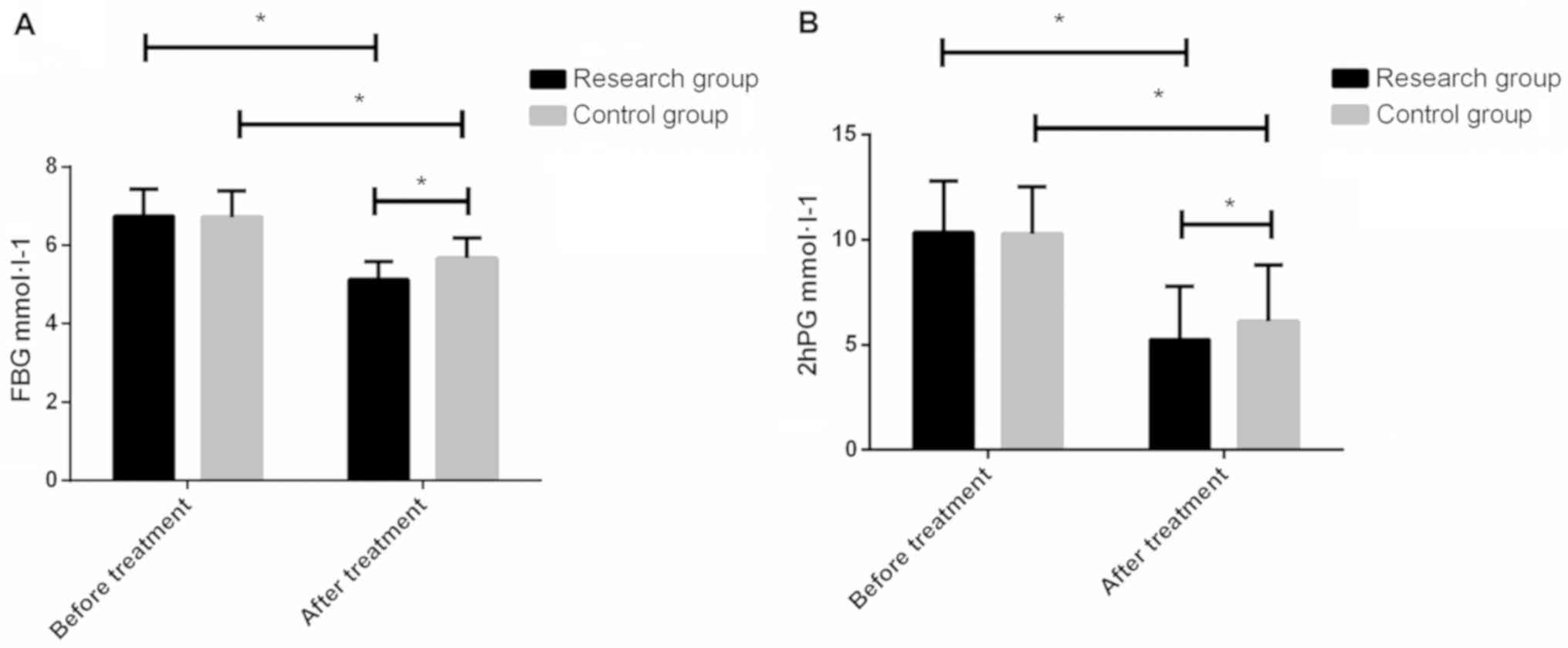
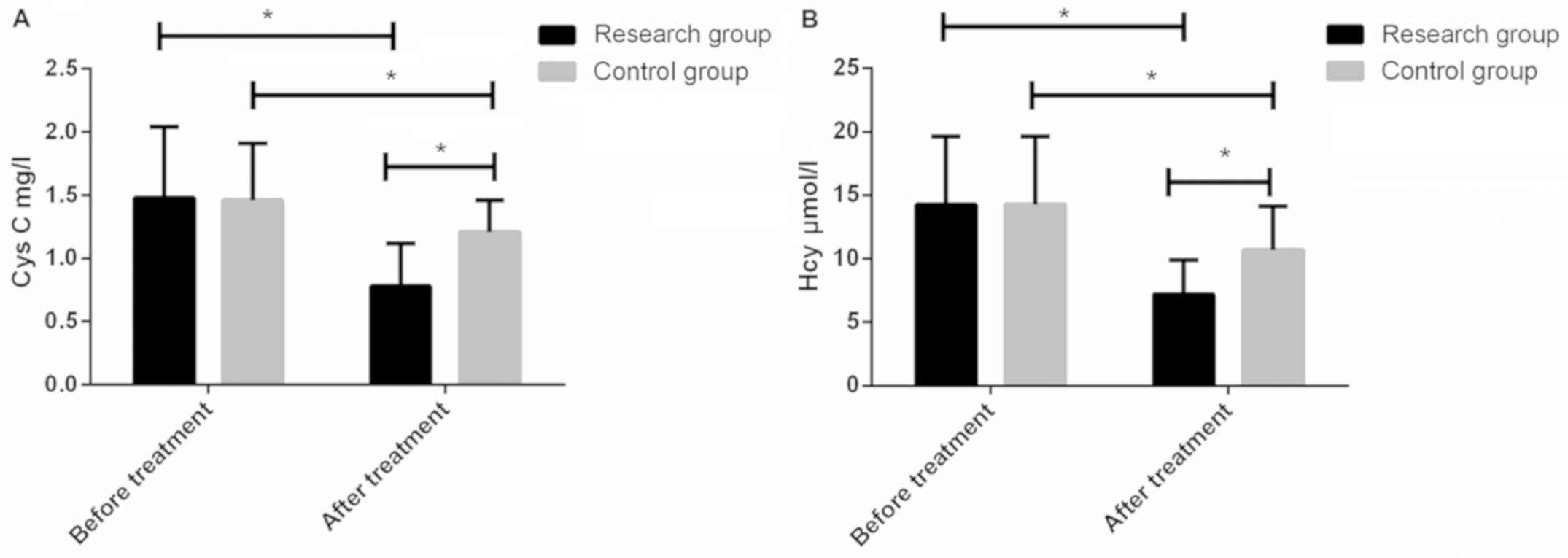
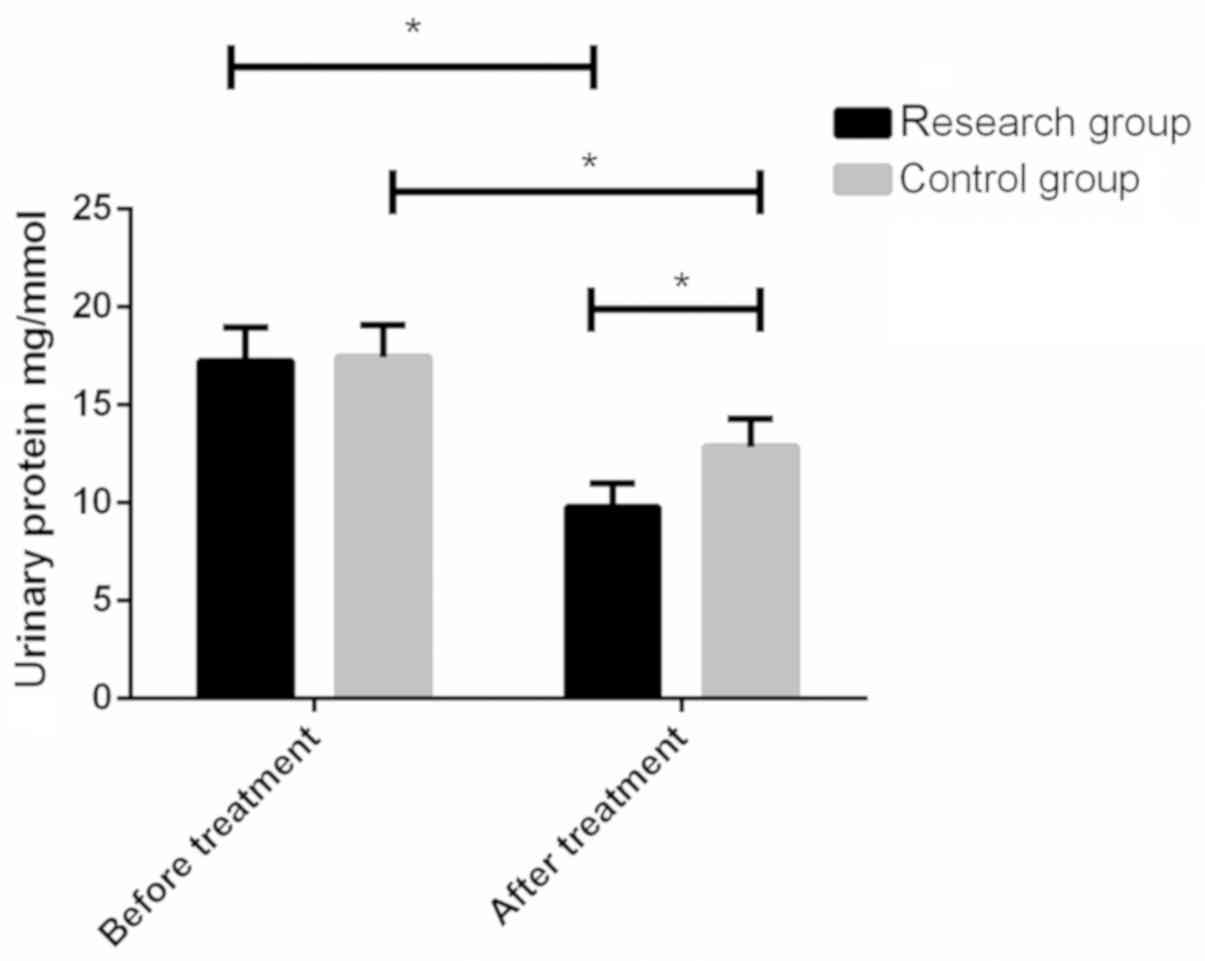
|
1
|
Szmuilowicz ED, Josefson JL and Metzger
BE: Gestational diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
48:479–493. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lu X, Wu F, Jiang M, Sun X and Tian G:
Curcumin ameliorates gestational diabetes in mice partly through
activating AMPK. Pharm Biol. 57:250–254. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ustebay S, Baykus Y, Deniz R, Ugur K,
Yavuzkir S, Yardim M, Kalayci M, Çaglar M and Aydin S: Chemerin and
dermcidin in human milk and their alteration in gestational
diabetes. J Hum Lact. 35:550–558. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Budak MS, Kahramanoglu I, Vitale SG, Akgol
S, Dilek ME, Kartal S, Caruso S, Kahveci B, Obut M, Bademkiran MH,
