|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal Cancer Statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lan YT, Chang SC, Yang SH, Lin CC, Wang
HS, Jiang JK, Chen WS, Lin TC, Chiou SH and Lin JK: Comparison of
clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis between early and
late recurrence after curative surgery for colorectal cancer. Am J
Surg. 207:922–930. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guraya SY: Pattern, stage, and time of
recurrent colorectal cancer after curative surgery. Clin Colorectal
Cancer. 18:e223–e228. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Makishima H, Yasuda S, Isozaki Y, Kasuya
G, Okada N, Miyazaki M, Mohamad O, Matsufuji N, Yamada S, Tsuji H,
et al Liver Cancer Working Group, : Single fraction carbon ion
radiotherapy for colorectal cancer liver metastasis: A dose
escalation study. Cancer Sci. 110:303–309. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen H, Xu Z and Liu D: Small non-coding
RNA and colorectal cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 23:3050–3057. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim VN, Han J and Siomi MC: Biogenesis of
small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:126–139. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xi XP, Zhuang J, Teng MJ, Xia LJ, Yang MY,
Liu QG and Chen JB: MicroRNA-17 induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition consistent with the cancer stem cell phenotype by
regulating CYP7B1 expression in colon cancer. Int J Mol Med.
38:499–506. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fang L, Li H, Wang L, Hu J, Jin T, Wang J
and Yang BB: MicroRNA-17-5p promotes chemotherapeutic drug
resistance and tumour metastasis of colorectal cancer by repressing
PTEN expression. Oncotarget. 5:2974–2987. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu CW, Dong YJ, Liang QY, He XQ, Ng SS,
Chan FK, Sung JJ and Yu J: MicroRNA-18a attenuates DNA damage
repair through suppressing the expression of ataxia telangiectasia
mutated in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e570362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Liu R, Yang F, Cheng R, Chen X, Cui
S, Gu Y, Sun W, You C, Liu Z, et al: miR-19a promotes colorectal
cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1. Mol Cancer.
16:532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang L, Cai JL, Huang PZ, Kang L, Huang
MJ, Wang L and Wang JP: miR19b-3p promotes the growth and
metastasis of colorectal cancer via directly targeting ITGB8. Am J
Cancer Res. 7:1996–2008. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
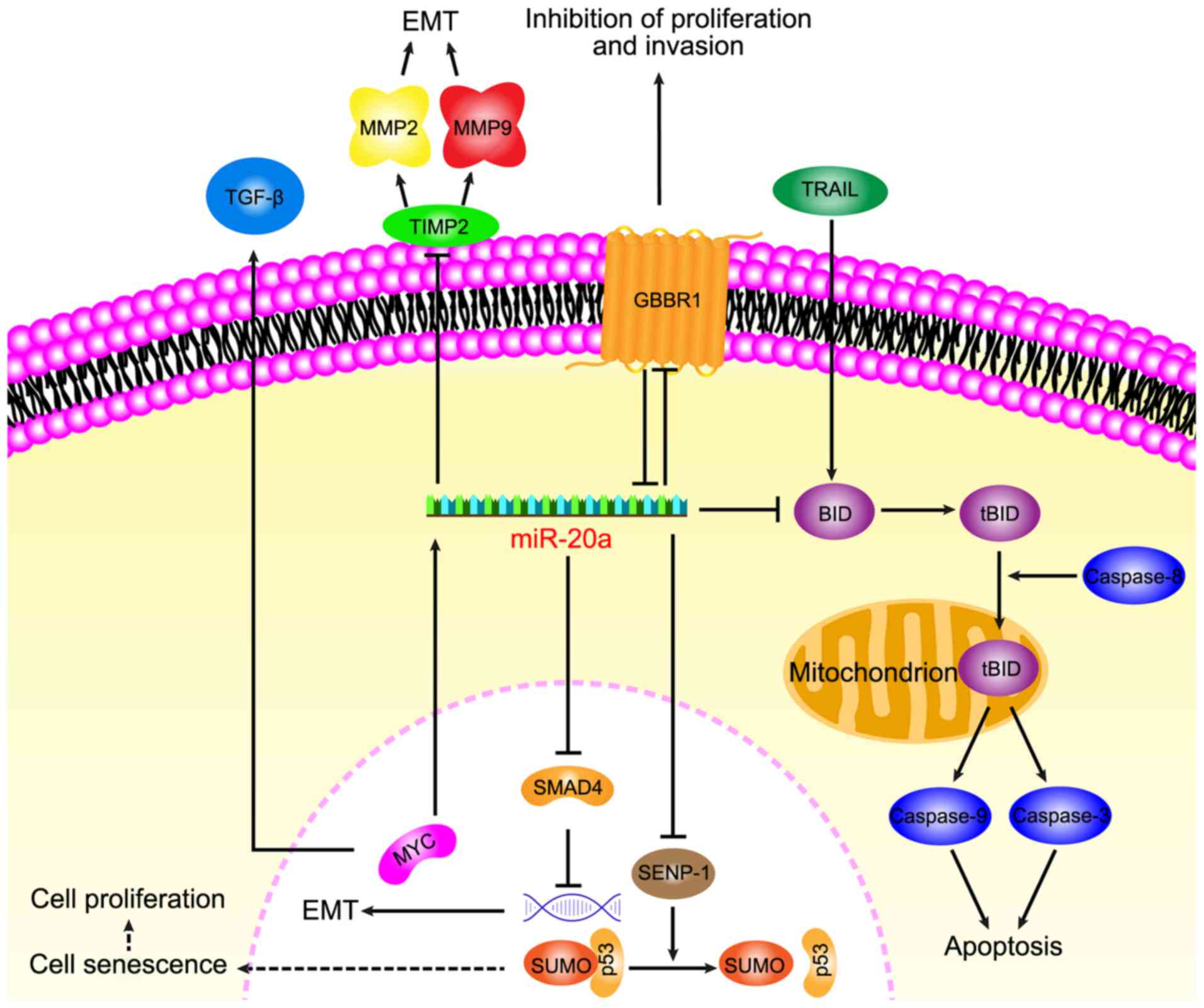
Huang G, Chen X, Cai Y, Wang X and Xing C:
miR-20a-directed regulation of BID is associated with the TRAIL
sensitivity in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 37:571–578. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu T, Jing C, Shi Y, Miao R, Peng L, Kong
S, Ma Y and Li L: microRNA-20a enhances the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells by
modulating matrix metalloproteinases. Exp Ther Med. 10:683–688.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dalmasso G, Cougnoux A, Delmas J,
Darfeuille-Michaud A and Bonnet R: The bacterial genotoxin
