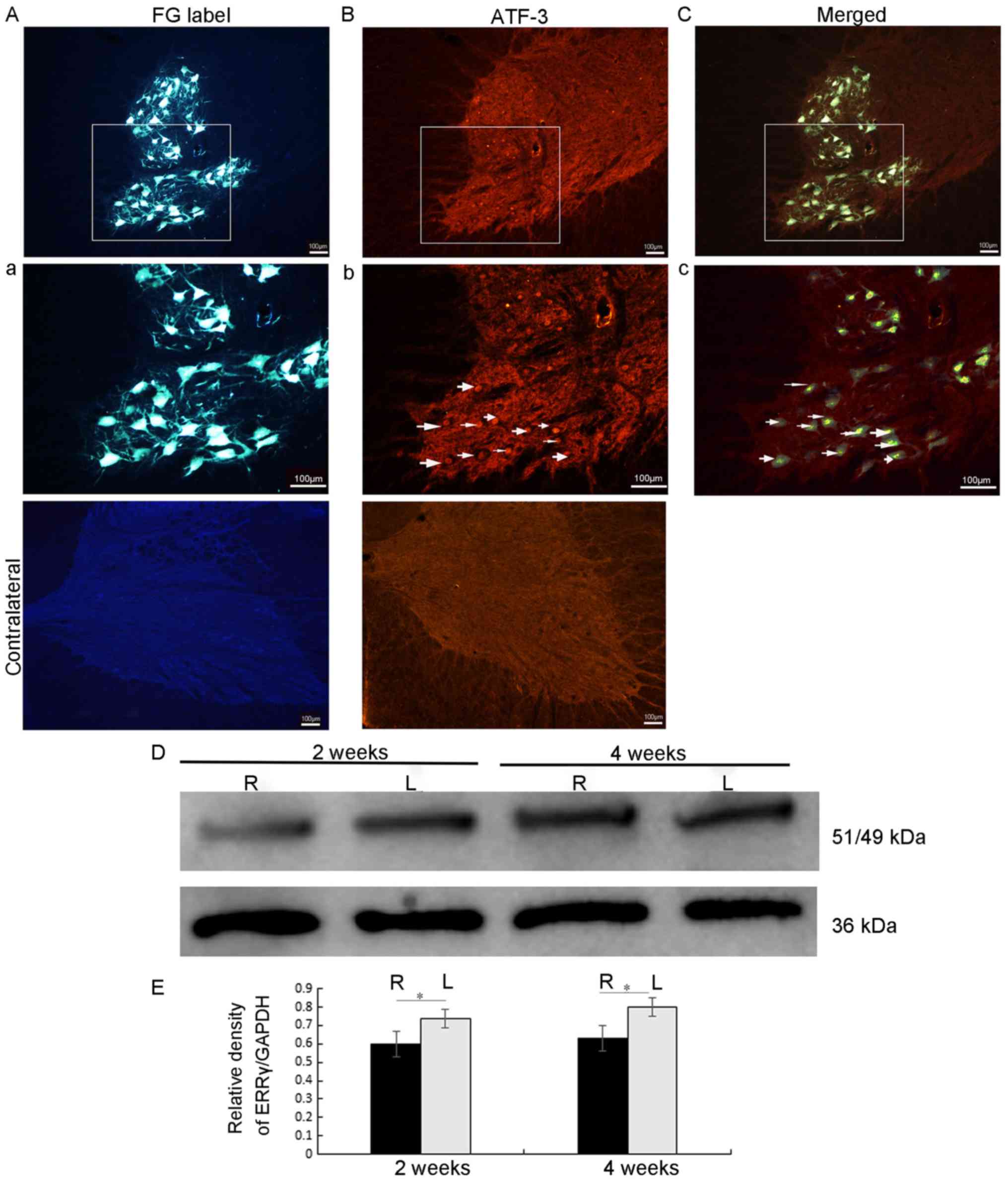
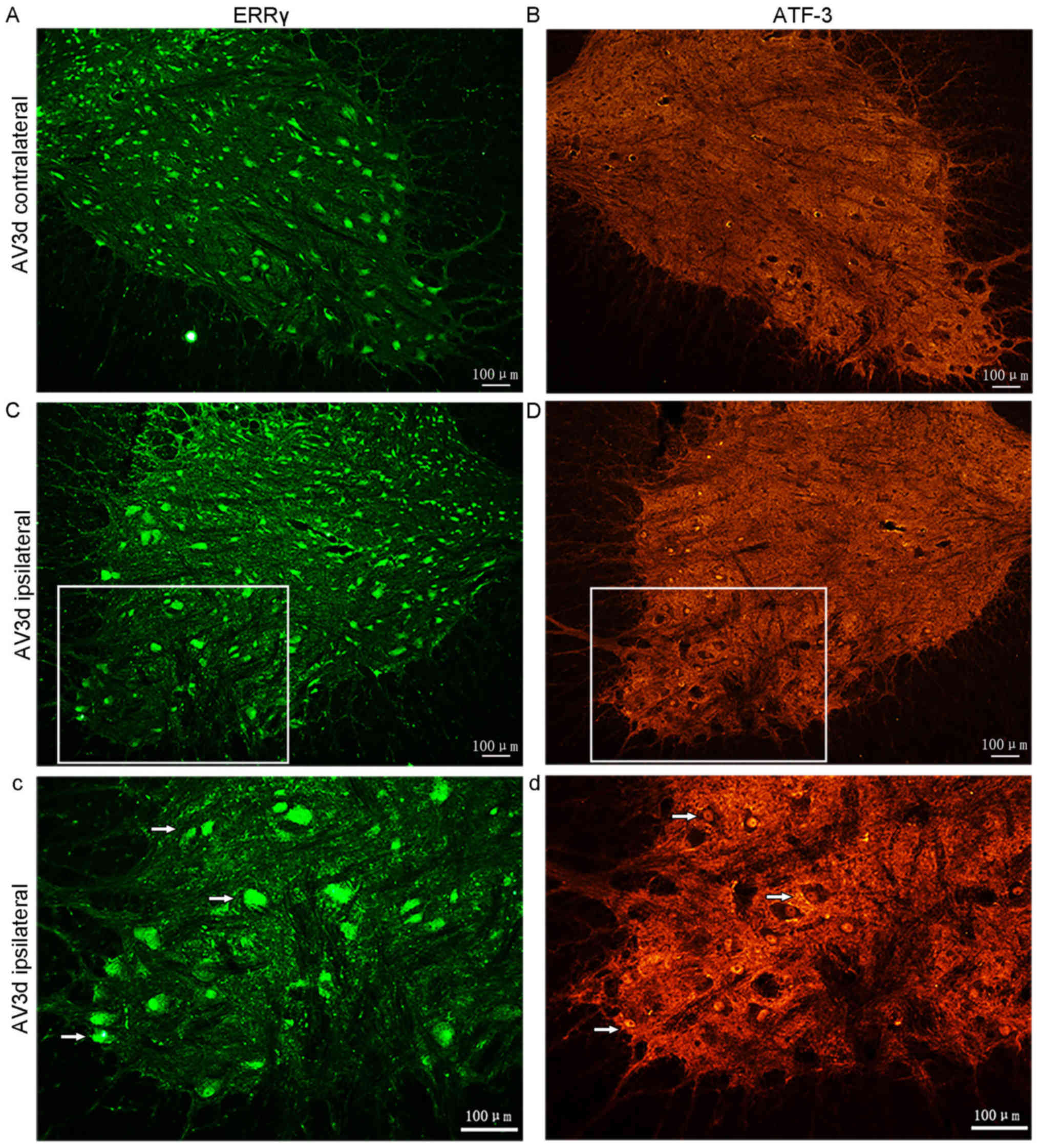
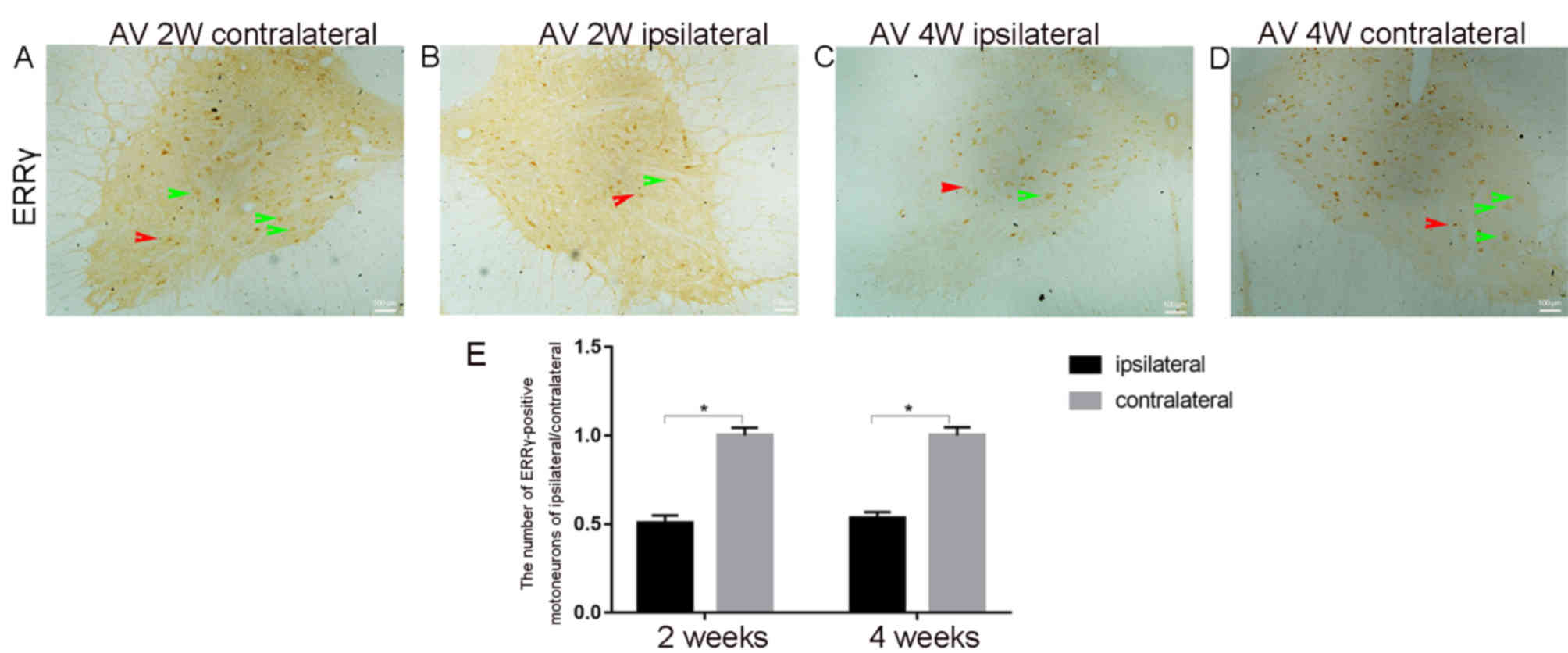
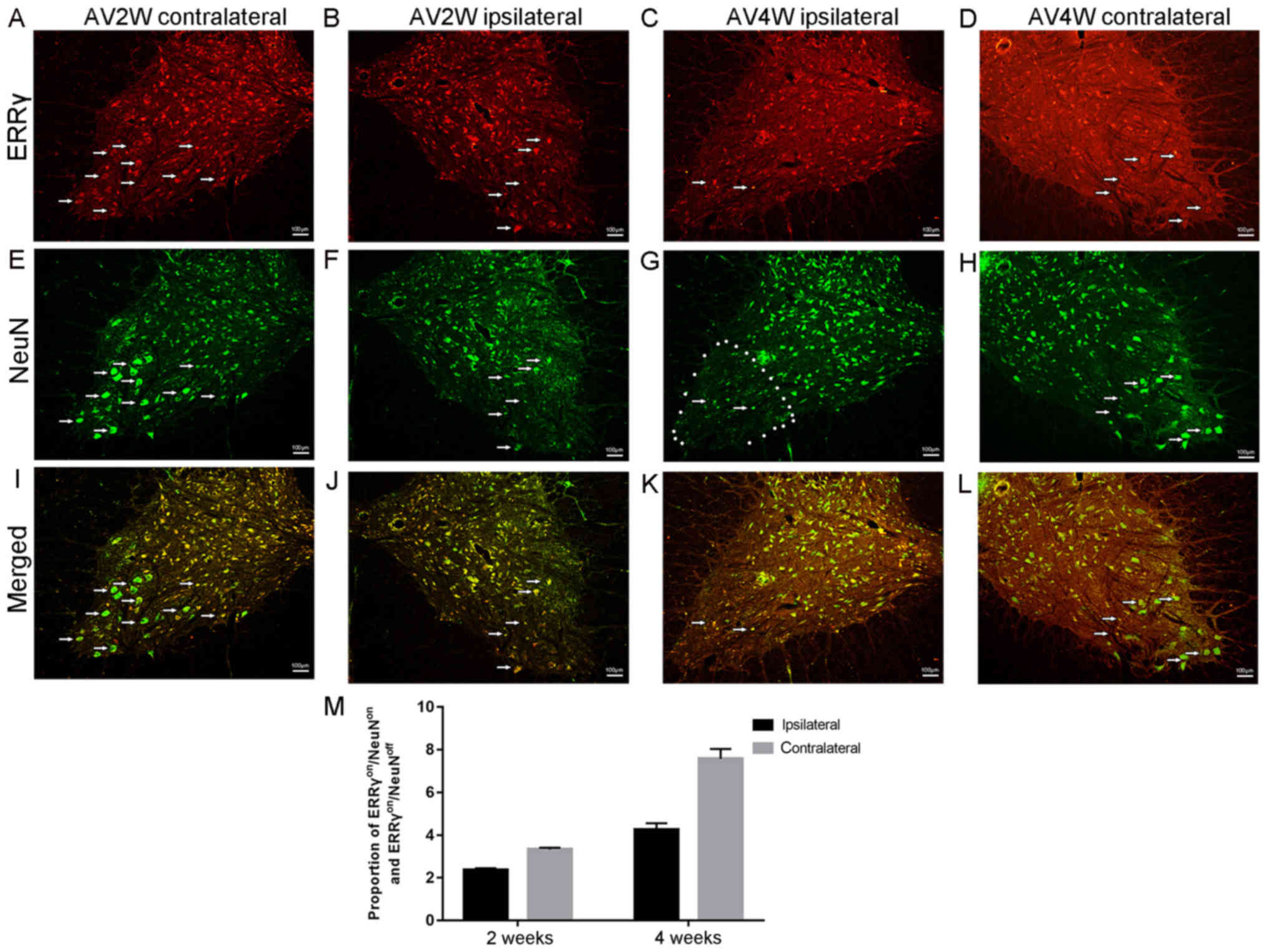
|
1
|
Lu Y, Liu H, Hua X, Xu WD, Xu JG and Gu
YD: Supplementary motor cortical changes explored by resting-state
functional connectivity in brachial plexus injury. World Neurosurg.
88:300–305. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Noristani HN, Sabourin JC, Boukhaddaoui H,
Chan-Seng E, Gerber YN and Perrin FE: Spinal cord injury induces
astroglial conversion towards neuronal lineage. Mol Neurodeger.
11:68–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Stifani N: Motor neurons and the
generation of spinal motor neuron diversity. Front Cell Neurosci.
8:293–302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Manuel M and Zytnicki D: Alpha, beta and
gamma motoneurons: Functional diversity in the motor system's final
pathway. J Integr Neurosci. 10:243–276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Friese A, Kaltschmidt JA, Ladle DR,
Sigrist M, Jessell TM and Arber S: Gamma and alpha motor neurons
distinguished by expression of transcription factor ERR3. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:13588–13593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tremblay AM and Giguère V: The NR3B
subgroup: An overview. Nucl Recept Signal. 5:e0092009.
|
|
7
|
Giguère V: Transcriptional control of
energy homeostasis by the estrogen related receptors. Endocr Rev.
