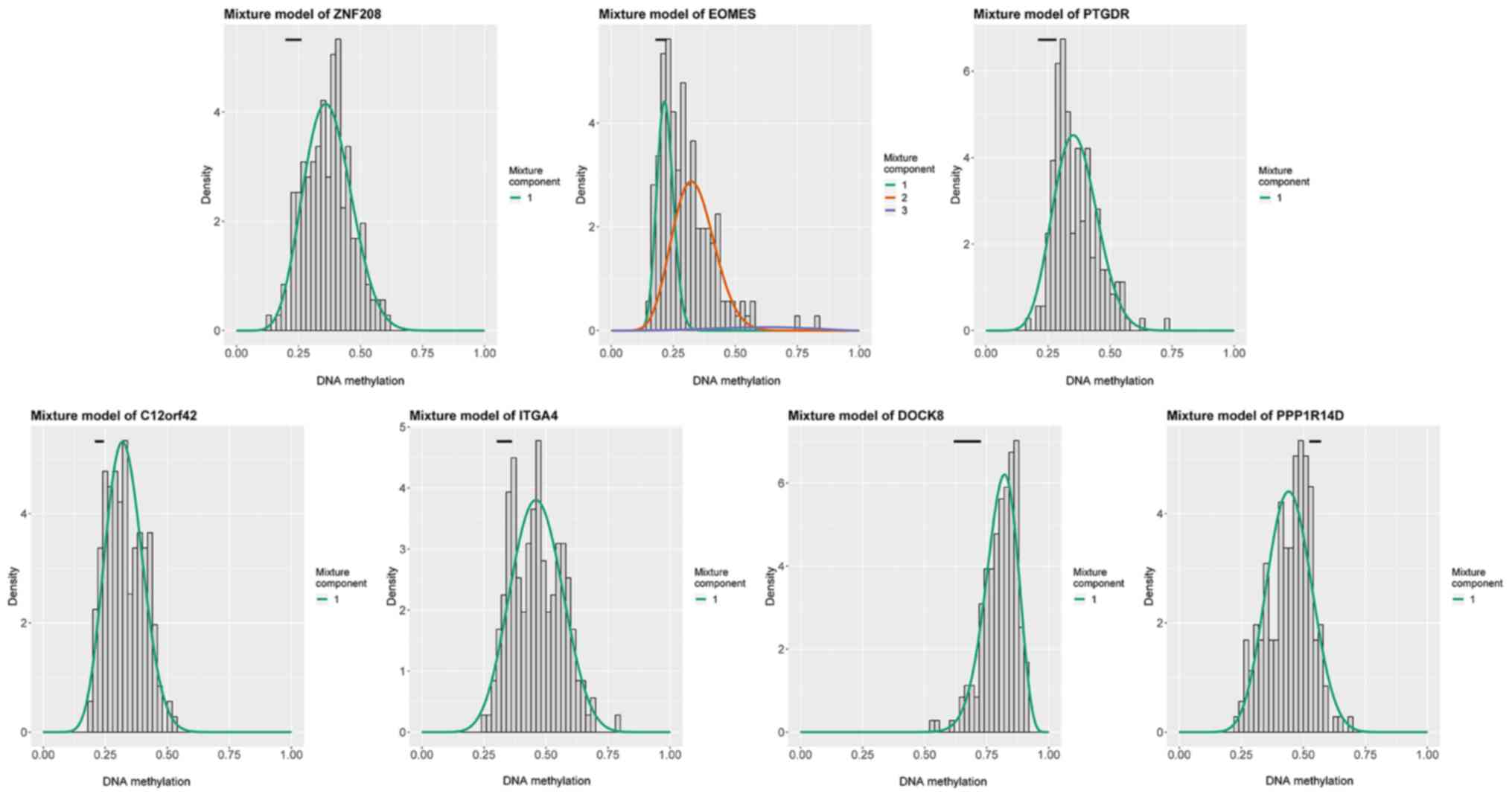