colibactin promotes colon tumor growth by modifying the tumor
microenvironment. Gut Microbes. 5:675–680. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA,
Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S and Allgayer H: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21)
post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and
stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin H, Shi X, Zhao Y, Peng M, Kong Y, Qin
D and Lv X: MicroRNA-30a mediates cell migration and invasion by
targeting metadherin in colorectal cancer. Technol Cancer Res
Treat. 17:15330338187581082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun D, Yu F, Ma Y, Zhao R, Chen X, Zhu J,
Zhang CY, Chen J and Zhang J: MicroRNA-31 activates the RAS pathway
and functions as an oncogenic microRNA in human colorectal cancer
by repressing RAS p21 GTPase activating protein 1 (RASA1). J Biol
Chem. 288:9508–9518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Akao Y, Noguchi S, Iio A, Kojima K, Takagi
T and Naoe T: Dysregulation of microRNA-34a expression causes
drug-resistance to 5-FU in human colon cancer DLD-1 cells. Cancer
Lett. 300:197–204. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang G, Zhou H, Xiao H, Liu Z, Tian H and
Zhou T: MicroRNA-92a functions as an oncogene in colorectal cancer
by targeting PTEN. Dig Dis Sci. 59:98–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cappuzzo F, Sacconi A, Landi L, Ludovini
V, Biagioni F, D'Incecco A, Capodanno A, Salvini J, Corgna E,
Cupini S, et al: MicroRNA signature in metastatic colorectal cancer
patients treated with anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies. Clin
Colorectal Cancer. 13:37–45.e4. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lian B, Yang D, Liu Y, Shi G, Li J, Yan X,
Jin K, Liu X, Zhao J, Shang W, et al: miR-128 Targets the
SIRT1/ROS/DR5 Pathway to Sensitize Colorectal Cancer to
TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:2151–2162. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Salem SM, Hamed AR, Fayez AG and Nour
Eldeen G: Non-target genes regulate miRNAs-mediated migration
steering of colorectal carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 25:559–566.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu K, Liu X, Mao X, Xue L, Wang R, Chen L
and Chu X: MicroRNA-149 suppresses colorectal cancer cell migration
and invasion by directly targeting forkhead box transcription
factor FOXM1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:499–515. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li LX, Lam IH, Liang FF, Yi SP, Ye LF,
Wang JT, Guo WW and Xu M: MiR-198 affects the proliferation and
apoptosis of colorectal cancer through regulation of
ADAM28/JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:1487–1493. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Z, Zhong X, Xiao Y and Chen C:
MicroRNA-296 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and enhances
apoptosis by targeting ARRB1-mediated AKT activation. Oncol Rep.
41:619–629. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan F, Tu Z, Duan L, Wang D and Lin F:
MicroRNA-383 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in
colorectal cancer by directly targeting paired box 6. Mol Med Rep.
