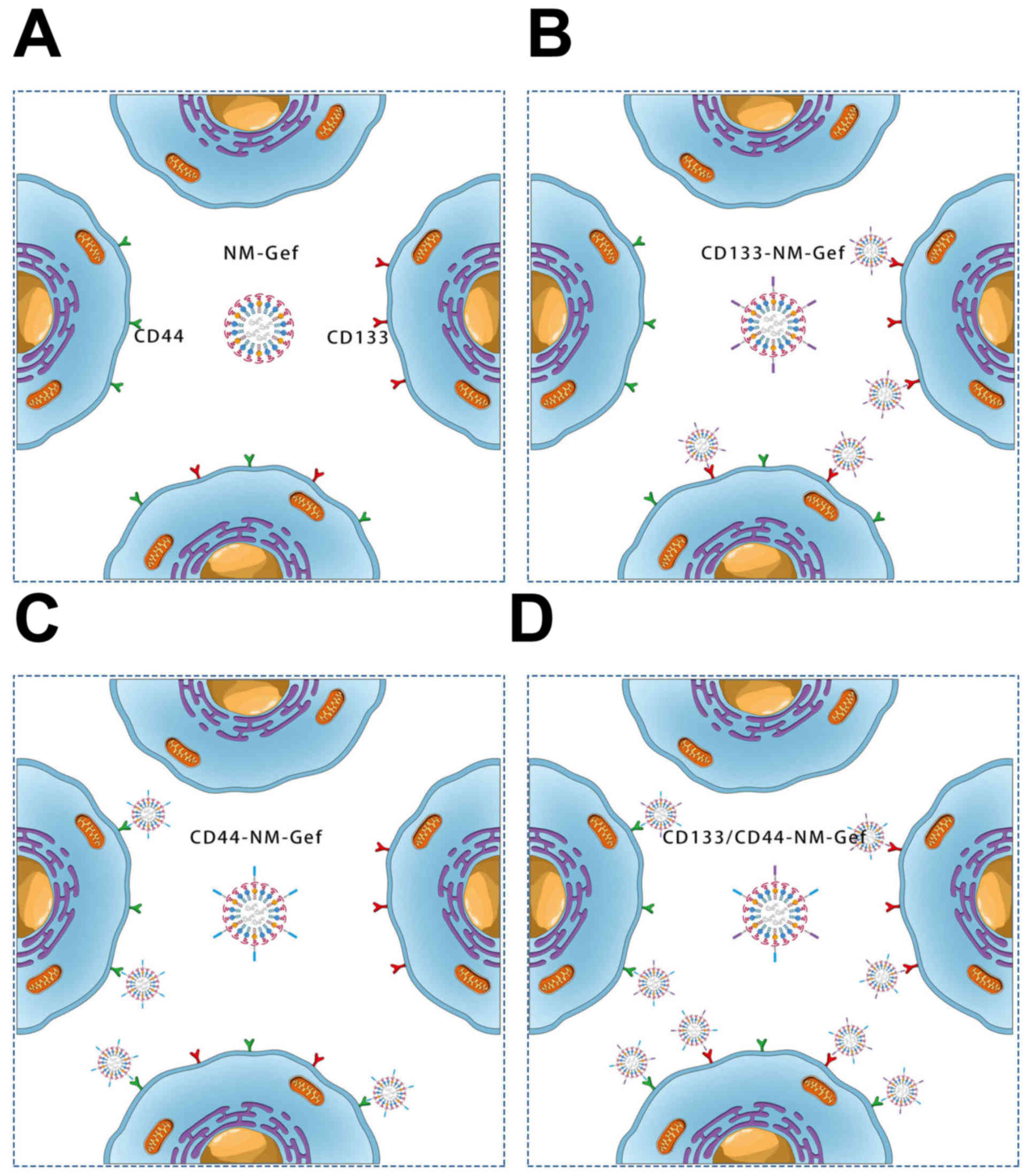
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eramo A, Lotti F, Sette G, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Di Virgilio A, Conticello C, Ruco L, Peschle C and De
Maria R: Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung
cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ. 15:504–514. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim JJ and Tannock IF: Repopulation of
cancer cells during therapy: An important cause of treatment
failure. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:516–525. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zakaria N, Satar NA, Abu Halim NH, Ngalim
SH, Yusoff NM, Lin J and Yahaya BH: Targeting lung cancer stem
