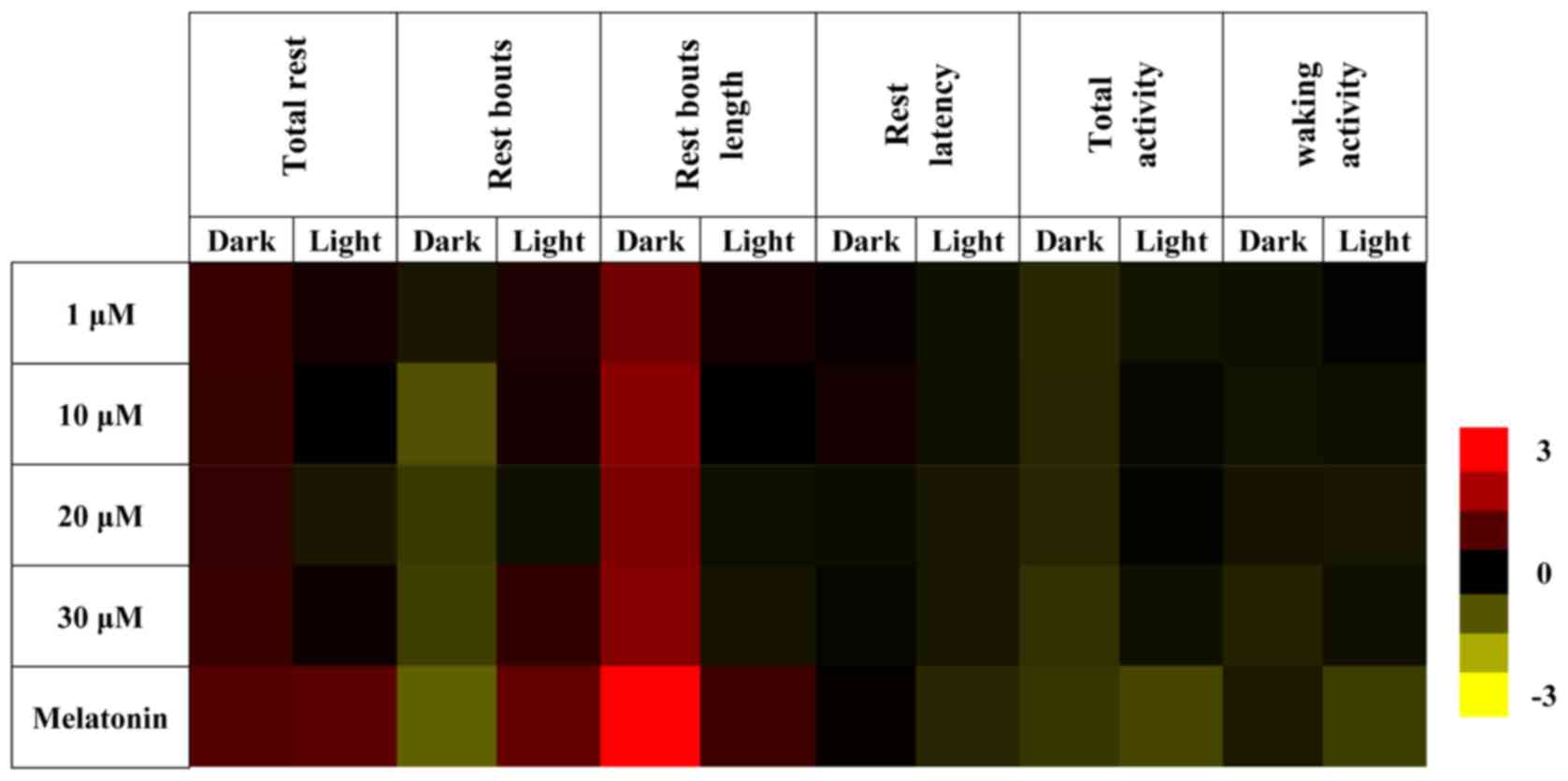
|
1
|
Roth T: Insomnia: Definition, prevalence,
etiology, and consequences. J Clin Sleep Med. 3 (Suppl 5):S7–S10.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Léger D, Morin CM, Uchiyama M, Hakimi Z,
Cure S and Walsh JK: Chronic insomnia, quality-of-life, and utility
scores: Comparison with good sleepers in a cross-sectional
international survey. Sleep Med. 13:43–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Asnis GM, Thomas M and Henderson MA:
Pharmacotherapy treatment options for insomnia: A primer for
clinicians. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Swinney DC: The contribution of
mechanistic understanding to phenotypic screening for
first-in-class medicines. J Biomol Screen. 18:1186–1192. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ek F, Malo M, Åberg Andersson M, Wedding
C, Kronborg J, Svensson P, Waters S, Petersson P and Olsson R:
Behavioral analysis of dopaminergic activation in zebrafish and
rats reveals similar phenotypes. ACS Chem Neurosci. 7:633–646.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ellis LD and Soanes KH: A larval zebrafish
model of bipolar disorder as a screening platform for
neuro-therapeutics. Behav Brain Res. 233:450–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Levitas-Djerbi T and Appelbaum L: Modeling
sleep and neuropsychiatric disorders in zebrafish. Curr Opin
Neurobiol. 44:89–93. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhdanova IV, Wang SY, Leclair OU and
Danilova NP: Melatonin promotes sleep-like state in zebrafish.
