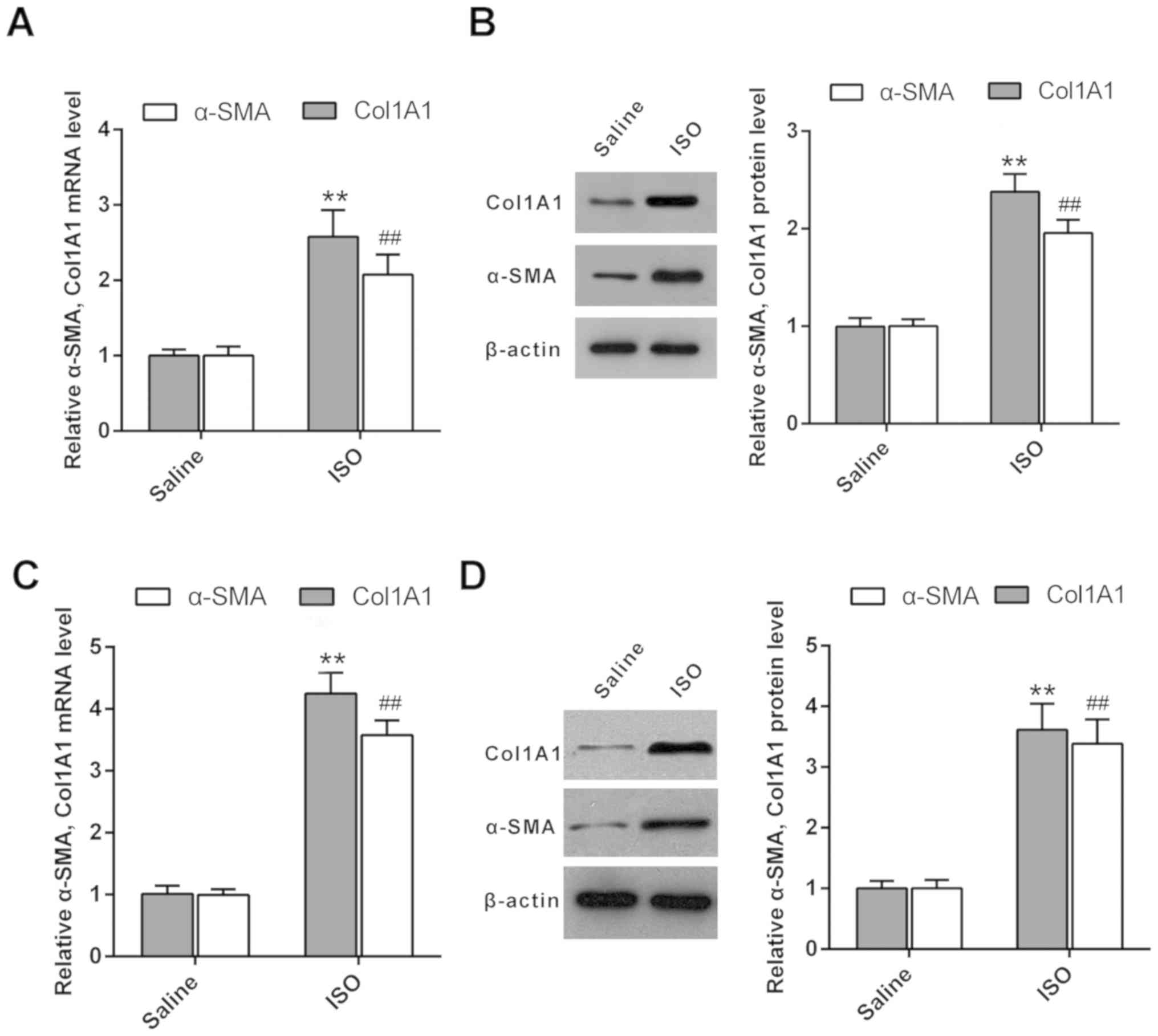
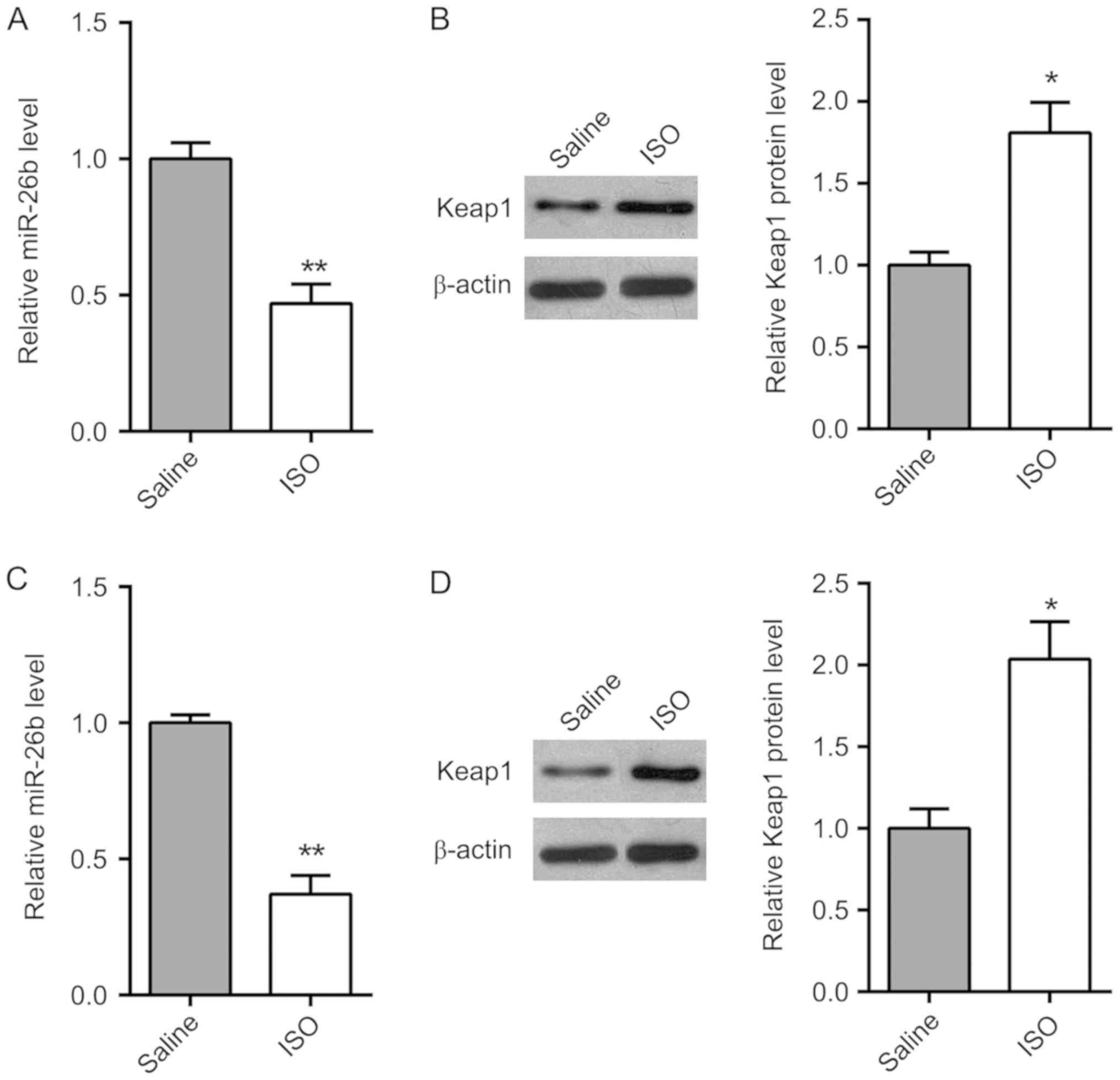
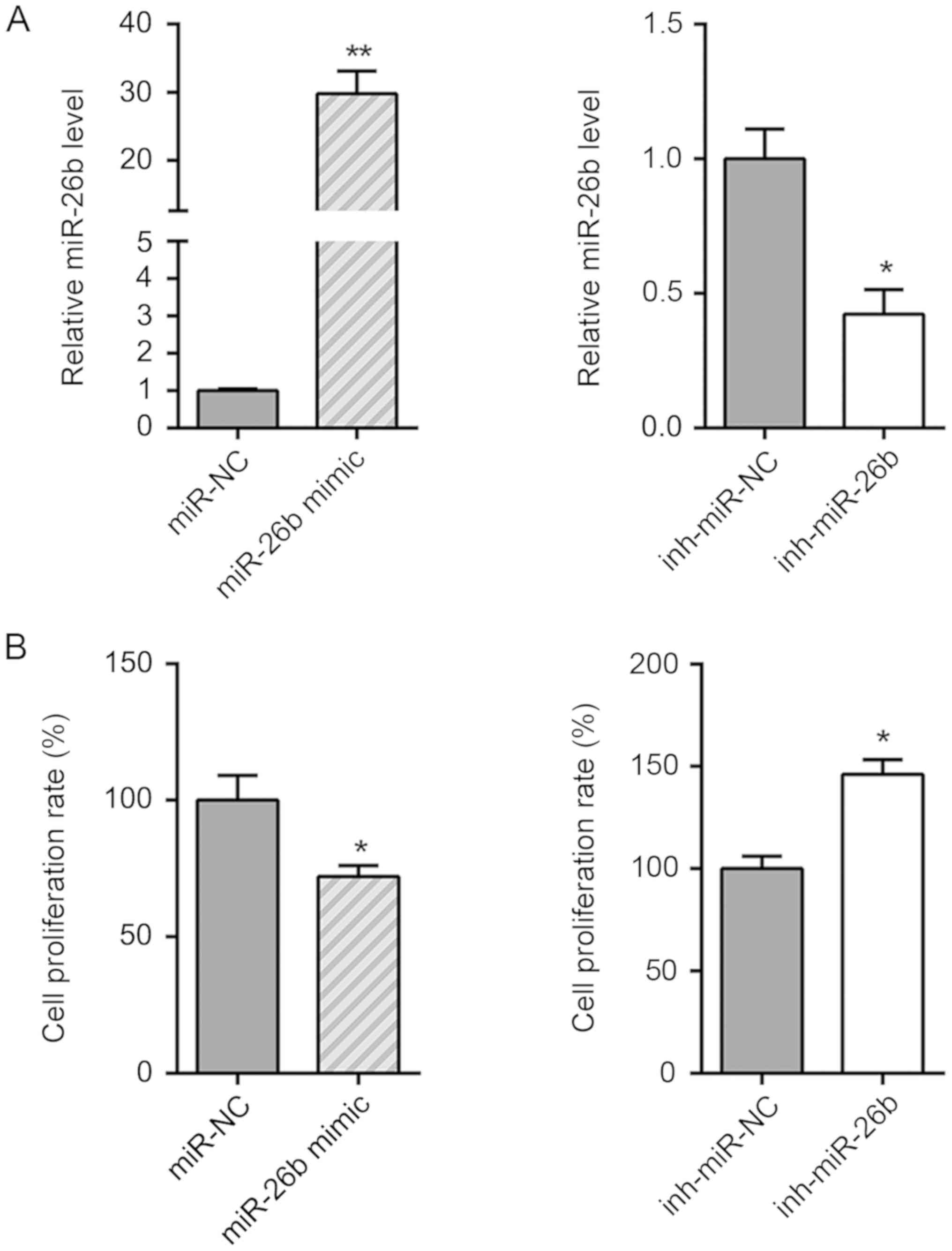
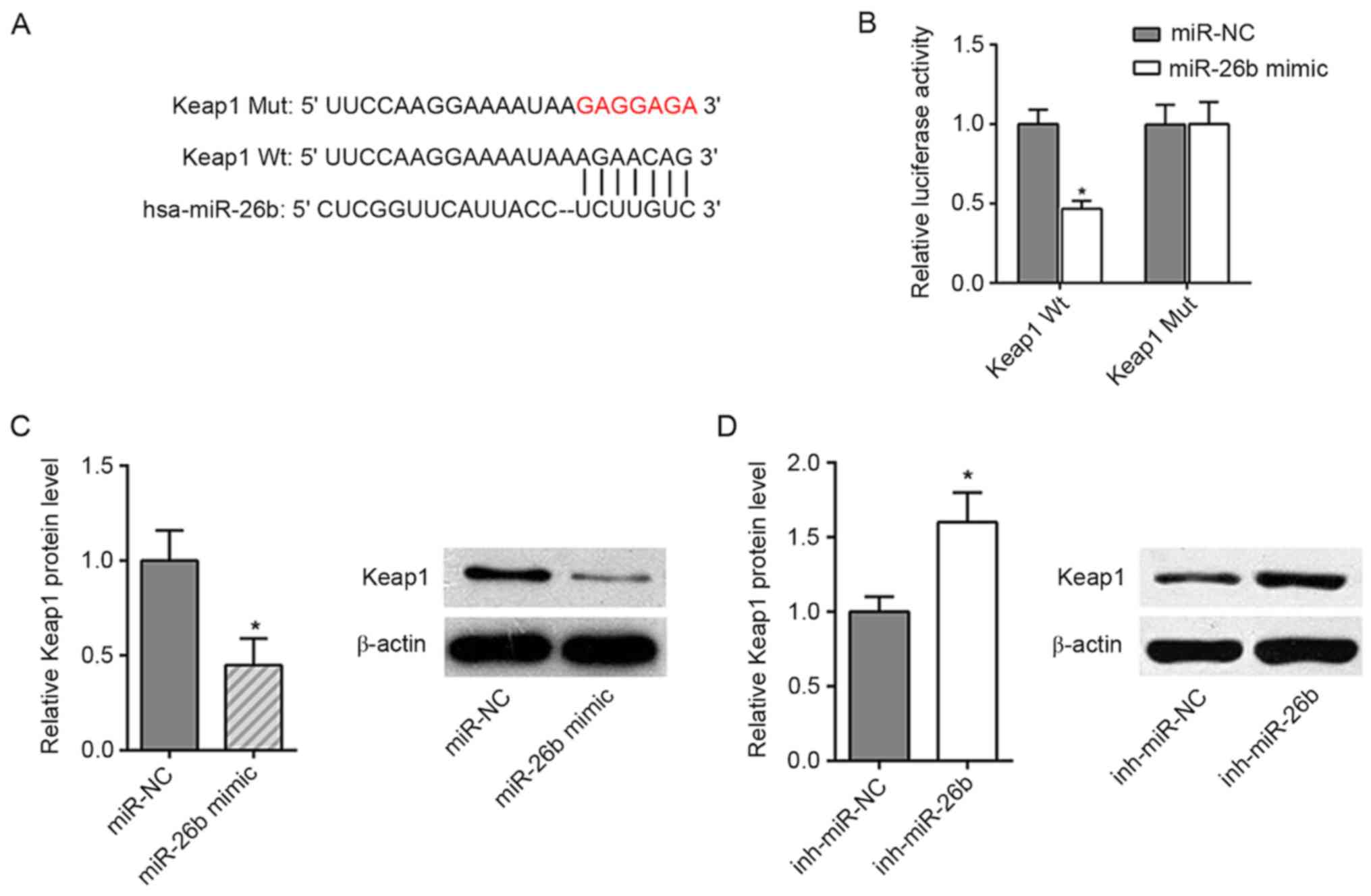
|
1
|
Molkentin JD, Bugg D, Ghearing N, Dorn LE,
Kim P, Sargent MA, Gunaje J, Otsu K and Davis J:
Fibroblast-specific genetic manipulation of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase in vivo reveals its central regulatory role in
fibrosis. Circulation. 136:549–561. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Segura AM, Frazier OH and Buja LM:
Fibrosis and heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 19:173–185. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Edgley AJ, Krum H and Kelly DJ: Targeting
fibrosis for the treatment of heart failure: A role for