17:6893–6901. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang W, He Y, Rui J and Xu MQ: miR-410
acts as an oncogene in colorectal cancer cells by targeting
dickkopf-related protein 1 via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Oncol Lett. 17:807–814. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li T, Jian X, He H, Lai Q, Li X, Deng D,
Liu T, Zhu J, Jiao H, Ye Y, et al: MiR-452 promotes an aggressive
colorectal cancer phenotype by regulating a Wnt/β-catenin positive
feedback loop. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:2382018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li KP, Fang YP, Liao JQ, Duan JD, Feng LG,
Luo XZ and Liang ZJ: Upregulation of miR-598 promotes cell
proliferation and cell cycle progression in human colorectal
carcinoma by suppressing INPP5E expression. Mol Med Rep.
17:2991–2997. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang L, Xu M, Lu P and Zhou F:
microRNA-769 is downregulated in colorectal cancer and inhibits
cancer progression by directly targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 1.
OncoTargets Ther. 11:9013–9025. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yang D, Li R, Xia J, Li W and Zhou H:
miR-3666 suppresses cellular proliferation and invasion in
colorectal cancer by targeting SATB2. Mol Med Rep. 18:4847–4854.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu H, Li D, Fang H and Ning J:
Species-specific function of microRNA-7702 in human colorectal
cancer cells via targeting TADA1. Am J Transl Res. 10:2579–2589.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mogilyansky E and Rigoutsos I: The
miR-17/92 cluster: A comprehensive update on its genomics,
genetics, functions and increasingly important and numerous roles
in health and disease. Cell Death Differ. 20:1603–1614. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang L, Wang X, Wen C, Yang X, Song M,
Chen J, Wang C, Zhang B, Wang L, Iwamoto A, et al: Hsa-miR-19a is
associated with lymph metastasis and mediates the TNF-α induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep.
5:133502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hao S, Huo S, Du Z, Yang Q, Ren M, Liu S,
Liu T and Zhang G: MicroRNA-related transcription factor regulatory
networks in human colorectal cancer. Medicine (Baltimore).
98:e151582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shirafkan N, Mansoori B, Mohammadi A,
Shomali N, Ghasbi M and Baradaran B: MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers
for colorectal cancer: New outlooks. Biomed Pharmacother.
97:1319–1330. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo Y, Bao Y and Yang W: Regulatory miRNAs
in colorectal carcinogenesis and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci.
18:182017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Takatsuno Y, Tanaka
F, Mimori K, Uetake H, Sugihara K and Mori M: Over- and
under-expressed microRNAs in human colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol.
34:1069–1075. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yau TO, Wu CW, Tang CM, Chen Y, Fang J,
Dong Y, Liang Q, Ng SS, Chan FK, Sung JJ, et al: MicroRNA-20a in
human faeces as a non-invasive biomarker for colorectal cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:1559–1568. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Moradi-Marjaneh R, Hassanian SM, Mehramiz
M, Rezayi M, Ferns GA, Khazaei M and Avan A: Reactive oxygen
species in colorectal cancer: The therapeutic impact and its
potential roles in tumor progression via perturbation of cellular
and physiological dysregulated pathways. J Cell Physiol.
234:10072–10079. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zeng X, Xiang J, Wu M, Xiong W, Tang H,
Deng M, Li X, Liao Q, Su B, Luo Z, et al: Circulating miR-17,
miR-20a, miR-29c, and miR-223 combined as non-invasive biomarkers
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e463672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang R, Fu Y, Zeng Y, Xiang M, Yin Y, Li
L, Xu H, Zhong J and Zeng X: Serum miR-20a is a promising biomarker
for gastric cancer. Biomed Rep. 6:429–434. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhu SY, Wu QY, Zhang CX, Wang Q, Ling J,
Huang XT, Sun X, Yuan M, Wu D and Yin HF: miR-20a inhibits the
killing effect of natural killer cells to cervical cancer cells by
downregulating RUNX1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 505:309–316.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li S, Qiang Q, Shan H, Shi M, Gan G, Ma F
and Chen B: miR-20a and miR-20b negatively regulate autophagy by
targeting RB1CC1/FIP200 in breast cancer cells. Life Sci.
147:143–152. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fan MQ, Huang CB, Gu Y, Xiao Y, Sheng JX
and Zhong L: Decrease expression of microRNA-20a promotes cancer
cell proliferation and predicts poor survival of hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 32:212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liao C, Chen W and Wang J: MicroRNA-20a
regulates glioma cell proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis by
targeting CUGBP elav-like family member 2. World Neurosurg.
