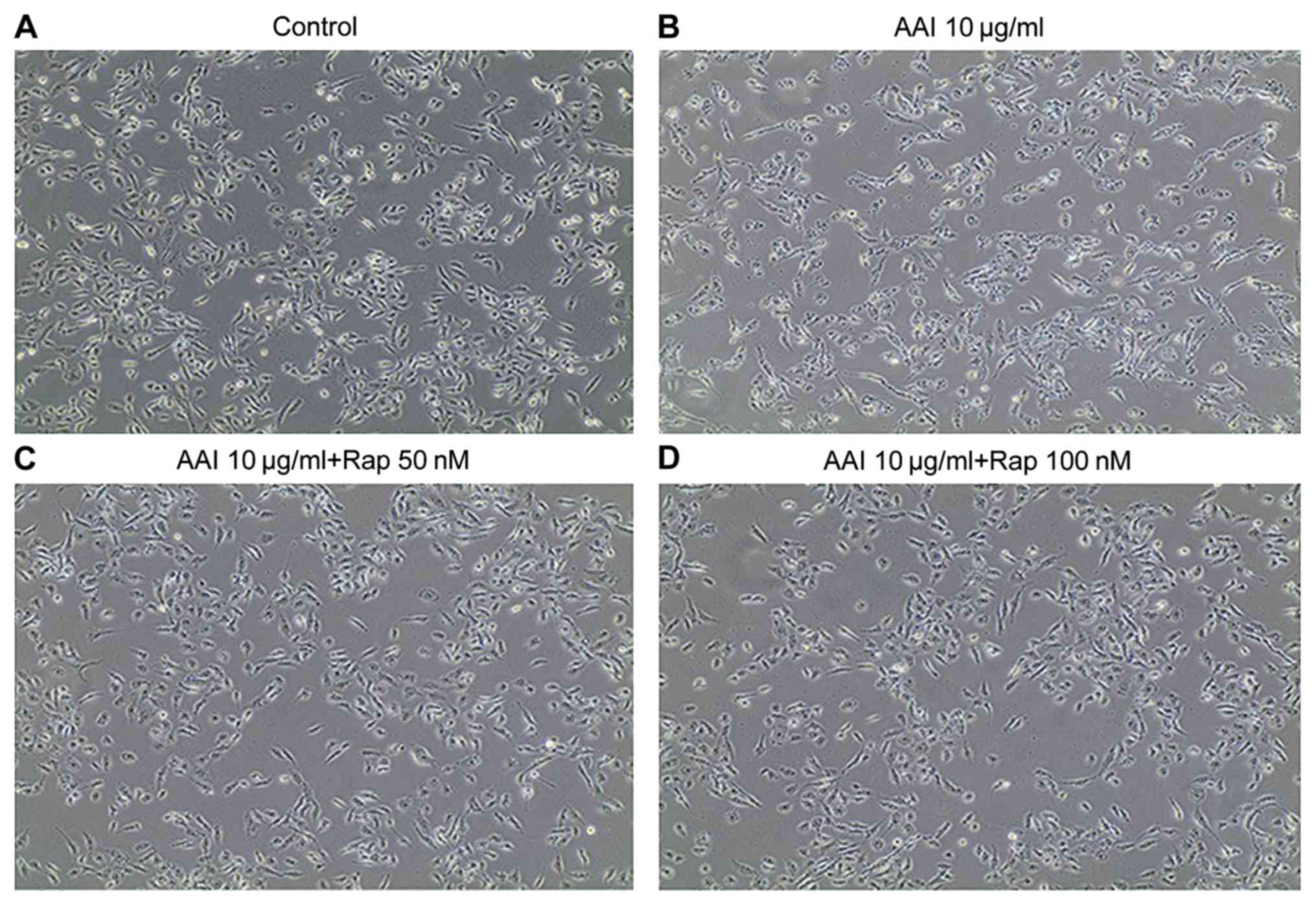
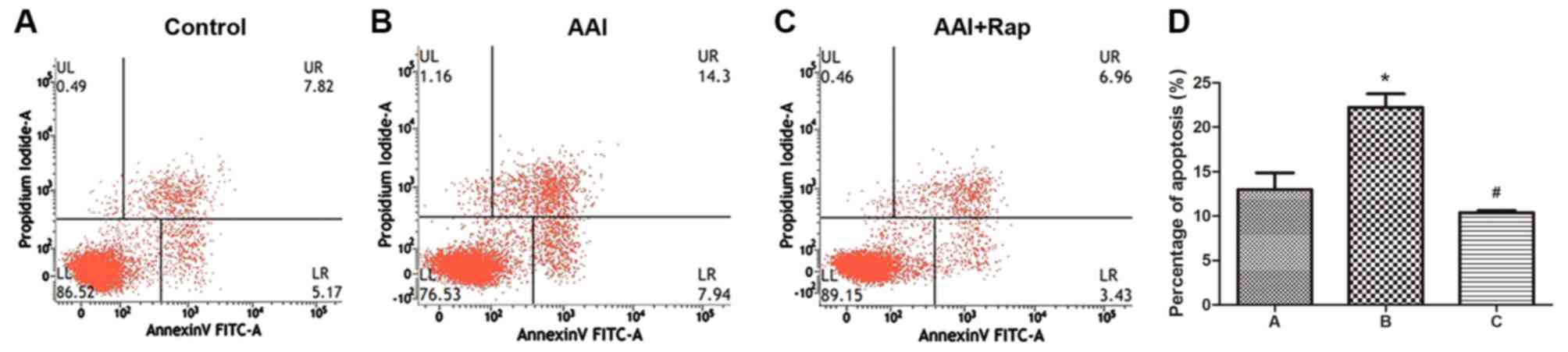
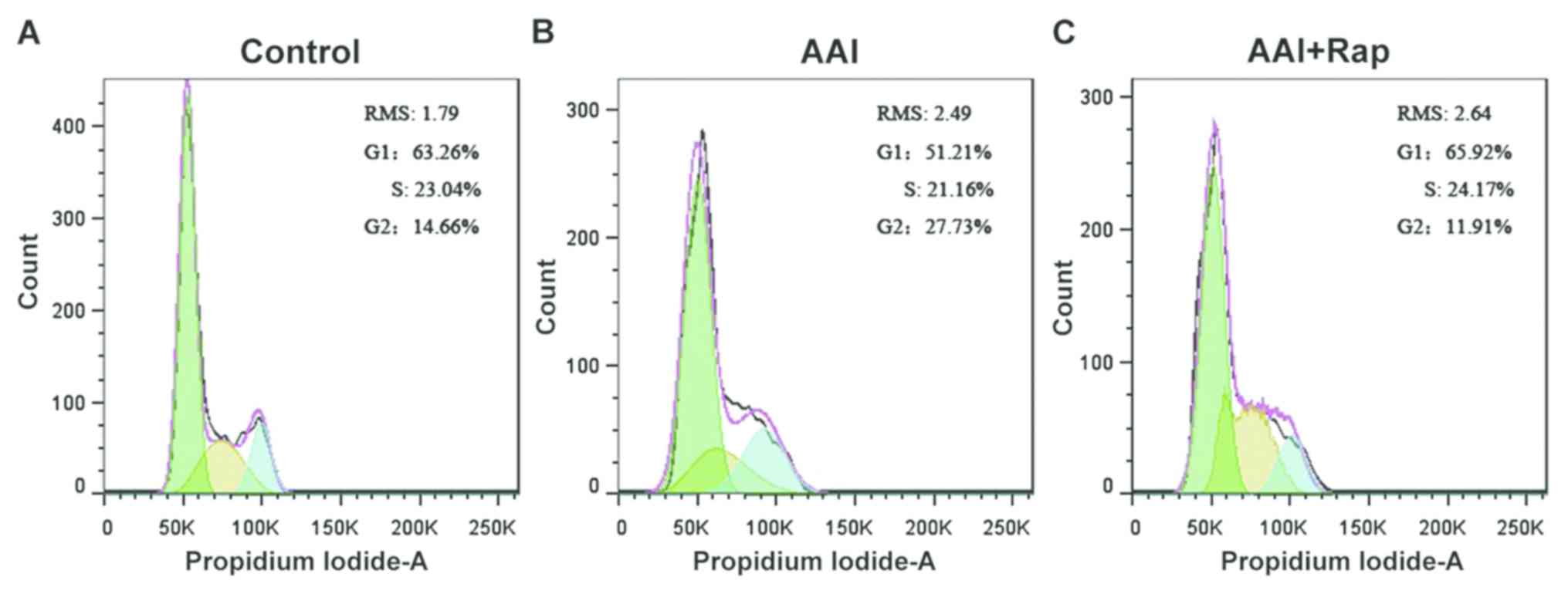
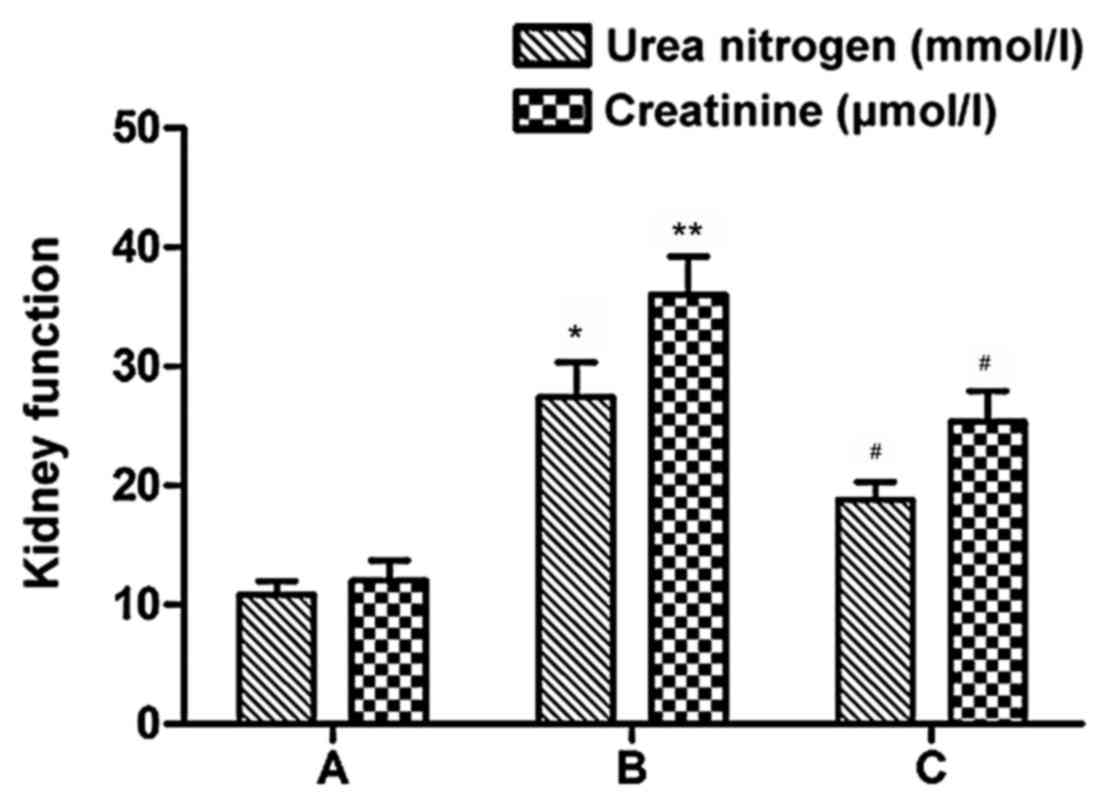
|
1
|
Vanherweghem JL, Depierreux M, Tielemans
C, Abramowicz D, Dratwa M, Jadoul M, Richard C, Vandervelde D,
Verbeelen D, Vanhaelen-Fastre R, et al: Rapidly progressive
interstitial renal fibrosis in young women: Association with
slimming regimen including Chinese herbs. Lancet. 341:387–391.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nortier JL, Martinez MC, Schmeiser HH,
Arlt VM, Bieler CA, Petein M, Depierreux MF, De Pauw L, Abramowicz
D, Vereerstraeten P and Vanherweghem JL: Urothelial carcinoma
associated with the use of a Chinese herb (Aristolochia fangchi). N
Engl J Med. 342:1686–1692. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Heinrich M, Chan J, Wanke S, Neinhuis C
and Simmonds MS: Local uses of Aristolochia species and content of
nephrotoxic aristolochic acid 1 and 2-a global assessment based on