cells: Research and clinical impacts. Front Oncol. 7:802017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bertolini G, Roz L, Perego P, Tortoreto M,
Fontanella E, Gatti L, Pratesi G, Fabbri A, Andriani F, Tinelli S,
et al: Highly tumorigenic lung cancer CD133+ cells
display stem-like features and are spared by cisplatin treatment.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:16281–16286. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
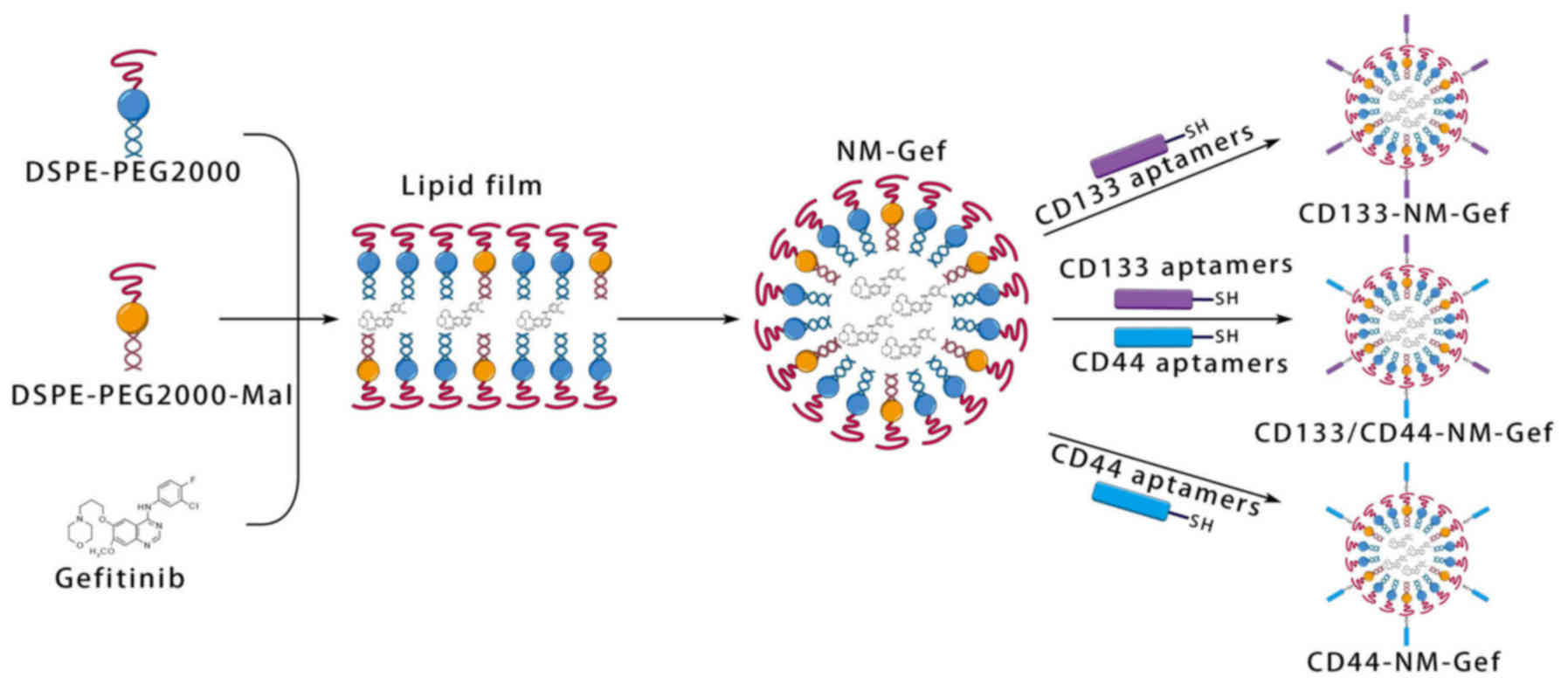
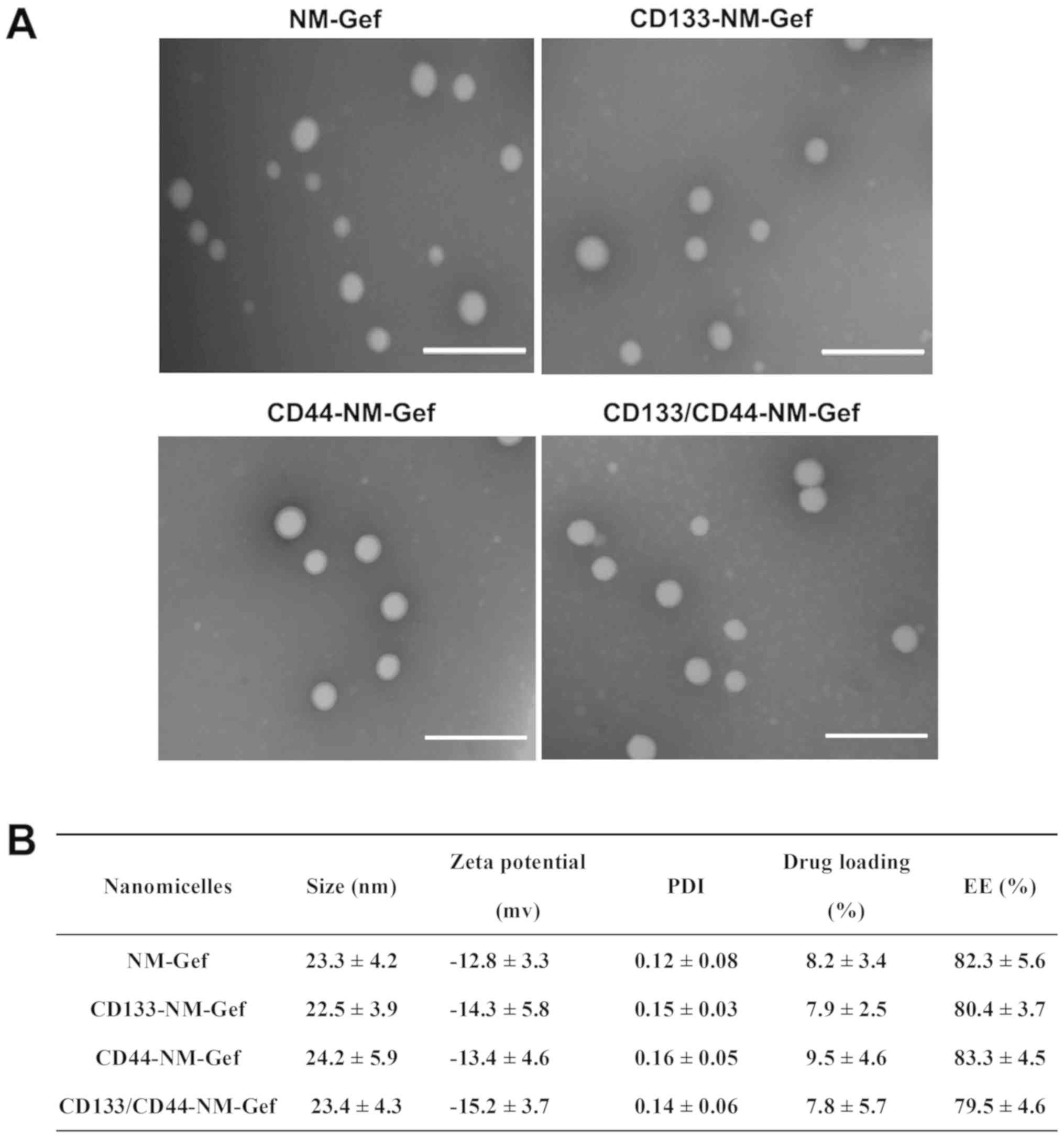
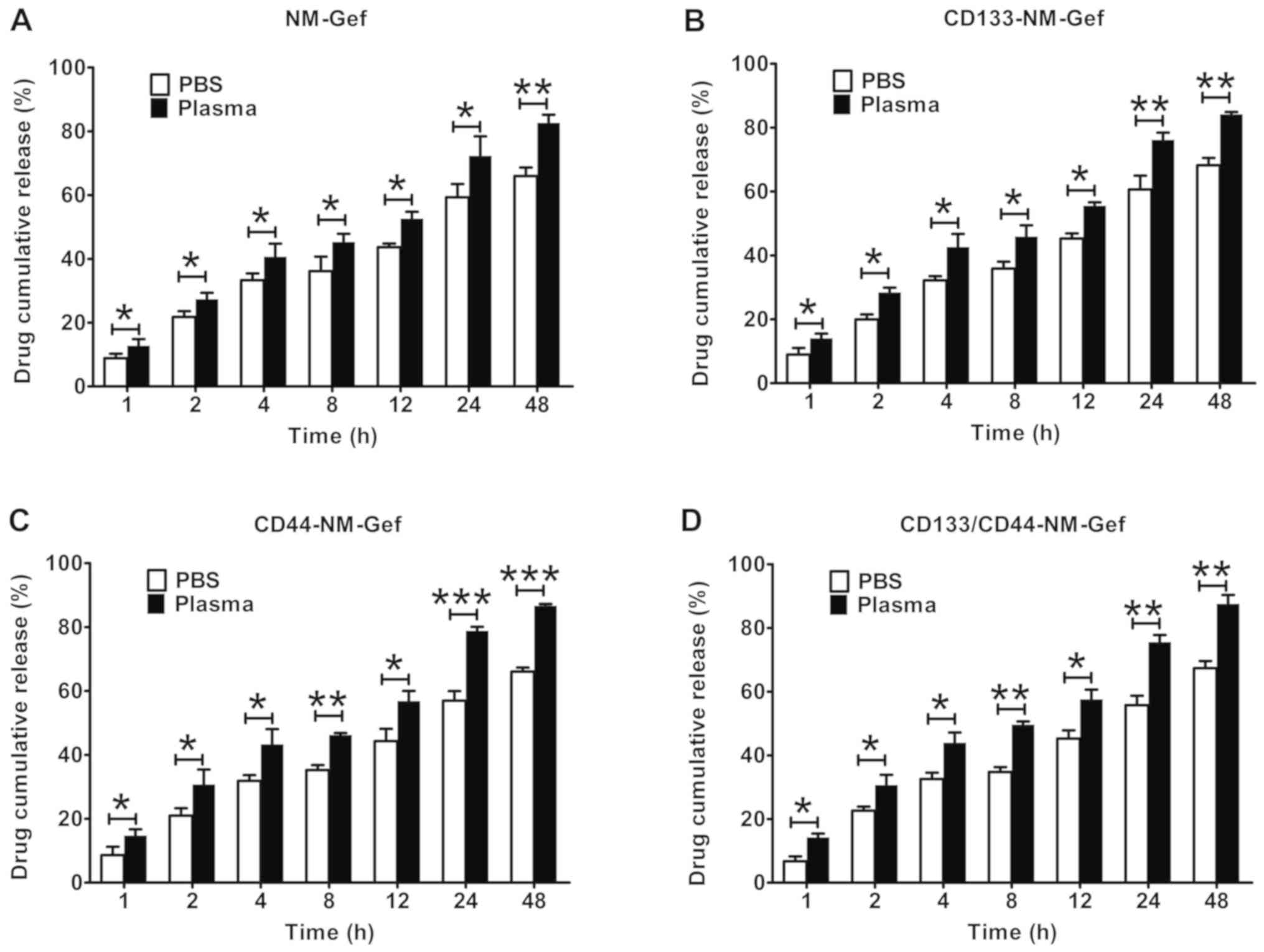
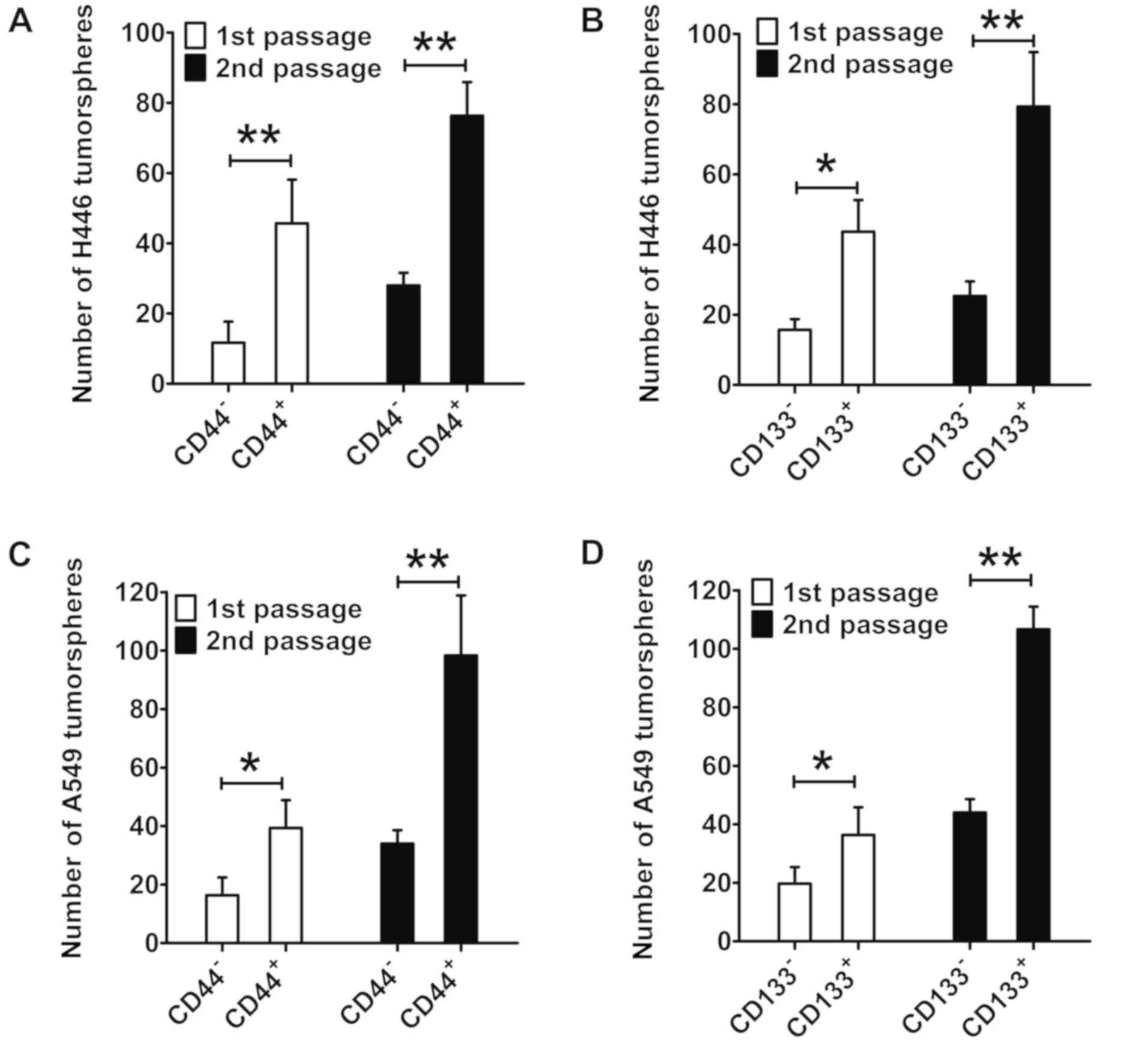
Huang X, Huang J, Leng D, Yang S, Yao Q,
Sun J and Hu J: Gefitinib-loaded DSPE-PEG2000 nanomicelles with
