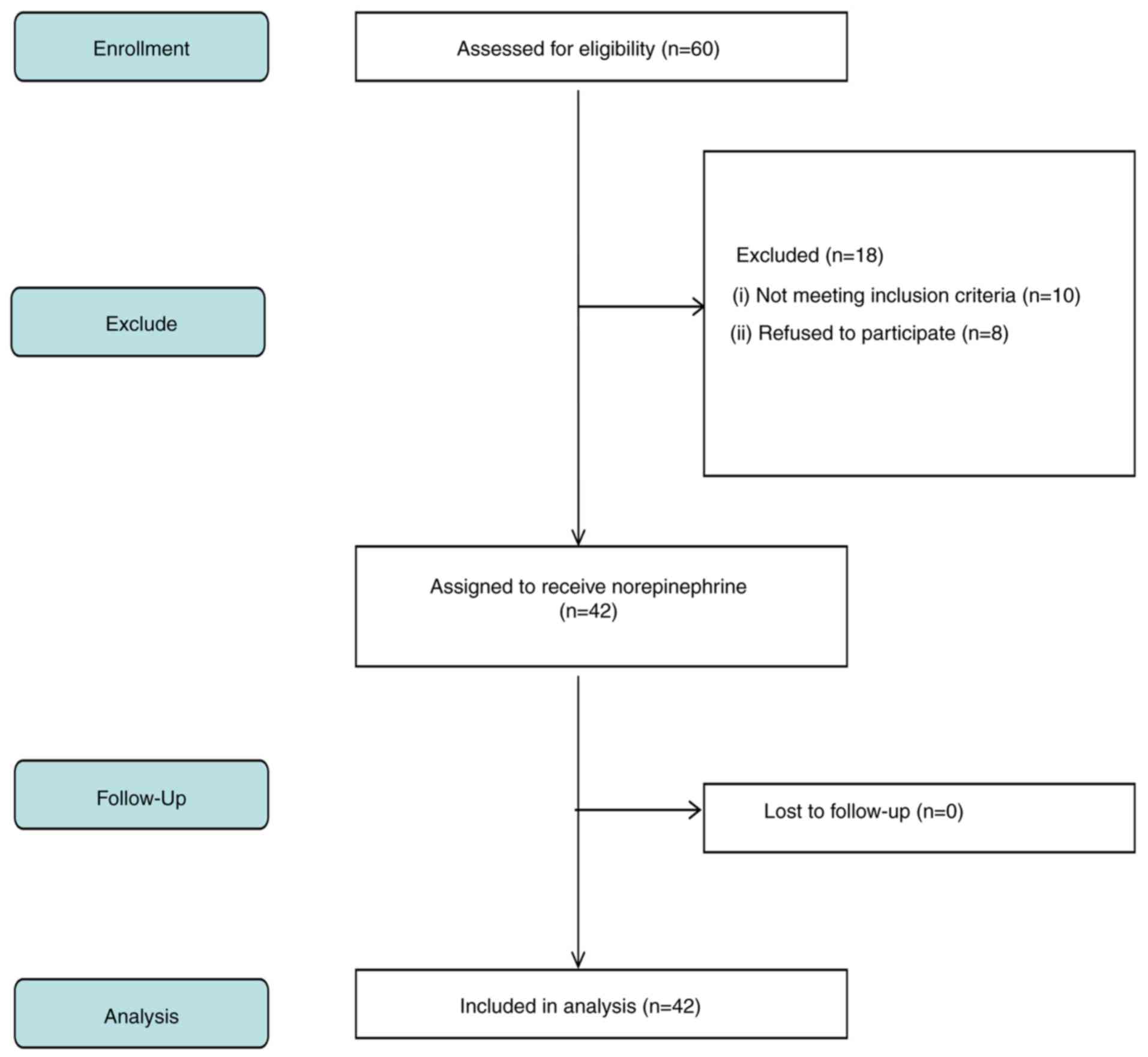
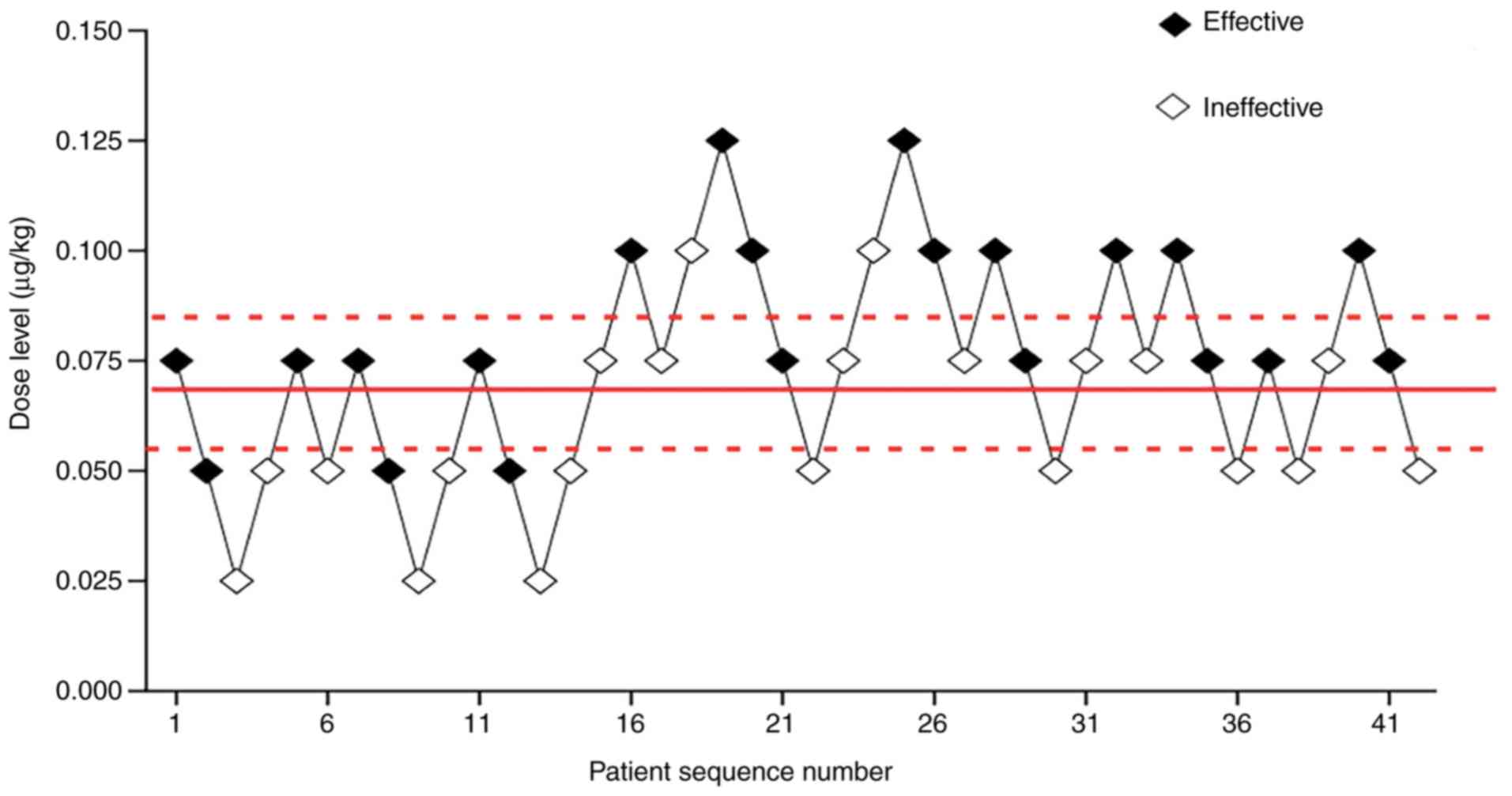
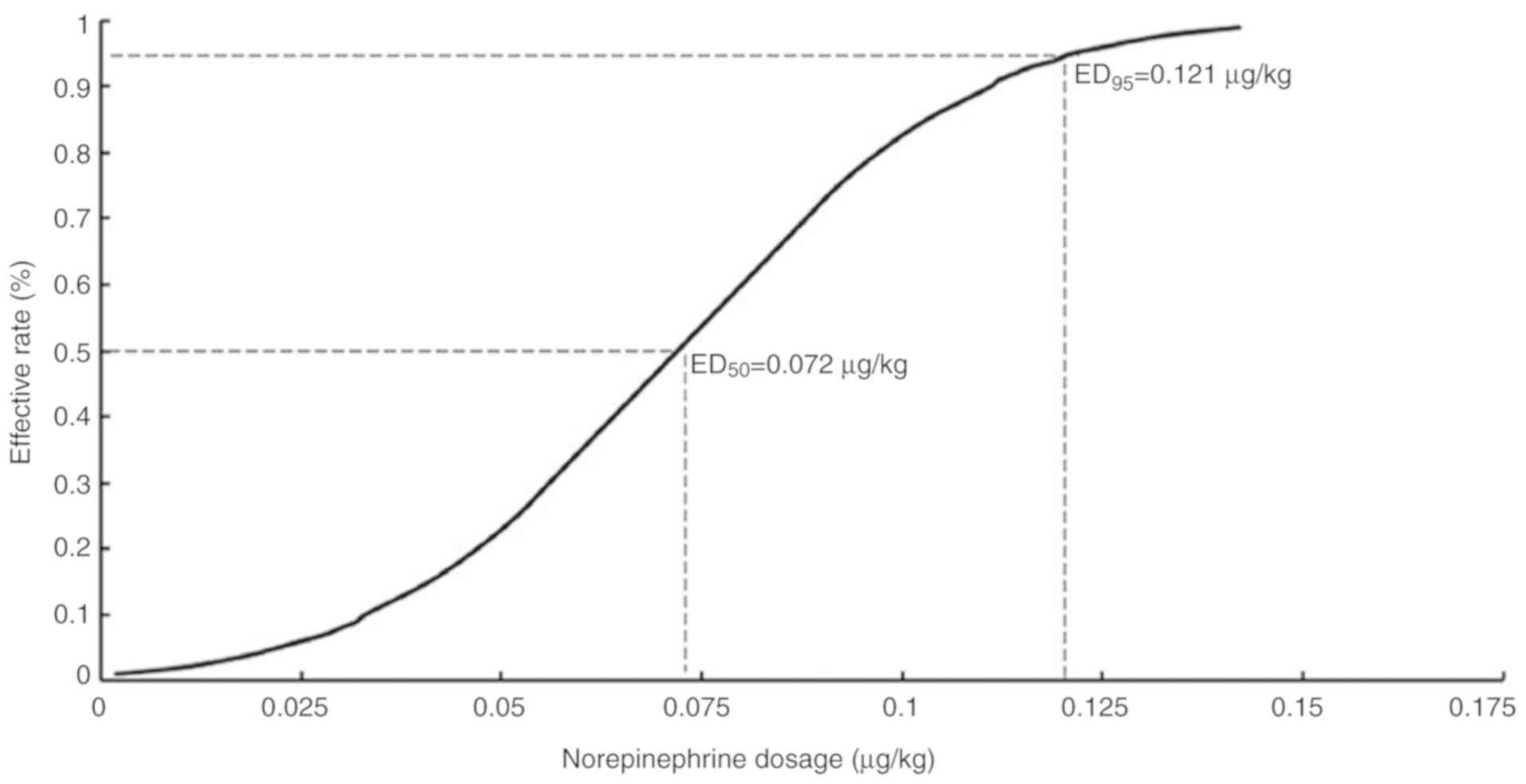
|
1
|
Mercier FJ, Augè M, Hoffmann C, Fischer C
and Gouez AL: Maternal hypotension during spinal anesthesia for
caesarean delivery. Minerva Anestesiol. 79:62–73. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Antoine C and Young BK: Fetal lactic
acidosis with epidural anesthesia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 142:55–59.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ali Elnabtity AM and Selim MF:
Norepinephrine versus ephedrine to maintain arterial blood pressure
during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery: A prospective
double-blinded trial. Anesth Essays Res. 12:92–97. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee A, Kee WD and Gin T: A quantitative,
systematic review of randomized controlled trials of ephedrine
versus phenylephrine for the management of hypotension during
spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery. Anesth Analg. 94:920–926.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ngan Kee WD, Lee A, Khaw KS, Ng FF,
Karmakar MK and Gin T: A randomized double-blinded comparison of
phenylephrine and ephedrine infusion combinations to maintain blood
