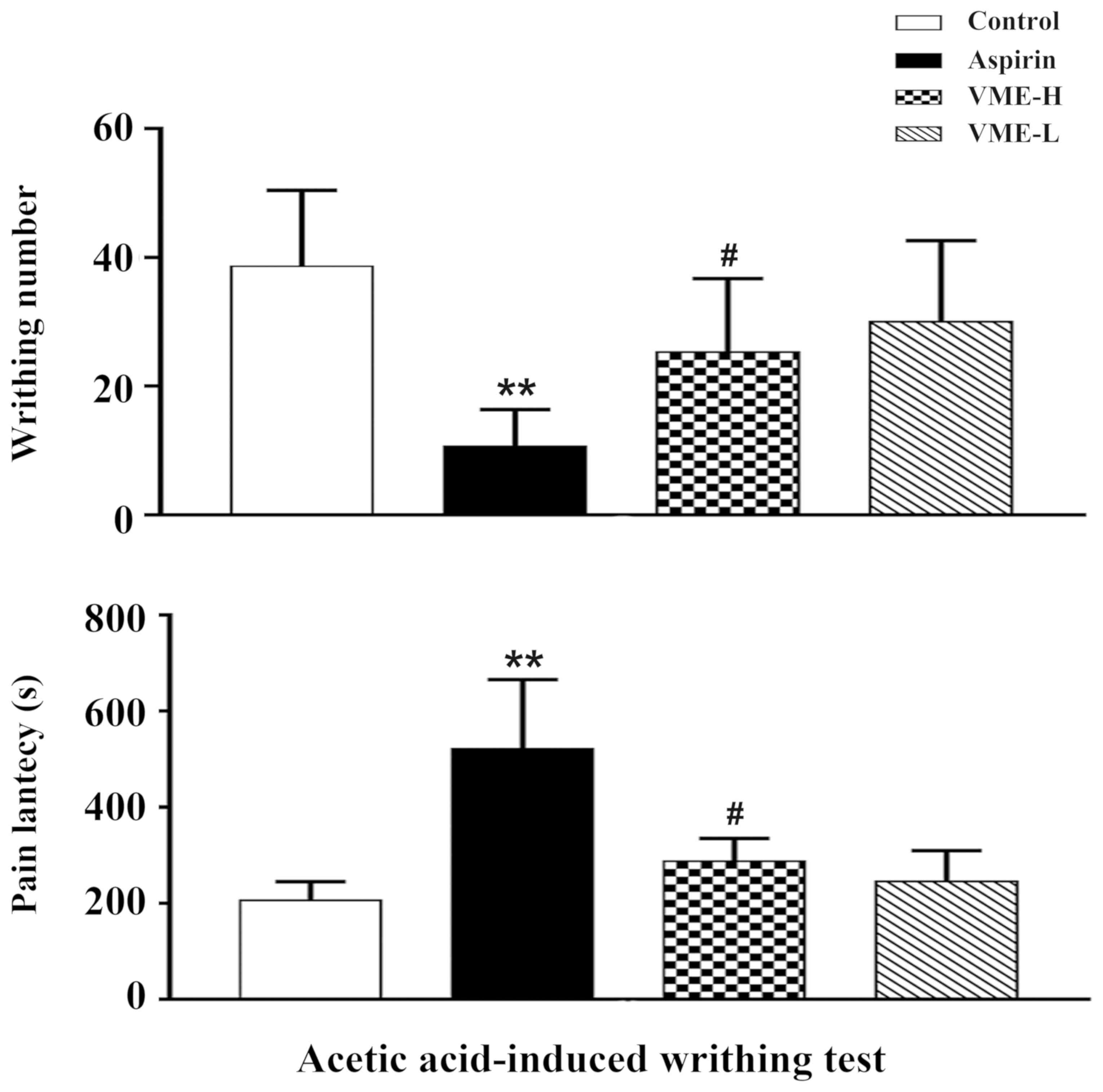
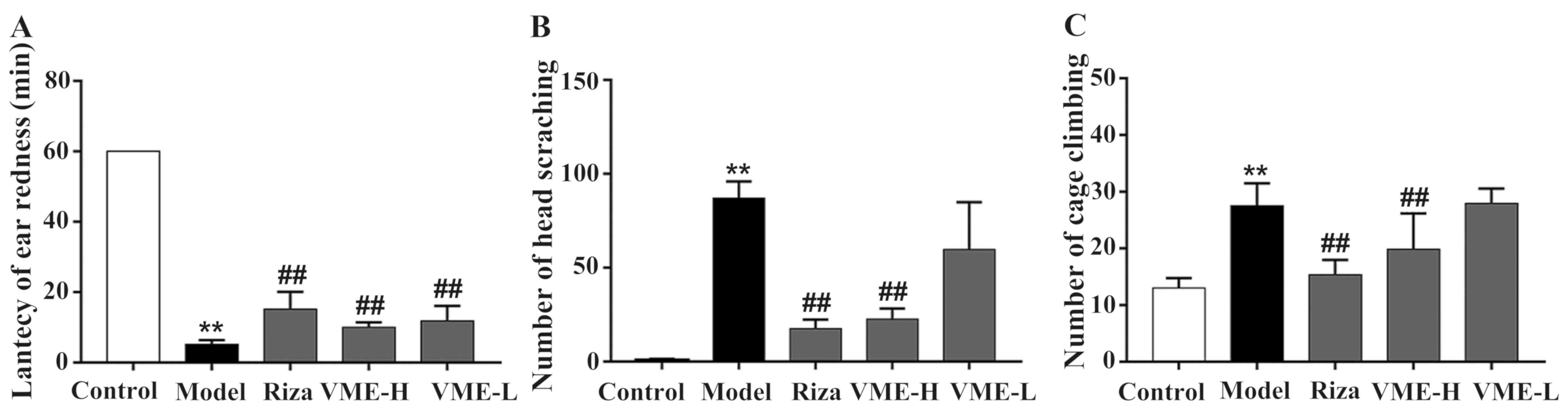
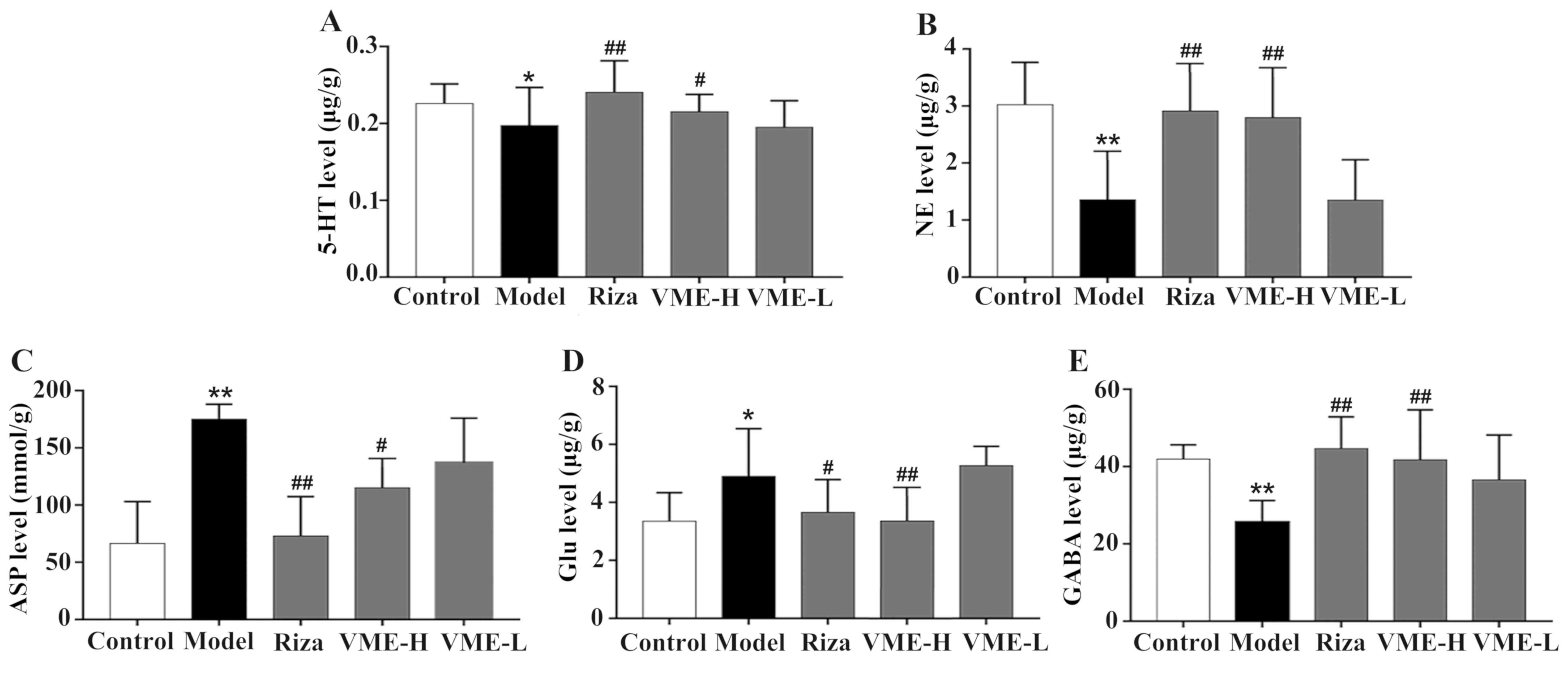
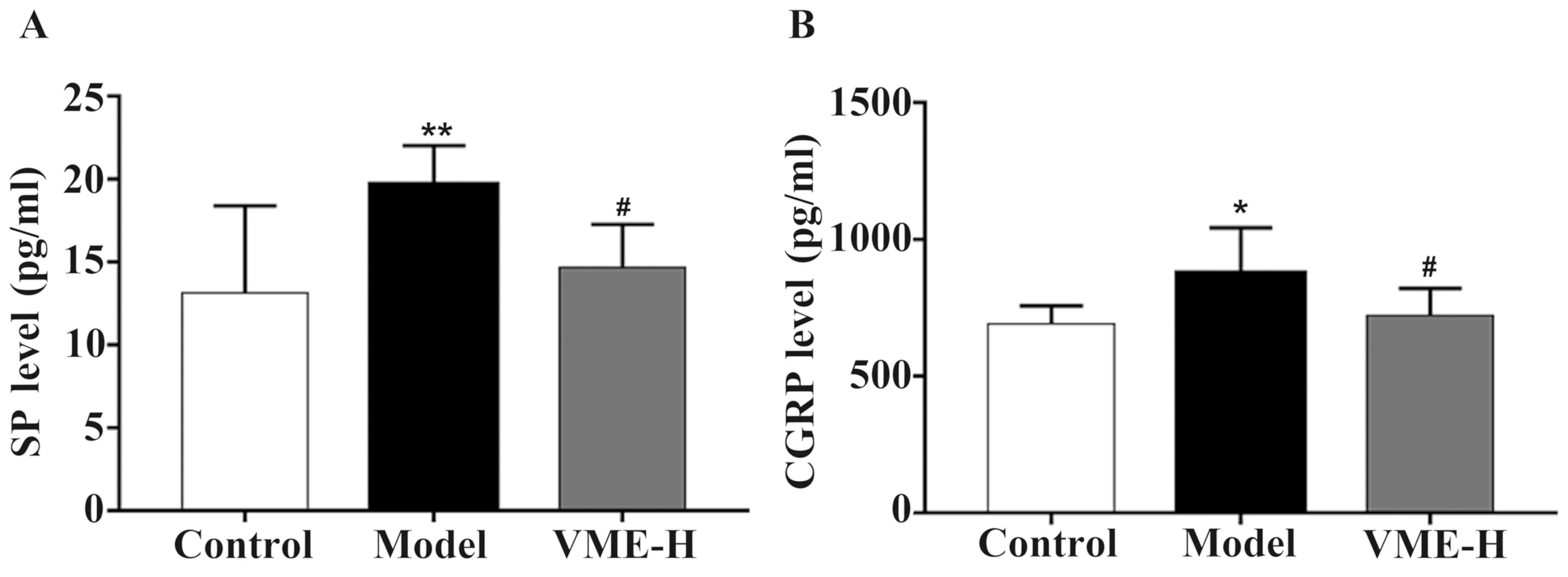