121:e519–e527. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu X: Up-regulation of miR-20a by HPV16
E6 exerts growth-promoting effects by targeting PDCD6 in cervical
carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 102:996–1002. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhou L, Li X, Zhou F, Jin Z, Chen D, Wang
P, Zhang S, Zhuge Y, Shang Y and Zou X: Downregulation of
leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 1 by
microRNA-20a modulates gastric cancer multidrug resistance. Cancer
Sci. 109:1044–1054. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wei L and Ran F: MicroRNA-20a promotes
proliferation and invasion by directly targeting early growth
response 2 in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
15:271–277. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yu Y, Zhang J, Jin Y, Yang Y, Shi J, Chen
F, Han S, Chu P, Lu J, Wang H, et al: MiR-20a-5p suppresses tumor
proliferation by targeting autophagy-related gene 7 in
neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell Int. 18:52018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhao F, Pu Y, Qian L, Zang C, Tao Z and
Gao J: MiR-20a-5p promotes radio-resistance by targeting NPAS2 in
nasopharyngeal cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:105873–105881. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xiong Y, Sun F, Dong P, Watari H, Yue J,
Yu MF, Lan CY, Wang Y and Ma ZB: iASPP induces EMT and cisplatin
resistance in human cervical cancer through miR-20a-FBXL5/BTG3
signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Huang D, Bian G, Pan Y, Han X, Sun Y, Wang
Y, Shen G, Cheng M, Fang X and Hu S: MiR-20a-5p promotes
radio-resistance by targeting Rab27B in nasopharyngeal cancer
cells. Cancer Cell Int. 17:322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhu M, Zhou X, Du Y, Huang Z, Zhu J, Xu J,
Cheng G, Shu Y, Liu P, Zhu W, et al: miR-20a induces cisplatin
resistance of a human gastric cancer cell line via targeting CYLD.
Mol Med Rep. 14:1742–1750. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dhar S, Kumar A, Rimando AM, Zhang X and
Levenson AS: Resveratrol and pterostilbene epigenetically restore
PTEN expression by targeting oncomiRs of the miR-17 family in
prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 6:27214–27226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Du Y, Zhu M, Zhou X, Huang Z, Zhu J, Xu J,
Cheng G, Shu Y, Liu P, Zhu W, et al: miR-20a enhances cisplatin
resistance of human gastric cancer cell line by targeting NFKBIB.
Tumour Biol. 37:1261–1269. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wei J, Qi X, Zhan Q, Zhou D, Yan Q, Wang
Y, Mo L, Wan Y, Xie D, Xie J, et al: miR-20a mediates
temozolomide-resistance in glioblastoma cells via negatively
regulating LRIG1 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 71:112–118. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhao S, Yao D, Chen J, Ding N and Ren F:
MiR-20a promotes cervical cancer proliferation and metastasis in
vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 10:e01209052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang Y, Han T, Wei G and Wang Y:
Inhibition of microRNA-17/20a suppresses cell proliferation in
gastric cancer by modulating UBE2C expression. Oncol Rep.
33:2529–2536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang X, Kong Y, Xu X, Xing H, Zhang Y,
Han F, Li W, Yang Q, Zeng J, Jia J, et al: F-box protein FBXO31 is
down-regulated in gastric cancer and negatively regulated by miR-17
and miR-20a. Oncotarget. 5:6178–6190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhou J, Liu R, Luo C, Zhou X, Xia K, Chen
X, Zhou M, Zou Q, Cao P and Cao K: MiR-20a inhibits cutaneous
squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and proliferation by directly
targeting LIMK1. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:1340–1349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xiong Y, Zhang L and Kebebew E: MiR-20a is
upregulated in anaplastic thyroid cancer and targets LIMK1. PLoS
One. 9:e961032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xie J, Liu M, Li Y, Nie Y, Mi Q and Zhao
S: Ovarian tumor-associated microRNA-20a decreases natural killer
cell cytotoxicity by downregulating MICA/B expression. Cell Mol
Immunol. 11:495–502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Qiang XF, Zhang ZW, Liu Q, Sun N, Pan LL,
Shen J, Li T, Yun C, Li H and Shi LH: miR-20a promotes prostate
cancer invasion and migration through targeting ABL2. J Cell
Biochem. 115:1269–1276. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Chang Y, Liu C, Yang J, Liu G, Feng F,
Tang J, Hu L, Li L, Jiang F, Chen C, et al: MiR-20a triggers
metastasis of gallbladder carcinoma. J Hepatol. 59:518–527. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Bai X, Han G, Liu Y, Jiang H and He Q:
MiRNA-20a-5p promotes the growth of triple-negative breast cancer
cells through targeting RUNX3. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:1482–1489.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhao W, Geng D, Li S, Chen Z and Sun M:
