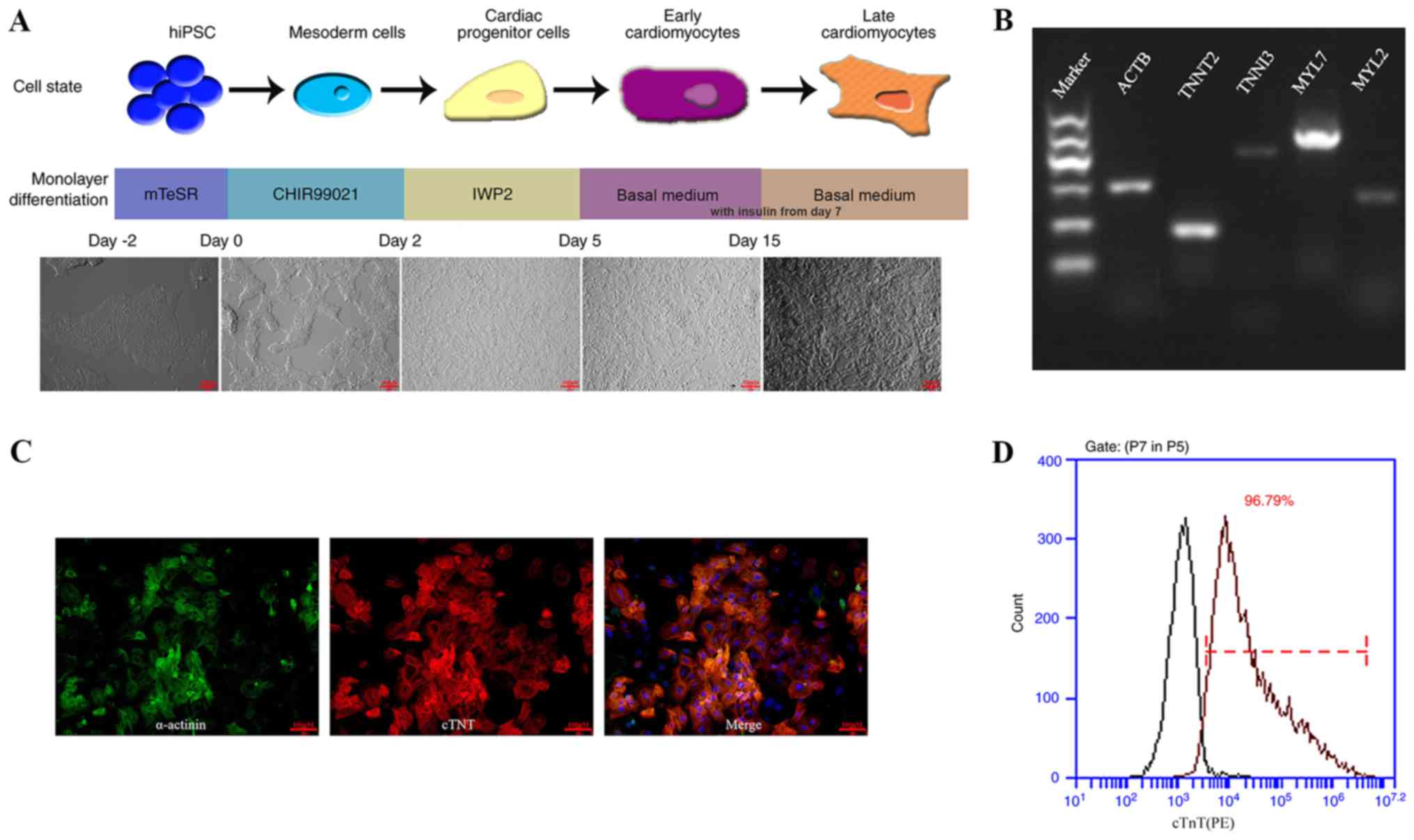
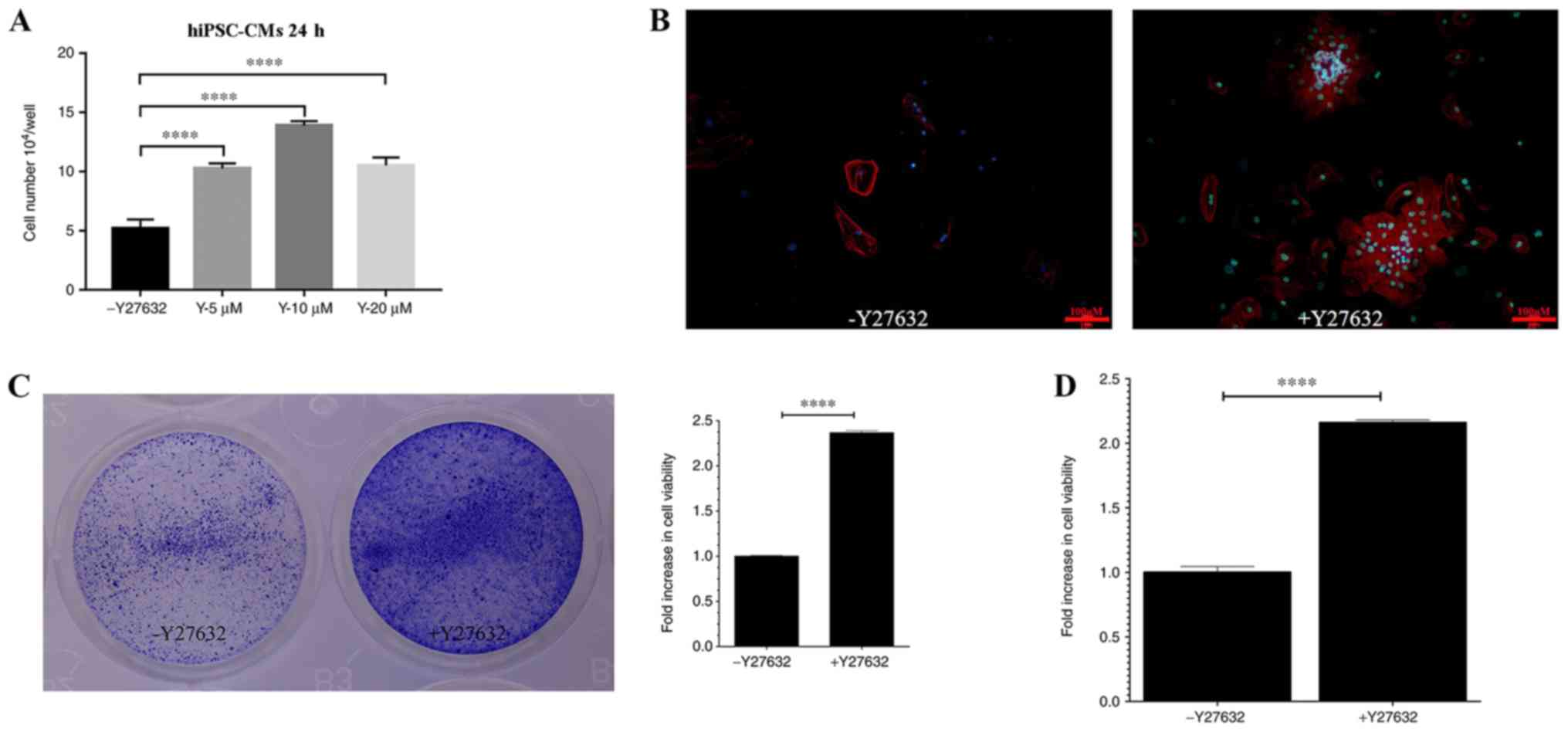
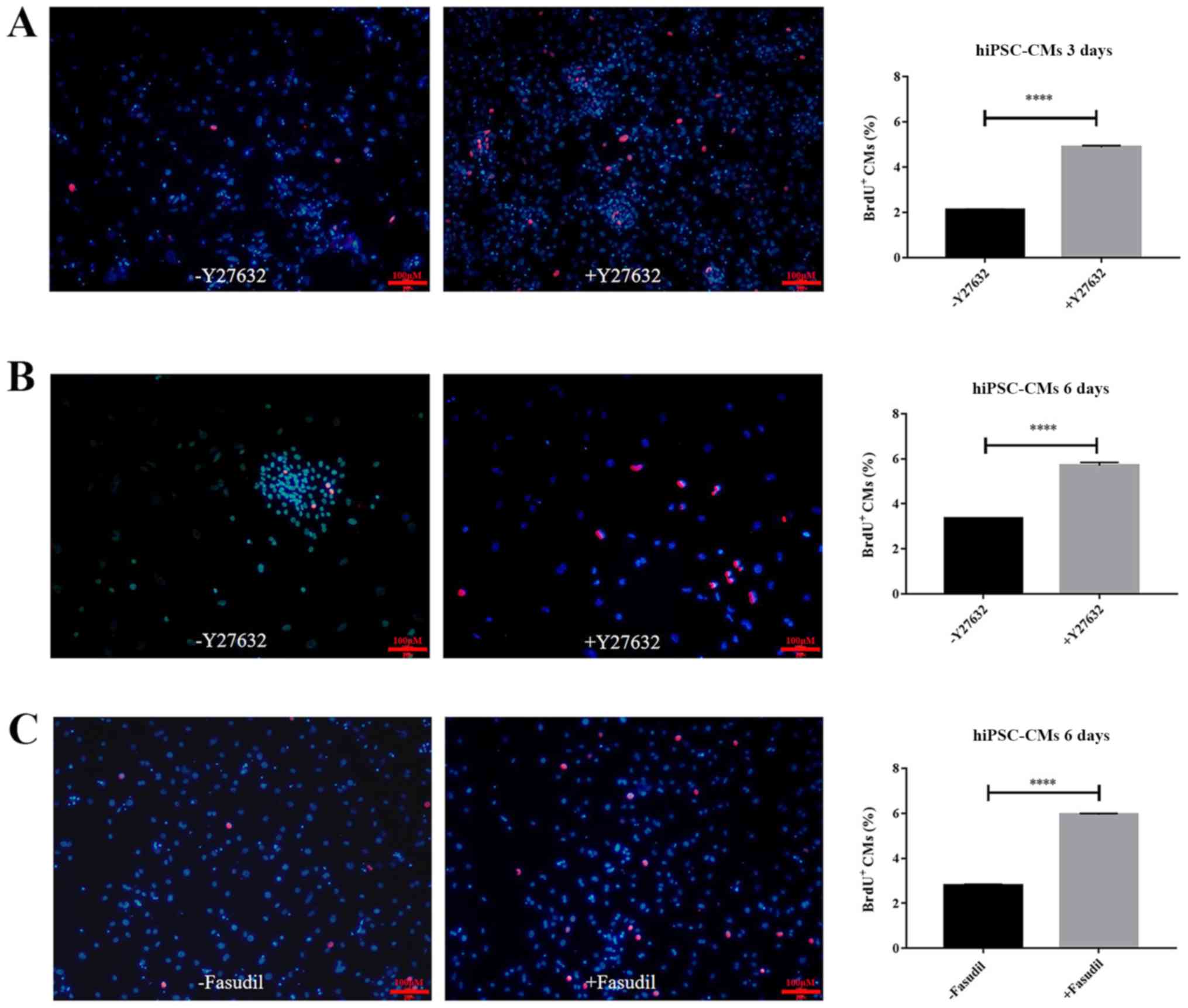
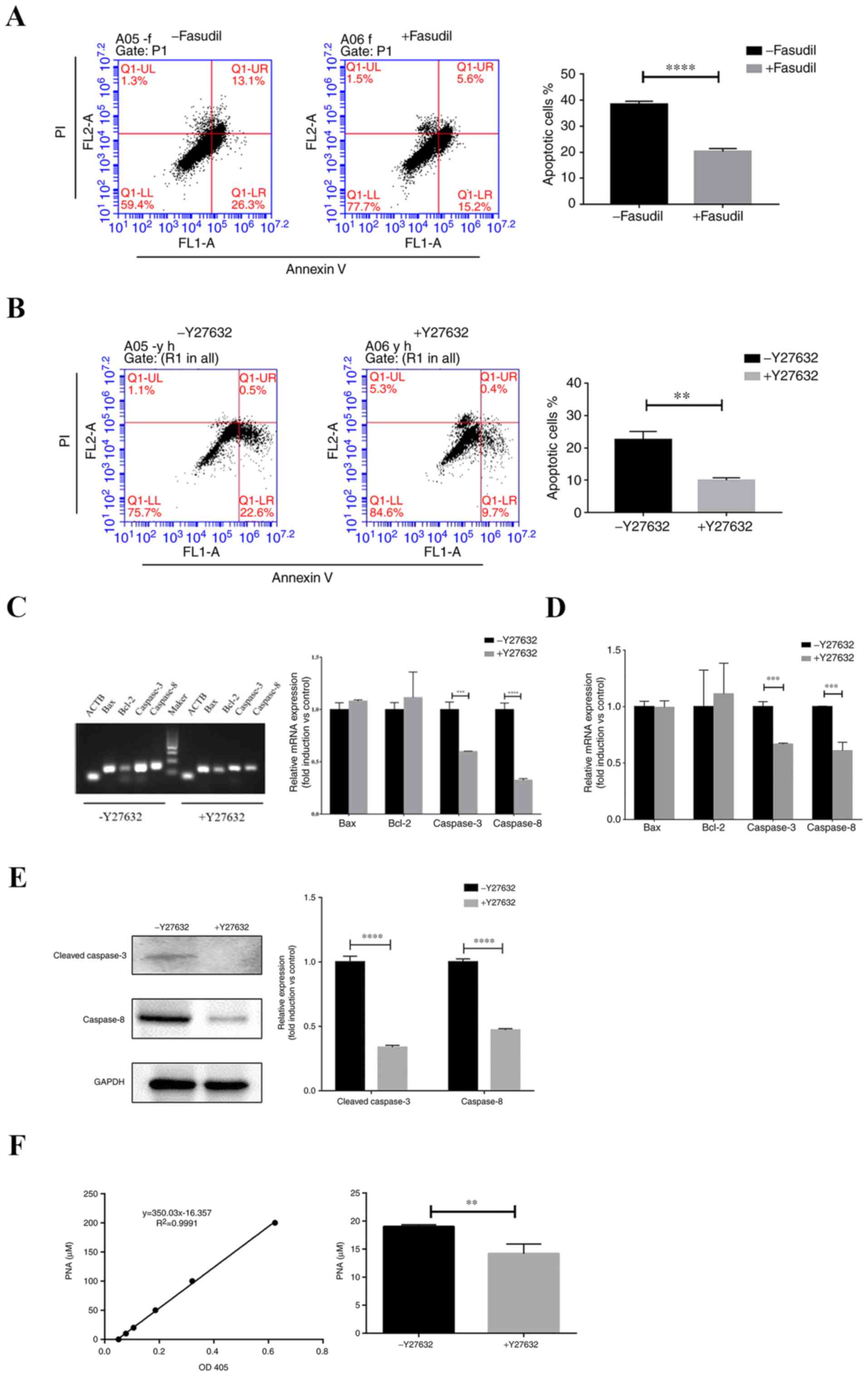
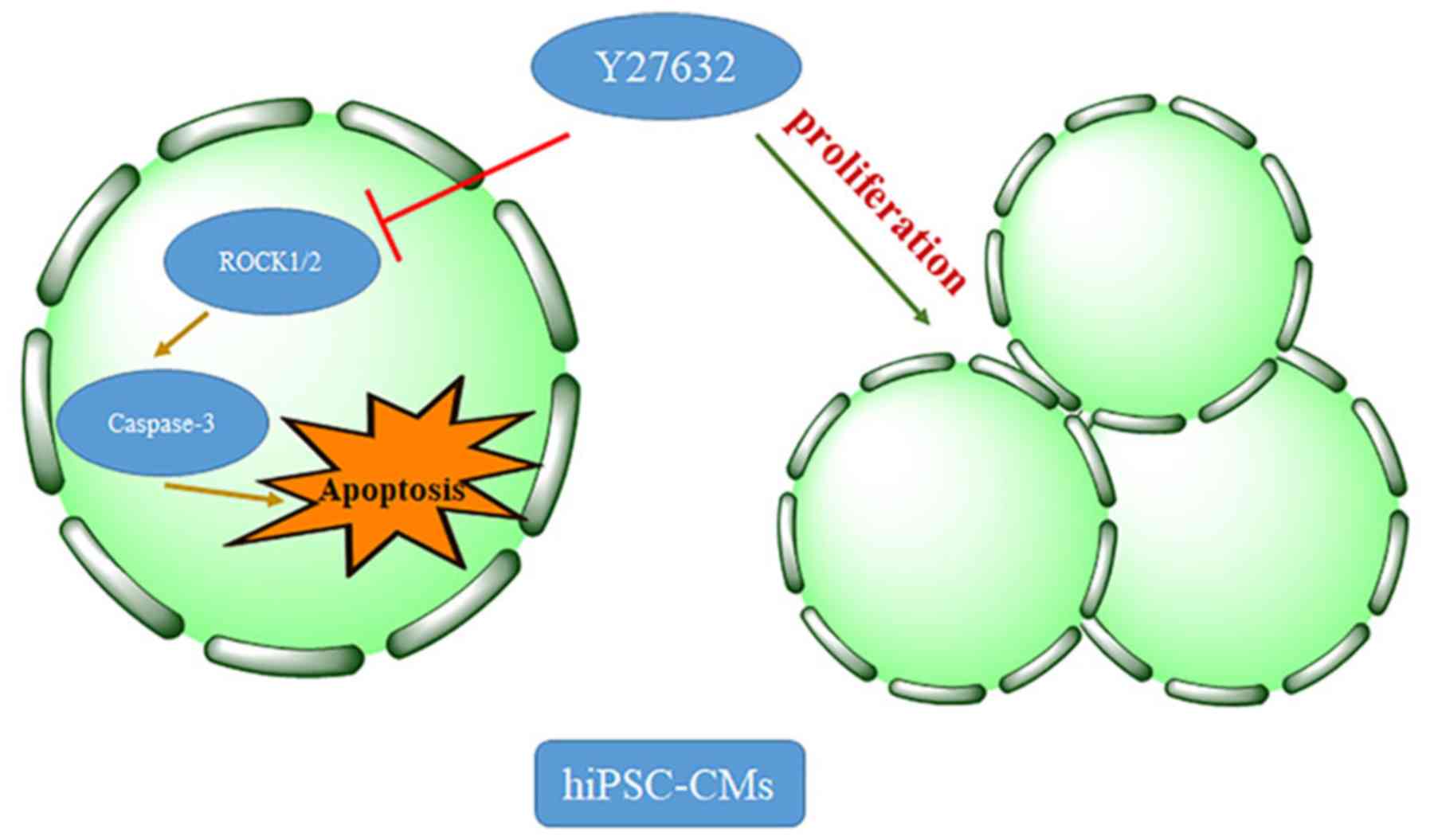
|
1
|
Ebert AD, Diecke S, Chen IY and Wu JC:
Reprogramming and transdifferentiation for cardiovascular
development and regenerative medicine: Where do we stand? EMBO Mol
Med. 7:1090–1103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hartman ME, Dai DF and Laflamme MA: Human
pluripotent stem cells: Prospects and challenges as a source of
cardiomyocytes for in vitro modeling and cell-based cardiac repair.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 96:3–17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kehat I, Kenyagin-Karsenti D, Snir M,
Segev H, Amit M, Gepstein A, Livne E, Binah O, Itskovitz-Eldor J
and Gepstein L: Human embryonic stem cells can differentiate into
myocytes with structural and functional properties of
cardiomyocytes. J Clin Invest. 108:407–414. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burridge PW, Matsa E, Shukla P, Lin ZC,
Churko JM, Ebert AD, Lan F, Diecke S, Huber B, Mordwinkin NM, et
al: Chemically defined generation of human cardiomyocytes. Nat
Methods. 11:855–860. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lian X, Zhang J, Azarin SM, Zhu K,
Hazeltine LB, Bao X, Hsiao C, Kamp TJ and Palecek SP: Directed
cardiomyocyte differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells by
modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling under fully defined conditions.