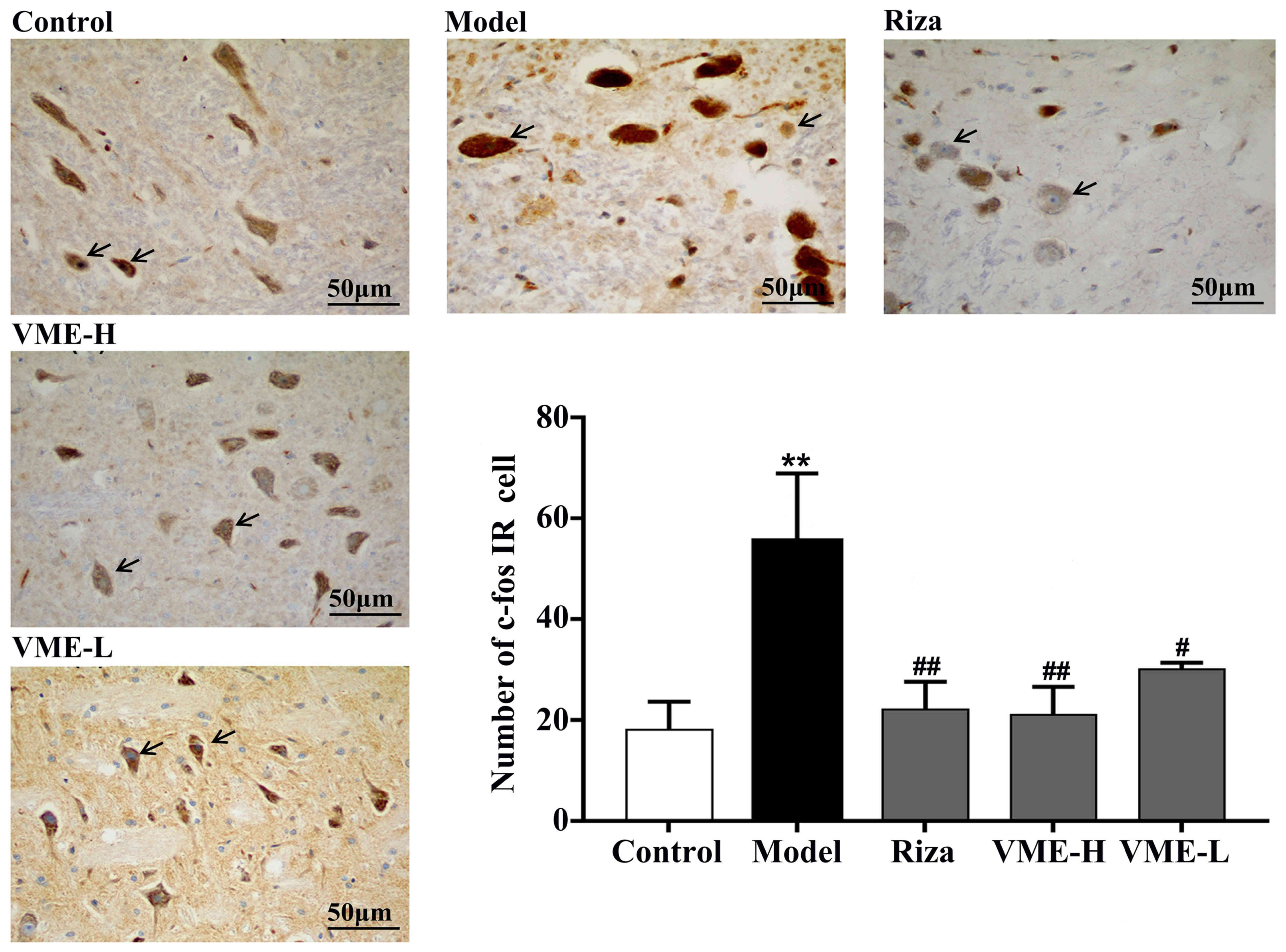
|
1
|
GBD 2015 Neurological Disorders
Collaborator Group, : Global, regional, and national burden of
neurological disorders during 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for
the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Neurol. 16:877–897.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Patton GC, Olsson CA, Skirbekk V, Saffery
R, Wlodek ME, Azzopardi PS, Stonawski M, Rasmussen B, Spry E,
Francis K, et al: Adolescence and the next generation. Nature.