LncRNA HOTAIR influences cell growth, migration, invasion, and
apoptosis via the miR-20a-5p/HMGA2 axis in breast cancer. Cancer
Med. 7:842–855. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yuan G, Zhao Y, Wu D, Gao C and Jiao Z:
miRNA-20a upregulates TAK1 and increases proliferation in
osteosarcoma cells. Future Oncol. 14:461–469. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Si W, Shen J, Du C, Chen D, Gu X, Li C,
Yao M, Pan J, Cheng J, Jiang D, et al: A miR-20a/MAPK1/c-Myc
regulatory feedback loop regulates breast carcinogenesis and
chemoresistance. Cell Death Differ. 25:406–420. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhao F, Pu Y, Cui M, Wang H and Cai S:
MiR-20a-5p represses the multi-drug resistance of osteosarcoma by
targeting the SDC2 gene. Cancer Cell Int. 17:1002017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Liu L, He J, Wei X, Wan G, Lao Y, Xu W, Li
Z, Hu H, Hu Z, Luo X, et al: MicroRNA-20a-mediated loss of
autophagy contributes to breast tumorigenesis by promoting genomic
damage and instability. Oncogene. 36:5874–5884. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Karimkhanloo H, Mohammadi-Yeganeh S,
Ahsani Z and Paryan M: Bioinformatics prediction and experimental
validation of microRNA-20a targeting Cyclin D1 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176983612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Shen J, Pan J, Du C, Si W, Yao M, Xu L,
Zheng H, Xu M, Chen D, Wang S, et al: Silencing NKG2D
ligand-targeting miRNAs enhances natural killer cell-mediated
cytotoxicity in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 8:e27402017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Chen Y, Wang X, Cheng J, Wang Z, Jiang T,
Hou N, Liu N, Song T and Huang C: MicroRNA-20a-5p targets RUNX3 to
regulate proliferation and migration of human hepatocellular cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 36:3379–3386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Pu Y, Yi Q, Zhao F, Wang H, Cai W and Cai
S: MiR-20a-5p represses multi-drug resistance in osteosarcoma by
targeting the KIF26B gene. Cancer Cell Int. 16:642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhang Y, Zheng L, Ding Y, Li Q, Wang R,
Liu T, Sun Q, Yang H, Peng S, Wang W, et al: MiR-20a Induces Cell
Radioresistance by Activating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
92:1132–1140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Laussmann MA, Passante E, Hellwig CT,
Tomiczek B, Flanagan L, Prehn JH, Huber HJ and Rehm M: Proteasome
inhibition can impair caspase-8 activation upon submaximal
stimulation of apoptotic tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis
inducing ligand (TRAIL) signaling. J Biol Chem. 287:14402–14411.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ and Yuan J: Cleavage of
BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas
pathway of apoptosis. Cell. 94:491–501. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Orzechowska EJ, Girstun A, Staron K and
Trzcinska-Danielewicz J: Synergy of BID with doxorubicin in the
killing of cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 33:2143–2150. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Eskes R, Desagher S, Antonsson B and
Martinou JC: Bid induces the oligomerization and insertion of Bax
into the outer mitochondrial membrane. Mol Cell Biol. 20:929–935.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang GJ, Li Y, Zhou H, Xiao HX and Zhou
T: miR-20a is an independent prognostic factor in colorectal cancer
and is involved in cell metastasis. Mol Med Rep. 10:283–291. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Cheng D, Zhao S, Tang H, Zhang D, Sun H,
Yu F, Jiang W, Yue B, Wang J, Zhang M, et al: MicroRNA-20a-5p
promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by
downregulating Smad4. Oncotarget. 7:45199–45213. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Gonzalez DM and Medici D: Signaling
mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal.
7:re82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Longqiu Y, Pengcheng L, Xuejie F and Peng
Z: A miRNAs panel promotes the proliferation and invasion of
colorectal cancer cells by targeting GABBR1. Cancer Med.
5:2022–2031. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Jiang X, Su L, Zhang Q, He C, Zhang Z, Yi
P and Liu J: GABAB receptor complex as a potential target for tumor
therapy. J Histochem Cytochem. 60:269–279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Peters HC, Kämmer G, Volz A, Kaupmann K,
Ziegler A, Bettler B, Epplen JT, Sander T and Riess O: Mapping,
genomic structure, and polymorphisms of the human GABABR1 receptor
gene: Evaluation of its involvement in idiopathic generalized
epilepsy. Neurogenetics. 2:47–54. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yates KE, Korbel GA, Shtutman M, Roninson
IB and DiMaio D: Repression of the SUMO-specific protease Senp1
induces p53-dependent premature senescence in normal human
fibroblasts. Aging Cell. 7:609–621. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Melchior F and Hengst L: SUMO-1 and p53.