et al: Maternal abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness as a simple
predictor for gestational diabetes mellitus. J Perinat Med.
47:605–610. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zheng H, Shen H, Oprea I, Worrall C,
Stefanescu R, Girnita A and Girnita L: β-Arrestin-biased agonism as
the central mechanism of action for insulin-like growth factor 1
receptor-targeting antibodies in Ewing's sarcoma. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:20620–20625. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mitchell PL, Nachbar R, Lachance D,
St-Pierre P, Trottier J, Barbier O and Marette A: Treatment with a
novel agent combining docosahexaenoate and metformin increases
protectin DX and IL-6 production in skeletal muscle and reduces
insulin resistance in obese diabetic db/db mice. Diabetes Obes
Metab. 19:313–319. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wan J, Hu Z, Zeng K, Yin Y, Zhao M, Chen M
and Chen Q: The reduction in circulating levels of estrogen and
progesterone in women with preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens.
11:18–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heerspink HJ, Andress DL, Bakris G,
Brennan JJ, Correa-Rotter R, Dey J, Hou FF, Kitzman DW, Kohan D,
Makino H, et al: Rationale and protocol of the Study Of diabetic
Nephropathy with AtRasentan (SONAR) trial: A clinical trial design
novel to diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Obes Metab. 20:1369–1376.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Garcia-Carretero R, Vigil-Medina L,
Mora-Jimenez I, Soguero-Ruiz C, Goya-Esteban R, Ramos-Lopez J and
Barquero-Perez O: Cardiovascular risk assessment in prediabetic
patients in a hypertensive population: The role of cystatin C.