554:458–466. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mawet J, Kurth T and Ayata C: Migraine and
stroke: In search of shared mechanisms. Cephalalgia. 35:165–181.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bolay H, Reuter U, Dunn AK, Huang Z, Boas
DA and Moskowitz MA: Intrinsic brain activity triggers trigeminal
meningeal afferents in a migraine model. Nat Med. 8:136–142. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Asghar MS, Hansen AE, Larsson HB, Olesen J
and Ashina M: Effect of CGRP and sumatriptan on the BOLD response
in visual cortex. J Headache Pain. 13:159–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iyengar S, Ossipov MH and Johnson KW: The
role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and central
pain mechanisms including migraine. Pain. 158:543–559. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyoshi H and Nakaya Y: Calcitonin
gene-related peptide activates the K+ channels of vascular smooth
muscle cells via adenylate cyclase. Basic Res Cardiol. 90:332–336.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Basbaum AI, Bautista DM, Scherrer G and
Julius D: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. Cell.
139:267–284. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Demartini C, Tassorelli C, Zanaboni AM,
Tonsi G, Francesconi O, Nativi C and Greco R: The role of the
transient receptor potential ankyrin type-1 (TRPA1) channel in
migraine pain: Evaluation in an animal model. J Headache Pain.
18:942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Borkum JM: Migraine triggers and oxidative
stress: A narrative review and synthesis. Headache. 56:12–35. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bohár Z, Fejes-Szabó A, Tar L, Varga H,
Tajti J, Párdutz Á and Vécsei L: Evaluation of c-Fos
immunoreactivity in the rat brainstem nuclei relevant in migraine
pathogenesis after electrical stimulation of the trigeminal
ganglion. Neurol Sci. 34:1597–1604. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dodick DW: Migraine. Lancet.
391:1315–1330. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moye LS and Pradhan AAA: Animal model of
chronic migraine-associated pain. Curr Protoc Neurosci.
