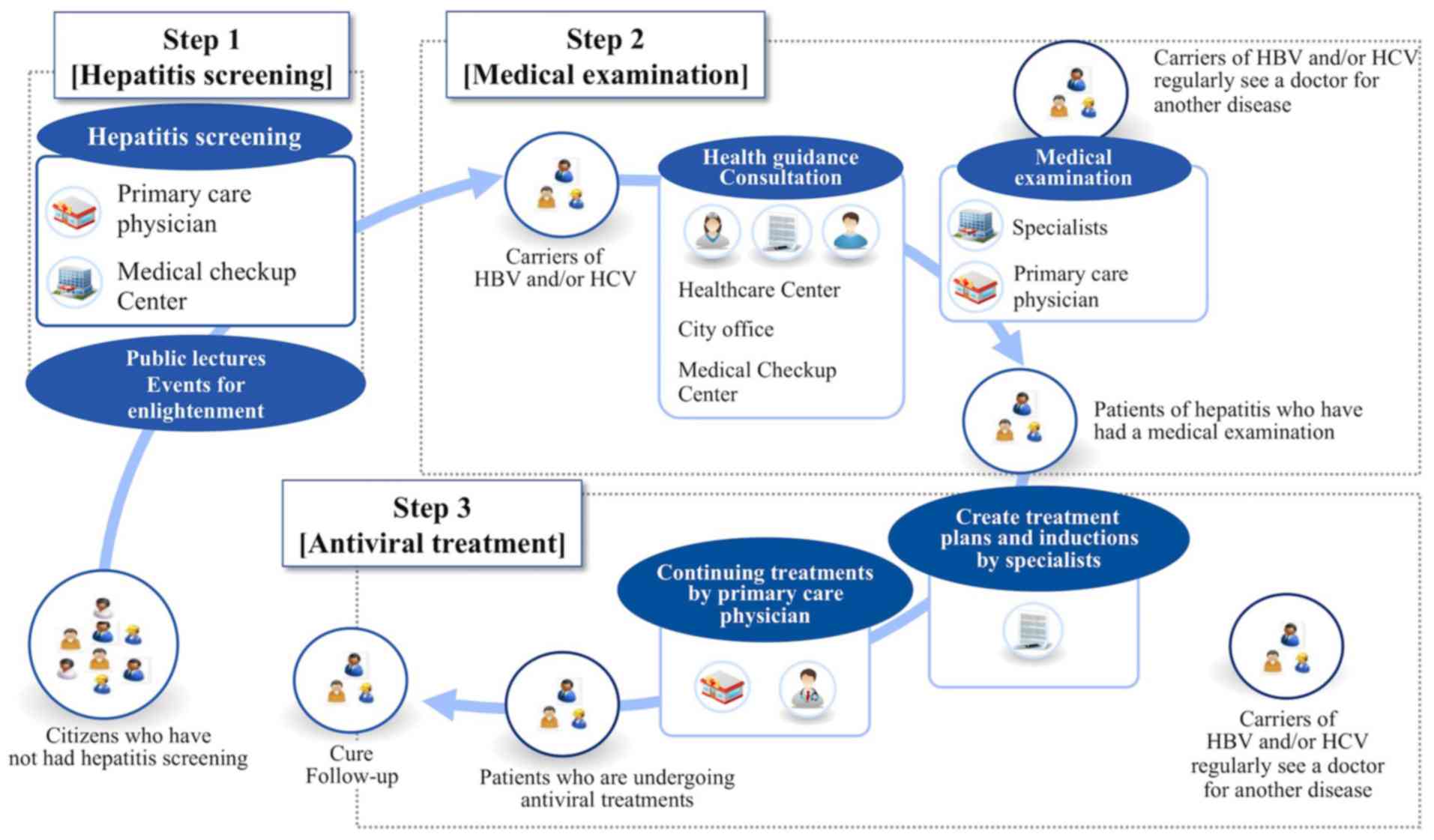
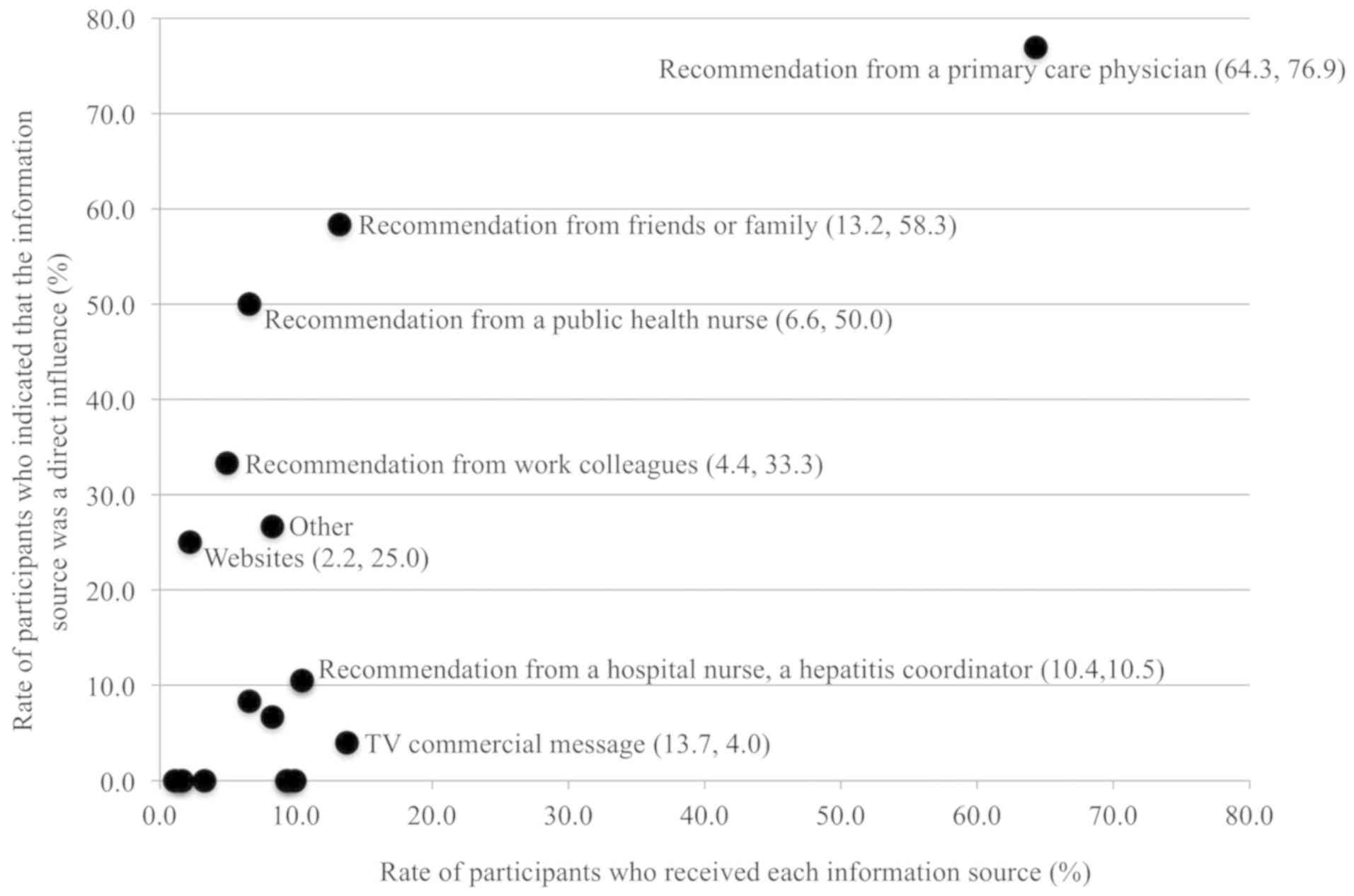
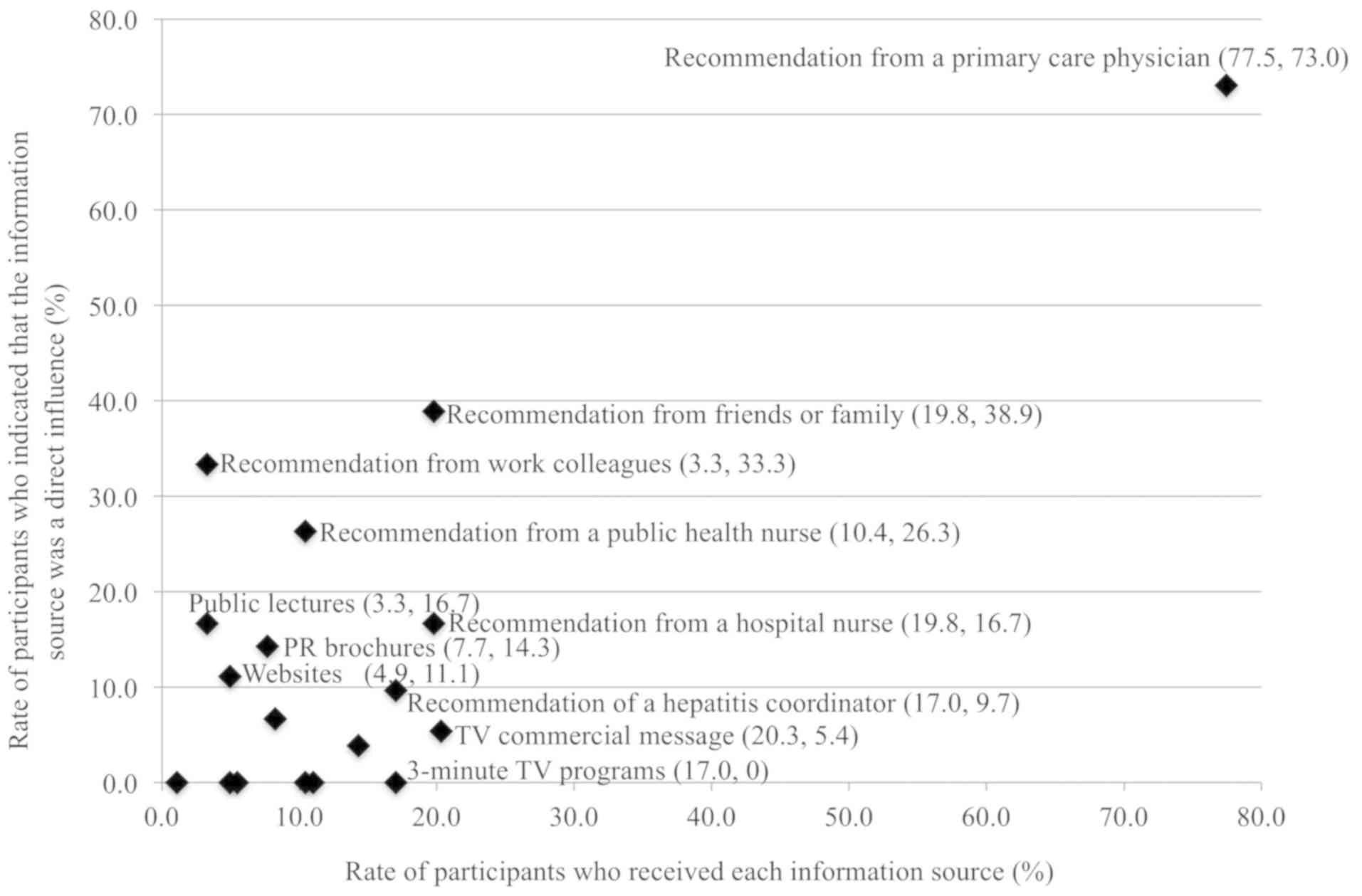
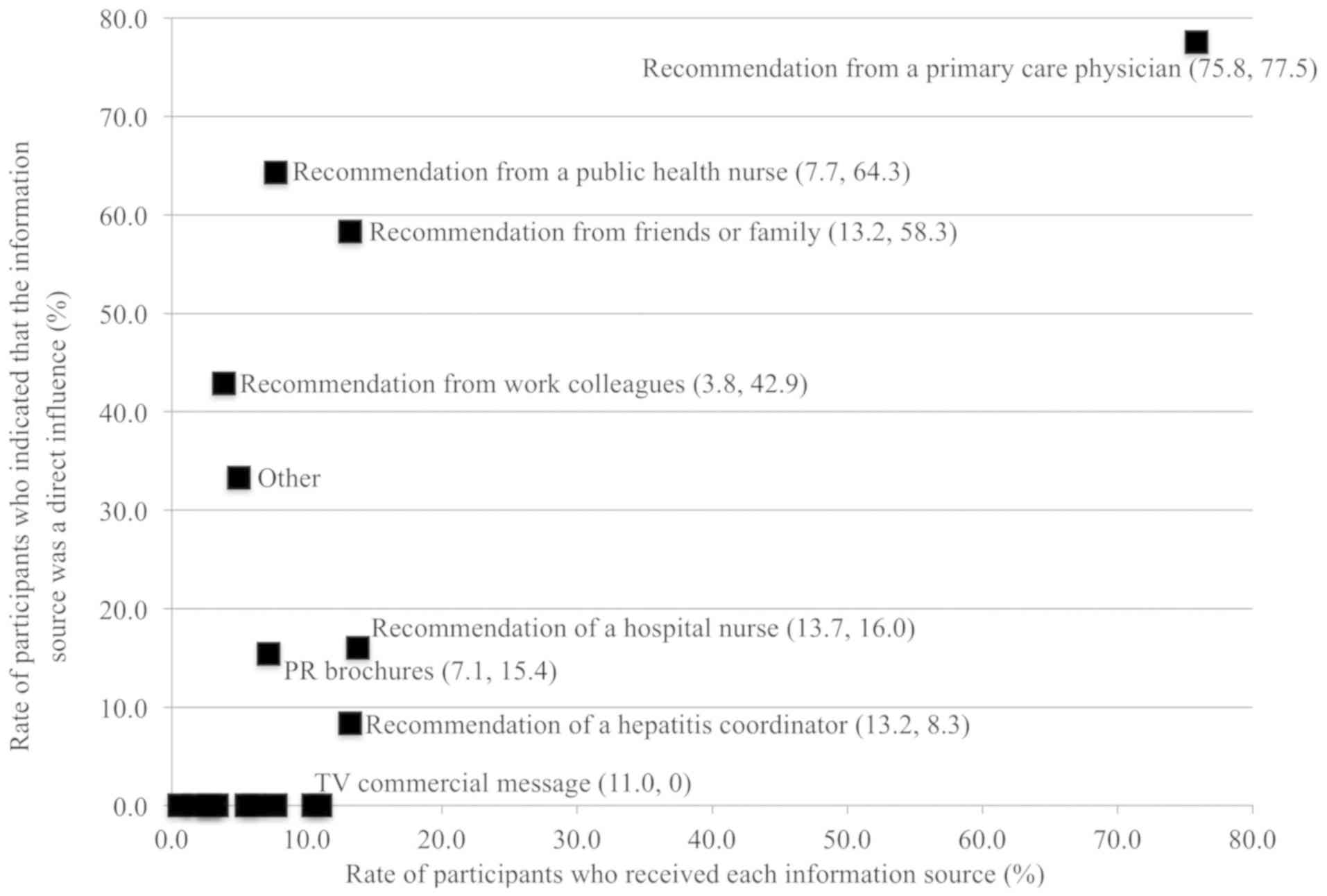
|
1
|
Kiyosawa K, Sodeyama T, Tanaka E, Gibo Y,
Yoshizawa K, Nakano Y, Furuta S, Akahane Y, Nishioka K, Purcell RH,
et al: Interrelationship of blood transfusion, non-A, non-B
hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis by detection of
antibody to hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 12:671–675.