Nat Protoc. 8:162–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shimizu T and Liao JK: Rho kinases and
cardiac remodeling. Circ J. 80:1491–1498. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Narumiya S and Thumkeo D: Rho signaling
research: History, current status and future directions. FEBS Lett.
592:1763–1776. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shimizu T, Narang N, Chen P, Yu B, Knapp
M, Janardanan J, Blair J and Liao JK: Fibroblast deletion of ROCK2
attenuates cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and diastolic
dysfunction. JCI Insight. 2(pii): 931872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Surma M, Wei L and Shi J: Rho kinase as a
therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Future Cardiol.
7:657–671. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shibuya M and Suzuki Y: Treatment of
cerebral vasospasm by a protein kinase inhibitor AT 877. No To
Shinkei. 45:819–824. 1993.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chang J, Xie M, Shah VR, Schneider MD,
Entman ML, Wei L and Schwartz RJ: Activation of Rho-associated
coiled-coil protein kinase 1 (ROCK-1) by caspase-3 cleavage plays
an essential role in cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:14495–14500. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hartmann S, Ridley AJ and Lutz S: The
function of Rho-associated kinases ROCK1 and ROCK2 in the
pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Front Pharmacol. 6:2762015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong M, Ding W, Liao Y, Liu Y, Yan D,
Zhang Y, Wang R, Zheng N, Liu S and Liu J: Polydatin prevents
hypertrophy in phenylephrine induced neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes
and pressure-overload mouse models. Eur J Pharmacol. 746:186–197.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sawada N and Liao JK: Rho/Rho-associated
coiled-coil forming kinase pathway as therapeutic targets for
statins in atherosclerosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:1251–1267.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tohyama S, Hattori F, Sano M, Hishiki T,
Nagahata Y, Matsuura T, Hashimoto H, Suzuki T, Yamashita H and
Satoh Y: Distinct metabolic flow enables large-scale purification
of mouse and human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.
Cell Stem Cell. 12:127–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang L, Li Q, Li H, He Z, Cheng Z, Chen J
and Guo L: Inhibition of intracellular Ca2+ release by a
Rho-kinase inhibitor for the treatment of ischemic damage in
primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Eur J Pharmacol.