CD133 aptamers target lung cancer stem cells. World J Surg Oncol.
15:1672017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meyer MJ, Fleming JM, Lin AF, Hussnain SA,
Ginsburg E and Vonderhaar BK: CD44posCD49fhiCD133/2hi defines
xenograft-initiating cells in estrogen receptor-negative breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 70:4624–4633. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stewart JM, Shaw PA, Gedye C, Bernardini
MQ, Neel BG and Ailles LE: Phenotypic heterogeneity and instability
of human ovarian tumor-initiating cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:6468–6473. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Leung EL, Fiscus RR, Tung JW, Tin VP,
Cheng LC, Sihoe AD, Fink LM, Ma Y and Wong MP: Non-small cell lung
cancer cells expressing CD44 are enriched for stem cell-like
properties. PLoS One. 5:e140622010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jain RK and Stylianopoulos T: Delivering
nanomedicine to solid tumors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 7:653–664. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li W, Li J, Gao J, Li B, Xia Y, Meng Y, Yu
Y, Chen H, Dai J, Wang H, et al: The fine-tuning of thermosensitive
and degradable polymer micelles for enhancing intracellular uptake
and drug release in tumors. Biomaterials. 32:3832–3844. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li W, Zhao H, Qian W, Li H, Zhang L, Ye Z,
Zhang G, Xia M, Li J, Gao J, et al: Chemotherapy for gastric cancer
by finely tailoring anti-Her2 anchored dual targeting
immunomicelles. Biomaterials. 33:5349–5362. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ashok B, Arleth L, Hjelm RP, Rubinstein I
and Onyüksel H: In vitro characterization of PEGylated phospholipid
micelles for improved drug solubilization: Effects of PEG chain
length and PC incorporation. J Pharm Sci. 93:2476–2487. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao BJ, Ke XY, Huang Y, Chen XM, Zhao X,
Zhao BX, Lu WL, Lou JN, Zhang X and Zhang Q: The antiangiogenic
efficacy of NGR-modified PEG-DSPE micelles containing paclitaxel
(NGR-M-PTX) for the treatment of glioma in rats. J Drug Target.
