|
1
|
Hoegberg LC, Bania TC, Lavergne V, Bailey
B, Turgeon AF, Thomas SH, Morris M, Miller-Nesbitt A, Mégarbane B,
Magder S, et al: Systematic review of the effect of intravenous
lipid emulsion therapy for local anesthetic toxicity. Clin Toxicol
(Phila). 54:167–193. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mather LE: The acute toxicity of local
anesthetics. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 6:1313–1332. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Butterworth JF IV: Models and mechanisms
of local anesthetic cardiac toxicity: A review. Reg Anesth Pain
Med. 35:167–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weinberg G: Lipid rescue resuscitation
from local anaesthetic cardiac toxicity. Toxicol Rev. 25:139–145.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gray LD and Morris C: The principles and
conduct of anaesthesia for emergency surgery. Anaesthesia. 68
(Suppl):S14–S29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Abubaih A and Weissman C: Anesthesia for
patients with concomitant sepsis and cardiac dysfunction.
Anesthesiol Clin. 34:761–774. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gottschalk A and Poepping DM: Epidural
analgesia in combination with general anesthesia. Anasthesiol
Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 50:484–493. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hadimioglu N, Ulugol H, Akbas H,
Coskunfirat N, Ertug Z and Dinckan A: Combination of epidural
anesthesia and general anesthesia attenuates stress response to
renal transplantation surgery. Transplant Proc. 44:2949–2954. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Copeland SE, Ladd LA, Gu XQ and Mather LE:
The effects of general anesthesia on the central nervous and
cardiovascular system toxicity of local anesthetics. Anesth Analg.
106:1429–1439. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stewart J, Kellett N and Castro D: The
central nervous system and cardiovascular effects of
levobupivacaine and ropivacaine in healthy volunteers. Anesth
Analg. 97:412–416. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Heavner JE, Dryden CF Jr, Sanghani V,
Huemer G, Bessire A and Badgwell JM: Severe hypoxia enhances
central nervous system and cardiovascular toxicity of bupivacaine
in lightly anesthetized pigs. Anesthesiology. 77:142–147. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rosen MA, Thigpen JW, Shnider SM, Foutz
SE, Levinson G and Koike M: Bupivacaine-induced cardiotoxicity in
hypoxic and acidotic sheep. Anesth Analg. 64:1089–1096. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Chen Z, Feng N, Tang, Zhao X, Liu
C, Xu H and Zhang M: Protective effect of propofol preconditioning
on ischemia-reperfusion injury in human hepatocyte. J Thorac.
9:702–710. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Zhong D, Lei L, Jia Y, Zhou H and
Yang B: Propofol prevents renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via
inhibiting the oxidative stress pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.
37:14–26. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsai YC, Huang CC, Chu LM and Liu YC:
Differential influence of propofol on different cell types in terms
of the expression of various oxidative stress-related enzymes in an
experimental endotoxemia model. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan.
50:159–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang B, Luo T, Chen D and Ansley DM:
Propofol reduces apoptosis and up-regulates endothelial nitric
oxide synthase protein expression in hydrogen peroxide-stimulated
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Anesth Analg.
105:1027–1033. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Xia Y, Xu Z and Deng X: Propofol
suppressed hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in hbvsmc by
regulation of the expression of bcl-2, bax, caspase3, kir6.1, and
p-JNK. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:15187382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu Y, Gu Y, Ding X, Wang J, Chen J and
Miao C: Intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and JAK1/STAT3 pathway are
involved in the protective effect ofpropofol on BV2 microglia
against hypoxia-induced inflammation and apoptosis. PLoS One.