80:9.60.1–9.60.9. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rains JC, Penzien DB, McCrory DC and Gray
RN: Behavioral headache treatment: History, review of the empirical
literature, and methodological critique. Headache. 45 (45
Suppl):S92–S109. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gallagher RM and Kunkel R: Migraine
medication attributes important for patient compliance: Concerns
about side effects may delay treatment. Headache. 43:36–43. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen DQ, Cao G, Chen H, Argyopoulos CP, Yu
H, Su W, Chen L, Samuels DC, Zhuang S, Bayliss GP, et al:
Identification of serum metabolites associating with chronic kidney
disease progression and anti-fibrotic effect of
5-methoxytryptophan. Nat Commun. 10:14762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen DQ, Feng YL, Cao G and Zhao YY:
Natural products as a source for antifibrosis therapy. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 39:937–952. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao L, Chen J, Li Y, Sun X, Chang X,
Zheng H, Gong B, Huang Y, Yang M, Wu X, et al: The Long-term effect
of acupuncture for migraine prophylaxis: A randomized clinical
trial. JAMA Intern Med. 177:508–515. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun YY, Zhang WJ, Dong CL, Zhang XF, Ji J,
Wang X, Wang L, Hu WL, Du WJ, Cui CL, et al: Baicalin alleviates
Nitroglycerin-induced migraine in rats via the trigeminovascular
system. Phytother Res. 31:899–905. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu Y, Pan X, Xu Y, Lu X, He S, He R and
Gong M: Optimization of combinations of ginsenoside-Rg1,
ginsenoside-Rb1, evodiamine and rutaecarpine for effective therapy
of mouse migraine. J Nat Med. 70:207–216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hou M, Tang Q, Xue Q, Zhang X, Liu Y, Yang
S, Chen L and Xu X: Pharmacodynamic action and mechanism of Du
Liang soft capsule, a traditional Chinese medicine capsule, on
treating nitroglycerin-induced migraine. J Ethnopharmacol.
195:231–237. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu Y, Xin HL, Zhang QY, Zheng HC, Rahman K
and Qin LP: Anti-nociceptive and anti-hyperprolactinemia activities
of Fructus Viticis and its effective fractions and chemical
constituents. Phytomedicine. 14:668–674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guan R, Wang D, Yu Z, Wang X and Lan T:
Preparative isolation and purification of the active components
from Viticis Fructus by high-speed counter-current
chromatography. Se Pu. 28:1043–1047. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yan YY, Dai JZ, Yang CX and Zhang GM:
Analysis of traditional Chinese medicine syndromes in 159 German
migraine patients. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 42:2599–2605.
2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu P, Xing B, Chu Z, Liu F, Lei G, Zhu L,
Gao Y, Chen T and Dang YH: Dopamine D3 receptor knockout mice
exhibitabnormal nociception in a sex-different manner. J Neurosci
Res. 95:1438–1445. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang G, Hu Z, Song X, Cui Q, Fu Q, Jia R,
Zou Y, Li L and Yin Z: Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory activities
of resveratrol through classic models in mice and rats. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2017:51975672017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zakaria A, Jais MR and Ishak R: Analgesic
properties of nigella sativa and eucheuma cottonii extracts. J Nat
Sci Biol Med. 9:23–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nair AB and Jacob S: A simple practice
guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin
Pharm. 7:27–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fu W, Dai Y, Ma T, Wei J, Chen H and Xu S:
Tongluo Xingnao effervescent tablet reverses memory deficit and
reduces plaque load in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. Exp Ther Med.
15:4005–4013. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Burstein R, Noseda R and Borsook D:
Migraine: Multiple processes, complex pathophysiology. J Neurosci.
35:6619–6629. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pradhan AA, Smith ML, McGuire B, Tarash I,
Evans CJ and Charles A: Characterization of a novel model of
chronic migraine. Pain. 155:269–274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tang Y, Liu S, Shu H, Xing Y and Tao F:
AMPA receptor GluA1 Ser831 phosphorylation is critical for
nitroglycerin-induced migraine-like pain. Neuropharmacology.
133:462–469. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ben Aissa M, Tipton AF, Bertels Z, Gandhi
R, Moye LS, Novack M, Bennett BM, Wang Y, Litosh V, Lee SH, et al:
Soluble guanylyl cyclase is a critical regulator of
migraine-associated pain. Cephalalgia. 38:1471–1484. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Becerra L, Bishop J, Barmettler G, Kainz
V, Burstein R and Borsook D: Brain network alterations in the
inflammatory soup animal model of migraine. Brain Res. 1660:36–46.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Munro G, Jansen-Olesen I and Olesen J:
Animal models of pain and migraine in drug discovery. Drug Discov
Today. 22:1103–1111. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
D'Andrea G and Leon A: Pathogenesis of
migraine: From neurotransmitters to neuromodulators and beyond.
