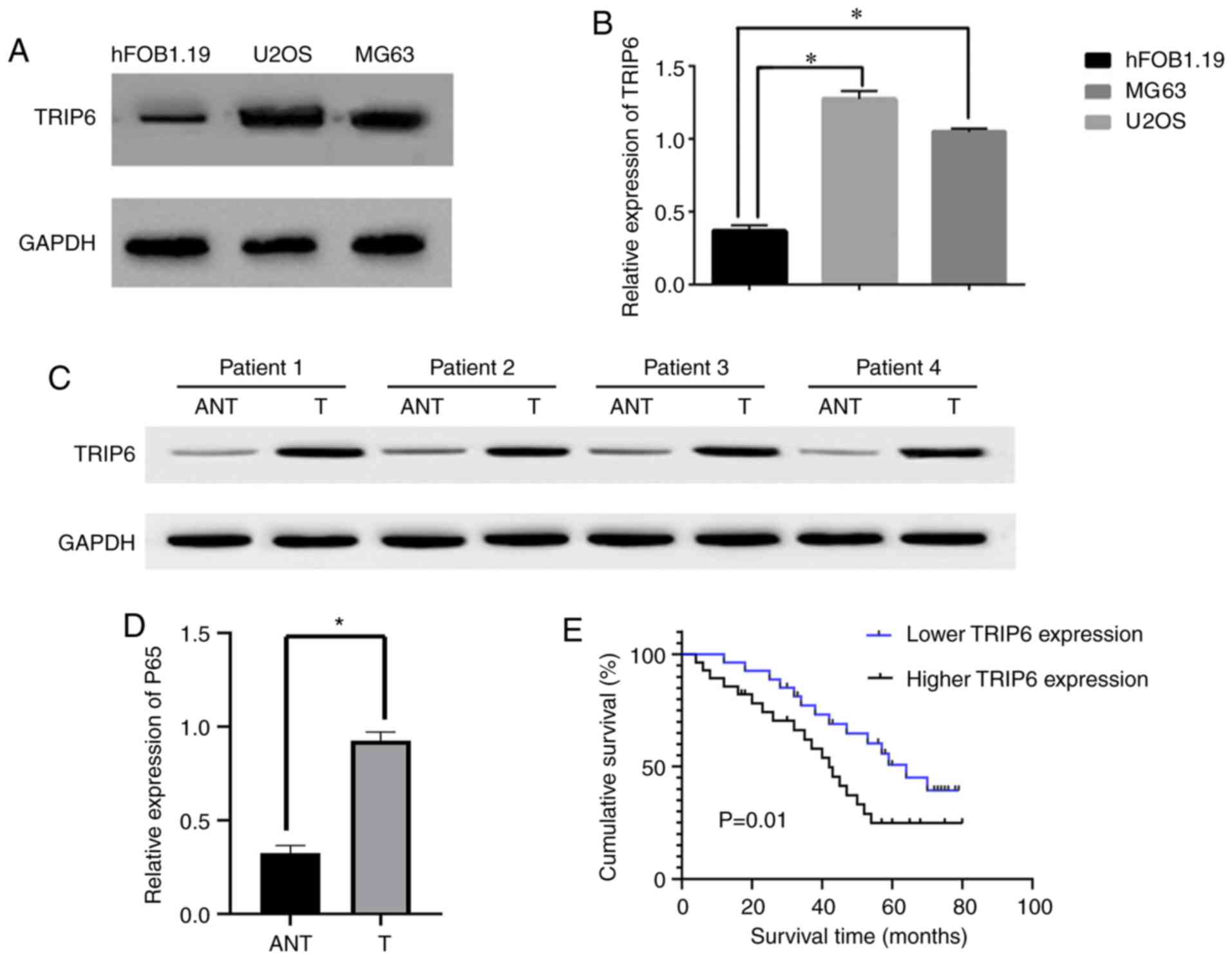
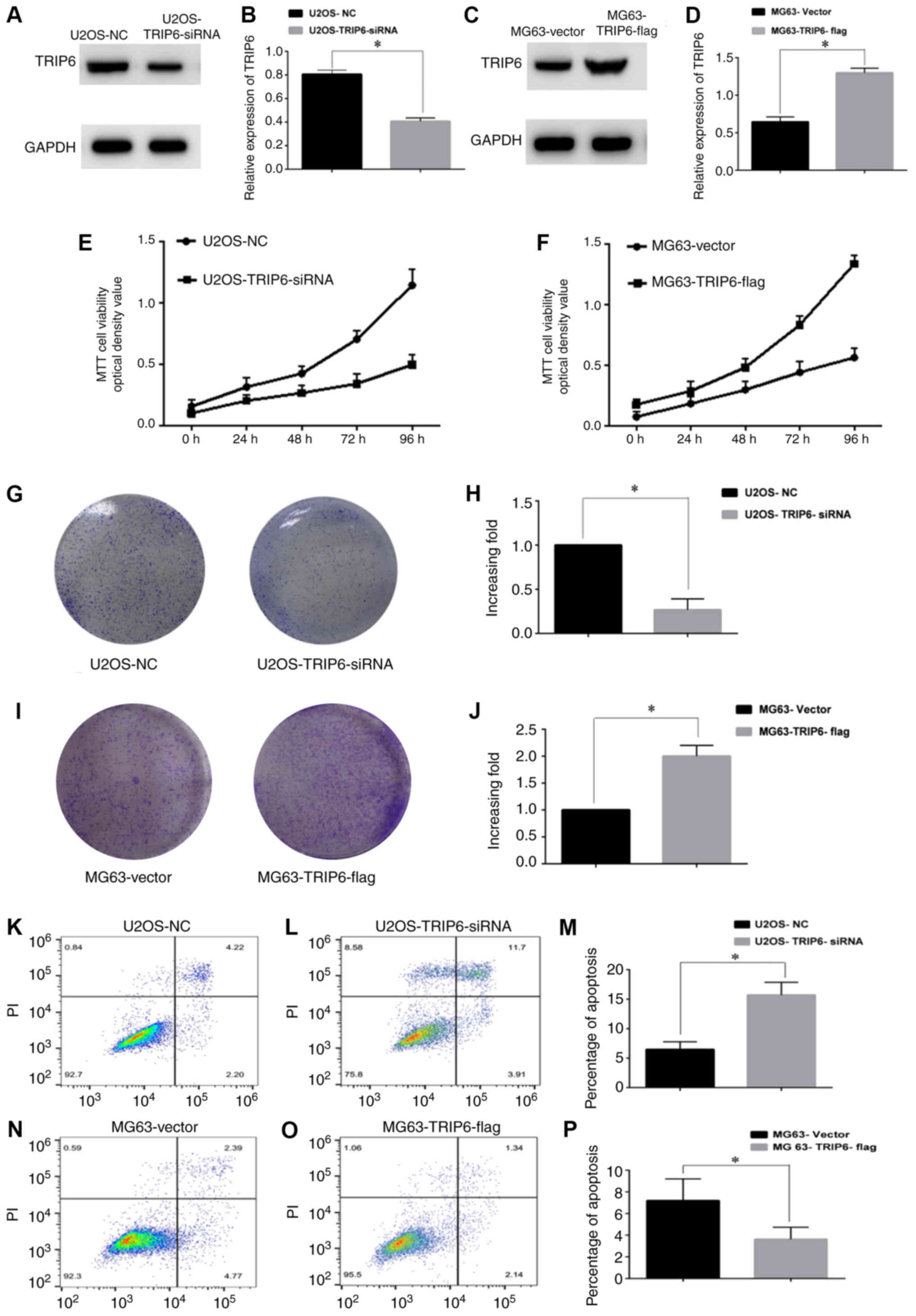
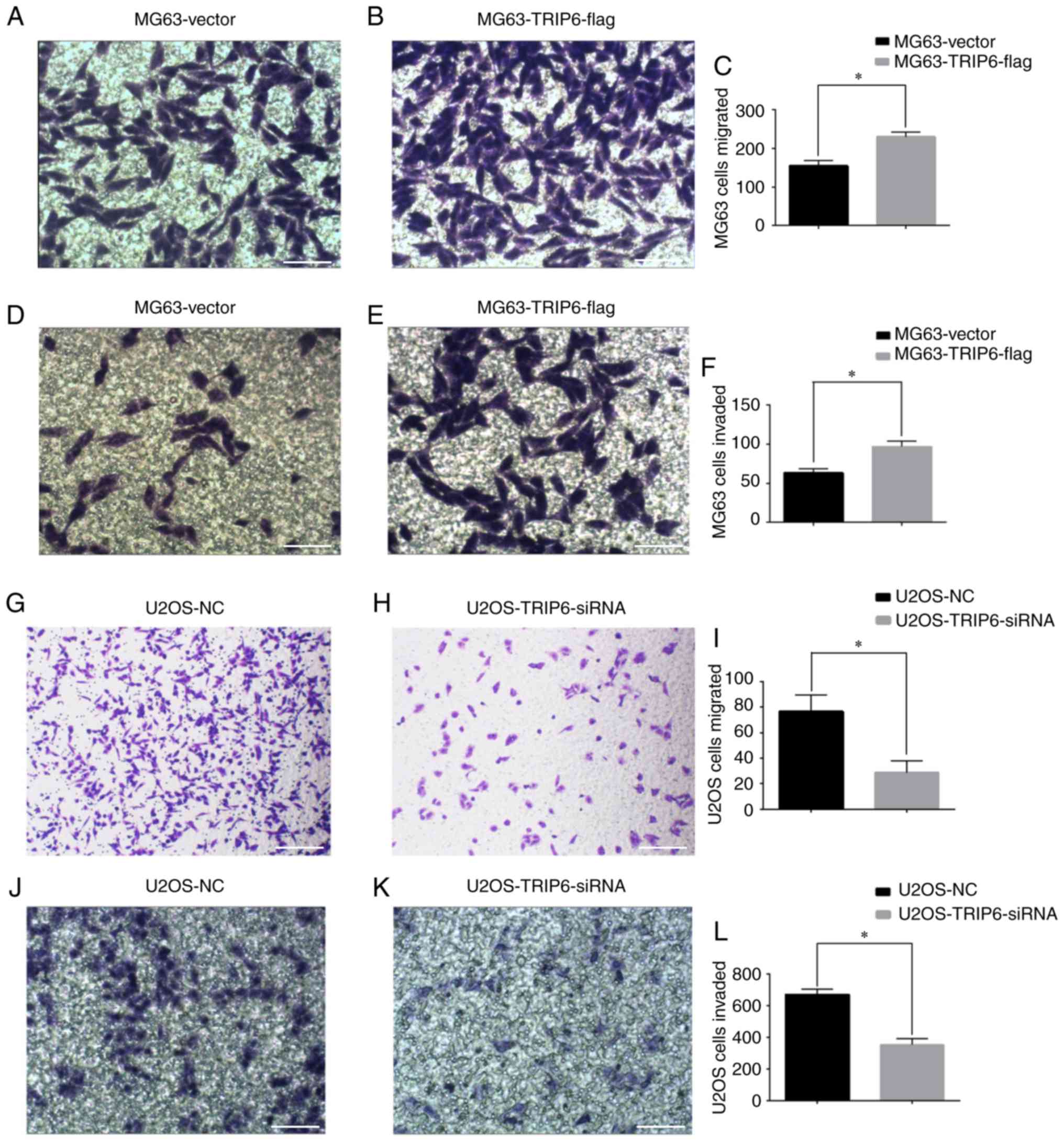
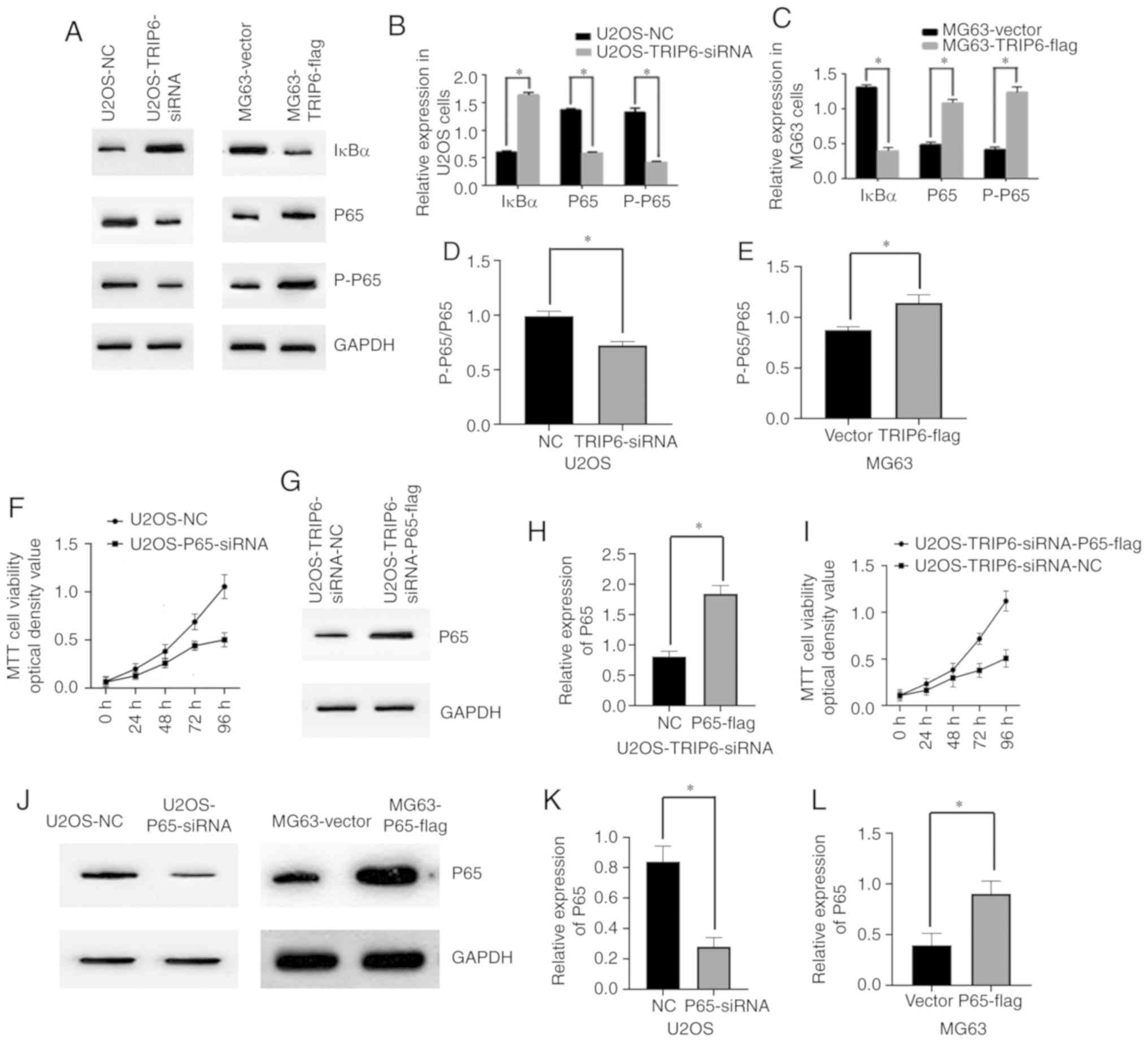
|
1
|
Zhao Z, Lin X, Tong Y and Li W: Silencing
lncRNA ZFAS1 or elevated microRNA-135a represses proliferation,
migration, invasion and resistance to apoptosis of osteosarcoma
cells. Cancer Cell Int. 19:3262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gill J, Ahluwalia MK, Geller D and Gorlick
R: New targets and approaches in osteosarcoma. Pharmacol Ther.
137:89–99. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang C, Ma K and Li WY: Cinobufagin
suppresses the characteristics of osteosarcoma cancer cells by
inhibiting the IL-6-OPN-STAT3 pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther.