Diabetes Metab Syndr. 12:625–629. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gong T, Wang J, Yang M, Shao Y, Liu J, Wu
Q, Xu Q, Wang H, He X, Chen Y, et al: Serum homocysteine level and
gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. J Diabetes
Investig. 7:622–628. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li B, Wu J, Jiang P, Li M, Liu Q, Cao Y
and Wang S: Serum fatty acid binding protein 4 is positively
associated with early stroke recurrence in nondiabetic ischemic
stroke. Aging (Albany NY). 11:1977–1989. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maesa JM, Fernandez-Riejos P,
Gonzalez-Rodriguez C and Sanchez-Margalet V: Screening for
gestational diabetes mellitus by measuring glycated hemoglobin can
reduce the use of the glucose challenge test. Ann Lab Med.
39:524–529. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salman L, Pardo A, Krispin E, Oron G,
Toledano Y and Hadar E: Perinatal outcome in gestational diabetes
according to different diagnostic criteria. J Perinat Med.
47:553–557. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pheiffer C, Dias S, Rheeder P and Adam S:
MicroRNA profiling in HIV-infected South African women with
gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol Diagn Ther. 23:499–505. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Catalano PM, McIntyre HD, Cruickshank JK,
McCance DR, Dyer AR, Metzger BE, Lowe LP, Trimble ER, Coustan DR,
Hadden DR, et al HAPO Study Cooperative Research Group, : The
hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcome study: Associations of
GDM and obesity with pregnancy outcomes. Diabetes Care. 35:780–786.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qian D, Zhang T, Zheng P, Liang Z, Wang S,
Xie J, Zhao L, Zhang Y and Situ B: Comparison of oral antidiabetic
drugs as add-in treatments in patients with type 2 diabetes
uncontrolled on metformin: A Network Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Ther.
9:1945–1958. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chaturvedi R, Desai C, Patel P, Shah A and
Dikshit RK: An evaluation of the impact of antidiabetic medication
on treatment satisfaction and quality of life in patients of
diabetes mellitus. Perspect Clin Res. 9:15–22. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li YT, Kuo TC and Wang PH: Low serum level
of irisin and gestational diabetes mellitus. Taiwan J Obstet
Gynecol. 58:443–444. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Formoso G, Ginestra F, Di Dalmazi G and
Consoli A: Empagliflozin, metformin and insulin degludec, during
pregnancy: A case report. Acta Diabetol. 55:759–761. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chong PL, Pisharam J, Abdullah A and Chong
VH: Gestational diabetes insipidus. QJM. 112:123–124. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tavakoli R and Lebreton G: Biomarkers for
early detection of cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury.
J Thorac Dis. 10 (Suppl 33):S3914–S3918. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma L, Liu Q, Jiang Y, Zhao H, Zhao T, Cao
Y, Li P and Niu W: Genetically elevated circulating homocysteine
concentrations increase the risk of diabetic kidney disease in
Chinese diabetic patients. J Cell Mol Med. 23:2794–2800. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kawasaki M, Arata N and Ogawa Y: Obesity
and abnormal glucose tolerance in the offspring of mothers with
diabetes. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 30:361–368. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fu Z, Yang X, Shen M, Xue H, Qian G, Cao
F, Guo J, Dong W and Chen Y: Prognostic ability of cystatin C and
homocysteine plasma levels for long-term outcomes in very old acute
myocardial infarction patients. Clin Interv Aging. 13:1201–1209.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hiersch L and Yogev Y: Impact of
gestational hyperglycemia on maternal and child health. Curr Opin
Clin Nutr Metab Care. 17:255–260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guillén-Sacoto MA, Barquiel B, Hillman N,
Burgos MÁ and Herranz L: Gestational diabetes mellitus: Glycemic
control during pregnancy and neonatal outcomes of twin and
singleton pregnancies. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr. 65:319–327. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|