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fattovich G, Bortolotti F and Donato F:
Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: Special emphasis on disease
progression and prognostic factors. J Hepatol. 48:335–352.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ganem D and Prince AM: Hepatitis B virus
infection-natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med.
350:1118–1129. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cardoso AC, Moucari R, Figueiredo-Mendes
C, Ripault MP, Giuily N, Castelnau C, Boyer N, Asselah T,
Martinot-Peignoux M, Maylin S, et al: Impact of peginterferon and
ribavirin therapy on hepatocellular carcinoma: Incidence and
survival in hepatitis C patients with advanced fibrosis. J Hepatol.
52:652–657. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ikeda K, Saitoh S, Arase Y, Chayama K,
Suzuki Y, Kobayashi M, Tsubota A, Nakamura I, Murashima N, Kumada H
and Kawanishi M: Effect of interferon therapy on hepatocellular
carcinogenesis in patients with chronic hepatitis type C: A
long-term observation study of 1,643 patients using statistical
bias correction with proportional hazard analysis. Hepatology.
29:1124–1130. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kasahara A, Hayashi N, Mochizuki K,
Takayanagi M, Yoshioka K, Kakumu S, Iijima A, Urushihara A,
Kiyosawa K, Okuda M, et al: Risk factors for hepatocellular
carcinoma and its incidence after interferon treatment in patients
with chronic hepatitis C. Osaka Liver Disease Study Group.