12:e01780982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ou W, Lv J, Zou X, Yao Y, Wu J, Yang J,
Wang Z and Ma Y: Propofol inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth
and invasion through the HMGA2-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Exp
Ther Med. 13:2501–2506. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang S, Liang S, Zhao X, He Y and Qi Y:
Propofol inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in rheumatoid
arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via the nuclear factor-κB
pathway. Am J Transl Res. 9:2429–2436. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
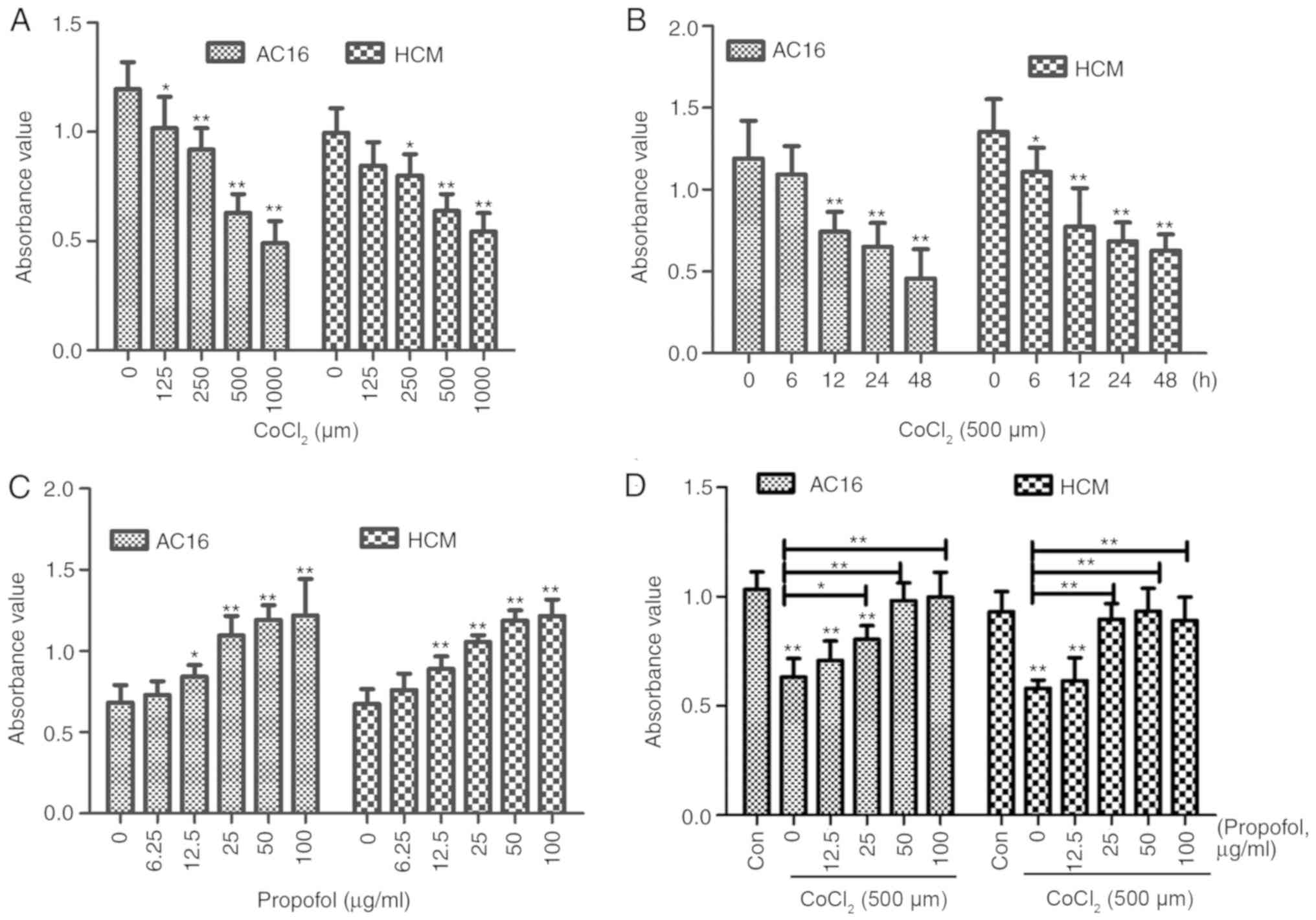
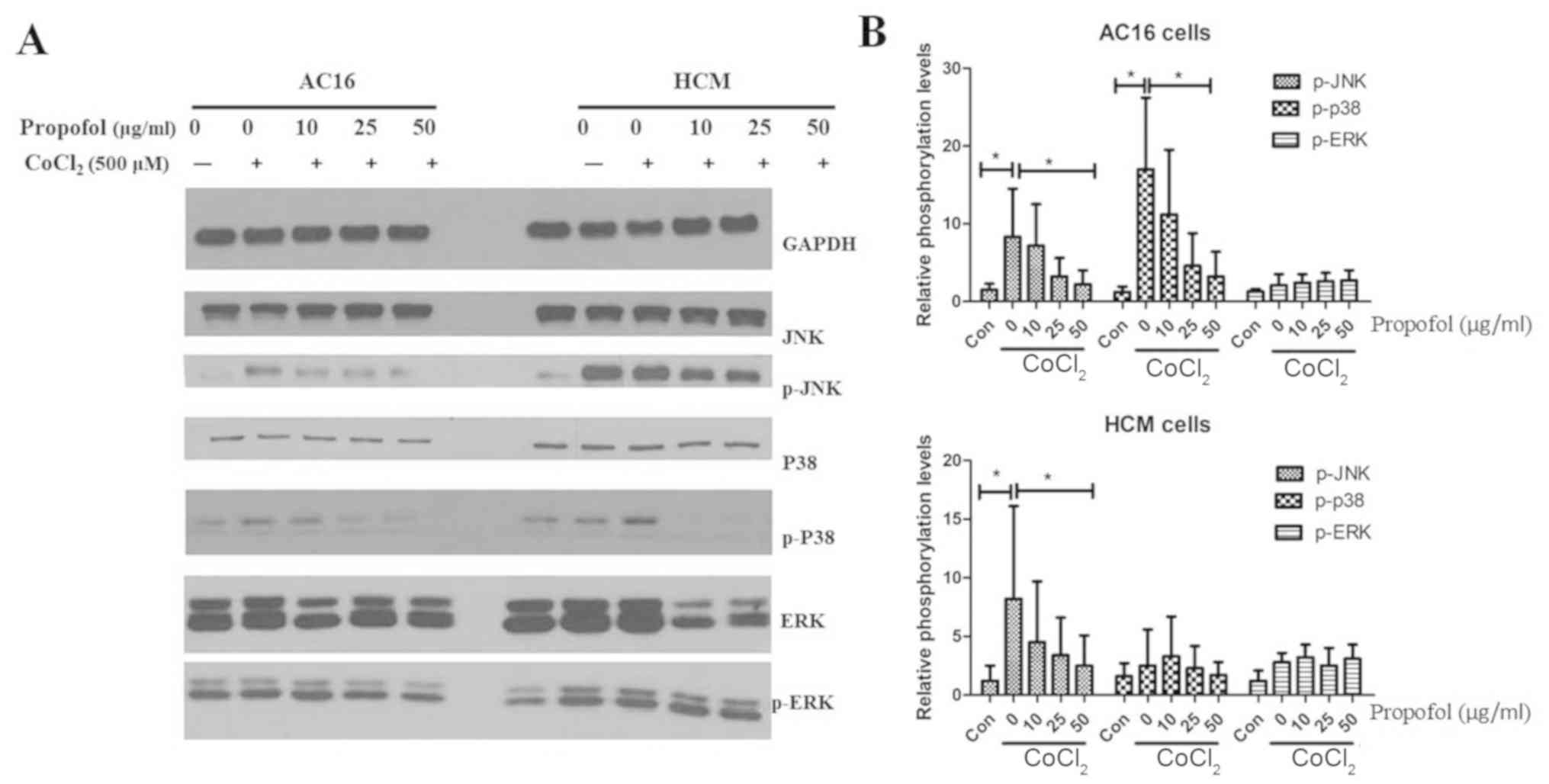