Cell Cycle. 1:245–249. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Agostini M, Pucciarelli S, Calore F, Bedin
C, Enzo M and Nitti D: miRNAs in colon and rectal cancer: A
consensus for their true clinical value. Clin Chim Acta.
411:1181–1186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Slattery ML, Herrick JS, Pellatt DF,
Stevens JR, Mullany LE, Wolff E, Hoffman MD, Samowitz WS and Wolff
RK: MicroRNA profiles in colorectal carcinomas, adenomas and normal
colonic mucosa: Variations in miRNA expression and disease
progression. Carcinogenesis. 37:245–261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Tan YG, Zhang YF, Guo CJ, Yang M and Chen
MY: Screening of differentially expressed microRNA in ulcerative
colitis related colorectal cancer. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 6:972–976.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Bovell L, Shanmugam C, Katkoori VR, Zhang
B, Vogtmann E, Grizzle WE and Manne U: miRNAs are stable in
colorectal cancer archival tissue blocks. Front Biosci (Elite Ed).
4:1937–1940. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Pellatt DF, Stevens JR, Wolff RK, Mullany
LE, Herrick JS, Samowitz W and Slattery ML: Expression profiles of
miRNA subsets distinguish human colorectal carcinoma and normal
colonic mucosa. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 7:e1522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Liu X, Xu T, Hu X, Chen X, Zeng K, Sun L
and Wang S: Elevated circulating miR-182 acts as a diagnostic
biomarker for early colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res.
10:857–865. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Emami SS, Akbari A, Zare AA, Agah S,
Masoodi M, Talebi A, Minaeian S, Fattahi A and Moghadamnia F:
MicroRNA expression levels and histopathological features of
colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Cancer. 50:276–284. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Brunet Vega A, Pericay C, Moya I, Ferrer
A, Dotor E, Pisa A, Casalots À, Serra-Aracil X, Oliva JC, Ruiz A,
et al: microRNA expression profile in stage III colorectal cancer:
Circulating miR-18a and miR-29a as promising biomarkers. Oncol Rep.
30:320–326. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zhang JX, Song W, Chen ZH, Wei JH, Liao
YJ, Lei J, Hu M, Chen GZ, Liao B, Lu J, et al: Prognostic and
predictive value of a microRNA signature in stage II colon cancer:
A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 14:1295–1306. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zekri AR, Youssef AS, Lotfy MM, Gabr R,
Ahmed OS, Nassar A, Hussein N, Omran D, Medhat E, Eid S, et al:
Circulating serum miRNAs as diagnostic markers for colorectal
cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01541302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Eslamizadeh S, Heidari M, Agah S,
Faghihloo E, Ghazi H, Mirzaei A and Akbari A: The role of microRNA
signature as diagnostic biomarkers in different clinical stages of
colorectal cancer. Cell J. 20:220–230. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Yang Q, Wang S, Huang J, Xia C, Jin H and
Fan Y: Serum miR-20a and miR-486 are potential biomarkers for
discriminating colorectal neoplasia: A pilot study. J Cancer Res
Ther. 14:1572–1577. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Yamazaki N, Koga Y, Yamamoto S, Kakugawa
Y, Otake Y, Hayashi R, Saito N and Matsumura Y: Application of the
fecal microRNA test to the residuum from the fecal occult blood
test. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 43:726–733. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Rotelli MT, Di Lena M, Cavallini A,
Lippolis C, Bonfrate L, Chetta N, Portincasa P and Altomare DF:
Fecal microRNA profile in patients with colorectal carcinoma before
and after curative surgery. Int J Colorectal Dis. 30:891–898. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, Wehbe H,
Maheshwari S, Mendell JT, Jiang J, Schmittgen TD and Patel T:
Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to
chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines.