Hepatology. 27:1394–1402. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kumada H, Suzuki Y, Ikeda K, Toyota J,
Karino Y, Chayama K, Kawakami Y, Ido A, Yamamoto K, Takaguchi K, et
al: Daclatasvir plus asunaprevir for chronic HCV genotype 1b
infection. Hepatology. 59:2083–2091. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zeuzem S, Dusheiko GM, Salupere R, Mangia
A, Flisiak R, Hyland RH, Illeperuma A, Svarovskala E, Brainard DM,
Symonds WT, et al: Sofosbuvir and ribavirin in HCV genotypes 2 and
3. N Engl J Med. 370:1993–2001. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Afdhal N, Zeuzem S, Kwo P, Chojkier M,
Gitlin N, Puoti M, Romero-Gomes M, Zarski JP, Agarwal K, Buggisch
P, et al: Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for untreated HCVgenotype 1
infection. N Engl J Med. 370:1889–1898. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Feld JJ, Kowdley KV, Coakley E, Sigal S,
Nelson DR, Crawford D, Weiland O, Aguilar H, Xiong J, Pilot-Matias
T, et al: Treatment of HCV with ABT-450/r-ombitasvir and dasabuvir
with ribavirin. N Engl J Med. 370:1594–1603. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Piratvisuth T, Lau G, Chao YC, Jin R,
Chutaputti A, Zhang QB, Tanwandee T, Button P and Popescu M:
Sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a (40 kD) with or without
lamivudine in Asian patients with HBeAg-positive and HBeAg-negative
chronic hepatitis. B Hepatol Int. 2:102–110. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ono A, Suzuki F, Kawamura Y, Sezaki H,
Hosaka T, Akuta N, Kobayashi M, Suzuki Y, Saitou S, Arase Y, et al:
Long-term continuous entecavir therapy in nucleos(t)ide-naive
chronic hepatitis B patients. J Hepatol. 57:508–514.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wong GL, Chan HL, Mak CW, Lee SK, Ip ZM,
Lam AT, Iu HW, Leung JM, Lai JW, Lo AO, et al: Entecavir treatment
reduces hepatic events and deaths in chronic hepatitis B patients
with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology. 58:1537–1547. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Marcellin P, Heathcote EJ, Buti M, Gane E,
de Man RA, Krastev Z, Germanidis G, Lee SS, Flisiak R, Kaita K, et
al: Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate versus adefovir dipivoxil for
chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 359:2442–2455. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Eguchi Y, Maeyama K, Ozaki I and Hrai K:
Medical system for liver disease treatment in response to basic act
on hepatitis measures. Nihon Naikagakkai Zasshi. 103:11–18.
2014.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
SagaPrefectural Government: Saga Liver
Disease Measures promotion Plan (In Japanese). Available at:
http://www.pref.saga.lg.jp/kiji00334103/3_34103_1_20134893825.pdf.
Accessed January 15, 2017.
|
|
17
|
Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare,
Japan. Investigation Committee for blood business sectional meeting
security technology 2011 first (In Japanese) Available at:
http://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/shingi/2r98520000020hlt.html.
Accessed January 15, 2017.
|
|
18
|
Cancer Information and Service National
Cancer Center Japan. Cancer Registry and Statistics (In Japanese).
Available at: http://ganjoho.jp/reg_stat/statistics/dl/index.html.
Accessed January 15, 2017.
|
|
19
|
Tateno Y, Miyazaki Y, Tsuboi S and Uehara
R: Can screening invitations from primary care physicians increase
participation in cancer screenings on remote islands? General
Medicine. 14:40–47. 2013.
|
|
20
|
Lacaille D and Pam R: Why are people with
rheumatoid arthritis (RA) not using DMARDs? Understanding gaps in
care. J Rheumatol. 46(1218)2008.
|
|
21
|
Penson DF: Factors influencing patients'
acceptance and adherence to active surveillance. J Natl Cancer Inst
Monogr. 2012:207–212. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
McAllister KA and Schmitt ML: Impact of a
nurse navigator on genomic testing and timely treatment decision
making in patients with breast cancer. Clin J Oncol Nurs.
19:510–512. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|