pressure during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery: The
effects on fetal acid-base status and hemodynamic control. Anesth
Analg. 107:1295–1302. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ngan Kee WD, Khaw KS, Tam YH, Ng FF and
Lee SW: Performance of a closed-loop feedback computer-controlled
infusion system for maintaining blood pressure during spinal
anaesthesia for caesarean section: A randomized controlled
comparison of norepinephrine versus phenylephrine. J Clin Monit
Comput. 31:617–623. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stewart A, Fernando R, McDonald S, Hignett
R, Jones T and Columb M: The dose-dependent effects of
phenylephrine for elective cesarean delivery under spinal
anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 111:1230–1237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ngan Kee WD, Lee SW, Ng FF, Tan PE and
Khaw KS: Randomized double-blinded comparison of norepinephrine and
phenylephrine for maintenance of blood pressure during spinal
anesthesia for cesarean delivery. Anesthesiology. 122:736–745.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chooi C, Cox JJ, Lumb RS, Middleton P,
Chemali M, Emmett RS, Simmons SW and Cyna AM: Techniques for
preventing hypotension during spinal anaesthesia for caesarean
section. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 8:CD0022512017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen D, Qi X, Huang X, Xu Y, Qiu F, Yan Y
and Li Y: Efficacy and safety of different norepinephrine regimens
for prevention of spinal hypotension in cesarean section: A
randomized trial. Biomed Res Int. 2018:27081752018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Onwochei DN, Ngan Kee WD, Fung L, Downey
K, Ye XY and Carvalho JC: Norepinephrine intermittent intravenous
boluses to prevent hypotension during spinal anesthesia for
cesarean delivery: A sequential allocation dose-finding study.
Anesth Analg. 125:212–218. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Doyle DJ and Garmon EH: American Society
of Anesthesiologists Classification (ASA Class). StatPearls
Publishing LLC; Treasure Island, FL: 2019
|
|
13
|
Harten JM, Boyne I, Hannah P, Varveris D
and Brown A: Effects of a height and weight adjusted dose of local
anaesthetic for spinal anaesthesia for elective Caesarean section.
Anaesthesia. 60:348–353. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vallejo MC, Attaallah AF, Elzamzamy OM,
Cifarelli DT, Phelps AL, Hobbs GR, Shapiro RE and Ranganathan P: An
open-label randomized controlled clinical trial for comparison of
continuous phenylephrine versus norepinephrine infusion in
prevention of spinal hypotension during cesarean delivery. Int J
Obstet Anesth. 29:18–25. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Apgar V: A proposal for a new method of
evaluation of the newborn infant. Anesthesia Analgesia. 32:250–259.
1953. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ngan Kee WD: A Random-allocation graded
dose-response study of norepinephrine and phenylephrine for
treating hypotension during spinal anesthesia for cesarean
delivery. Anesthesiology. 127:934–941. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ngan Kee WD, Khaw KS and Ng FF: Comparison
of phenylephrine infusion regimens for maintaining maternal blood
pressure during spinal anaesthesia for Caesarean section. Br J
Anaesth. 92:469–474. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu H, Huang Y, Diao M, Li H, Ma Y, Lin X
and Zhou J: Determination of the 90% effective dose (ED90) of
phenylephrine for hypotension during elective cesarean delivery
using a continual reassessment method. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod
Biol. 194:136–140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stylianou M and Flournoy N: Dose finding
using the biased coin up-and-down design and isotonic regression.