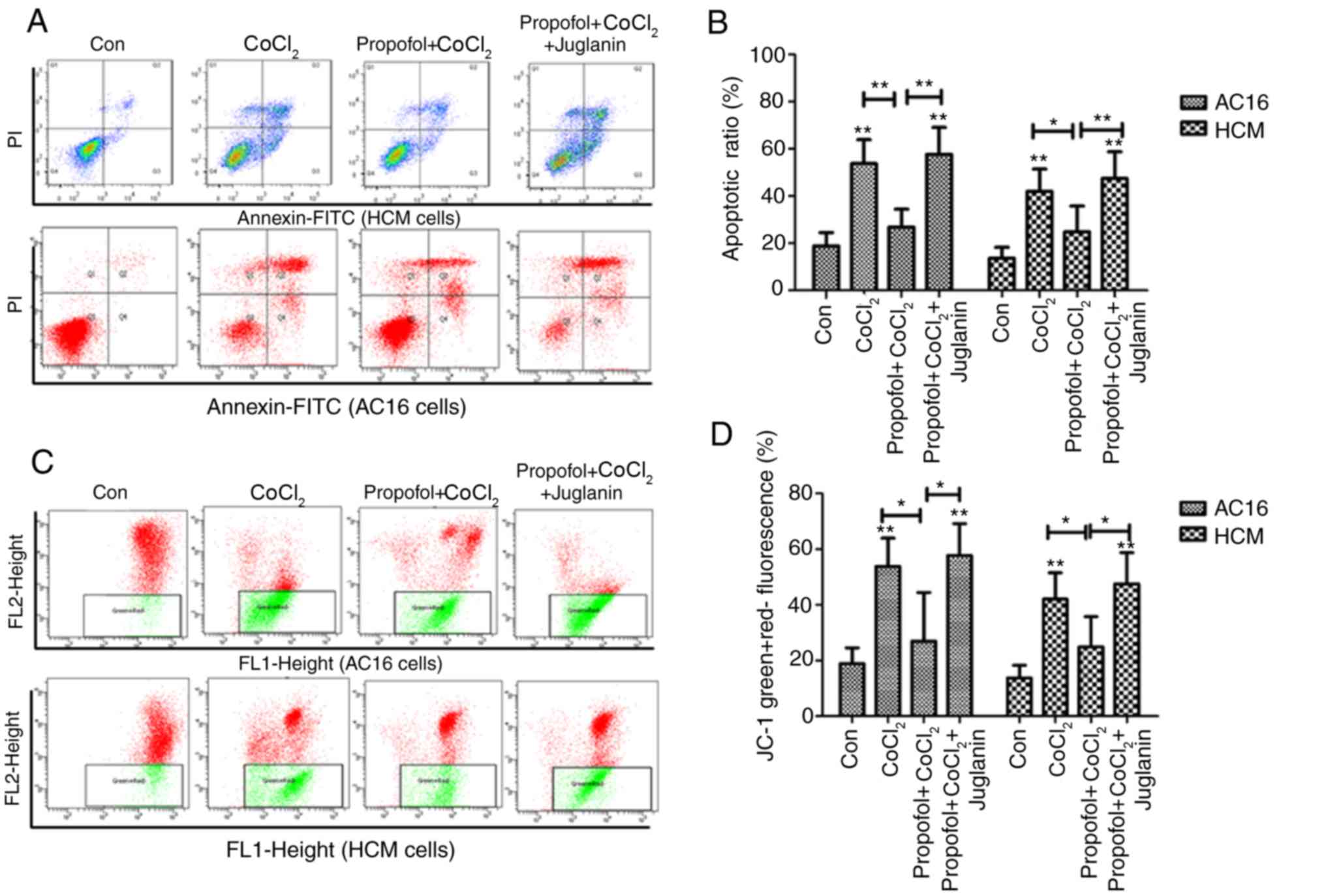
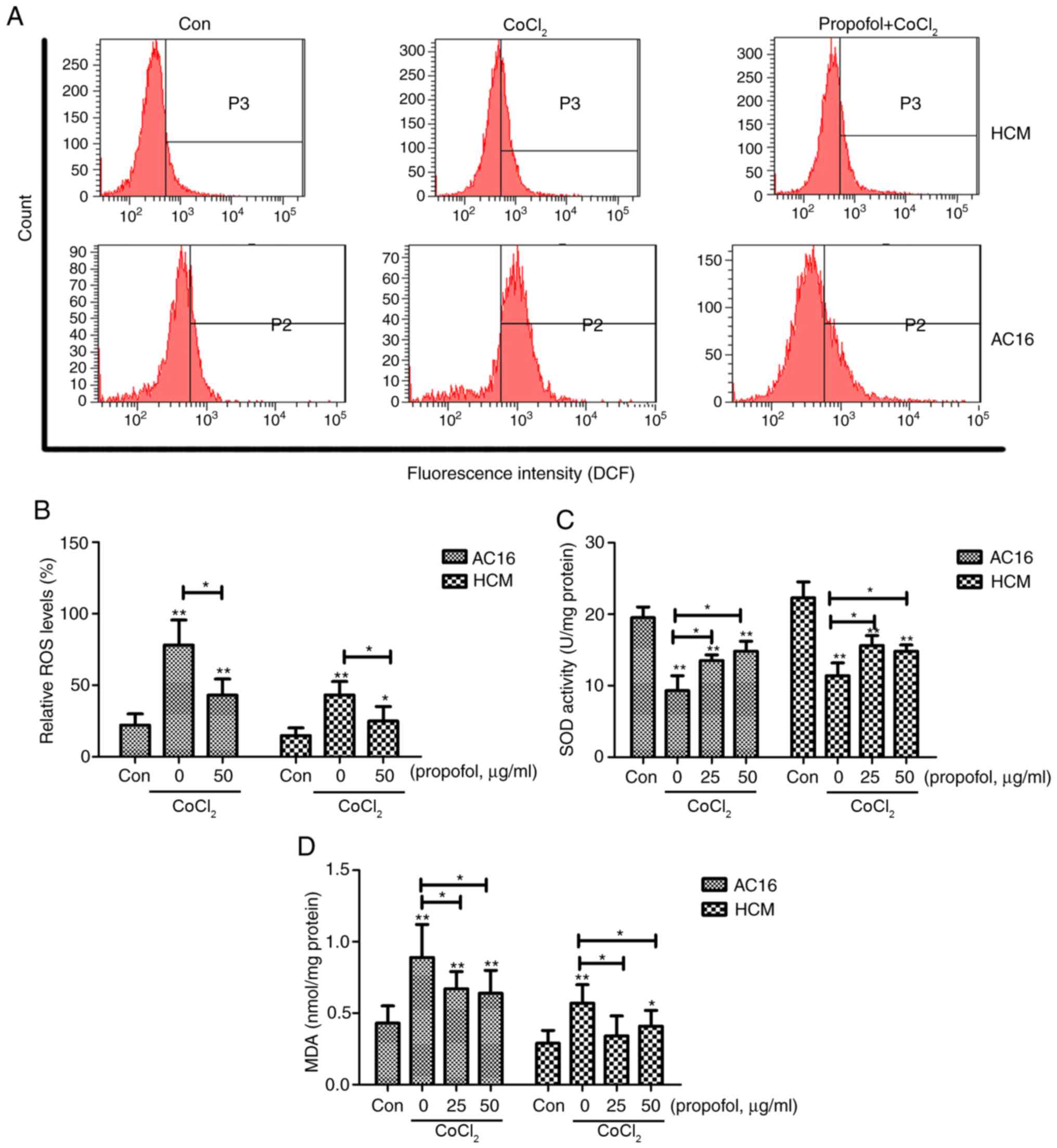
Li Q, Qi X and Jia W:
3,3′,5-triiodothyroxine inhibits apoptosis and oxidative stress by
the PKM2/PKM1 ratio during oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion
AC16 and HCM-a cells: T3 inhibits apoptosis and oxidative stress by
PKM2/PKM1 ratio. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 475:51–56. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mao SY, Meng XY, Xu ZW, Zhang WC, Jin XH,
Chen X, Zhou X, Li YM and Xu RC: The role of ZFP580, a novel zinc
finger protein, in TGF-mediated cytoprotection against chemical
hypoxia induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiac myocytes. Mol Med Rep.