19:382–390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mao X, Liu J, Gong Z, Zhang H, Lu Y, Zou
H, Yu Y, Chen Y, Sun Z, Li W, et al: iRGD-conjugated DSPE-PEG2000
nanomicelles for targeted delivery of salinomycin for treatment of
both liver cancer cells and cancer stem cells. Nanomedicine (Lond).
10:2677–2695. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2 (-Delta Delta C (T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cushing BL, Kolesnichenko VL and O'Connor
CJ: Recent advances in the liquid-phase syntheses of inorganic
nanoparticles. Chem Rev. 104:3893–3946. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao J, Ochyl LJ, Yang E and Moon JJ:
Cationic liposomes promote antigen cross-presentation in dendritic
cells by alkalizing the lysosomal pH and limiting degradation of
antigens. J Nanomedicine. 12:1251–1264. 2017.
|
|
20
|
Gao J, Chen H, Song H, Su X, Niu F, Li W,
Li B, Dai J, Wang H and Guo Y: Antibody-targeted immunoliposomes
for cancer treatment. Mini Rev Med Chem. 13:2026–2035. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Passiglia F, Listì A, Castiglia M, Perez
A, Rizzo S, Bazan V and Russo A: EGFR inhibition in NSCLC: New
findings and opened questions? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 112:126–135.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ng EW, Shima DT, Calias P, Cunningham ET
Jr, Guyer DR and Adamis AP: Pegaptanib, a targeted anti-VEGF
aptamer for ocular vascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
5:123–132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao J, Li W, Guo Y and Feng SS:
Nanomedicine strategies for sustained, controlled and targeted
treatment of cancer stem cells. Nanomedicine (Lond). 11:3261–3282.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gong Z, Chen D, Xie F, Liu J, Zhang H, Zou
H, Yu Y, Chen Y, Sun Z, Wang X, et al: Codelivery of salinomycin
and doxorubicin using nanoliposomes for targeting both liver cancer
cells and cancer stem cells. Nanomedicine (Lond). 11:2565–2579.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie F, Zhang S, Liu J, Gong Z, Yang K,
Zhang H, Lu Y, Zou H, Yu Y, Chen Y, et al: Codelivery of
salinomycin and chloroquine by liposomes enables synergistic
antitumor activity in vitro. Nanomedicine (Lond). 11:1831–1846.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang M, Xie F, Wen X, Chen H, Zhang H, Liu
J, Zhang H, Zou H, Yu Y, Chen Y, et al: Therapeutic PEG-ceramide
nanomicelles synergize with salinomycin to target both liver cancer
cells and cancer stem cells. Nanomedicine (Lond). 12:1025–1042.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Naujokat C and Steinhart R: Salinomycin as
a drug for targeting human cancer stem cells. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:9506582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao J, Feng SS and Guo Y: Antibody
engineering promotes nanomedicine for cancer treatment.
Nanomedicine (Lond). 5:1141–1145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mamot C, Ritschard R, Wicki A, Stehle G,
Dieterle T, Bubendorf L, Hilker C, Deuster S, Herrmann R and
Rochlitz C: Tolerability, safety, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of
doxorubicin-loaded anti-EGFR immunoliposomes in advanced solid
tumours: A phase 1 dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol.
13:1234–1241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miller K, Cortes J, Hurvitz SA, Krop IE,
Tripathy D, Verma S, Riahi K, Reynolds JG, Wickham TJ, Molnar I, et
al: HERMIONE: A randomized Phase 2 trial of MM-302 plus trastuzumab
versus chemotherapy of physician's choice plus trastuzumab in
patients with previously treated, anthracycline-naïve,
HER2-positive, locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 16:3522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|