Biometracs. 58:171–177. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dixon WJ: Staircase bioassay: The
up-and-down method. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 15:47–50. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pace NL and Stylianou MP: Advances in and
limitations of up-and-down methodology: A précis of clinical use,
study design, and dose estimation in anesthesia research.
Anesthesiology. 107:144–152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dixon WJ: The up-and-down method from
small samples. J Am Stat Assoc. 60:967–978. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Miller JM Jr, Bernard M, Brown HL, St
Pierre JJ and Gaber HA: Umbilical cord blood gases for term healthy
newborns. Am J Perinatol. 7:157–159. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sell A, Olkkola KT, Jalonen J and Aantaa
R: Minimum effective local anaesthetic dose of isobaric
levobupivacaine and ropivacaine administered via a spinal catheter
for hip replacement surgery. Br J Anaesth. 94:239–242. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lynde GC: Determination of ED50
of hydromorphone for postoperative analgesia following cesarean
delivery. Int J Obstet Anesth. 28:17–21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Johnston DF, Sondekoppam RV, Giffin R,
Litchfield R and Ganapathy S: Determination of ED50 and
ED95 of 0.5% Ropivacaine in adductor canal block to produce
Quadriceps weakness: A dose-finding study. Reg Anesth Pain Med.
42:731–736. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tallarida RJ: Drug Synergism and
Dose-Effect Data Analysis. Chapman and Hall/CRC; New York, NY: pp.
21–39. 2000
|
|
28
|
Macarthur A and Riley ET: Obstetric
anesthesia controversies Vasopressor choice for postspinal
hypotension during cesarean delivery. Int Anesthesiol Clin.
45:115–132. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thomas D, Robson S, Redfern N, Hughes D
and Boys R: Randomized trial of bolus phenylephrine or ephedrine
for maintenance of arterial pressure during spinal anaesthesia for
Caesarean section. Br J Anaesth. 76:61–65. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ngan Kee WD, Khaw KS, Lee BB, Lau TK and
Gin T: A dose-response study of prophylactic intravenous ephedrine
for the prevention of hypotension during spinal anesthesia for
cesarean delivery. Anesth Analg. 90:1390–1395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Puolakka J, Kauppila A, Tuimala R,
Jouppila R and Vuori J: The effect of parturition on umbilical
blood plasma levels of norepinephrine. Obstet Gynecol. 61:19–21.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kinsella SM, Carvalho B, Dyer RA, Fernando
R, McDonnell N, Mercier FJ, Palanisamy A, Sia AT, Van de Velde M
and Vercueil A; Consensus Statement Collaborators, : International
consensus statement on the management of hypotension with
vasopressors during caesarean section under spinal anaesthesia.
Anaesthesia. 73:71–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Doherty A, Ohashi Y, Downey K and Carvalho
JC: Phenylephrine infusion versus bolus regimens during cesarean
delivery under spinal anesthesia: A double-blind randomized
clinical trial to assess hemodynamic changes. Anesth Analg.
115:1343–1350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Langesæter E, Rosseland LA and Stubhaug A:
A randomized, double-blind comparison of low-dose versus high-dose
spinal anesthesia with intravenous phenylephrine or placebo
infusion. Anesthesiology. 109:856–863. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Smiley RM: More perfect? Int J Obstet
Anesth. 29:1–4. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Greenwald HP, Gootnick A, Luger NM and
King JA: Tissue necrosis following subcutaneous infiltration with
nor-epinephrine; Report of two cases. N Engl J Med. 246:252–253.
1952. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Turner DA and Kleinman ME: The use of
vasoactive agents via peripheral intravenous access during
transport of critically III infants and children. Pediatr Emerg
Care. 26:563–566. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Medlej K, Kazzi AA, El Hajj Chehade A,
Saad Eldine M, Chami A, Bachir R, Zebian D and Abou Dagher G:
Complications from administration of vasopressors through
peripheral venous catheters: An observational study. J Emerg Med.
54:47–53. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|