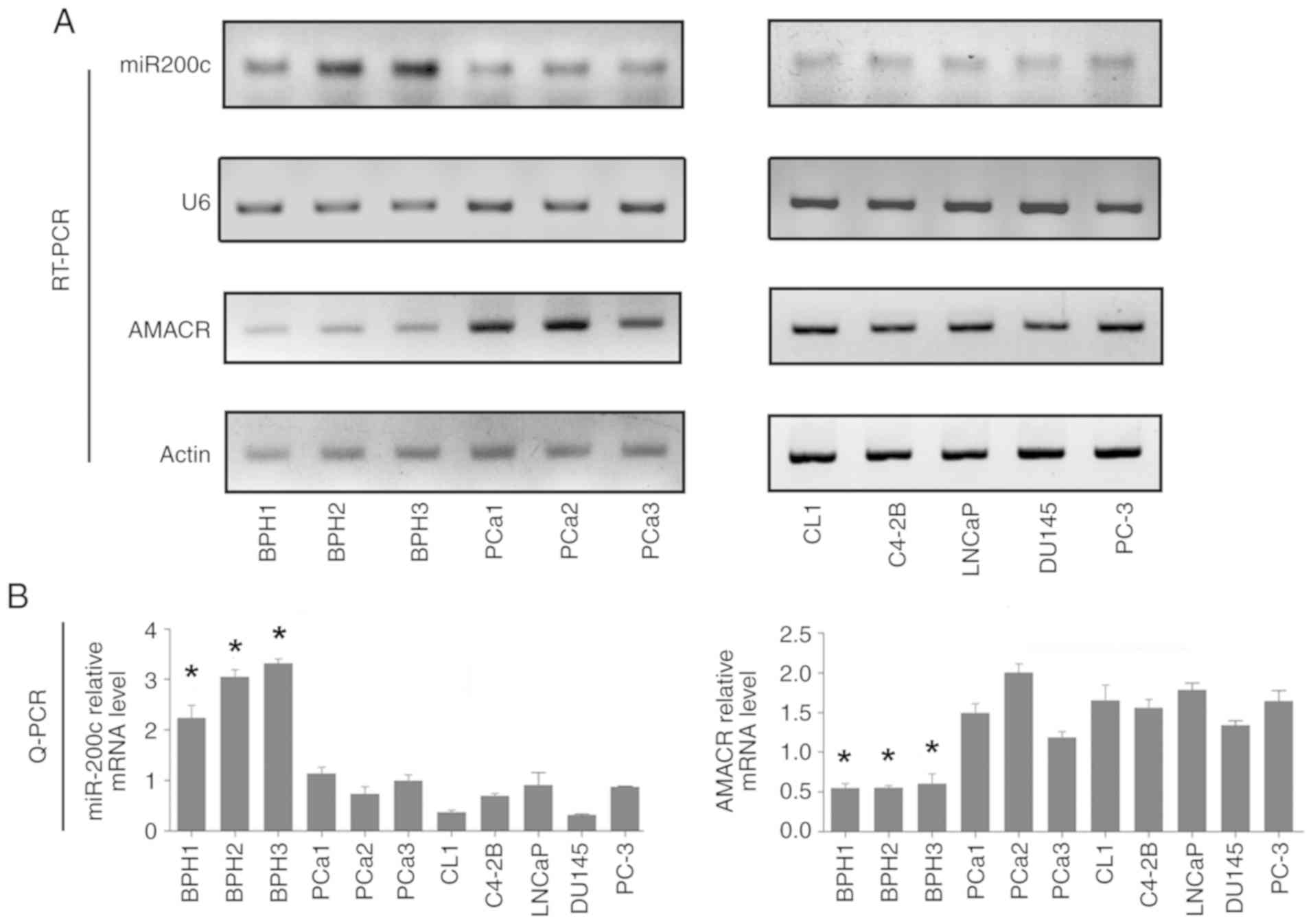
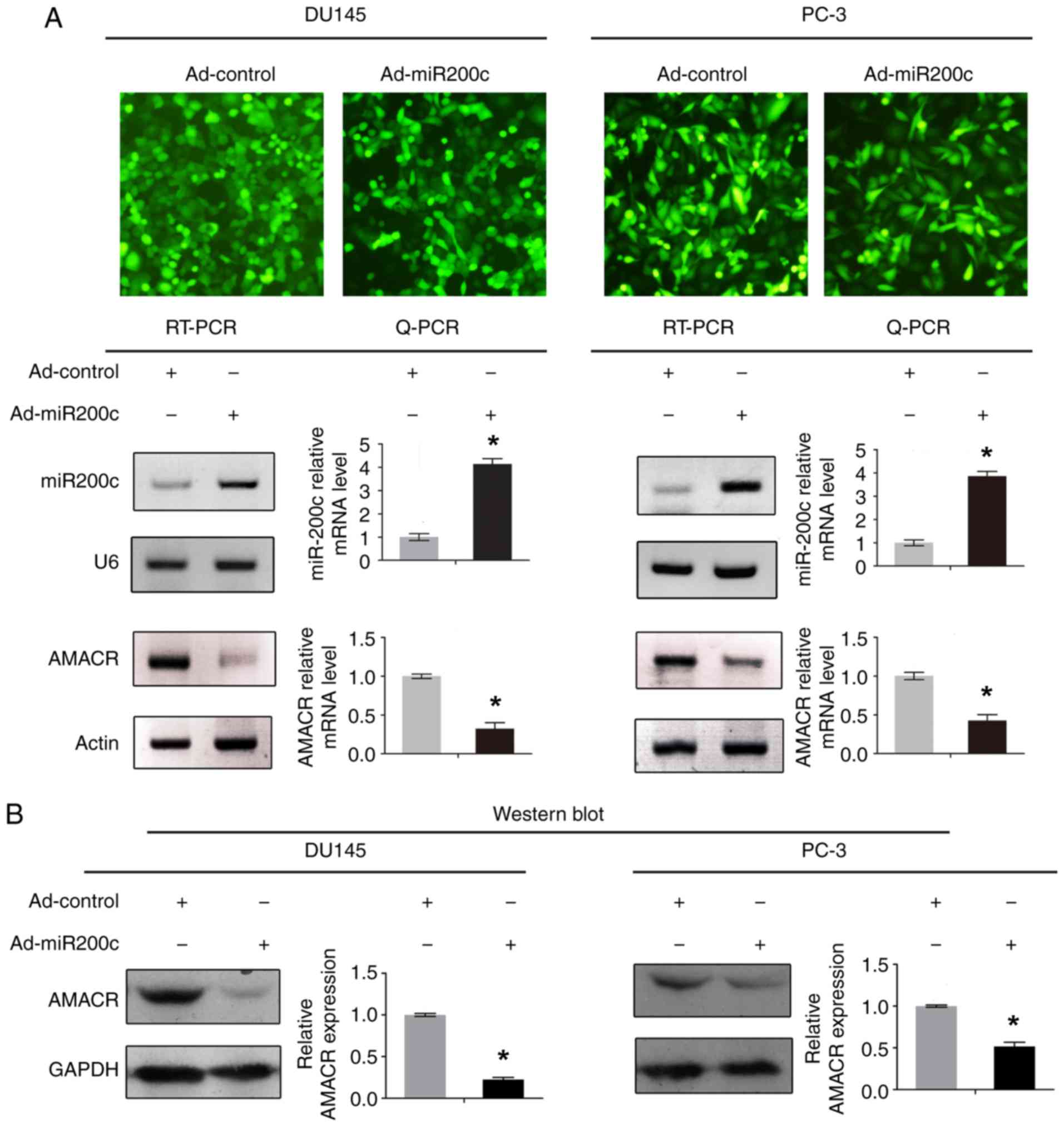