bibliographic sources. J Ethnopharmacol. 125:108–144.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hamano Y, Aoki T, Shirai R, Hatano M,
Kimura R, Ogawa M, Yokosuka O and Ueda S: Low-dose darbepoetin
alpha attenuates progression of a mouse model of aristolochic acid
nephropathy through early tubular protection. Nephron Exp Nephrol.
114(e69-e81)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pozdzik AA, Salmon IJ, Husson CP,
Decaestecker C, Rogier E, Bourgeade MF, Deschodt-Lanckman MM,
Vanherweghem JL and Nortier JL: Patterns of interstitial
inflammation during the evolution of renal injury in experimental
aristolochic acid nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
23:2480–2491. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhou L, Fu P, Huang XR, Liu F, Lai KN and
Lan HY: Activation of p53 promotes renal injury in acute
aristolochic acid nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:31–41.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Arlt VM, Stiborova M and Schmeiser HH:
Aristolochic acid as a probable human cancer hazard in herbal
remedies: A review. Mutagenesis. 17:265–277. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Wang Z, Wang S, Zhao J, Zhang J and
Huang Y: Gremlin-mediated decrease in bone morphogenetic protein
signaling promotes aristolochic acid-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in HK-2 cells.
Toxicology. 297:68–75. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rui HL, Wang YY, Cheng H and Chen YP:
JNK-dependent AP-1 activation is required for aristolochic
acid-induced TGF-β1 synthesis in human renal proximal epithelial
cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 302(F1569-F1575)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wu CJ, Chou YC, Cheng YW, Hsiao CJ, Wang
CH, Wang HY, Sheu JR and Hsiao G: Aristolochic acid downregulates
monocytic matrix metalloproteinase-9 by inhibiting nuclear factor-κ
activation. Chem Biol Interact. 192:209–219. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hartford CM and Ratain MJ: Rapamycin:
Something old, something new, sometimes borrowed and now renewed.