13:4075–4090. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lindsey BA, Markel JE and Kleinerman ES:
Osteosarcoma overview. Rheumatol Ther. 4:25–43. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Friebele JC, Peck J, Pan X, Abdel-Rasoul M
and Mayerson JL: Osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis and review of the
literature. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 44:547–553.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jour G, Wang L, Middha S, Zehir A, Chen W,
Sadowska J, Healey J, Agaram NP, Choi L, Nafa K and Hameed M: The
molecular landscape of extraskeletal osteosarcoma: A
clinicopathological and molecular biomarker study. J Pathol Clin
Res. 29:9–20. 2015.
|
|
7
|
Dong S, Xiao Y, Ma X, He W, Kang J, Peng
Z, Wang L and Li Z: miR-193b increases the chemosensitivity of
osteosarcoma cells by promoting FEN1-mediated autophagy. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:10089–10098. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoshizawa M, Nakamura S, Sugiyama Y, Tamai
S, Ishida Y, Sueyoshi M, Toda Y, Hosogi S, Yano Y and Ashihara E:
6-Hydroxythiobinupharidine inhibits migration of LM8 osteosarcoma
cells by decreasing expression of LIM domain kinase 1. Anticancer
Res. 39:6507–6513. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I and Juergens
H: Osteosarcoma treatment-Where do we stand? A state of the art
review. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xue M, Shen J, Cui J, Wu J, Qiao W, Ding
N, Song C and Shan B: MicroRNA-638 expression change in
osteosarcoma patients via PLD1 and VEGF expression. Exp Ther Med.
17:3899–3906. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cai W, Xu Y, Yin J, Zuo W and Su Z:
miR-552-5p facilitates osteosarcoma cell proliferation and
metastasis by targeting WIF1. Exp Ther Med. 17:3781–3788.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu H, He Y, Chen H, Liu Y, Wei B, Chen G
and Lin H and Lin H: LncRNA THOR increases osteosarcoma cell
stemness and migration by enhancing SOX9 mRNA stability. FEBS Open
Bio. 9:781–790. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin VT and Lin FT: TRIP6: An adaptor
protein that regulates cell motility, anti-apoptotic signaling and
transcriptional activity. Cell Signal. 23:1691–1697. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao MK, Wang Y, Murphy K, Yi J, Beckerle
MC and Gilmore TD: Gilmore TD LIM domain-containing protein trip6
can act as a coactivator for the v-Rel transcription factor. Gene
Expr. 8:207–217. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Erdmann KS: The protein tyrosine
phosphatase PTP-Basophil/Basophil-like. Interacting proteins and
molecular functions. Eur J Biochem. 270:4789–4798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bashirova AA, Markelov ML, Shlykova TV,
Levshenkova EV, Alibaeva RA and Frolova EI: The human RIL gene:
Mapping to human chromosome 5q31.1, genomic organization and
alternative transcripts. Gene. 210:239–245. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miao X, Xu X, Wu Y, Zhu X, Chen X, Li C,
Lu X, Chen Y, Liu Y, Huang J, et al: Overexpression of TRIP6
promotes tumor proliferation and reverses cell adhesion-mediated
drug resistance (CAM-DR) via regulating nuclear p27(Kip1)
expression in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Tumor Biol. 37:1369–1378.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Grunewald TG, Willier S, Janik D, Unland
R, Reiss C, Prazeres da Costa O, Buch T, Dirksen U, Richter GH,
Neff F, et al: The Zyxin-related protein thyroid receptor
interacting protein 6 (TRIP6) is overexpressed in Ewing's sarcoma
and promotes migration, invasion and cell growth. Biol Cell.
105:535–547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fei J, Li J, Shen S and Zhou W:
Characterization of TRIP6-dependent nasopharyngeal cancer cell
migration. Tumor Biol. 34:2329–2335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lai YJ, Lin VT, Zheng Y, Benveniste EN and
Lin FT: The adaptor protein TRIP6 antagonizes fas-induced apoptosis
but promotes its effect on cell migration. Mol Cell Biol.