15:2154–2162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Solaini G, Baracca A, Lenaz G and Sgarbi
G: Hypoxia and mitochondrial oxidative metabolism. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1797:1171–1177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pascual-Ahuir A, Manzanares-Estreder S and
Proft M: Pro- and antioxidant functions of the
peroxisome-mitochondria connection and its impact on aging and
disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:98608412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng AY, Kaye AD, Kaye RJ, Belani K and
Urman RD: Novel propofol derivatives and implications for
anesthesia practice. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 33:9–15. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Keyl C, Schneider A, Dambacher M,
Wegenhorst U, Ingenlath M, Gruber M and Bernardi L: Dynamic
cardiocirculatory control during propofol anesthesia in
mechanically ventilatedpatients. Anesth Analg. 91:1188–1195. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiang Y and Li YH: Comparison of 1.5%
lidocaine and 0.5% ropivacaine epidural anesthesia combined with
propofolgeneral anesthesia guided by bispectral index. J Zhejiang
Univ Sci B. 8:428–434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Osaka Y, Inomata S, Tanaka E, Nakamura T,
Honda K, Miyabe M, Toyooka H and Tanaka M: Effect of propofol on
ropivacaine metabolism in human liver microsomes. J Anesth.
20:60–63. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ginouves M, Carme B, Couppie P and Prevot
G: Comparison of tetrazolium salt assays for evaluation of drug
activity against Leishmania spp. J Clin Microbiol.
52:2131–2138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeon YJ, Kim HS, Song KS, Han HJ, Park SH,
Chang W and Lee MY: Protective effect of dieckol against chemical
hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity in primary cultured mouse hepatocytes.
Drug Chem Toxicol. 38:180–187. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Romuk E, Szczurek W, Nowak P, Skowron M,
Prudel B, Hudziec E, Chwalińska E1 and Birkner E: Effects of
propofol on oxidative stress parameters in selected parts of the
brain in a rat model of parkinson disease. Postepy Hig Med Dosw
(Online). 70:1441–1450. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen XH, Zhou X, Yang XY, Zhou ZB, Lu DH,
Tang Y, Ling ZM, Zhou LH and Feng X: Propofol protects against
H2O2-induced oxidative injury in differentiated pc12 cells via
inhibition of Ca(2+)-Dependent NADPH oxidase. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
36:541–551. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Z, Yang P and Qi Y: Role of
microRNA-134 in the neuroprotective effects of propofol against
oxygen-glucosedeprivation and related mechanisms. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:20617–206123. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gokcinar D, Ergin V, Cumaoglu A, Menevse A
and Aricioglu A: Effects of ketamine, propofol, and ketofol on
proinflammatory cytokines and markers of oxidative stress in a rat
model of endotoxemia-induced acute lung injury. Acta Biochim Pol.
60:451–456. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Eriksson O, Pollesello P and Saris NE:
Inhibition of lipid peroxidation in isolated rat liver mitochondria
by the general anaesthetic propofol. Biochem Pharmacol. 44:391–393.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang S, Liu Y, Huang L, Zhang F and Kang
R: Effects of propofol on cancer development and chemotherapy:
Potential mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol. 831:46–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang Z, Song F, Li Y, Xue D, Zhao N,
Zhang J, Deng G, Li M, Liu X and Wang Y: Capsular polysaccharide of
mycoplasma ovipneumoniae induces sheep airway epithelial cell
apoptosis via Ros-dependent JNK/P38 MAPK pathways. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2017:61758412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xiong T, Dong W, Fu H, Li Q, Deng C, Lei X
and Guo L: Involvement of the nuclear factor-κB pathway in the
adhesion of neutrophils to renal tubular cells after injury induced
by neonatal postasphyxial serum. Mol Cell Biochem. 388:85–94. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|