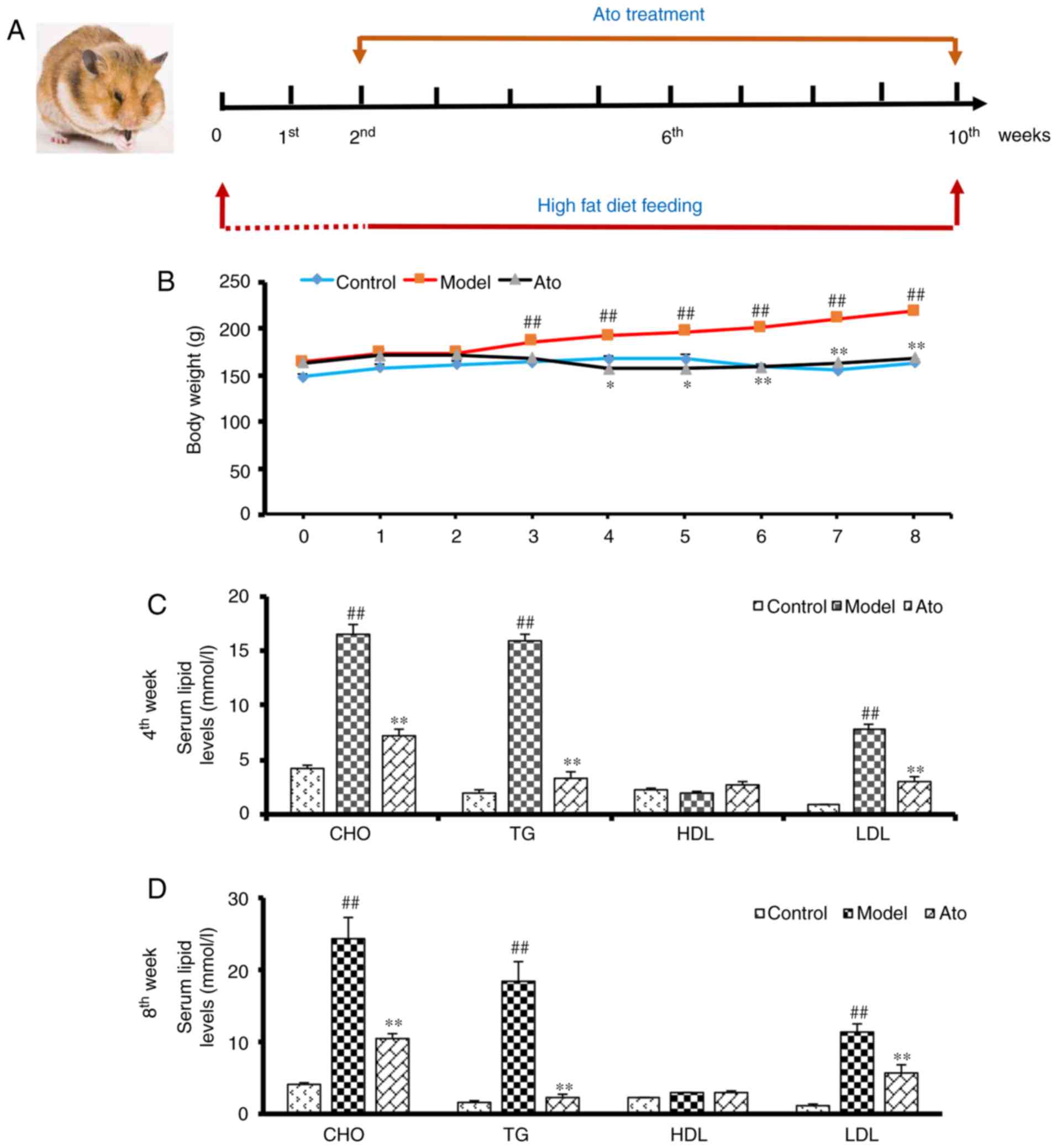
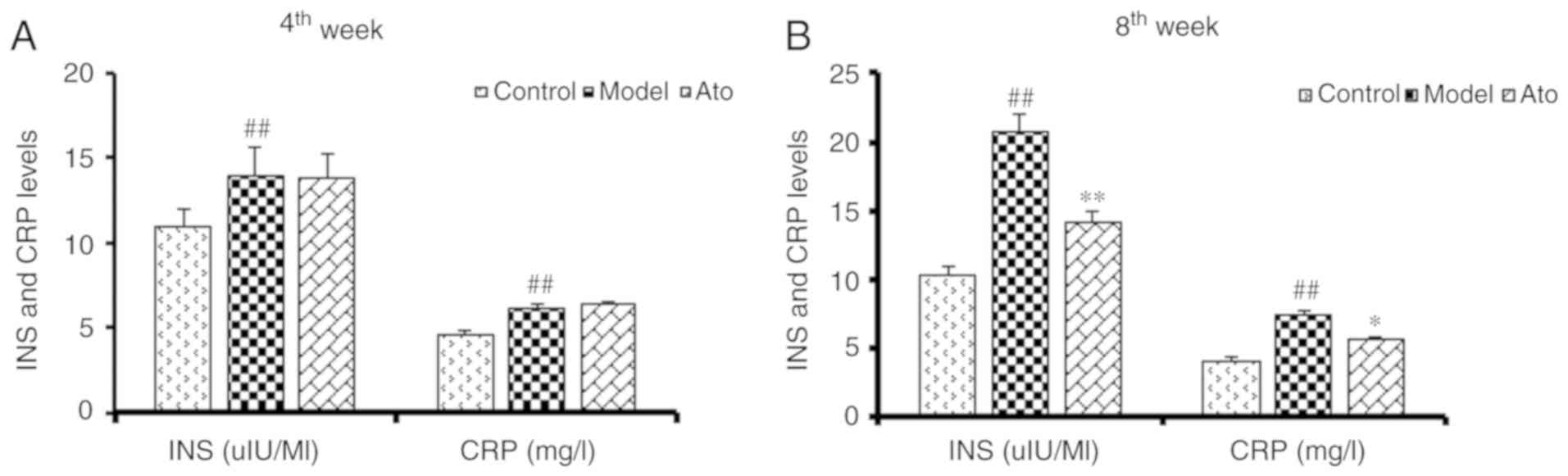
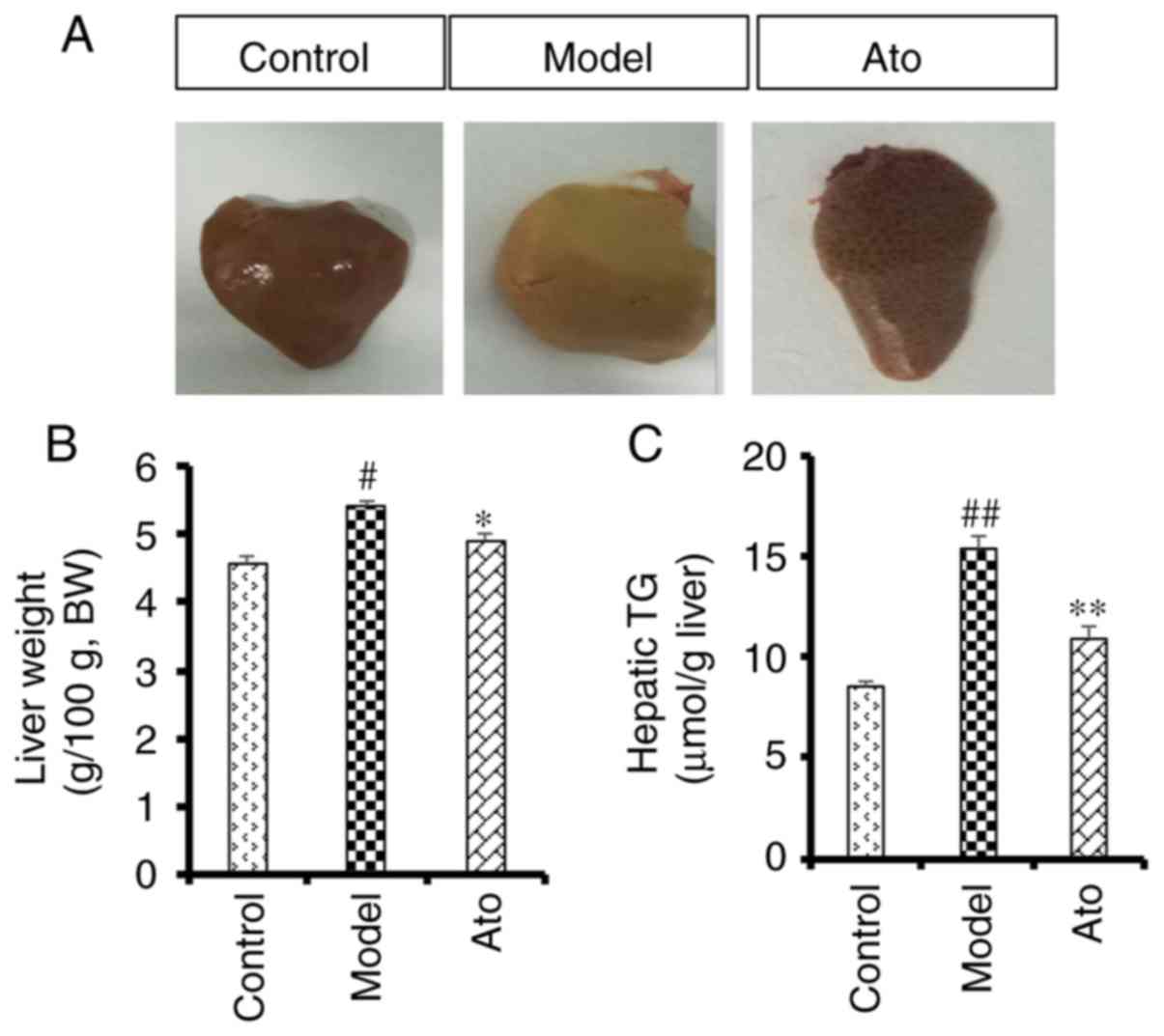
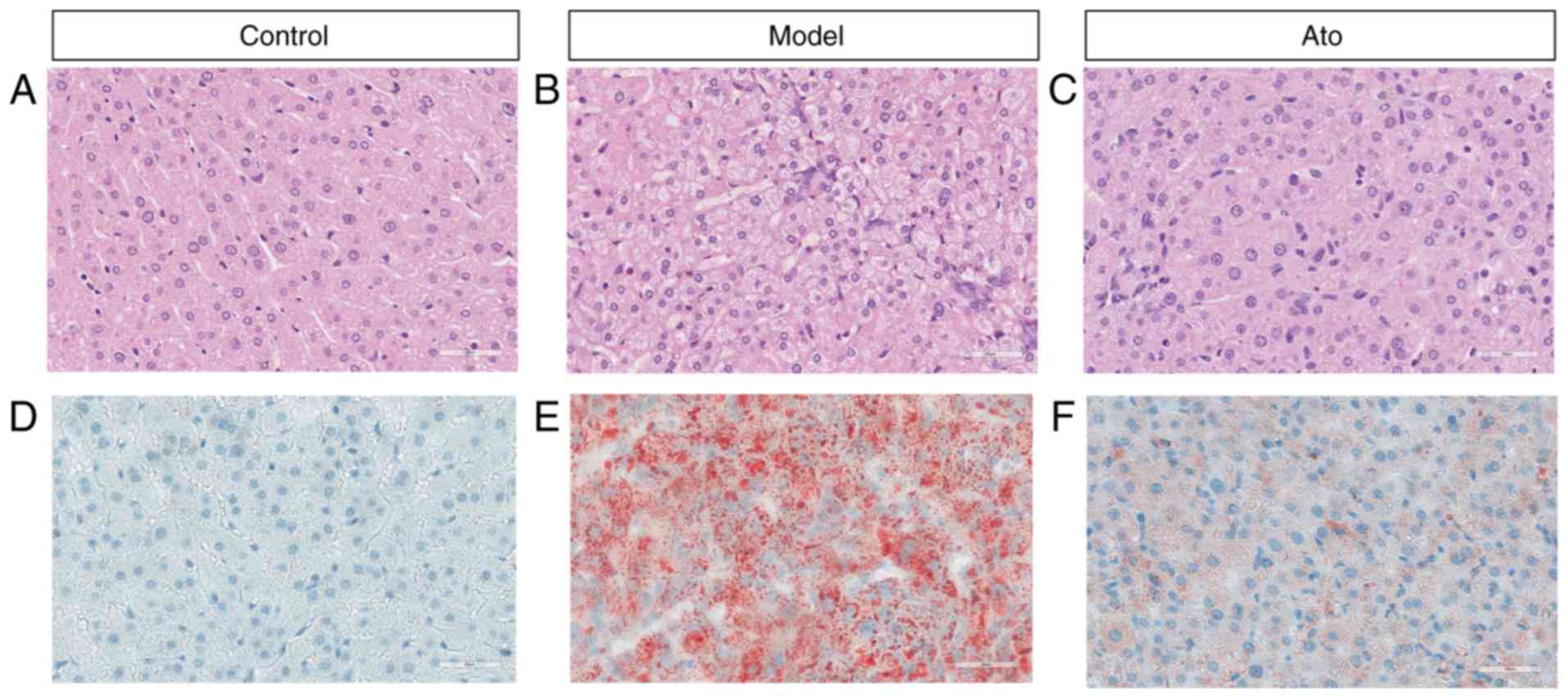
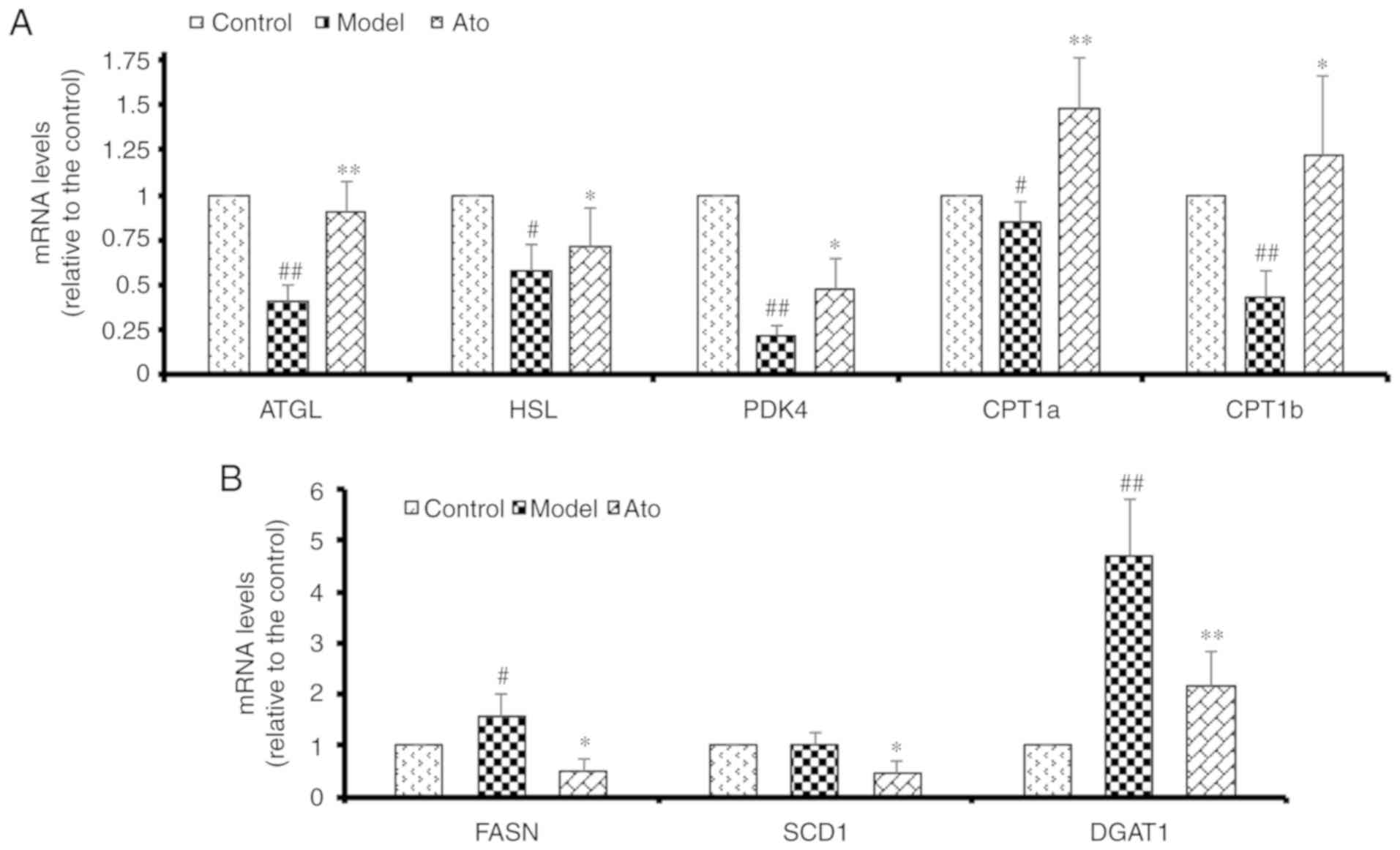
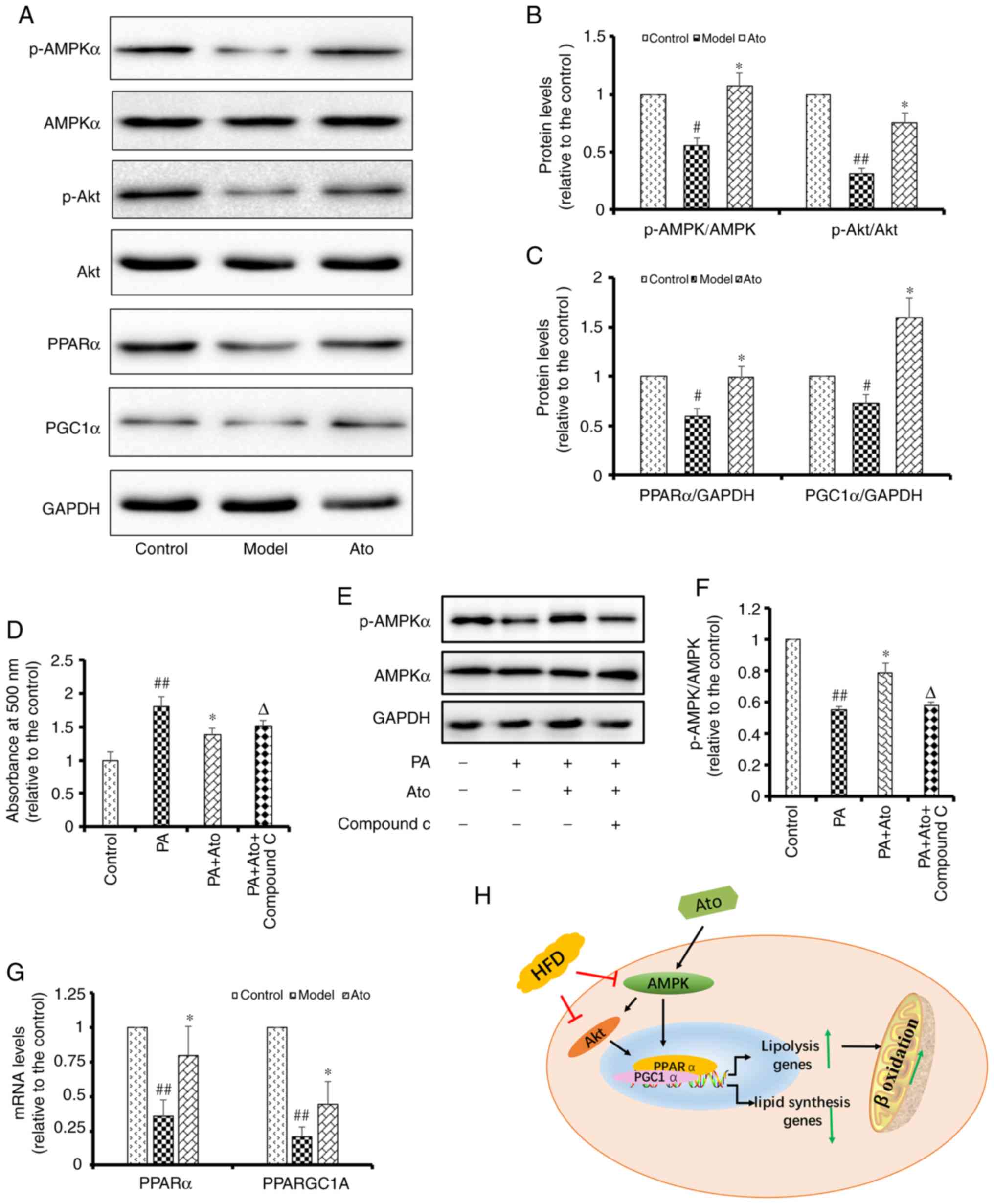
|
1
|
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel
Y, Henry L and Wymer M: Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence,