30:5582–5596. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu L, Xu X, Tang Y and Zhu X: TRIP6
functions as a potential oncogene and facilitated proliferation and
metastasis of gastric cancer. Biologics. 13:101–110.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun BQ, Sui YD, Huang H, Zou XB, Chen SC
and Yu ZK: Effect of lncRNA CRNDE on sepsis-related kidney injury
through the TLR3/NF-κB pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:10489–10497. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Su XF, Li N, Meng FL, Chu YL, Li T and Gao
XZ: MiR-16 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by
targeting FEAT through NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 23:10274–10282. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Zhou X, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Wang X
and Cheng L: Involvement of NF-κB signaling pathway in the
regulation of PRKAA1-mediated tumorigenesis in gastric cancer.
Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:3677–3686. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li H, Wittwer T, Weber A, Schneider H,
Moreno R, Maine GN, Kracht M, Schmitz ML and Burstein E: Regulation
of NF-κB activity by competition between RelA acetylation and
ubiquitination. Oncogene. 31:611–623. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schmitz ML, Mattioli I, Buss H and Kracht
M: Nf-kappaB: A multifaceted transcription factor regulated at
several levels. Chembiochem. 5:1348–1358. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wietek C and O'Neill LA: Diversity and
regulation in the NF-kappaB system. Trends Biochem Sci. 32:311–319.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pan D and Lin X: Epithelial growth factor
receptor-activated nuclear factor κB signaling and its role in
epithelial growth factor receptor-associated tumors. Cancer J.
19:461–467. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang T, Grabiner B, Zhu Y, Jiang C, Li H,
You Y, Lang J, Hung MC and Lin X: CARMA3 is crucial for
EGFR-Induced activation of NF-κB and tumor progression. Cancer Res.
71:2183–2192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gu NJ, Wu MZ, He L, Wang XB, Wang S, Qiu
XS, Wang EH and Wu GP: HPV 16 E6/E7 up-regulate the expression of
both HIF-1α and GLUT1 by inhibition of RRAD and activation of NF-κB
in lung cancer cells. J Cancer. 10:6903–6909. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Natoli G, Saccani S, Bosisio D and Marazzi
I: Interactions of NF-kappaB with chromatin: The art of being at
the right place at the right time. Nat Immunol. 6:439–445. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Duan Y, An W, Wu H and Wu Y: Salvianolic
acid C attenuates LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis in human
periodontal ligament stem cells via toll-like receptors 4
(TLR4)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. Med Sci Monit.
25:9499–9508. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oliveira IDSDS, Colares AV, Cardoso FO,
Tellis CJM, Chagas MDSDS, Behrens MD, Calabrese KDS, Almeida-Souza
F and Abreu-Silva AL: Vernonia polysphaera Baker: Anti-inflammatory
activity in vivo and inhibitory effect in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7
cells. PLoS One. 14:e02252752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fei J, Ling YM, Zeng MJ and Zhang KW:
Shixiang plaster, a traditional Chinese medicine, promotes healing
in a rat model of diabetic ulcer through the receptor for advanced
glycation end products (RAGE)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/vascular cell adhesion
molecule-1 (VCAM-1)/endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)
signaling pathways. Med Sci Monit. 25:9446–9457. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pasquali S and Gronchi A: Neoadjuvant
chemotherapy in soft tissue sarcomas: Latest evidence and clinical
implications. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 9:415–429. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kouloulia S, Hallin EI, Simbriger K,
Amorim IS, Lach G, Amvrosiadis T, Chalkiadaki K, Kampaite A, Truong
VT, Hooshmandi M, et al: Raptor-mediated proteasomal degradation of
deamidated 4E-BP2 regulates postnatal neuronal translation and
NF-κB activity. Cell Rep. 29:3620–3635.e7. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sehgal K and Barbie DA: Clonal selection
drives NF-κB activation in recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 79:5915–5916. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Biswas DK and Iglehart JD: Linkage between