transforming growth factor-β. Cardiovasc Ther. 30:e30–e40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Espira L and Czubryt MP: Emerging concepts
in cardiac matrix biology. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 87:996–1008.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fan D, Takawale A, Lee J and Kassiri Z:
Cardiac fibroblasts, fibrosis and extracellular matrix remodeling
in heart disease. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 5:152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Barnes JL and Gorin Y: Myofibroblast
differentiation during fibrosis: Role of NAD(P)H oxidases. Kidney
Int. 79:944–956. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Weber KT, Sun Y, Tyagi SC and Cleutjens
JP: Collagen network of the myocardium: Function, structural
remodeling and regulatory mechanisms. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
26:279–292. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Swynghedauw B: Molecular mechanisms of
myocardial remodeling. Physiol Rev. 79:215–262. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Romaine SP, Tomaszewski M, Condorelli G
and Samani NJ: MicroRNAs in cardiovascular disease: An introduction
for clinicians. Heart. 101:921–928. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gurha P: MicroRNAs in cardiovascular
disease. Curr Opin Cardiol. 31:249–254. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li L, Bounds KR, Chatterjee P and Gupta S:
MicroRNA-130a, a potential antifibrotic target in cardiac fibrosis.
J Am Heart Assoc. 6(pii): e0067632017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Du W, Liang H, Gao X, Li X, Zhang Y, Pan
Z, Li C, Wang Y, Liu Y, Yuan W, et al: MicroRNA-328, a potential
anti-fibrotic target in cardiac interstitial fibrosis. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 39:827–836. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen L, Ji Q, Zhu H, Ren Y, Fan Z and Tian
N: miR-30a attenuates cardiac fibrosis in rats with myocardial
infarction by inhibiting CTGF. Exp Ther Med. 15:4318–4324.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qin RH, Tao H, Ni SH, Shi P, Dai C and Shi
KH: microRNA-29a inhibits cardiac fibrosis in Sprague-Dawley rats
by downregulating the expression of DNMT3A. Anatol J Cardiol.