29:677–696. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Deblois G and Giguère V: Functional and
physiological genomics of estrogenrelated receptors (ERRs) in
health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1812:1032–1040. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huss JM, Garbacz WG and Xie W:
Constitutive activities of estrogen-related receptors:
Transcriptional regulation of metabolism by the ERR pathways in
health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1912–1927. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He H, Xi G and Lu X: Molecular cloning,
characterization, and expression analysis of an estrogen
receptor-related receptor homologue in the cricket, Teleogryllus
emma. J Insect Sci. 10:188–196. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoshihara E, Wei Z, Lin CS, Fang S,
Ahmadian M, Kida Y, Tseng T, Dai Y, Yu RT, Liddle C, et al: ERRγ is
required for the metabolic maturation of therapeutically functional
glucose-responsive β cells. Cell Metab. 23:622–634. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deblois G and Giguère V: Oestrogen-related
receptors in breast cancer: Control of cellular metabolism and
beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:27–36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Audet-Walsh É and Giguère V: The multiple
universes of estrogen-related receptor alpha and gamma in metabolic
control and related diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 36:51–61. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo J, Sladek R, Bader JA, Matthyssen A,
Rossant J and Giguère V: Placental abnormalities in mouse embryos
lacking the orphan nuclear receptor ERR-β. Nature. 388:778–782.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bonnelye E, Vanacker JM, Spruyt N, Alric
S, Fournier B, Desbiens X and Laudet V: Expression of the
estrogen-related receptor 1 (ERR-1) orphan receptor during mouse
development. Mech Dev. 65:71–85. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu JZ, Long H, Wu TD, Zhou Y and Lu HB:
The effect of estrogen-related receptor α on the regulation of
angiogenesis after spinal cord injury. Neuroscience. 290:570–580.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dufour CR, Wilson BJ, Huss JM, Kelly DP,
Alaynick WA, Downes M, Evans RM, Blanchette M and Giguere V:
Genome-wide orchestration of cardiac functions by the orphan
nuclear receptors ERRα and γ. Cell Metab. 5:345–356. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kwon DH, Eom GH, Kee HJ, Nam YS, Cho YK,
Kim DK, Koo JY, Kim HS, Nam KI, Kim KK, et al: Estrogen-related
receptor gamma induces cardiac hypertrophy by activating GATA4. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 65:88–97. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Murray J, Auwerx J and Huss JM: Impaired
myogenesis in estrogen-related receptor γ (ERRγ)-deficient skeletal
myocytes due to oxidative stress. FASEB J. 27:135–150. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pei L, Mu Y, Leblanc M, Alaynick W, Barish
GD, Pankratz M, Tseng TW, Kaufman S, Liddle C, Yu RT, et al:
Dependence of hippocampal function on ERRγ-regulated mitochondrial
metabolism. Cell Metab. 21:628–636. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kida YS, Kawamura T, Wei Z, Sogo T,
Jacinto S, Shigeno A, Kushige H, Yoshihara E, Liddle C, Ecker JR,
et al: ERRs mediate a metabolic switch required for somatic cell
reprogramming to pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell. 16:547–555. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mattson MP, Gleichmann M and Cheng A:
Mitochondria in neuroplasticity and neurological disorders. Neuron.
60:748–766. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fleming JC, Norenberg MD, Ramsay DA,
Dekaban GA, Marcillo AE, Saenz AD, Pasquale-Styles M, Dietrich WD
and Weaver LC: The cellular inflammatory response in human spinal
cords after injury. Brain. 129:3249–3269. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou LH, Han S, Xie YY, Wang LL and Yao
ZB: Differences in c-jun and nNOS expression levels in motoneurons
following different kinds of axonal injury in adult rats. Brain
Cell Biol. 36:213–227. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu W, Liuzzi FJ, Schinco FP, Depto AS, Li
Y, Mong JA, Dawson TM and Snyder SH: Neuronal nitric oxide synthase
is induced in spinal neurons by traumatic injury. Neurosci.
