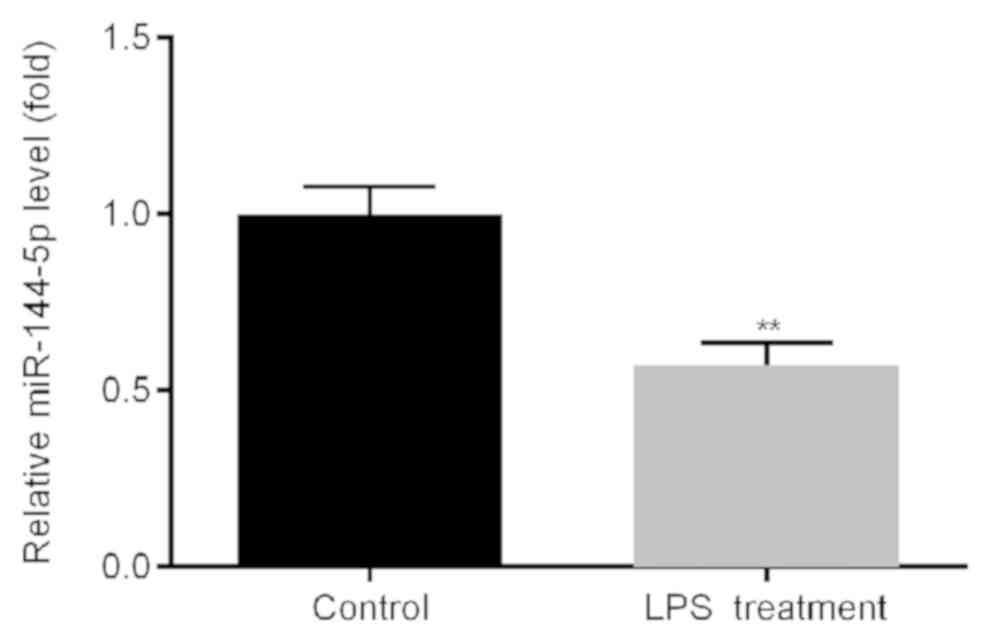
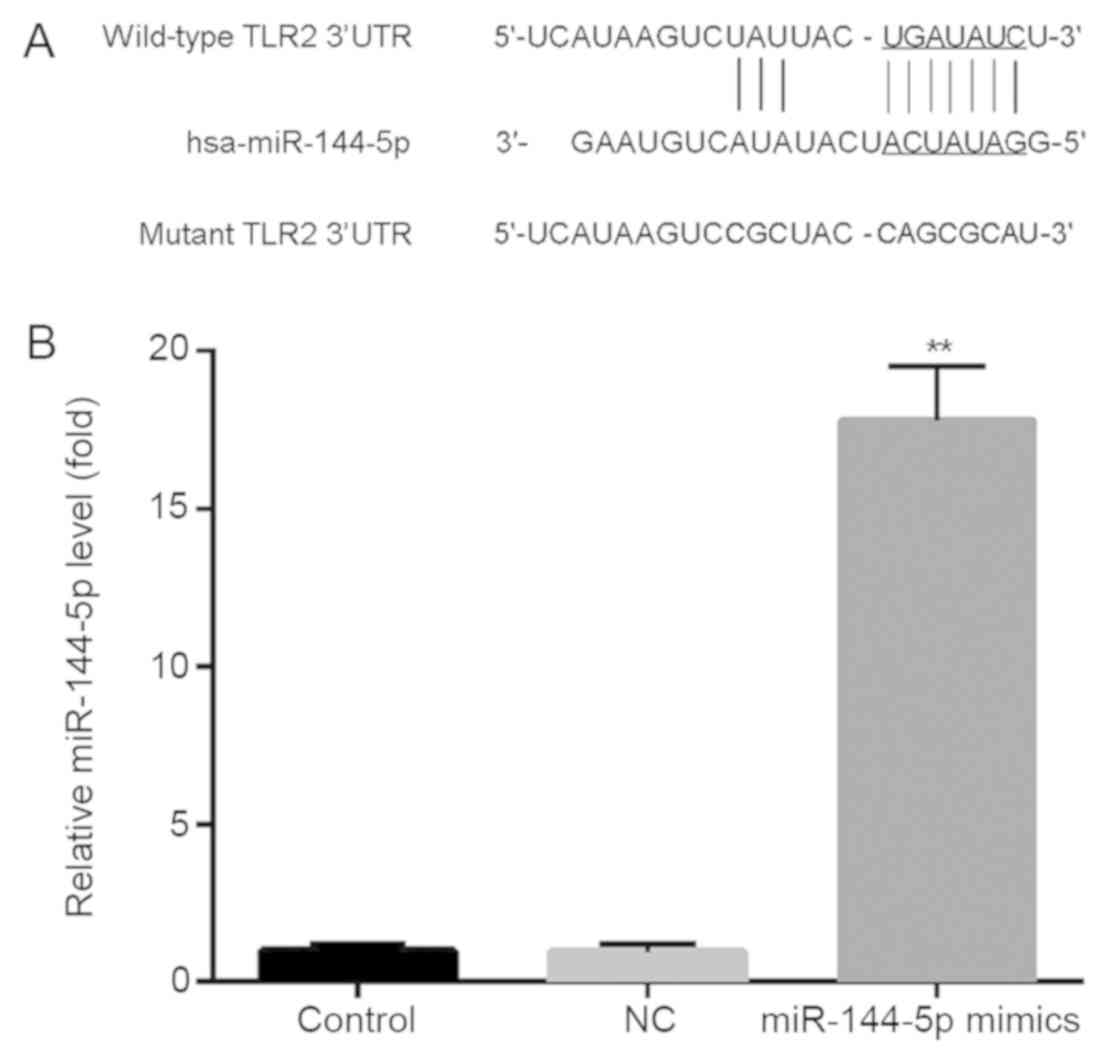
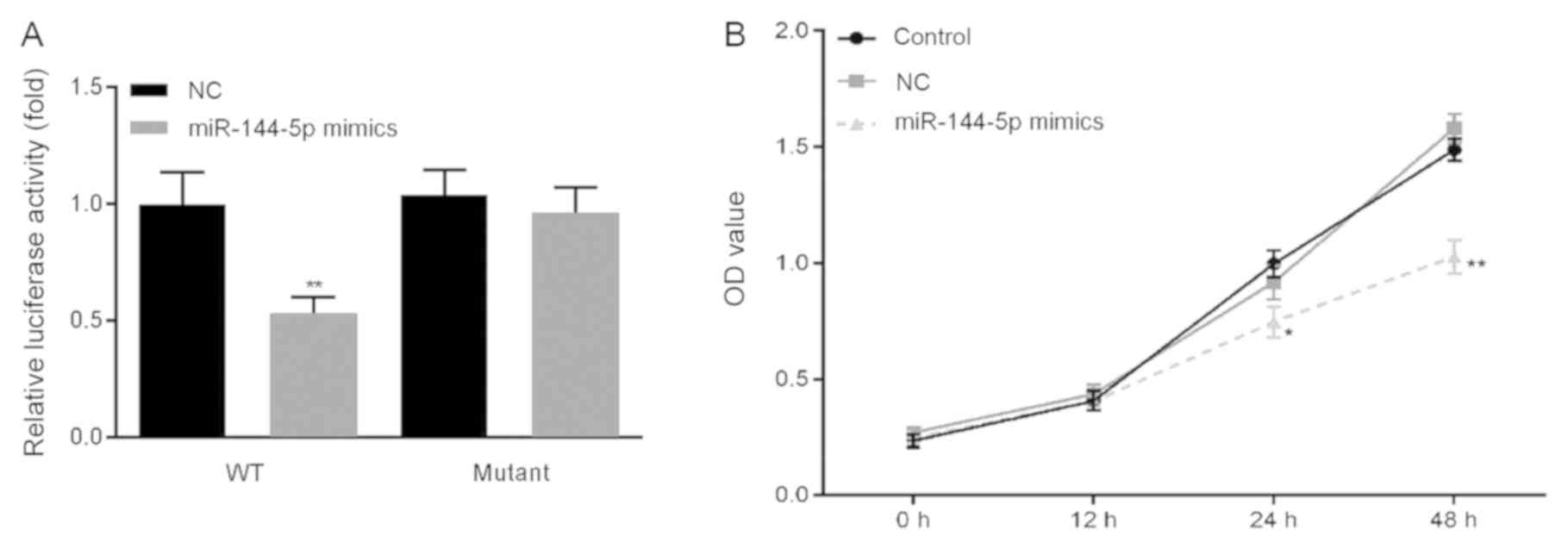
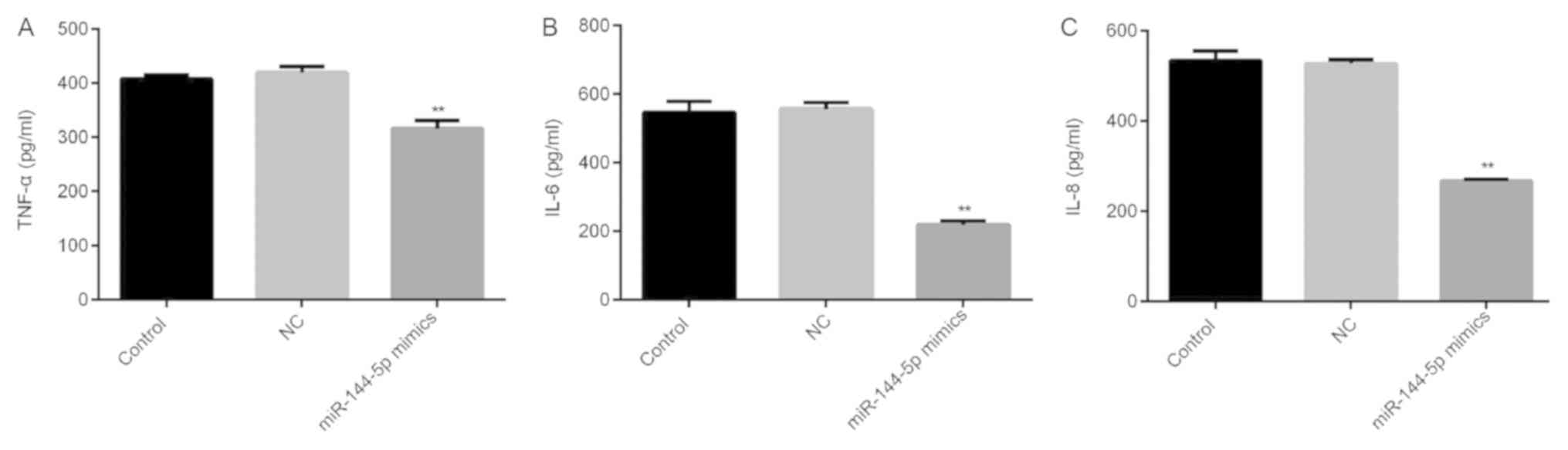
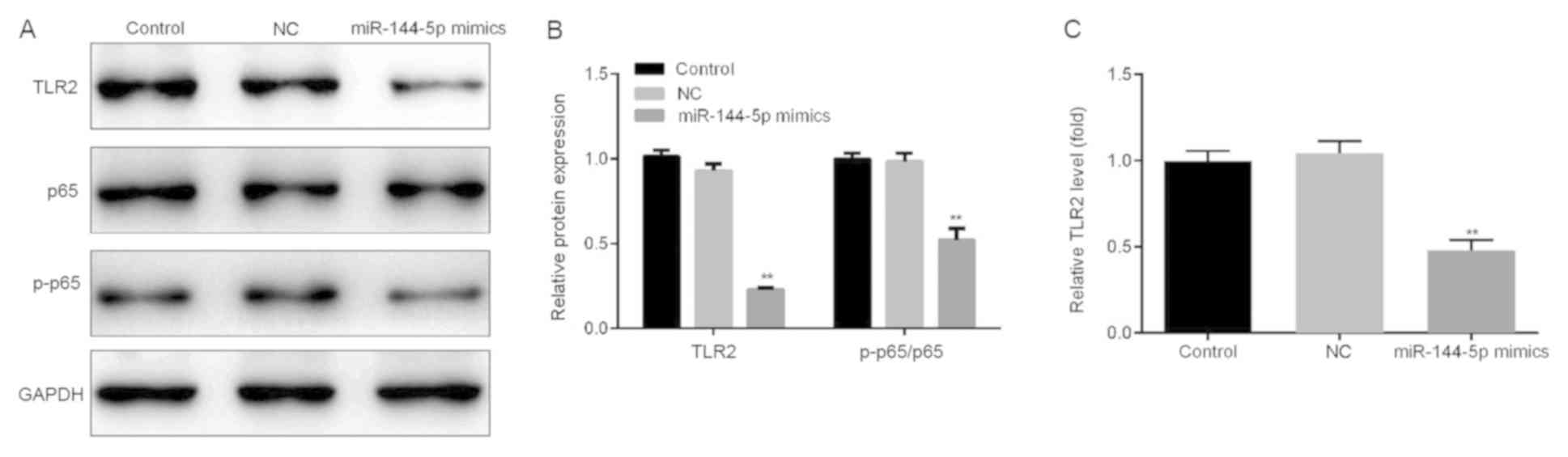
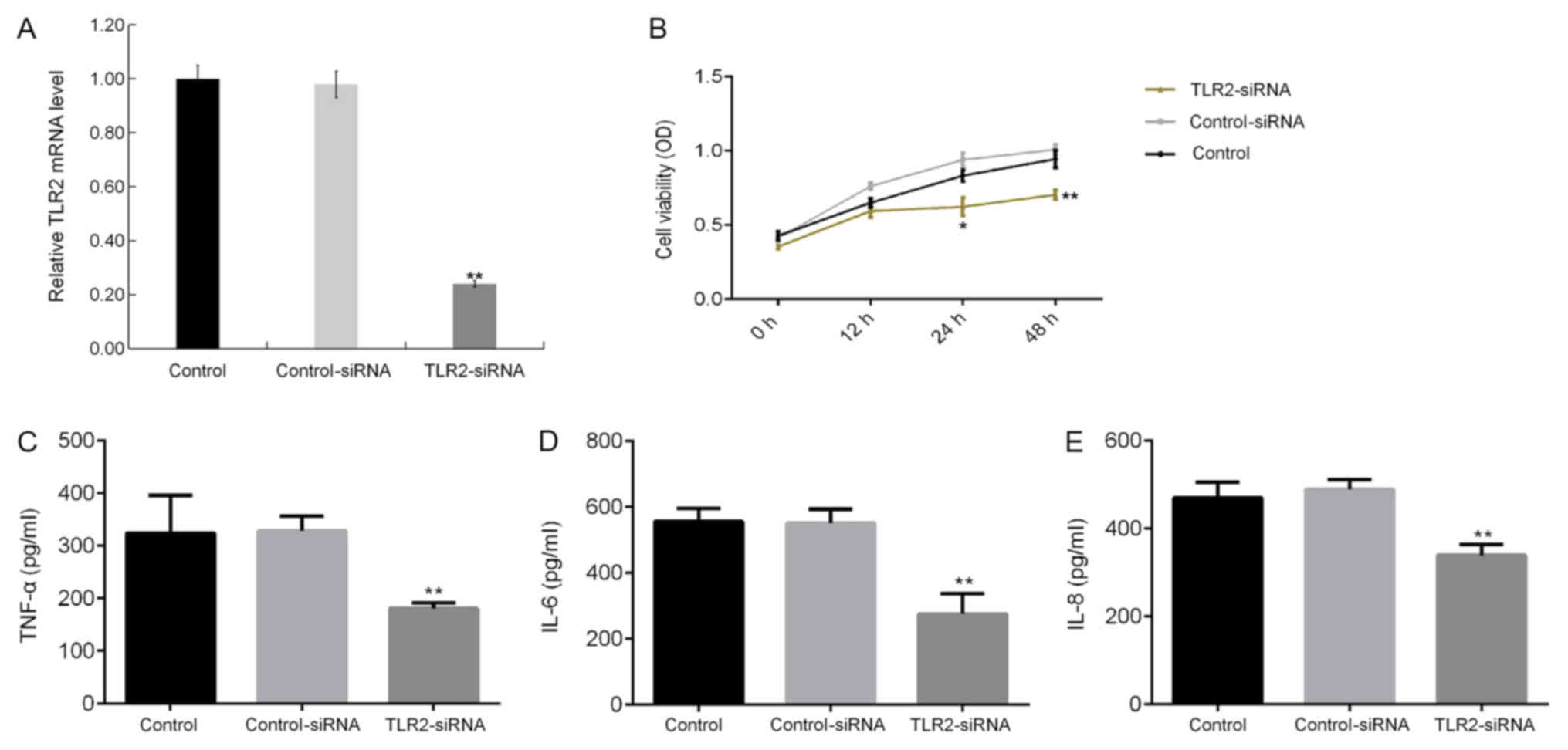
|
1
|
Abeles AM and Pillinger MH: The role of
the synovial fibroblast in rheumatoid arthritis: Cartilage
destruction and the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Bull
NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 64:20–24. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jeannin P, Paolini L, Adam C and Delneste
Y: The roles of CSFs on the functional polarization of
tumor-associated macrophages. FEBS J. 285:680–699. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou D, Chen L, Yang K, Jiang H, Xu W and
Luan J: SOCS molecules: The growing players in macrophage
polarization and function. Oncotarget. 8:60710–60722.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kokkonen H, Söderström I, Rocklöv J,
Hallmans G, Lejon K and Rantapää Dahlqvist S: Up-regulation of