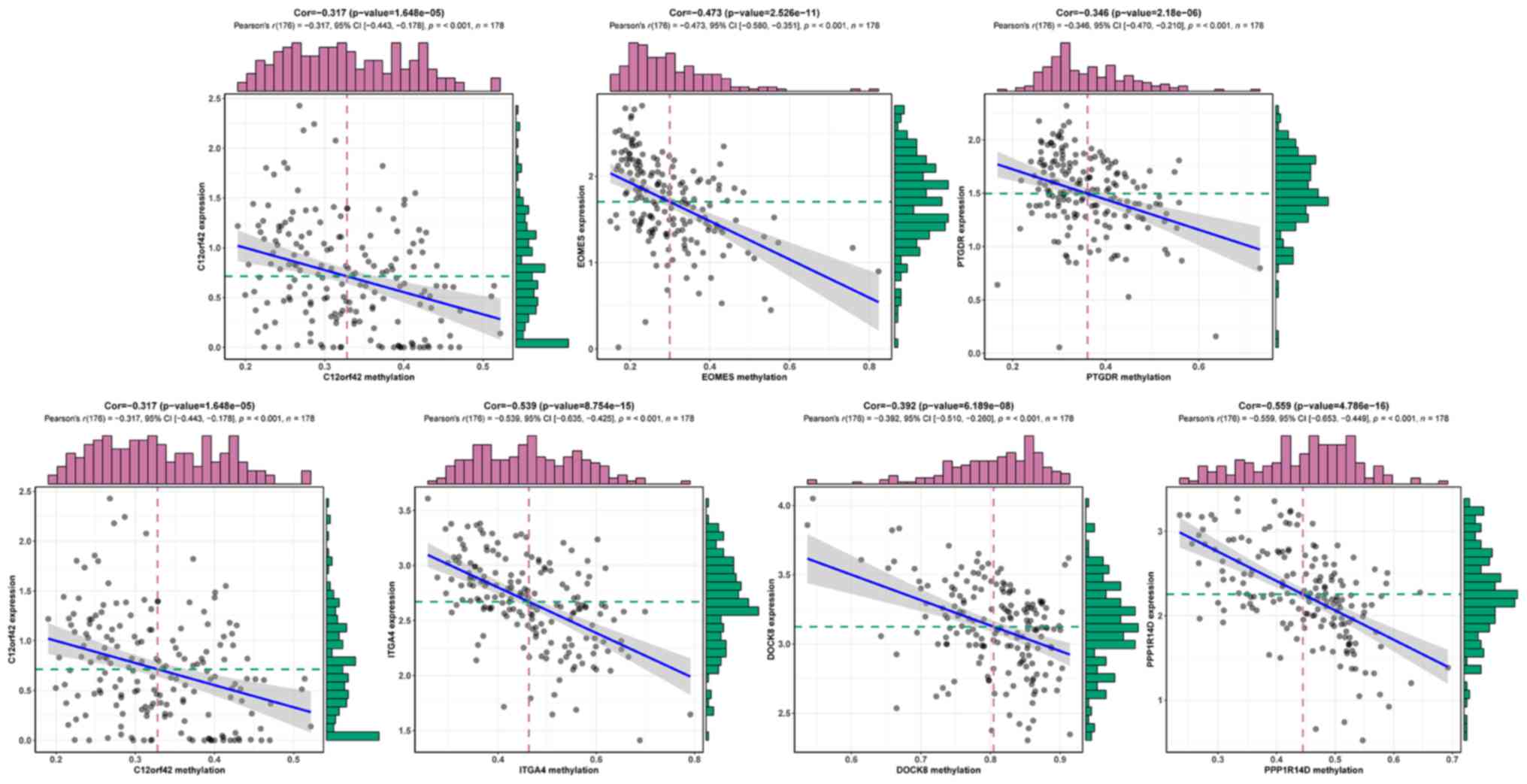