61:719–726. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fu R, Tang Y, Ling ZM, Li YQ, Cheng X,
Song FH, Zhou LH and Wu W: Lithium enhances survival and regrowth
of spinal motoneurons after ventral root avulsion. BMC Neurosci.
15:84–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang Y, Ling ZM, Fu R, Li YQ, Cheng X,
Song FH, Luo HX and Zhou LH: Time-specific microRNA changes during
spinal motoneuron degeneration in adult rats following unilateral
BPRA: Ipsilateral vs. contralateral changes. BMC Neurosci.
15:92–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang J, Yan L, Zhao X, Wu W and Zhou LH:
The diversity of nNOS gene expression in avulsion-injured spinal
motoneurons among laboratory rodents. Nitric Oxide. 22:37–42. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou L and Wu W: Antisense oligos to
neuronal nitric oxide synthase aggravate motoneuron death induced
by spinal root avulsion in the adult rat. Exp Neurol. 197:84–92.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li YQ, Tang Y, Fu R, Meng QH, Zhou X, Ling
ZM, Cheng X, Tian SW, Wang GJ, Liu XG and Zhou LH: Efficient
labeling in vitro with non-ionic gadolinium magnetic
resonance imaging contrast agent and fluorescent transfection agent
in bone marrow stromal cells of neonatal rats. Mol Med Rep.
12:913–920. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Linda H, Skold MK and Ochsmann T:
Activating transcription factor 3, a useful marker for a
regenerative response after nerve root injury. Front Neurol.
2:30–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen BP, Wolfgang CD and Hai T: Analysis
of ATF3, a transcription factor induced by physiological stresses
and modulated by gadd153/Chop10. Mol Cell Biol. 16:1157–1168. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yin T, Sandhu G, Wolfgang CD, Burrier A,
Webb RL, Rigel DF, Hai T and Whelan J: Tissue-specific pattern of
stress kinase activation in ischemic/reperfused heart and kidney. J
Biol Chem. 272:19943–19950. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Powis RA and Gillingwater TH: Selective
loss of alpha motor neurons with sparing of gamma motor neurons and
spinal cord cholinergic neurons in a mouse model of spinal muscular
atrophy. J Anat. 228:443–451. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lalancette-Hebert M, Sharma A, Lyashchenko
AK and Shneider NA: Gamma motor neurons survive and exacerbate
alpha motor neuron degeneration in ALS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E8316–E8325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Martín MC, Balfagón G, Minoves N and
Blanco J: Androgen deprivation increases neuronal nitric oxide
metabolism and its vasodilator effect in rat mesenteric arteries.
Nitric Oxide. 12:163–176. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Raivich G, Bohatschek M, Da Costa C, Iwata
O, Galiano M, Hristova M, Nateri AS, Makwana M, Riera-Sans L,
Wolfer DP, et al: The AP-1 transcription factor c-jun is required
for efficient axonal regeneration. Neuron. 43:57–67. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Giguère V, Yang N, Segui P and Evans RM:
Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors. Nature.
331:91–94. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hong H, Yang L and Stallcup: MR
Hormone-independent transcriptional activation and coactivator
binding by novel orphan nuclear receptor ERR3. J Biol Chem.
274:22618–22626. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Z and Teng CT: Interplay between
estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha) and gamma (ERRgamma) on
the regulation of ERRalpha gene expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
264:128–141. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sladek R, Bader JA and Giguère V: The
orphan nuclear receptor estrogenrelated receptor alpha is a
transcriptional regulator of the human medium-chain acyl coenzyme A
dehydrogenase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 17:5400–5409. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cao J and Patisaul HB: Sexually dimorphic
expression of hypothalamic estrogen receptors α and β and Kiss1 in
neonatal male and female rats. J Comp Neurol. 519:2954–2977. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|