Brain Res. 903:263–268. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Blank M, Guerim LD, Cordeiro RF and Vianna
MR: A one-trial inhibitory avoidance task to zebrafish: Rapid
acquisition of an NMDA-dependent long-term memory. Neurobiol Learn
Mem. 92:529–534. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pather S and Gerlai R: Shuttle box
learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav Brain Res. 196:323–327.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Egan RJ, Bergner CL, Hart PC, Cachat JM,
Canavello PR, Elegante MF, Elkhayat SI, Bartels BK, Tien AK, Tien
DH, et al: Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of
stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav Brain Res. 205:38–44. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rihel J, Prober DA, Arvanites A, Lam K,
Zimmerman S, Jang S, Haggarty SJ, Kokel D, Rubin LL, Peterson RT
and Schier AF: Zebrafish behavioral profiling links drugs to
biological targets and rest/wake regulation. Science. 327:348–351.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sánchez-Ortuño MM, Bélanger L, Ivers H,
LeBlanc M and Morin CM: The use of natural products for sleep: A
common practice? Sleep Med. 10:982–987. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wing YK: Herbal treatment of insomnia.
Hong Kong Med J. 7:392–402. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
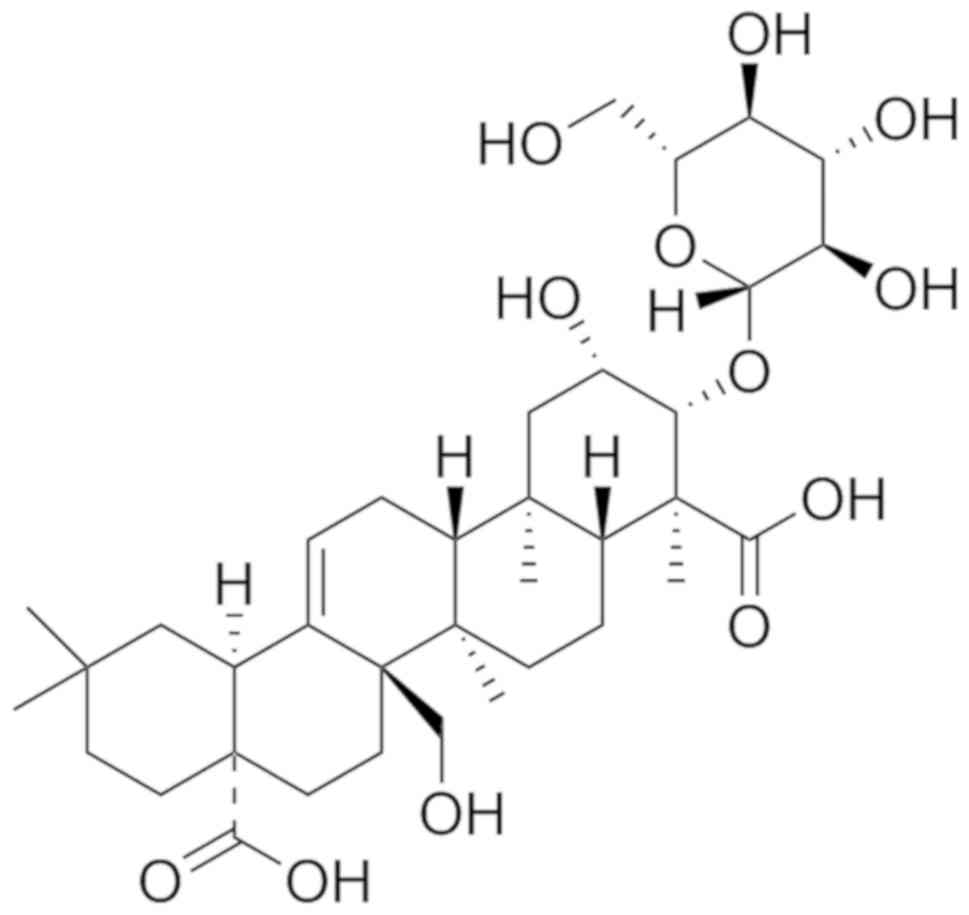
Cao Q, Jiang Y, Cui SY, Tu PF, Chen YM, Ma
XL, Cui XY, Huang YL, Ding H, Song JZ, et al: Tenuifolin, a saponin
derived from Radix Polygalae, exhibits sleep-enhancing effects in
mice. Phytomedicine. 23:1797–1805. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ling Y, Li Z, Chen M, Sun Z, Fan M and
Huang C: Analysis and detection of the chemical constituents of
Radix Polygalae and their metabolites in rats after oral
administration by ultra high-performance liquid chromatography
coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight
tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 85:1–13. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng MC, Li CY, Ko HC, Ko FN, Lin YL and
Wu TS: Antidepressant principles of the roots of Polygala
tenuifolia. J Nat Prod. 69:1305–1309. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shin EJ, Oh KW, Kim KW, Kwon YS, Jhoo JH,
Jhoo WK, Cha JY, Lim YK, Kim IS and Kim HC: Attenuation of
cocaine-induced conditioned place preference by Polygala