602:238–244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K,
Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, Nie J, Jonsdottir GA,
Ruotti V, Stewart R, et al: Induced pluripotent stem cell lines
derived from human somatic cells. Science. 318:1917–1920. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsa E, Ahrens JH and Wu JC: Human
induced pluripotent stem cells as a platform for personalized and
precision cardiovascular medicine. Physiol Rev. 96:1093–1126. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qiu XX, Liu Y, Zhang YF, Guan YN, Jia QQ,
Wang C, Liang H, Li YQ, Yang HT and Qin YW: Rapamycin and CHIR99021
coordinate robust cardiomyocyte differentiation from human
pluripotent stem cells via reducing p53-dependent apoptosis. J Am
Heart Assoc. 6(pii): e0052952017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim WH, Jung DW and Williams DR: Making
cardiomyocytes with your chemistry set: Small molecule-induced
cardiogenesis in somatic cells. World J Cardiol. 7:125–133. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu R, Blazeski A, Poon E, Costa KD, Tung
L and Boheler KR: Physical developmental cues for the maturation of
human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 5:1172014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Uosaki H, Magadum A, Seo K, Fukushima H,
Takeuchi A, Nakagawa Y, Moyes KW, Narazaki G, Kuwahara K, Laflamme
M, et al: Identification of chemicals inducing cardiomyocyte
proliferation in developmental stage-specific manner with
pluripotent stem cells. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 6:624–633. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mohamed TMA, Ang YS, Radzinsky E, Zhou P,
Huang Y, Elfenbein A, Foley A, Magnitsky S and Srivastava D:
Regulation of cell cycle to stimulate adult cardiomyocyte
proliferation and cardiac regeneration. Cell. 173:104–116. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bao W, Hu E, Tao L, Boyce R, Mirabile R,
Thudium DT, Ma XL, Willette RN and Yue TL: Inhibition of Rho-kinase
protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc
Res. 61:548–558. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong M, Yan BP, Liao JK, Lam YY, Yip GW
and Yu CM: Rho-kinase inhibition: A novel therapeutic target for
the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Drug Discov Today.
15:622–629. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Feng Y, LoGrasso PV, Defert O and Li R:
Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitors and their therapeutic potential. J Med
Chem. 59:2269–2300. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Y, Zhu W, Tao J, Xin P, Liu M, Li J and
Wei M: Fasudil protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion
injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress and modulating
SERCA activity: The differential role for PI3K/Akt and JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathways. PLoS One. 7:e481152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bian H, Zhou Y, Yu B, Shang D, Liu F, Li B
and Qi J: Rho-kinase signaling pathway promotes the expression of
PARP to accelerate cardiomyocyte apoptosis in ischemia/reperfusion.
Mol Med Rep. 16:2002–2008. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dong LY, Qiu XX, Zhuang Y and Xue S:
Y-27632, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, attenuates myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Int J Mol Med. 43:1911–1919.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao M, Fan C, Ernst PJ, Tang Y, Zhu H,
Mattapally S, Oduk Y, Borovjagin AV, Zhou L, Zhang J and Zhu W:
Y-27632 preconditioning enhances transplantation of human-induced
pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in myocardial
infarction mice. Cardiovasc Res. 115:343–356. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Martinez-Rico C, Pincet F, Thiery JP and
Dufour S: Integrins stimulate E-cadherin-mediated intercellular
adhesion by regulating Src-kinase activation and actomyosin
contractility. J Cell Sci. 123:712–722. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Thuveson M, Gaengel K, Collu GM, Chin ML,
Singh J and Mlodzik M: Integrins are required for synchronous
ommatidial rotation in the Drosophila eye linking planar cell
polarity signalling to the extracellular matrix. Open Biol.
9:1901482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Martewicz S, Serena E, Zatti S, Keller G
and Elvassore N: Substrate and mechanotransduction influence
SERCA2a localization in human pluripotent stem cell-derived
cardiomyocytes affecting functional performance. Stem Cell Res.
25:107–114. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yan Y, Bejoy J, Xia J, Griffin K, Guan J
and Li Y: Cell population balance of cardiovascular spheroids
derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci Rep.
9:12952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Manzur MJ, Aguilera MO, Kotler ML, Berón W
and Ciuffo GM: Focal adhesion kinase, RhoA, and p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase modulates apoptosis mediated by
angiotensin II AT2 receptors. J Cell Biochem.
120:1835–1849. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Vitillo L, Baxter M, Iskender B, Whiting P
and Kimber SJ: Integrin-associated focal adhesion kinase protects
human embryonic stem cells from apoptosis, detachment, and
differentiation. Stem Cell Reports. 7:167–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|