Gastroenterology. 130:2113–2129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, Pan Y, Zhao L, Sun
S, Hong L, Liu J and Fan D: miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug
resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 123:372–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Kovalchuk O, Filkowski J, Meservy J,
Ilnytskyy Y, Tryndyak VP, Chekhun VF and Pogribny IP: Involvement
of microRNA-451 in resistance of the MCF-7 breast cancer cells to
chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2152–2159.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Ma J, Dong C and Ji C: MicroRNA and drug
resistance. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:523–531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Li X, Wang H, Wang J, Chen Y, Yin X, Shi
G, Li H, Hu Z and Liang X: Emodin enhances cisplatin-induced
cytotoxicity in human bladder cancer cells through ROS elevation
and MRP1 downregulation. BMC Cancer. 16:5782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Zhang L, He L, Zhang H and Chen Y:
Knockdown of miR-20a enhances sensitivity of colorectal cancer
cells to cisplatin by increasing ASK1 expression. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 47:1432–1441. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Molinari C, Salvi S, Foca F, Teodorani N,
Saragoni L, Puccetti M, Passardi A, Tamberi S, Avanzolini A, Lucci
E, et al: miR-17-92a-1 cluster host gene (MIR17HG) evaluation and
response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. Onco
Targets Ther. 9:2735–2742. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Azizian A, Kramer F, Jo P, Wolff HA,
Beißbarth T, Skarupke R, Bernhardt M, Grade M, Ghadimi BM and
Gaedcke J: Preoperative prediction of lymph node status by
circulating mir-18b and mir-20a during chemoradiotherapy in
patients with rectal cancer. World J Surg. 39:2329–2335. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Jo P, Azizian A, Salendo J, Kramer F,
Bernhardt M, Wolff HA, Gruber J, Grade M, Beißbarth T, Ghadimi BM,
et al: Changes of microrna levels in plasma of patients with rectal
cancer during chemoradiotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 18:182017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y and Goel A: An update
on microRNAs as colorectal cancer biomarkers: Where are we and
what's next? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 14:999–1021. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhang J, Zhang K, Bi M, Jiao X, Zhang D
and Dong Q: Circulating microRNA expressions in colorectal cancer
as predictors of response to chemotherapy. Anticancer Drugs.
25:346–352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Xie T, Li Y, Li SL and Luo HF:
Astragaloside IV enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity in human
colorectal cancer via regulating NOTCH3. Oncol Res. 24:447–453.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Ma MZ, Chen G, Wang P, Lu WH, Zhu CF, Song
M, Yang J, Wen S, Xu RH, Hu Y, et al: Xc- inhibitor sulfasalazine
sensitizes colorectal cancer to cisplatin by a GSH-dependent
mechanism. Cancer Lett. 368:88–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Aouacheria A, Brunet F and Gouy M:
Phylogenomics of life-or-death switches in multicellular animals:
Bcl-2, BH3-Only, and BNip families of apoptotic regulators. Mol
Biol Evol. 22:2395–2416. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Chai H, Liu M, Tian R, Li X and Tang H:
miR-20a targets BNIP2 and contributes chemotherapeutic resistance
in colorectal adenocarcinoma SW480 and SW620 cell lines. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 43:217–225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Ezzati H, Ahmadi Z,
Farkhondeh T and Samarghandian S: Anti-tumor activity of propofol:
A focus on microRNAs. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 19:2019, https://doi.org/10.2174/1568009619666191023100046
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Ji R, Zhang X, Gu H, Ma J, Wen X, Zhou J,
Qian H, Xu W, Qian J and Lin J: miR-374a-5p: A New Target for
Diagnosis and Drug Resistance Therapy in Gastric Cancer. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 18:320–331. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Luo X, Burwinkel B, Tao S and Brenner H:
MicroRNA signatures: Novel biomarker for colorectal cancer? Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 20:1272–1286. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Caritg O, Navarro A, Moreno I,
Martínez-Rodenas F, Cordeiro A, Muñoz C, Ruiz-Martinez M,
Santasusagna S, Castellano JJ and Monzó M: Identifying high-risk
stage II colon cancer patients: A three-microRNA-based score as a
prognostic biomarker. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 15:e175–e182. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, Zanetti
KA, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, Yuen ST, Chan TL, Kwong DL, Au GK, et
al: MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and
therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 299:425–436.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Pesta M, Kucera R, Topolcan O, Karlikova
M, Houfkova K, Polivka J, Macanova T, Machova I, Slouka D and Kulda
V: Plasma microRNA levels combined with CEA and CA19-9 in the
follow-up of colorectal cancer patients. Cancers (Basel).