Clin Pharmacol Ther. 82:381–388. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hay N and Sonenberg N: Upstream and
downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18:1926–1945. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang X and Proud CG: mTORC1 signaling:
What we still don't know. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:206–220.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Burnett PE, Barrow RK, Cohen NA, Snyder SH
and Sabatini DM: RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational
regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:1432–1437. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Brown EJ, Beal PA, Keith CT, Chen J, Shin
TB and Schreiber SL: Control of p70 s6 kinase by kinase activity of
FRAP in vivo. Nature. 377:441–446. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li J, Zhang M, Mao Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Peng
X and Yu F: The potential role of aquaporin 1 on aristolochic acid
I induced epithelial mesenchymal transition on HK-2 cells. J Cell
Physiol. 233:4919–4925. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kan WC, Hwang JY, Chuang LY, Guh JY, Ye
YL, Yang YL and Huang JS: Effect of osthole on advanced glycation
end products-induced renal tubular hypertrophy and role of klotho
in its mechanism of action. Phytomedicine. 53:205–212.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhou Q, Du J, Hu Z, Walsh K and Wang XH:
Evidence for adipose-muscle cross talk: Opposing regulation of
muscle proteolysis by adiponectin and Fatty acids. Endocrinology.
148:5696–5705. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dickman KG, Sweet DH, Bonala R, Ray T and
Wu A: Physiological and molecular characterization of aristolochic
acid transport by the kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 338:588–597.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ma DH, Zheng FL, Su Y, Li MX and Guo MH:
Influence and analysis of low-dosage steroid therapy in severe
aristolochic acid nephropathy patients. Nephrology (Carlton).
21:835–840. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Luciano RL and Perazella MA: Aristolochic
acid nephropathy: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and
treatment. Drug Saf. 38:55–64. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Stark GR and Taylor WR: Analyzing the G2/M
checkpoint. Methods Mol Biol. 280:51–82. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang L, Besschetnova TY, Brooks CR, Shah
JV and Bonventre JV: Epithelial cell cycle arrest in G2/M mediates
kidney fibrosis after injury. Nat Med. 16:535–543. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Buisson R, Niraj J, Rodrigue A, Ho CK,
Kreuzer J, Foo TK, Hardy EJ, Dellaire G, Haas W, Xia B, et al:
Coupling of homologous recombination and the checkpoint by ATR. Mol
Cell. 65:336–346. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Visconti R, Della Monica R and Grieco D:
Cell cycle checkpoint in cancer: A therapeutically targetable
double-edged sword. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35(153)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu MJ, Wen MC, Chiu YT, Chiou YY, Shu KH
and Tang MJ: Rapamycin attenuates unilateral ureteral
obstruction-induced renal fibrosis. Kidney Int. 69:2029–2036.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tian J, Wang Y, Liu X, Zhou X and Li R:
Rapamycin ameliorates IgA nephropathy via cell cycle-dependent
mechanisms. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 240:936–945. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Velagapudi C, Bhandari BS, Abboud-Werner
S, Simone S, Abboud HE and Habib SL: The tuberin/mTOR pathway
promotes apoptosis of tubular epithelial cells in diabetes. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 22:262–273. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu DD, Han CC, Wan HF, He F, Xu HY, Wei
SH, Du XH and Xu F: Effects of inhibiting PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway on
lipid metabolism homeostasis in goose primary hepatocytes. Animal.
10:1319–1327. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zeng R, Xiong Y, Zhu F, Ma Z, Liao W, He
Y, He J, Li W, Yang J, Lu Q, et al: Fenofibrate attenuated
glucose-induced mesangial cells proliferation and extracellular
matrix synthesis via PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2. PLoS One.
8(e76836)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Johnson A and DiPietro LA: Apoptosis and
angiogenesis: An evolving mechanism for fibrosis. FASEB J.
27:3893–3901. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Calastretti A, Bevilacqua A, Ceriani C,
Viganò S, Zancai P, Capaccioli S and Nicolin A: Damaged
microtubules can inactivate BCL-2 by means of the mTOR kinase.
Oncogene. 20:6172–6180. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
Regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shen YL, Sun L, Hu YJ, Liu HJ, Kuang XY,
Niu XL and Huang WY: P53 inhibitor pifithrin-alpha prevents the
renal tubular epithelial cells against injury. Am J Transl Res.
8:4040–4053. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bonventre JV: Dedifferentiation and
proliferation of surviving epithelial cells in acute renal failure.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 14 (Suppl 1)(S55-S61)2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gniadecki R, Hansen M and Wulf HC: Two
pathways for induction of apoptosis by ultraviolet radiation in
cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 109:163–169.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|