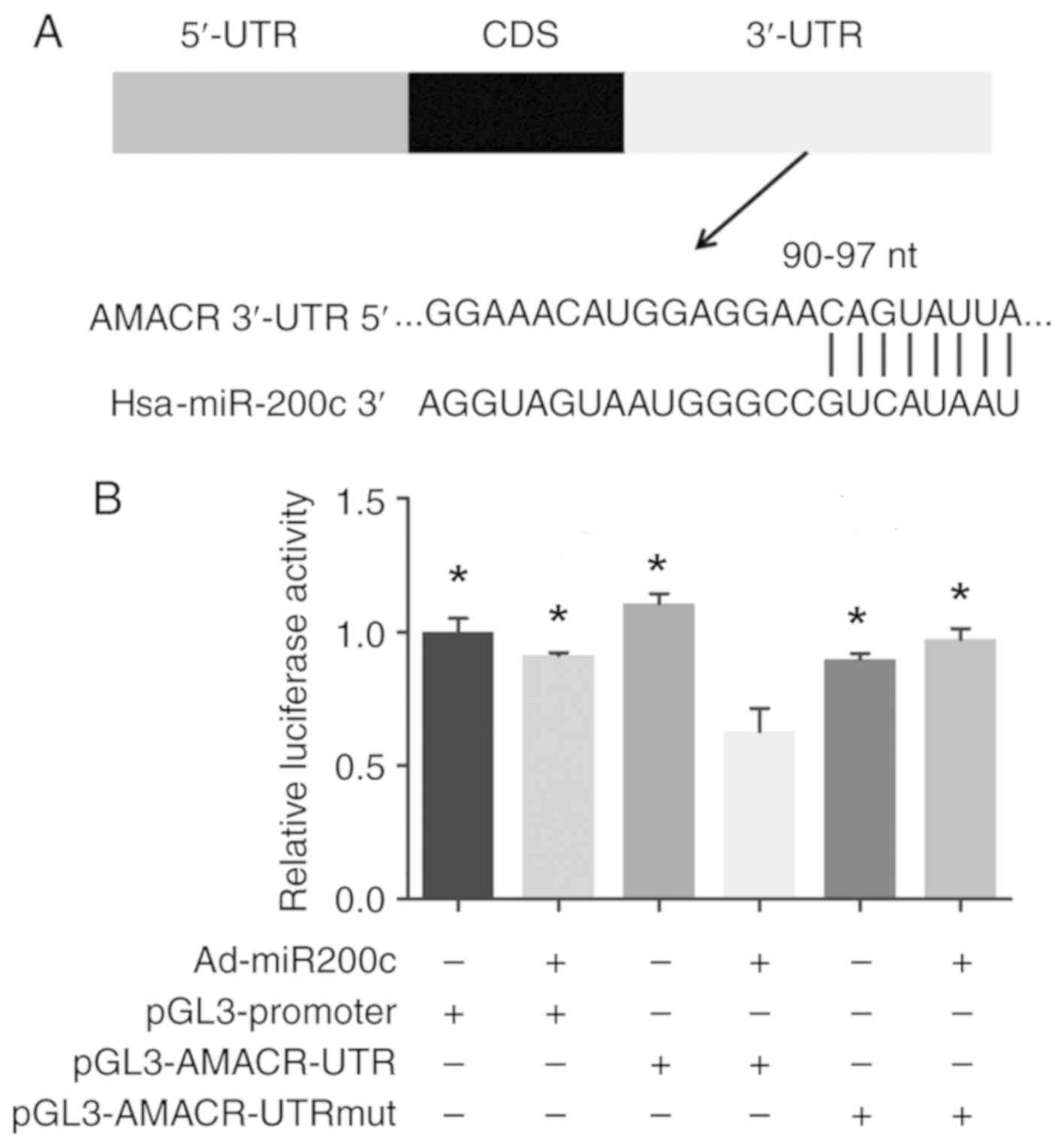
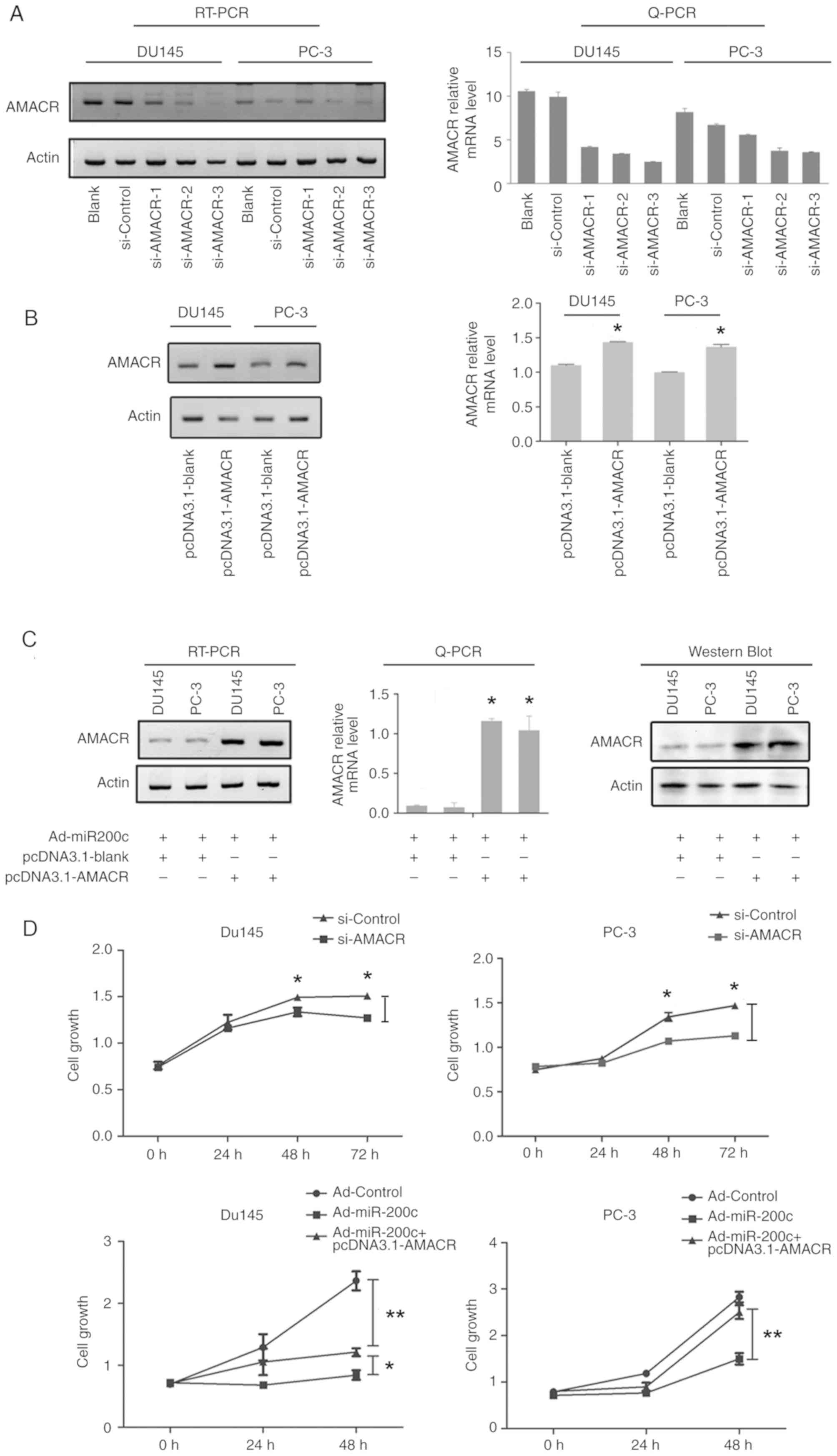
|
1
|
Knezevic J, Pfefferle AD, Petrovic I,
Greene SB, Perou CM and Rosen JM: Expression of miR-200c in
claudin-low breast cancer alters stem cell functionality, enhances
chemosensitivity and reduces metastatic potential. Oncogene.