and outcomes. Hepatology. 64:73–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Anderson EL, Howe LD, Jones HE, Higgins
JP, Lawlor DA and Fraser A: The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease in children and adolescents: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 10:e01409082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alisi A, Feldstein AE, Villani A, Raponi M
and Nobili V: Pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A
multidisciplinary approach. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
9:152–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ekstedt M, Hagström H, Nasr P, Fredrikson
M, Stål P, Kechagias S and Hultcrantz R: Fibrosis stage is the
strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after
up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology. 61:1547–1554. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Angulo P, Kleiner DE, Dam-Larsen S, Adams
LA, Bjornsson ES, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Mills PR, Keach JC,
Lafferty HD, Stahler A, et al: Liver fibrosis, but no other
histologic features, is associated with long-term outcomes of
patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology.
149:389–397.e310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanaka S, Hikita H, Tatsumi T, Sakamori R,
Nozaki Y, Sakane S, Shiode Y, Nakabori T, Saito Y, Hiramatsu N, et
al: Rubicon inhibits autophagy and accelerates hepatocyte apoptosis
and lipid accumulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice.
Hepatology. 64:1994–2014. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aller R, Fernández-Rodríguez C, Lo Iacono
O, Bañares R, Abad J, Carrión JA, García-Monzón C, Caballería J,
Berenguer M, Rodríguez-Perálvarez M, et al: Consensus document.