tenuifolia root extract. Life Sci. 75:2751–2764. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yao Y, Jia M, Wu JG, Zhang H, Sun LN, Chen
WS and Rahman K: Anxiolytic and sedative-hypnotic activities of
polygalasaponins from Polygala tenuifolia in mice. Pharm
Biol. 48:801–807. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee CI, Han JY, Hong JT and Oh KW:
3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid (TMCA), one of the constituents of
Polygalae Radix enhances pentobarbital-induced sleeping behaviors
via GABAAergic systems in mice. Arch Pharm Res. 36:1244–1251. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma B, Li X, Li J, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Yang X,
Sun J, Yao D, Liu L, Liu X and Ying H: Quantitative analysis of
tenuifolin concentrations in rat plasma and tissue using LC-MS/MS:
application to pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution study. J
Pharm Biomed Anal. 88:191–200. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wallace CK, Bright LA, Marx JO, Andersen
RP, Mullins MC and Carty AJ: Effectiveness of rapid cooling as a
method of euthanasia for young zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Am Assoc
Lab Anim Sci. 57:58–63. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
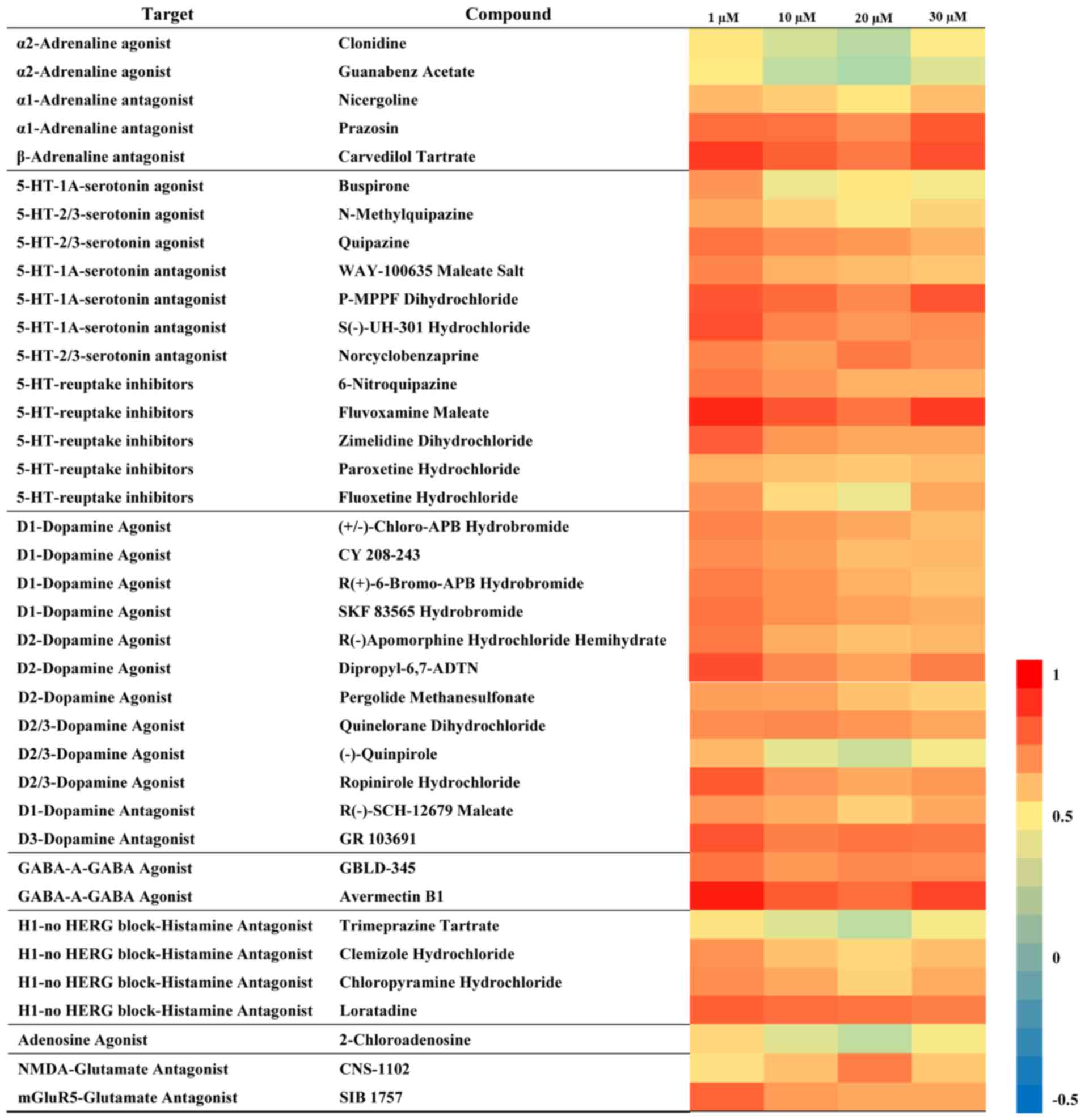
Wang YN, Hou YY, Sun MZ, Zhang CY, Bai G,
Zhao X and Feng XZ: Behavioural screening of zebrafish using
neuroactive traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions and
biological targets. Sci Rep. 4:53112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Melancon MO, Lorrain D and Dionne IJ:
Exercise and sleep in aging: Emphasis on serotonin. Pathol Biol
(Paris). 62:276–283. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dugovic C: Role of serotonin in sleep
mechanisms. Rev Neurol (Paris). 157:S16–S19. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heym J, Steinfels GF and Jacobs BL:
Activity of serotonin-containing neurons in the nucleus raphe
pallidus of freely moving cats. Brain Res. 251:259–276. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pastel RH and Fernstrom JD: Short-term
effects of fluoxetine and trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine on
electroencephalographic sleep in the rat. Brain Res. 436:92–102.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sommerfelt L and Ursin R: Behavioral,