EGFR family receptors and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)
signaling in breast cancer. J Cell Physiol. 209:645–652. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Biswas DK, Cruz AP, Gansberger E and
Pardee AB: Epidermal growth factor-induced nuclear factor kappa B
activation: A major pathway of cell-cycle progression in
estrogen-receptor negative breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 97:8542–8547. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang RK, Shao XM, Yang JP, Yan HL and Shao
Y: MicroRNA-145 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of
HepG2 cells by targeting ROCK1 through the ROCK1/NF-κB signaling
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:2777–2785. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ma X and Ning S: Shikimic acid promotes
estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer cells proliferation
via activation of NF-κB signaling. Toxicol Lett. 312:65–71. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zou PL, Zhang QH, Zhou JF, Lin RW, Chen ZQ
and Xiang ST: Inhibitory effect of polyphyllin I on the
proliferation of prostate cancer PC3 cells via ERK1/2/P65/DNMT1 and
its molecular mechanism. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 24:199–205. 2018.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou B, Yang Y and Li C: SIRT1 inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by promoting M1 macrophage
polarization via NF-κB pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 12:2519–2529.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li L, Bin LH, Li F, Liu Y, Chen D, Zhai Z
and Shu HB: TRIP6 is a RIP2-associated common signaling component
of multiple NF-kappaB activation pathways. J Cell Sci. 118:555–563.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kassel O, Schneider S, Heilbock C, Litfin
M, Göttlicher M and Herrlich P: A nuclear isoform of the focal
adhesion LIM-domain protein Trip6 integrates activating and
repressing signals at AP-1- and NF-kappaB-regulated promoters.
Genes Dev. 18:2518–2528. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li Q, Sun J, Mohammadtursun N, Wu J, Dong
J and Li L: Curcumin inhibits cigarette smoke-induced inflammation
via modulating the PPARγ-NF-κB signaling pathway. Food Funct.
10:7983–7994. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang P, Yin Y, Wang T, Li W, Li C, Zeng
X, Yang W, Zhang R, Tang Y, Shi L, et al: Maresin 1 mitigates
concanavalin A-induced acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting
ROS-mediated activation of NF-κB signaling. Free Radic Biol Med.
147:23–36. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ma X, Jiang Z, Li N, Jiang W, Gao P, Yang
M, Yu X, Wang G and Zhang Y: Ets2 suppresses inflammatory cytokines
through MAPK/NF-κB signaling and directly binds to the IL-6
promoter in macrophages. Aging (Albany NY). 11:10610–10625. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Guo G, Tian A, Lan X, Fu C, Yan Z and Wang
C: Nano hydroxyapatite induces glioma cell apoptosis by suppressing
NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 17:4080–4088.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang R, Li X, Wei L, Qin Y and Fang J:
Lemur tyrosine kinase 2 acts as a positive regulator of NF-κB
activation and colon cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Lett.
454:70–77. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fang W, Liao W, Zheng Y, Huang X, Weng X,
Fan S, Chen X, Zhang X, Chen J, Xiao S, et al: Neurotropin reduces
memory impairment and neuroinflammation via BDNF/NF-κB in a
transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Am J Transl Res.
11:1541–1554. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yu Y, Feng S, Wei S, Zhong Y, Yi G, Chen
H, Liang L, Chen H and Lu X: Extracellular ATP activates
P2X7R-NF-κB (p65) pathway to promote the maturation of bone
marrow-derived dendritic cells of mice. Cytokine. 119:175–181.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cai C, Zhu H, Ning X, Li L, Yang B, Chen
S, Wang L, Lu X and Gu D: LncRNA ENST00000602558.1 regulates ABCG1
expression and cholesterol efflux from vascular smooth muscle cells
through a p65-dependent pathway. Atherosclerosis. 285:31–39. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yamaguchi Y, Ayaki T, Li F, Tsujimura A,
Kamada M, Ito H, Maki T, Sawamoto N, Urushitani M and Takahashi R:
Phosphorylated NF-κB subunit p65 aggregates in granulovacuolar
degeneration and neurites in neurodegenerative diseases with
tauopathy. Neurosci Lett. 704:229–235. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|