34:5997–6006. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jurmeister S, Baumann M, Balwierz A,
Keklikoglou I, Ward A, Uhlmann S, Zhang JD, Wiemann S and Sahin Ö:
MicroRNA-200c represses migration and invasion of breast cancer
cells by targeting actin-regulatory proteins FHOD1 and PPM1F. Mol
Cell Biol. 32:633–651. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou X, Wang Y, Shan B, Han J, Zhu H, Lv
Y, Fan X, Sang M, Liu XD and Liu W: The downregulation of
miR-200c/141 promotes ZEB1/2 expression and gastric cancer
progression. Med Oncol. 32:4282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Valladares-Ayerbes M, Reboredo M,
Medina-Villaamil V, Iglesias-Díaz P, Lorenzo-Patiño MJ, Haz M,
Santamarina I, Blanco M, Fernández-Tajes J, Quindós M, et al:
Circulating miR-200c as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for
gastric cancer. J Transl Med. 10:1862012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Toiyama Y, Hur K, Tanaka K, Inoue Y,
Kusunoki M, Boland CR and Goel A: Serum miR-200c is a novel
prognostic and metastasis-predictive biomarker in patients with
colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 259:735–743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao YC and Wu J: MicroRNA-200c and
microRNA-141 as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for
ovarian cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:4843–4850. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Butz H, Szabó PM, Khella HW, Nofech-Mozes
R, Patocs A and Yousef GM: miRNA-target network reveals miR-124as a
key miRNA contributing to clear cell renal cell carcinoma
aggressive behaviour by targeting CAV1 and FLOT1. Oncotarget.
6:12543–12557. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Su W, Xu M, Chen X, Nie L, Chen N, Gong J,
Zhang M, Su Z, Huang L and Zhou Q: MiR200c targets IRS1 and
suppresses prostate cancer cell growth. Prostate. 75:855–862. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Puhr M, Hoefer J, Schäfer G, Erb HH, Oh
SJ, Klocker H, Heidegger I, Neuwirt H and Culig Z:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition leads to docetaxel resistance
in prostate cancer and is mediated by reduced expression of
miR-200c and miR-205. Am J Pathol. 181:2188–2201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Radisky DC: miR-200c at the nexus of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, resistance to apoptosis, and the
breast cancer stem cell phenotype. Breast Cancer Res. 13:1102011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qiu M, Liang Z, Chen L, Tan G, Liu L, Wang
K, Chen H and Liu J: MicroRNA-200c suppresses cell growth and
metastasis by targeting Bmi-1 and E2F3 in renal cancer cells. Exp
Ther Med. 13:1329–1336. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang H, Sun Z, Li Y, Fan D and Jiang H:
MicroRNA-200c binding to FN1 suppresses the proliferation,
migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 88:285–292. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen P, Guo X, Zhang L, Zhang W, Zhou Q,
Tian Z, Zheng Y, Liao Q, Wang H, Li G, et al: MiR-200c is a
cMyc-activated miRNA that promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
downregulating PTEN. Oncotarget. 8:5206–5218. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang M, Nie L, Su Z, Xu M, Chen N, Gong
J, Xie H, Zhong J, Tan J, Xu Y, et al: MicroRNA200c suppresses
urothelial carcinoma invasiveness by targeting FSCN1. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 10:5665–5674. 2017.