cytokines and chemokines predates the onset of rheumatoid
arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 62:383–391. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Han CC, Cui D, Li Y, Ma Y and Wei
W: Is macrophage polarization important in rheumatoid arthritis?
Int Immunopharmacol. 50:345–352. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H,
Takada H, Ogawa T, Takeda K and Akira S: Differential roles of TLR2
and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive
bacterial cell wall components. Immunity. 11:443–451. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park H, Park SG, Kim J, Ko YG and Kim S:
Signaling pathways for TNF production induced by human
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-associating factor, p43. Cytokine.
20:148–153. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Elias JA, Reynolds MM, Kotloff RM and Kern
JA: Fibroblast interleukin 1 beta: Synergistic stimulation by
recombinant interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor and
posttranscriptional regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
86:6171–6175. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Y and Lee CG: MicroRNA and
cancer-focus on apoptosis. J Cell Mol Med. 13:12–23. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bueno MJ, Pérez de Castro I and Malumbres
M: Control of cell proliferation pathways by microRNAs. Cell Cycle.
7:3143–3148. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamada Y, Arai T, Kojima S, Sugawara S,
Kato M, Okato A, Yamazaki K, Naya Y, Ichikawa T and Seki N:
Regulation of antitumor miR-144-5p targets oncogenes: Direct
regulation of syndecan-3 and its clinical significance. Cancer Sci.
109:2919–2936. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song L, Peng L, Hua S, Li X, Ma L, Jie J,
Chen D, Wang Y and Li D: miR-144-5p enhances the radiosensitivity
of non-small-cell lung cancer cells via targeting ATF2. Biomed Res
Int. 2018:51094972018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li J, Wang R, Ge Y, Chen D, Wu B and Fang
F: Assessment of microRNA-144-5p and its putative targets in
inflamed gingiva from chronic periodontitis patients. J Periodontal