Management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Clinical
practice guideline. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 41:328–349. 2018.(In
English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G,
Tomassetti S, Bugianesi E, Lenzi M, McCullough AJ, Natale S,
Forlani G and Melchionda N: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A
feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 50:1844–1850. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamasaki T and Tomita K: Relationship
between hyperuricemia and metabolic syndrome. Nihon Rinsho.
66:766–770. 2008.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim JY, Garcia-Carbonell R, Yamachika S,
Zhao P, Dhar D, Loomba R, Kaufman RJ, Saltiel AR and Karin M: ER
stress drives lipogenesis and steatohepatitis via caspase-2
activation of S1P. Cell. 175:133–145.e15. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park JG, Xu X, Cho S, Hur KY, Lee MS,
Kersten S and Lee AH: CREBH-FGF21 axis improves hepatic steatosis
by suppressing adipose tissue lipolysis. Sci Rep. 6:279382016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stavropoulos K, Imprialos K, Pittaras A,
Faselis C, Narayan P and Kokkinos P: Lifestyle modifications in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 16:239–245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mathews SE, Kumar RB and Shukla AP:
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, obesity, and cardiac dysfunction.
Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 25:315–320. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ye YC, Zhao XL and Zhang SY: Use of
atorvastatin in lipid disorders and cardiovascular disease in
Chinese patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 128:259–266. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bakker-Arkema RG, Davidson MH, Goldstein
RJ, Davignon J, Isaacsohn JL, Weiss SR, Keilson LM, Brown WV,
Miller VT, Shurzinske LJ and Black DM: Efficacy and safety of a new
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin, in patients with
hypertriglyceridemia. JAMA. 275:128–133. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Amarenco P, Bogousslavsky J, Callahan A
III, Goldstein LB, Hennerici M, Rudolph AE, Sillesen H, Simunovic
L, Szarek M, Welch KM, et al: High-dose atorvastatin after stroke
or transient ischemic attack. N Engl J Med. 355:549–559. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Taniguti EH, Ferreira YS, Stupp IJV,
Fraga-Junior EB, Doneda DL, Lopes L, Rios-Santos F, Lima E, Buss
ZS, Viola GG and Vandresen-Filho S: Atorvastatin prevents
lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behaviour in mice. Brain
Res Bull. 146:279–286. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cioboată R, Găman A, Traşcă D, Ungureanu
A, Docea AO, Tomescu P, Gherghina F, Arsene AL, Badiu C, Tsatsakis
AM, et al: Pharmacological management of non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease: Atorvastatin versus pentoxifylline. Exp Ther Med.
13:2375–2381. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brenachot X, Ramadori G, Ioris RM,
Veyrat-Durebex C, Altirriba J, Aras E, Ljubicic S, Kohno D,
Fabbiano S, Clement S, et al: Hepatic protein tyrosine phosphatase
receptor gamma links obesity-induced inflammation to insulin
resistance. Nat Commun. 8:18202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lerat H, Honda M, Beard MR, Loesch K, Sun
J, Yang Y, Okuda M, Gosert R, Xiao SY, Weinman SA and Lemon SM:
Steatosis and liver cancer in transgenic mice expressing the
structural and nonstructural proteins of hepatitis C virus.
Gastroenterology. 122:352–365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li M, Tang Y, Wu L, Mo F, Wang X, Li H, Qi
R, Zhang H, Srivastava A and Ling C: The hepatocyte-specific
HNF4alpha/miR-122 pathway contributes to iron overload-mediated
hepatic inflammation. Blood. 130:1041–1051. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nuñez-Durán E, Aghajan M, Amrutkar M, Sütt
S, Cansby E, Booten SL, Watt A, Ståhlman M, Stefan N, Häring HU, et
al: Serine/threonine protein kinase 25 antisense oligonucleotide
treatment reverses glucose intolerance, insulin resistance, and
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Hepatol Commun. 2:69–83.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee J, Yoon K, Ryu S, Chang Y and Kim HR:
High-normal levels of hs-CRP predict the development of
non-alcoholic fatty liver in healthy men. PLoS One.
12:e01726662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang JC, Li XX, Sun X, Li GY, Sun JL, Ye
YP, Cong LL, Li WM, Lu SY, Feng J, Liu PJ, et al: Activation of
AMPK by simvastatin inhibited breast tumor angiogenesis via
impeding HIF-1alpha-induced pro-angiogenic factor. Cancer Sci.