sleep-waking and EEG power spectral effects following the two
specific 5-HT uptake inhibitors zimeldine and alaproclate in cats.
Behav Brain Res. 45:105–115. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Weber M, Talmon S, Schulze I, Boeddinghaus
C, Gross G, Schoemaker H and Wicke KM: Running wheel activity is
sensitive to acute treatment with selective inhibitors for either
serotonin or norepinephrine reuptake. Psychopharmacology (Berl).
203:753–762. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Airhart MJ, Lee DH, Wilson TD, Miller BE,
Miller MN and Skalko RG: Movement disorders and neurochemical
changes in zebrafish larvae after bath exposure to fluoxetine
(PROZAC). Neurotoxicol Teratol. 29:652–664. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jones BE: Neurobiology of waking and
sleeping. Handb Clin Neurol. 98:131–149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Holst SC and Landolt HP: Sleep-Wake
Neurochemistry. Sleep Med Clin. 13:137–146. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Richey SM and Krystal AD: Pharmacological
advances in the treatment of insomnia. Curr Pharm Des.
17:1471–1475. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Martin DL and Rimvall K: Regulation of
gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in the brain. J Neurochem.
60:395–407. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Soghomonian JJ and Martin DL: Two isoforms
of glutamate decarboxylase: Why? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 19:500–505.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hortopan GA, Dinday MT and Baraban SC:
Spontaneous seizures and altered gene expression in GABA signaling
pathways in a mind bomb mutant zebrafish. The J Neurosci.
30:13718–13728. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kang TC, Kim HS, Seo MO, Park SK, Kwon HY,
Kang JH and Won MH: The changes in the expressions of
gamma-aminobutyric acid transporters in the gerbil hippocampal
complex following spontaneous seizure. Neurosci Lett. 310:29–32.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Meldrum BS and Rogawski MA: Molecular
targets for antiepileptic drug development. Neurotherapeutics.
4:18–61. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen NH, Reith ME and Quick MW: Synaptic
uptake and beyond: The sodium- and chloride-dependent
neurotransmitter transporter family SLC6. Pflugers Arch.
447:519–531. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|