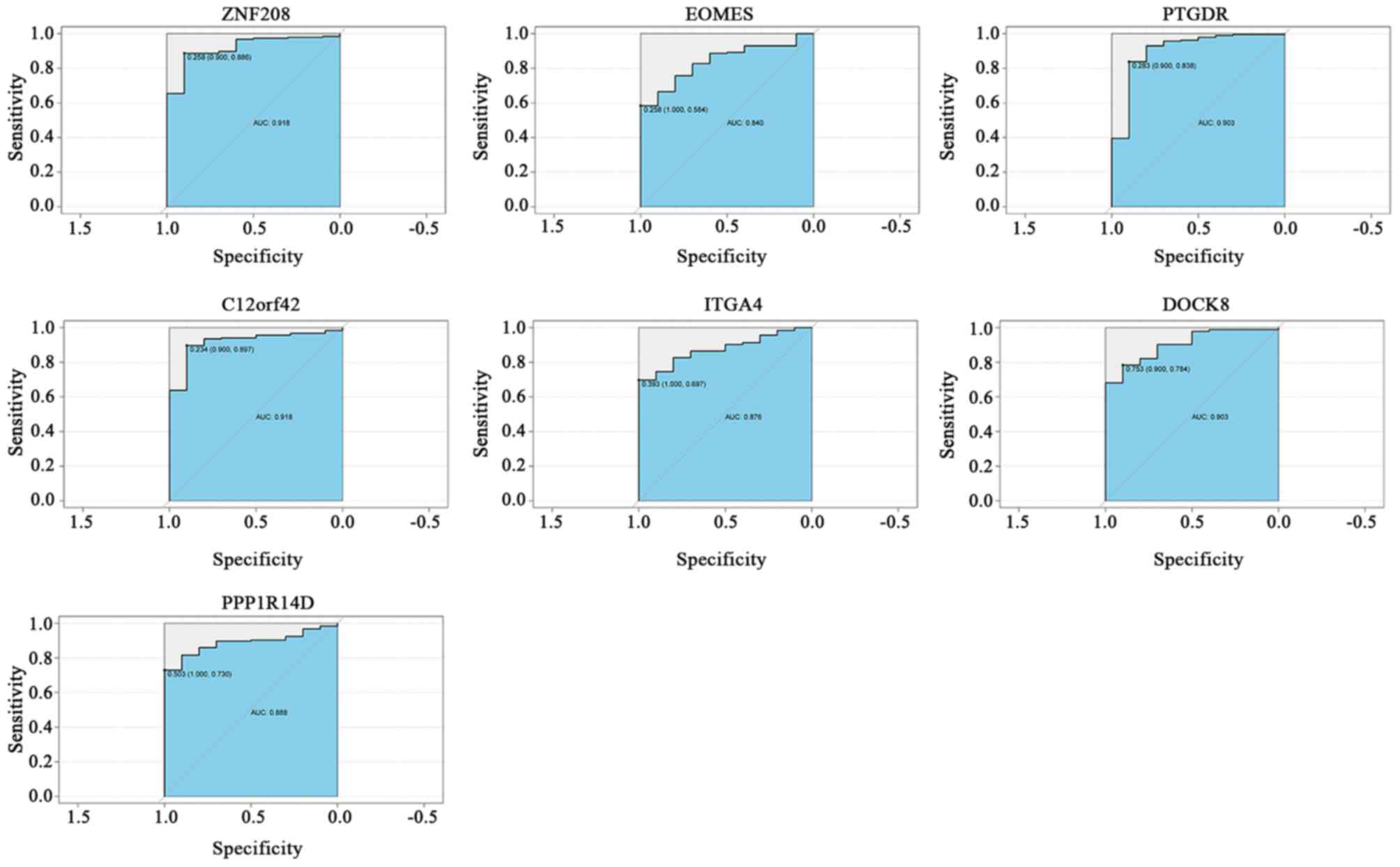