109:1627–1637. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han JS, Sung JH and Lee SK: Inhibition of
cholesterol synthesis in HepG2 cells by GINST-decreasing HMG-CoA
reductase expression via AMP-activated protein kinase. J Food Sci.
82:2700–2705. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dihingia A, Bordoloi J, Dutta P, Kalita J
and Manna P: Hexane-Isopropanolic Extract of Tungrymbai, a
North-East Indian fermented soybean food prevents hepatic steatosis
via regulating AMPK-mediated SREBP/FAS/ACC/HMGCR and
PPARalpha/CPT1A/UCP2 pathways. Sci Rep. 8:100212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gorowska-Wojtowicz E, Dutka P, Kudrycka M,
Pawlicki P, Milon A, Plachno BJ, Tworzydlo W, Pardyak L, Kaminska
A, Hejmej A, et al: Regulation of steroidogenic function of mouse
Leydig cells: G-coupled membrane estrogen receptor and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor partnership. J Physiol Pharmacol.
69:2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Muthukumaran P, Thiyagarajan G, Arun Babu
R and Lakshmi BS: Raffinose from Costus speciosus attenuates lipid
synthesis through modulation of PPARs/SREBP1c and improves insulin
sensitivity through PI3K/AKT. Chem Biol Interact. 284:80–89. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sirtori CR: The pharmacology of statins.
Pharmacol Res. 88:3–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Athyros VG, Boutari C, Stavropoulos K,
Anagnostis P, Imprialos KP, Doumas M and Karagiannis A: Statins: An
under-appreciated asset for the prevention and the treatment of
NAFLD or NASH and the related cardiovascular risk. Curr Vasc
Pharmacol. 16:246–253. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xue L, Lu X, He J, Zhang T, Wu X, Zhang Y,
Wang N, An Z, Xu J and Geng Y: Serum CK 18-M30 reflect liver
pathological severity during NAFLD progression in a rat model.
Pathol Res Pract. 214:1778–1786. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou D, Pan Q, Xin FZ, Zhang RN, He CX,
Chen GY, Liu C, Chen YW and Fan JG: Sodium butyrate attenuates
high-fat diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice by improving gut
microbiota and gastrointestinal barrier. World J Gastroenterol.
23:60–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ou TH, Tung YT, Yang TH and Chien YW:
Melatonin improves fatty liver syndrome by inhibiting the
lipogenesis pathway in hamsters with high-fat diet-induced
hyperlipidemia. Nutrients. 11:E7482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nwidu LL and Teme RE: Hot aqueous leaf
extract of Lasianthera africana (Icacinaceae) attenuates
rifampicin-isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity. J Integr Med.
16:263–272. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wires ES, Trychta KA, Bäck S, Sulima A,
Rice KC and Harvey BK: High fat diet disrupts endoplasmic reticulum
calcium homeostasis in the rat liver. J Hepatol. 67:1009–1017.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen Y, Qian Q and Yu J: Carbenoxolone
ameliorates insulin sensitivity in obese mice induced by high fat
diet via regulating the IkappaB-α/NF-κB pathway and NLRP3
inflammasome. Biomed Pharmacother. 115:1088682019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Goto R, Kamimura K, Shinagawa-Kobayashi Y,
Sakai N, Nagoya T, Niwa Y, Ko M, Ogawa K, Inoue R, Yokoo T, et al:
Inhibition of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) delays liver
fibrosis in a medaka model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
FEBS Open Bio. 9:643–652. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li Z, Xue J, Chen P, Chen L, Yan S and Liu
L: Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mainland of
China: A meta-analysis of published studies. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 29:42–51. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Caballería L, Pera G, Auladell MA, Torán
P, Muñoz L, Miranda D, Alumà A, Casas JD, Sánchez C, Gil D, et al:
Prevalence and factors associated with the presence of nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease in an adult population in Spain. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:24–32. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Söderberg C, Stål P, Askling J, Glaumann
H, Lindberg G, Marmur J and Hultcrantz R: Decreased survival of
subjects with elevated liver function tests during a 28-year
follow-up. Hepatology. 51:595–602. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wong CR, Nguyen MH and Lim JK:
Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. World J Gastroenterol. 22:8294–8303. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang X: Down-regulation of lncRNA-NEAT1
alleviated the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via mTOR/S6K1
signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 119:1567–1574. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu H, Li J, Tillman B, Morgan TR, French
BA and French SW: TLR3/4 signaling is mediated via the
NFkappaB-CXCR4/7 pathway in human alcoholic hepatitis and
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis which formed Mallory-Denk bodies. Exp
Mol Pathol. 97:234–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim JK, Fillmore JJ, Chen Y, Yu C, Moore
IK, Pypaert M, Lutz EP, Kako Y, Velez-Carrasco W, Goldberg IJ, et