Res. 54:266–277. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sokol RJ, Hudson G, James NT, Frost IJ and
Wales J: Human macrophage development: A morphometric study. J
Anat. 151:27–35. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam J and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li D, Wang X, Lan X, Li Y, Liu L, Yi J, Li
J, Sun Q, Wang Y, Li H, et al: Down-regulation of miR-144 elicits
proinflammatory cytokine production by targeting toll-like receptor
2 in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis of high-fat-diet-induced
metabolic syndrome E3 rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 402:1–12. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Lan X, Liu L, Yi J, Li J, Li Y,
Wang M, Li J, Song LM and Li D: MicroRNA 144 negatively regulates
Toll-like receptor 2 expression in rat macrophages. Nan Fang Yi Ke
Da Xue Xue Bao. 35:319–325. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma Y and Pope RM: The role of macrophages
in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Pharm Des. 11:569–580. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wei ST, Sun YH, Zong SH and Xiang YB:
Serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-α may correlate with activity and
severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Med Sci Monit. 25:4030–4038.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Korani S, Kazemi B, Haghighi A, Nikpoor AR
and Bandehpour M: The effect of human recombinant tumor necrosis
factor receptor-2 on reducing inflammatory of collagen -induced
arthritis in Balb/c Mice. Iran J Biotechnol. 17:e21532019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vasanthi P, Nalini G and Rajasekhar G:
Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rheumatoid arthritis: A
review. APLAR J Rheumatol. 10:270–274. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Edrees AF, Misra SN and Abodou NI:
Anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) therapy in rheumatoid arthritis:
Correlation of TNF-alpha serum level with clinical response and
benefit from changing dose or frequency of infliximab infusions.