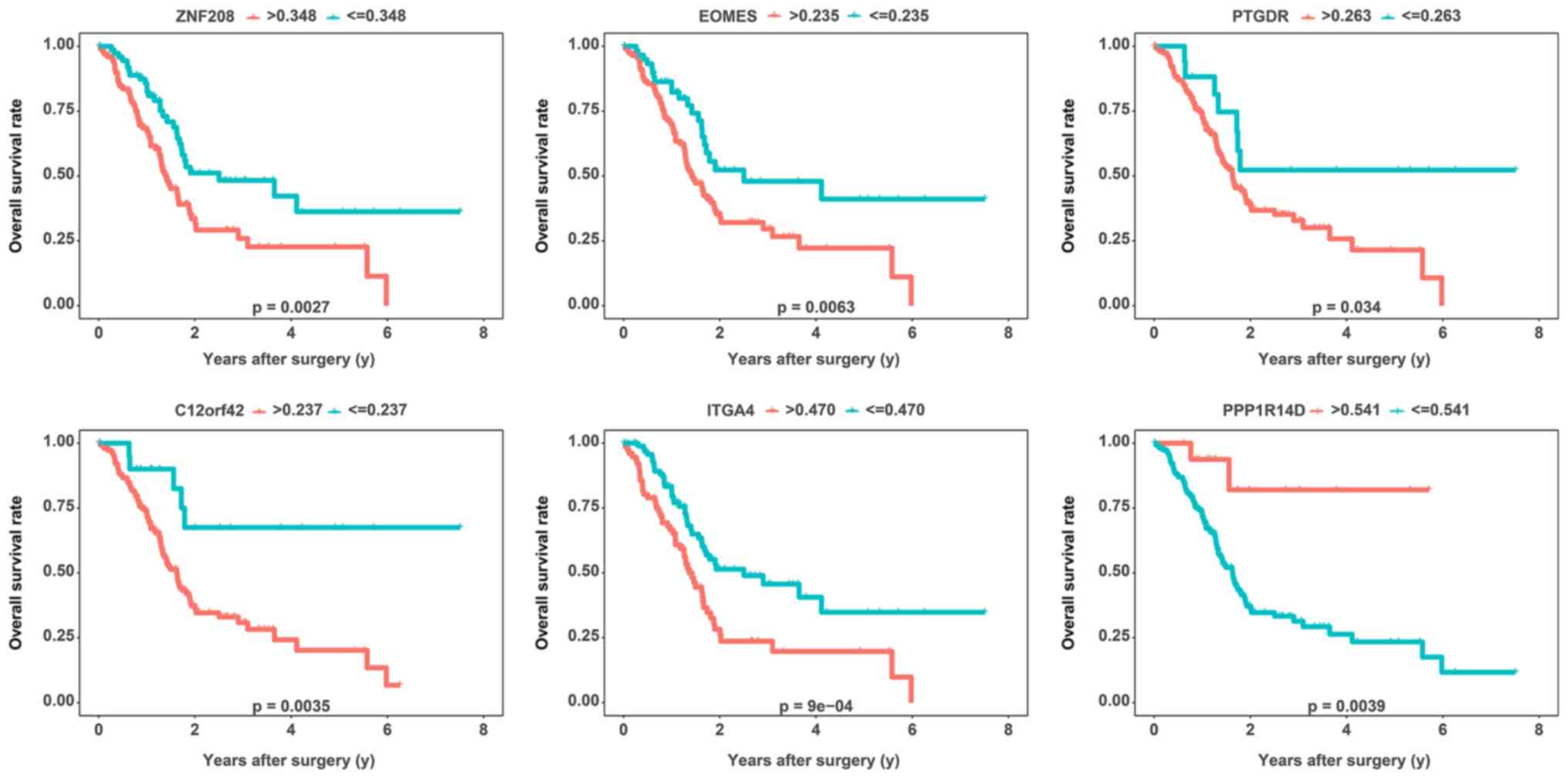