Neurol Sci. 31 (Suppl 1):S1–S7. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
State Pharmacopoeia Committee, .
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. Part I. Beijing:
China Medical Science and Technology Press. 2015.
|
|
38
|
Silberstein SD, Dodick DW, Bigal ME, Yeung
PP, Goadsby PJ, Blankenbiller T, Grozinski-Wolff M, Yang R, Ma Y
and Aycardi E: Fremanezumab for the preventive treatment of chronic
migraine. N Engl J Med. 377:2113–2122. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Akerman S, Holland PR, Lasalandra MP and
Goadsby PJ: Endocannabinoids in the brainstem modulate dural
trigeminovascular nociceptive traffic via CB1 and ‘triptan’
receptors: Implications in migraine. J Neurosci. 33:14869–14877.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Malhotra R: Understanding migraine:
Potential role of neurogenic inflammation. Ann Indian Acad Neurol.
19:175–182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Martins LB, Teixeira AL and Domingues RB:
Neurotrophins and migraine. Vitam Horm. 104:459–473. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rosa AC and Fantozzi R: The role of
histamine in neurogenic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 170:38–45.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Williamson DJ, Hargreaves RJ, Hill RG and
Shepheard SL: Intravital microscope studies on the effects of
neurokinin agonists and calcitonin gene-related peptide on dural
vessel diameter in the anaesthetized rat. Cephalalgia. 17:518–524.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Alvaro G and Di Fabio R: Neurokinin 1
receptor antagonists-current prospects. Curr Opin Drug Discov
Devel. 10:613–621. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhou L, Pinyi C, Ling L, Zhang Y, Liu X,
Wu Y, Jiang L, Cheng D, Huang W, Pettigrew JC and Yi D: Systematic
review and meta-analysis of traditional Chinese medicine in the
treatment of migraines. Am J Chin Med. 41:1011–1025. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hu HQ, Zhou YH and Wang XL: Clinical study
on effect of Xiaoyao Nose Drops in stopping episode of Migraine.
Chin J Integr Med. 12:112–117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li JC, Shen XF, Meng XL, Zhang Y and Lai
XR: Analgesic effect and mechanism of the three TCM-herbal
drug-combination Tou Feng Yu pill on treatment of migraine.
Phytomedicine. 18:788–794. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Song HM, Park GH, Park SB, Kim HS, Son HJ,
Um Y and Jeong JB: Vitex rotundifolia Fruit Suppresses the
proliferation of human colorectal cancer cells through
Down-regulation of Cyclin D1 and CDK4 via proteasomal-dependent
degradation and transcriptional inhibition. Am J Chin Med.
46:191–207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hara K, Haranishi Y, Terada T, Takahashi
Y, Nakamura M and Sata T: Effects of intrathecal and
intracerebroventricular administration of luteolin in a rat
neuropathic pain model. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 125:78–84. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Backhouse N, Delporte C, Apablaza C,
Farías M, Goïty L, Arrau S, Negrete R, Castro C and Miranda H:
Antinociceptive activity of Buddleja globosa (matico) in several
models of pain. J Ethnopharmacol. 119:160–165. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ishisaka M, Kakefuda K, Yamauchi M,
Tsuruma K, Shimazawa M, Tsuruta A and Hara H: Luteolin shows an
antidepressant-like effect via suppressing endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1481–1486. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee C, Lee JW, Jin Q, Lee HJ, Lee SJ, Lee
D, Lee MK, Lee CK, Hong JT, Lee MK and Hwang BY: Anti-inflammatory
constituents from the fruits of Vitex rotundifolia. Bioorg Med Chem
Lett. 23:6010–6014. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ambrosini A, Di Lorenzo C, Coppola G and
Pierelli F: Use of Vitex agnus-castus in migrainous women with
premenstrual syndrome: An open-label clinical observation. Acta
Neurol Belg. 113:25–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Noseda R, Borsook D and Burstein R:
Neuropeptides and neurotransmitters that modulate thalamo-cortical
pathways relevant to migraine headache. Headache. 57 (Suppl
2):S97–S111. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Andreou AP, Shields KG and Goadsby PJ:
GABA and valproate modulate trigeminovascular nociceptive
transmission in the thalamus. Neurobiol Dis. 37:314–323. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Janssen SP, Truin M, Van Kleef M and
Joosten EA: Differential GABAergic disinhibition during the
development of painful peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscience.