Clin Exp Rheumatol. 23:469–474. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Venkatesha SH, Dudics S, Acharya B and
Moudgil KD: Cytokine-modulating strategies and newer cytokine
targets for arthritis therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 16:887–906. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Doyle MK, Rahman MU, Frederick B, Birbara
CA, de Vries D, Toedter G, Wu X, Chen D, Ranganath VK, Westerman ME
and Furst DE: Effects of subcutaneous and intravenous golimumab on
inflammatory biomarkers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis:
Results of a phase 1, randomized, open-label trial. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 52:1214–1219. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang RY, Wu JQ, Liu ZH and Sun SL:
MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: What is the latest with regards
to diagnostics? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 19:363–366. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu C, Pan A, Chen X, Tu J, Xia X and Sun
L: MiR-5571-3p and miR-135b-5p, derived from analyses of microRNA
profile sequencing, correlate with increased disease risk and
activity of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 38:1753–1765.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gao J, Kong R, Zhou X, Ji L, Zhang J and
Zhao D: Correction to: MiRNA-126 expression inhibits IL-23R
mediated TNF-α or IFN-γ production in fibroblast-like synoviocytes
in a mice model of collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis.
Apoptosis. 24:3822019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu FY, Xie CQ, Jiang CL, Sun JT, Feng HC,
Li C and Huang XW: MiR-92a inhibits fibroblast-like synoviocyte
proliferation and migration in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting
AKT2. J Biosci. 43:911–919. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McGarry T, Biniecka M, Gao W, Cluxton D,
Canavan M, Wade S, Wade S, Gallagher L, Orr C, Veale DJ and Fearon
U: Resolution of TLR2-induced inflammation through manipulation of
metabolic pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep. 7:431652017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arjumand S, Shahzad M, Shabbir A and
Yousaf MZ: Thymoquinone attenuates rheumatoid arthritis by
downregulating TLR2, TLR4, TNF-α, IL-1, and NFκB expression levels.
Biomed Pharmacother. 111:958–963. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Quero L, Hanser E, Manigold T, Tiaden AN
and Kyburz D: TLR2 stimulation impairs anti-inflammatory activity
of M2-like macrophages, generating a chimeric M1/M2 phenotype.
Arthritis Res Ther. 19:2452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McGarry T, Veale DJ, Gao W, Orr C, Fearon
U and Connolly M: Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) induces migration and
invasive mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
17:1532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xie J, Li Q, Zhu XH, Gao Y and Zhao WH:
IGF2BP1 promotes LPS-induced NFκB activation and pro-inflammatory
cytokines production in human macrophages and monocytes. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 513:820–826. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Robertson RC, Guihéneuf F, Bahar B, Schmid
M, Stengel DB, Fitzgerald GF, Ross RP and Stanton C: The
anti-inflammatory effect of algae-derived lipid extracts on
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human THP-1 macrophages. Mar
Drugs. 13:5402–5424. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Roman-Blas JA and Jimenez SA: NF-kappaB as
a potential therapeutic target in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid
arthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 14:839–848. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Aravilli RK, Vikram SL and Kohila V:
Phytochemicals as potential antidotes for targeting NF-κB in
rheumatoid arthritis. 3 Biotech. 7:2532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang HJ, Wei QF, Wang SJ, Zhang HJ, Zhang
XY, Geng Q, Cui YH and Wang XH: LncRNA HOTAIR alleviates rheumatoid
arthritis by targeting miR-138 and inactivating NF-κB pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 50:283–290. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Luo X, Xiao B and Xiao Z:
Anti-inflammatory activity of adenosine 5′-trisphosphate in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial
cells through negative regulation of toll-like receptor MyD88
signaling. DNA Cell Biol. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|