al: Tissue-specific overexpression of lipoprotein lipase causes
tissue-specific insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:7522–7527. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ye D, Li FY, Lam KS, Li H, Jia W, Wang Y,
Man K, Lo CM, Li X and Xu A: Toll-like receptor-4 mediates
obesity-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis through activation of
X-box binding protein-1 in mice. Gut. 61:1058–1067. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ferreira DM, Castro RE, Machado MV,
Evangelista T, Silvestre A, Costa A, Coutinho J, Carepa F,
Cortez-Pinto H and Rodrigues CM: Apoptosis and insulin resistance
in liver and peripheral tissues of morbidly obese patients is
associated with different stages of non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Diabetologia. 54:1788–1798. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Smith GI, Shankaran M, Yoshino M,
Schweitzer GG, Chondronikola M, Beals JW, Okunade AL, Patterson BW,
Nyangau E, Field T, et al: Insulin resistance drives hepatic de
novo lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin
Invest. 134165Dec 5–2019.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang Q, Ou Y, Hu G, Wen C, Yue S, Chen C,
Xu L, Xie J, Dai H, Xiao H, et al: Naringenin attenuates
nonalocholic fatty liver disease by downregulating NLRP3/NF-kappaB
pathway in mice. Br J Pharmacol. Nov 23–2019.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kanda T, Matsuoka S, Yamazaki M, Shibata
T, Nirei K, Takahashi H, Kaneko T, Fujisawa M, Higuchi T, Nakamura
H, et al: Apoptosis and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. World J
Gastroenterol. 24:2661–2672. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li HH, Lin CL and Huang CN:
Neuroprotective effects of statins against amyloid β-induced
neurotoxicity. Neural Regen Res. 13:198–206. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hermida N, Markl A, Hamelet J, Van Assche
T, Vanderper A, Herijgers P, van Bilsen M, Hilfiker-Kleiner D,
Noppe G, Beauloye C, et al: HMGCoA reductase inhibition reverses
myocardial fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction through AMP-activated
protein kinase activation in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome.
Cardiovasc Res. 99:44–54. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jia F, Wu C, Chen Z and Lu G: Atorvastatin
inhibits homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress through
activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Cardiovasc Ther.
30:317–325. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lee WJ, Kim M, Park HS, Kim HS, Jeon MJ,
Oh KS, Koh EH, Won JC, Kim MS, Oh GT, et al: AMPK activation
increases fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle by activating
PPARalpha and PGC-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 340:291–295. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tzatsos A and Kandror KV: Nutrients
suppress phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling via
raptor-dependent mTOR-mediated insulin receptor substrate 1
phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 26:63–76. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chopra I, Li HF, Wang H and Webster KA:
Phosphorylation of the insulin receptor by AMP-activated protein
kinase (AMPK) promotes ligand-independent activation of the insulin
signalling pathway in rodent muscle. Diabetologia. 55:783–794.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zheng T, Yang X, Wu D, Xing S, Bian F, Li
W, Chi J, Bai X, Wu G, Chen X, et al: Salidroside ameliorates
insulin resistance through activation of a mitochondria-associated
AMPK/PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 172:3284–3301.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hinoi E, Iezaki T, Fujita H, Watanabe T,
Odaka Y, Ozaki K and Yoneda Y: PI3K/Akt is involved in brown
adipogenesis mediated by growth differentiation factor-5 in
association with activation of the Smad pathway. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 450:255–260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Docrat TF, Nagiah S, Krishnan A, Naidoo DB
and Chuturgoon AA: Atorvastatin induces MicroRNA-145 expression in
HEPG2 cells via regulation of the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. Chem
Biol Interact. 287:32–40. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ferrari A, Longo R, Fiorino E, Silva R,
Mitro N, Cermenati G, Gilardi F, Desvergne B, Andolfo A, Magagnotti
C, et al: HDAC3 is a molecular brake of the metabolic switch
supporting white adipose tissue browning. Nat Commun. 8:932017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Aoyama T, Peters JM, Iritani N, Nakajima
T, Furihata K, Hashimoto T and Gonzalez FJ: Altered constitutive
expression of fatty acid-metabolizing enzymes in mice lacking the
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha). J
Biol Chem. 273:5678–5684. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Patterson AD, Shah YM, Matsubara T, Krausz
KW and Gonzalez FJ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
alpha induction of uncoupling protein 2 protects against
acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity. Hepatology. 56:281–290. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|