184:183–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhu X, Han Y, Xiong W, Liu W, Lu S, Li J,
Wang H and Fan Z: Effects of heating coagulation of middle
meningeal artery on plasma CGRP level and c-fos expression in
migraine rat triggered by nitroglycerin. Neurol Sci. 32:589–594.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
van IJzendoorn DGP, Forghany Z, Liebelt F,
Vertegaal AC, Jochemsen AG, Bovée JVMG, Szuhai K and Baker DA:
Functional analyses of a human vascular tumor FOS variant identify
a novel degradation mechanism and a link to tumorigenesis. J Biol
Chem. 292:21282–21290. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang YH, Liang S, Xu DS, Lin X, He CY,
Feng Y and Hong YL: Effect and mechanism of senkyunolide I as an
anti-migraine compound from Ligusticum chuanxiong. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 63:261–266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tassorelli C and Joseph SA: Systemic
nitroglycerin induces Fos immunoreactivity in brainstem and
forebrain structures of the rat. Brain Res. 682:167–181. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Pan X, Wang M, Wu Y, Lu X, Shang Y, Xu Y,
Zhai Y, Li J, Li Z and Gong M: Identification of active ingredients
in Wuzhuyu decoction improving migraine in mice by spectral
efficiency association. Mol Med Rep. 12:1524–1534. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang ZH, Vaziri ND, Wei F, Cheng XL, Bai
X and Zhao YY: An integrated lipidomics and metabolomics reveal
nephroprotective effect and biochemical mechanism of Rheum
officinale in chronic renal failure. Sci Rep. 6:221512016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Guo Y, Cao DY, Tian YL,
Yao FR and Wang HS: Electrophysiological evidence for the
interaction of substance P and glutamate on Adelta and C afferent
fibre activity in rat hairy skin. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
33:1128–1133. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Gundersen V, Chaudhry FA, Bjaalie JG,
Fonnum F, Ottersen OP and Storm-Mathisen J: Synaptic vesicular
localization and exocytosis of L-aspartate in excitatory nerve
terminals: A quantitative immunogold analysis in rat hippocampus. J
Neurosci. 18:6059–6070. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Vikelis M and Mitsikostas DD: The role of
glutamate and its receptors in migraine. CNS Neurol Disord Drug
Targets. 6:251–257. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Gao R and Penzes P: Common mechanisms of
excitatory and inhibitory imbalance in schizophrenia and autism
spectrum disorders. Curr Mol Med. 15:146–167. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Young D, Ma J, Cherkerzian S, Froimowitz
MP, Ennulat DJ, Cohen BM, Evans ML and Lange N: Automated
identification of Fos expression. Biostatistics. 3:351–364. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Chen DQ, Chen H, Chen L, Vaziri ND, Wang
M, Li XR and Zhao YY: The link between phenotype and fatty acid
metabolism in advanced chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 32:1154–1166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Dou F, Miao H, Wang JW, Chen L, Wang M,
Chen H, Wen AD and Zhao YY: An integrated lipidomics and phenotype
study reveals protective effect and biochemical mechanism of
traditionally used Alisma orientale Juzepzuk in chronic
renal disease. Front Pharmacol. 9:532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pandey MK, Liu G, Cooper TK and Mulder KM:
Knockdown of c-Fos suppresses the growth of human colon carcinoma
cells in athymic mice. Int J Cancer. 130:213–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lu C, Shen Q, DuPré E, Kim H, Hilsenbeck S
and Brown PH: cFos is critical for MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth.
Oncogene. 24:6516–6524. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|