11:112019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
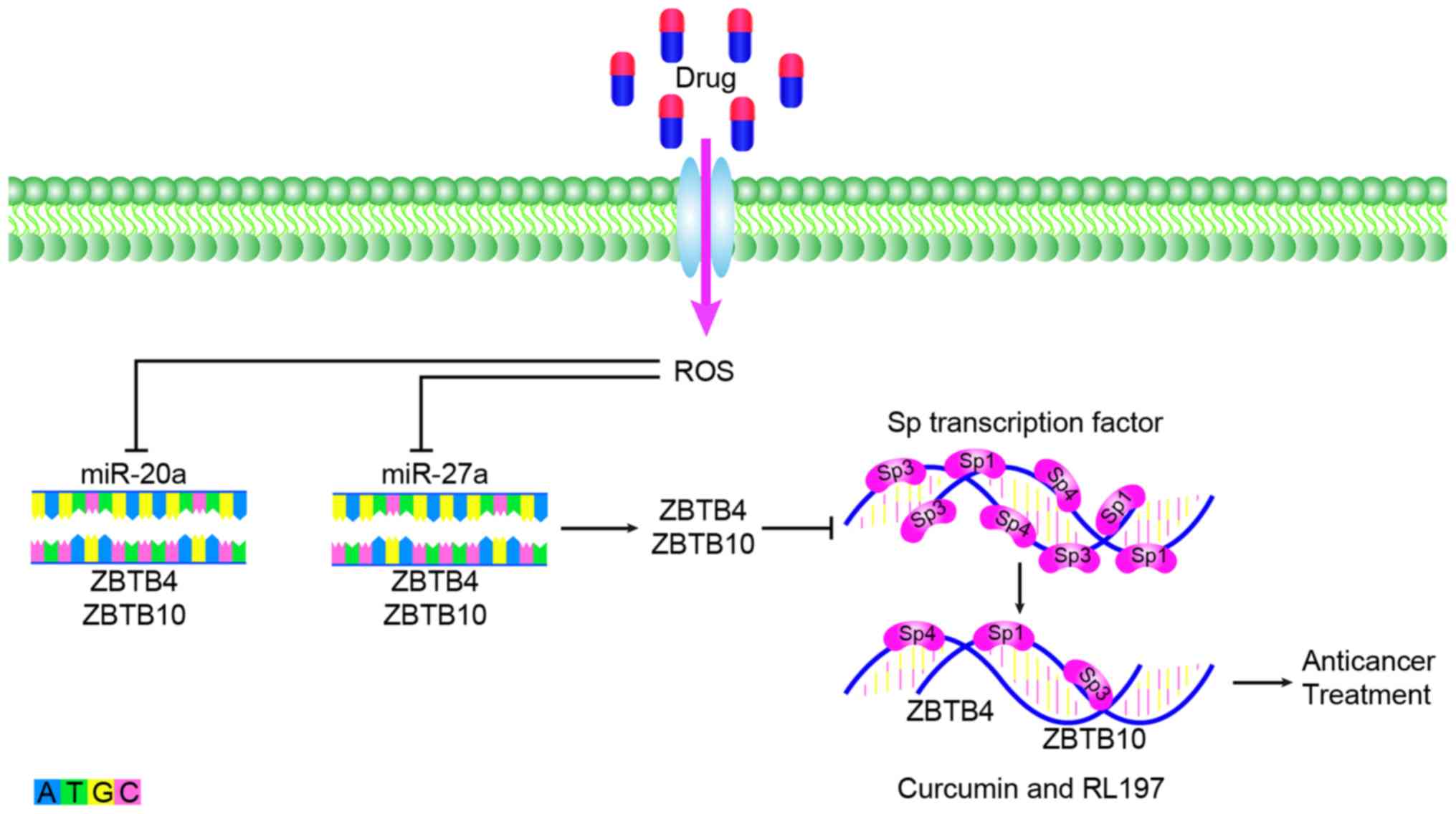
Gandhy SU, Kim K, Larsen L, Rosengren RJ
and Safe S: Curcumin and synthetic analogs induce reactive oxygen
species and decreases specificity protein (Sp) transcription
factors by targeting microRNAs. BMC Cancer. 12:5642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Choi JB, Kim JH, Lee H, Pak JN, Shim BS
and Kim SH: Reactive Oxygen Species and p53 Mediated Activation of
p38 and Caspases is Critically Involved in Kaempferol Induced
Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells. J Agric Food Chem.
66:9960–9967. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Pehserl AM, Ress AL, Stanzer S, Resel M,
Karbiener M, Stadelmeyer E, Stiegelbauer V, Gerger A, Mayr C,
Scheideler M, et al: Comprehensive Analysis of miRNome Alterations
in Response to Sorafenib Treatment in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int
J Mol Sci. 17:172016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Li R, Jiang J, Shi H, Qian H, Zhang X and
Xu W: CircRNA: A rising star in gastric cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci.
2019:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03345-5
|
|
132
|
Su Q and Lv X: Revealing new landscape of
cardiovascular disease through circular RNA-miRNA-mRNA axis.
Genomics. S0888-7543(19)30565-8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Xiu Y, Jiang G, Zhou S, Diao J, Liu H, Su
B and Li C: Identification of potential immune-related
circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in intestine of paralichthys
olivaceus during Edwardsiella tarda infection. Front Genet.
10:7312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Ping L, Jian-Jun C, Chu-Shu L, Guang-Hua L
and Ming Z: Silencing of circ_0009910 inhibits acute myeloid
leukemia cell growth through increasing miR-20a-5p. Blood Cells Mol
Dis. 75:41–47. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Zhang X, Wu N, Wang J and Li Z: LncRNA
MEG3 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in laryngeal
cancer via miR-23a/APAF-1 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 23:6708–6719. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Huang QR and Pan XB: Prognostic lncRNAs,
miRNAs, and mRNAs form a competing endogenous RNA network in colon
cancer. Front Oncol. 9:7122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|