20:198–205. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei C, Kim IK, Kumar S, Jayasinghe S, Hong
N, Castoldi G, Catalucci D, Jones WK and Gupta S: NF-κB mediated
miR-26a regulation in cardiac fibrosis. J Cell Physiol.
228:1433–1442. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han M, Yang Z, Sayed D, He M, Gao S, Lin
L, Yoon S and Abdellatif M: GATA4 expression is primarily regulated
via a miR-26b-dependent post-transcriptional mechanism during
cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. 93:645–654. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Niture SK, Khatri R and Jaiswal AK:
Regulation of Nrf2-an update. Free Radic Biol Med. 66:36–44. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baird L and Dinkova-Kostova AT: The
cytoprotective role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Arch Toxicol.
85:241–272. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shi H, Shi A, Dong L, Lu X, Wang Y, Zhao
J, Dai F and Guo X: Chlorogenic acid protects against liver
fibrosis in vivo and in vitro through inhibition of oxidative
stress. Clin Nutr. 35:1366–1373. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheresh P, Kim SJ, Tulasiram S and Kamp
DW: Oxidative stress and pulmonary fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1832:1028–1040. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang LP, Fan SJ, Li SM, Wang XJ, Gao JL
and Yang XH: Oxidative stress promotes myocardial fibrosis by
upregulating KCa3.1 channel expression in AGT-REN double transgenic
hypertensive mice. Pflugers Arch. 469:1061–1071. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu Y, Liu Y, Pan Y, Lu C, Xu H, Wang X,
Liu T, Feng K and Tang Y: MicroRNA-135a inhibits cardiac fibrosis
induced by isoproterenol via TRPM7 channel. Biomed Pharmacother.
104:252–260. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tao H, Zhang JG, Qin RH, Dai C, Shi P,
Yang JJ, Deng ZY and Shi KH: LncRNA GAS5 controls cardiac
fibroblast activation and fibrosis by targeting miR-21 via
PTEN/MMP-2 signaling pathway. Toxicology. 386:11–18. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu J, Wang QY, Zhou Y, Lu XC, Liu YH, Wu
Y, Guo Q, Ma YT and Tang YQ: AstragalosideIV against cardiac
fibrosis by inhibiting TRPM7 channel. Phytomedicine. 30:10–17.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Periasamy S, Chen SY and Liu MY: The study
of ISO induced heart failure rat model, Exp Mol Pathol.
2010;88:299-304. Exp Mol Pathol. 90:842011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Artaud-Macari E, Goven D, Brayer S, Hamimi
A, Besnard V, Marchal-Somme J, Ali ZE, Crestani B, Kerdine-Römer S,
Boutten A and Bonay M: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
nuclear translocation induces myofibroblastic dedifferentiation in
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 18:66–79.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou XL, Xu H, Liu ZB, Wu QC, Zhu RR and
Liu JC: miR-21 promotes cardiac fibroblast-to-myofibroblast
transformation and myocardial fibrosis by targeting Jagged1. J Cell
Mol Med. May 28–2018.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
29
|
Icli B, Wara AK, Moslehi J, Sun X, Plovie
E, Cahill M, Marchini JF, Schissler A, Padera RF, Shi J, et al:
MicroRNA-26a regulates pathological and physiological angiogenesis
by targeting BMP/SMAD1 signaling. Circ Res. 113:1231–1241. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Köhler UA, Kurinna S, Schwitter D, Marti
A, Schäfer M, Hellerbrand C, Speicher T and Werner S: Activated
Nrf2 impairs liver regeneration in mice by activation of genes
involved in cell-cycle control and apoptosis. Hepatology.
60:670–678. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gambhir L, Checker R, Thoh M, Patwardhan
RS, Sharma D, Kumar M and Sandur SK: 1,4-Naphthoquinone, a
pro-oxidant, suppresses immune responses via KEAP-1
glutathionylation. Biochem Pharmacol. 88:95–105. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Civantos E, Bosch E, Ramirez E, Zhenyukh
O, Egido J, Lorenzo O and Mas S: Sitagliptin ameliorates oxidative
stress in experimental diabetic nephropathy by diminishing the
miR-200a/Keap-1/Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Diabetes Metab Syndr
Obes. 10:207–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang JJ, Tao H, Hu W, Liu LP, Shi KH, Deng
ZY and Li J: MicroRNA-200a controls Nrf2 activation by target Keap1
in hepatic stellate cell proliferation and fibrosis. Cell Signal.
26:2381–2389. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|