|
|
15
|
D'Ippolito E, Plantamura I, Bongiovanni L,
Casalini P, Baroni S, Piovan C, Orlandi R, Gualeni AV, Gloghini A,
Rossini A, et al: miR-9 and miR-200 regulate PDGFRβ-mediated
endothelial differentiation of tumor cells in triple-negative
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 76:5562–5572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shimono Y, Zabala M, Cho RW, Lobo N,
Dalerba P, Qian D, Diehn M, Liu H, Panula SP, Chiao E, et al:
Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with
normal stem cells. Cell. 138:592–603. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang X, Tang X, Gal J, Kyprianou N, Zhu H
and Tang G: Detection of microRNAs in prostate cancer cells by
microRNA array. Methods Mol Biol. 732:69–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zha S, Ferdinandusse S, Denis S, Wanders
RJ, Ewing CM, Luo J, De Marzo AM and Isaacs WB:
Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase as an androgen-independent growth
modifier in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 63:7365–7376.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jindal Y, Singh A, Kumar R, Varma K, Misra
V, Misra SP and Dwivedi M: Expression of alpha methylacyl CoA
racemase (AMACR) in gastric adenocarcinoma and its correlation with
helicobacter pylori infection. J Clin Diagn Res. 10:EC10–EC12.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Leav I, Revelo MP, Deka R,
Medvedovic M, Jiang Z and Ho SM: Deletion hotspots in AMACR
promoter CpG island are cis-regulatory elements controlling the
gene expression in the colon. PLoS Genet. 5:e10003342009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li CF, Chen LT, Lan J, Chou FF, Lin CY,
Chen YY, Chen TJ, Li SH, Yu SC, Fang FM, et al: AMACR amplification
and overexpression in primary imatinib-naïve gastrointestinal
stromal tumors: A driver of cell proliferation indicating adverse
prognosis. Oncotarget. 5:11588–11603. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li CF, Fang FM, Lan J, Wang JW, Kung HJ,
Chen LT, Chen TJ, Li SH, Wang YH, Tai HC, et al: AMACR
amplification in myxofibrosarcomas: A mechanism of overexpression
that promotes cell proliferation with therapeutic relevance. Clin
Cancer Res. 20:6141–6152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pinto F, Pértega-Gomes N, Vizcaíno JR,
Andrade RP, Cárcano FM and Reis RM: Brachyury as a potential
modulator of androgen receptor activity and a key player in therapy
resistance in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 7:28891–28902. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen W, Wu W, Zhao J, Yu C, Liu W, Jiang A
and Zhang J: Molecular cloning and preliminary analysis of the
human alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase promoter. Mol Biol Rep.
36:423–430. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zha S and Isaacs WB: A nonclassic CCAAT
enhancer element binding protein binding site contributes to
alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase expression in prostate cancer. Mol
Cancer Res. 3:110–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen N, Chen X, Huang R, Zeng H, Gong J,
Meng W, Lu Y, Zhao F, Wang L and Zhou Q: BCL-xL is a target gene
regulated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1{alpha}. J Biol Chem.
284:10004–10012. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen X, Gong J, Zeng H, Chen N, Huang R,
Huang Y, Nie L, Xu M, Xia J, Zhao F, et al: MicroRNA145 targets
BNIP3 and suppresses prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res.
70:2728–2738. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ferdinandusse S, Denis S, IJlst L,
Dacremont G, Waterham HR and Wanders RJ: Subcellular localization
and physiological role of alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase. J Lipid
Res. 41:1890–1896. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mobley JA, Leav I, Zielie P, Wotkowitz C,
Evans J, Lam YW, L'Esperance BS, Jiang Z and Ho SM: Branched fatty
acids in dairy and beef products markedly enhance
alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase expression in prostate cancer cells
in vitro. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 12:775–783.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Erdmann K, Kaulke K, Thomae C, Huebner D,
Sergon M, Froehner M, Wirth MP and Fuessel S: Elevated expression
of prostate cancer-associated genes is linked to down-regulation of
microRNAs. BMC Cancer. 14:822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Festuccia C, Gravina GL, Mancini A, Muzi
P, Cesare ED, Kirk R, Smith M, Hughes S, Gibson R, Lian LY, et al:
Trifluoroibuprofen inhibits α-methylacyl coenzyme A racemase
(AMACR/P504S), reduces cancer cell proliferation and inhibits in
vivo tumor growth in aggressive prostate cancer models. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 14:1031–1041. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|