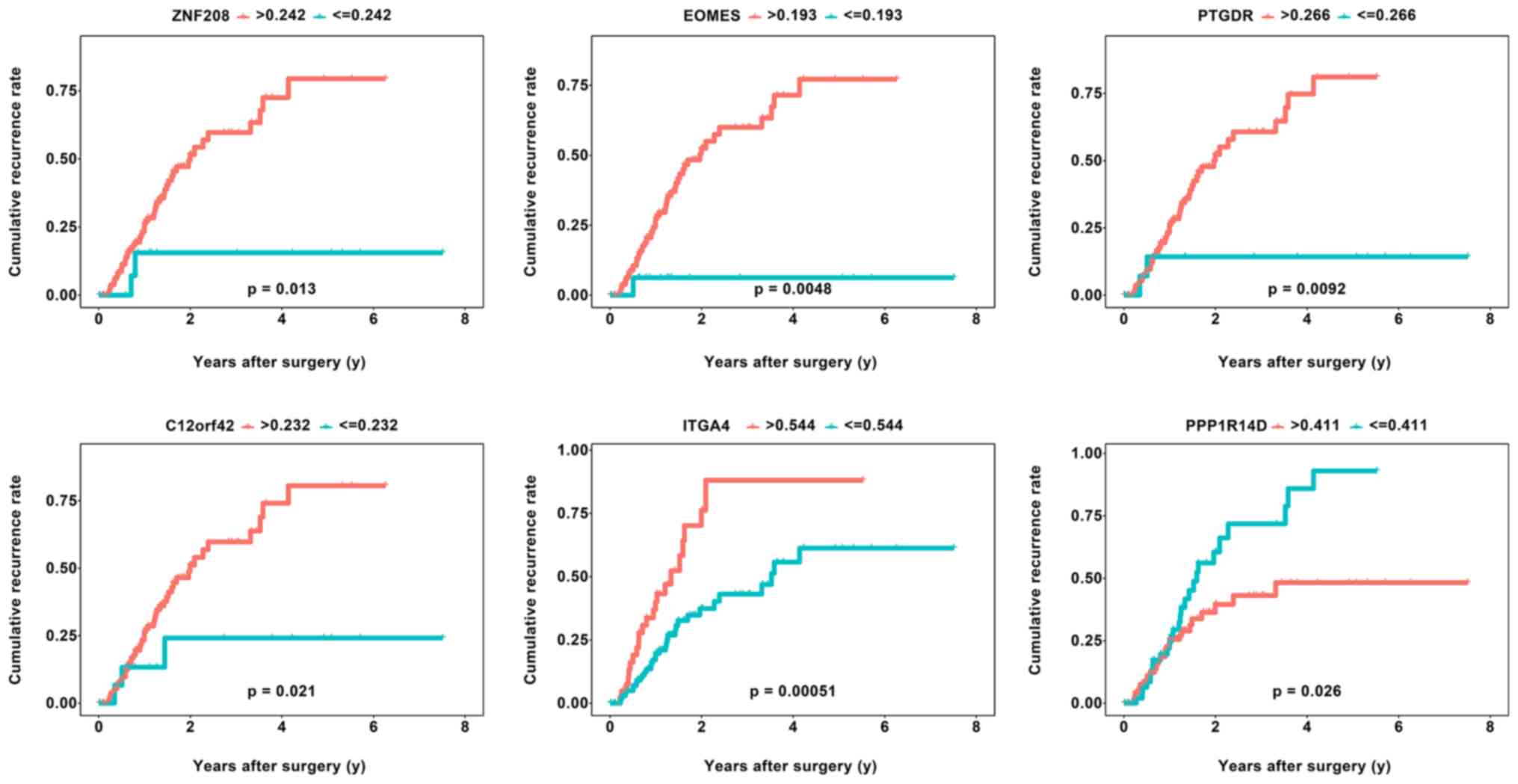
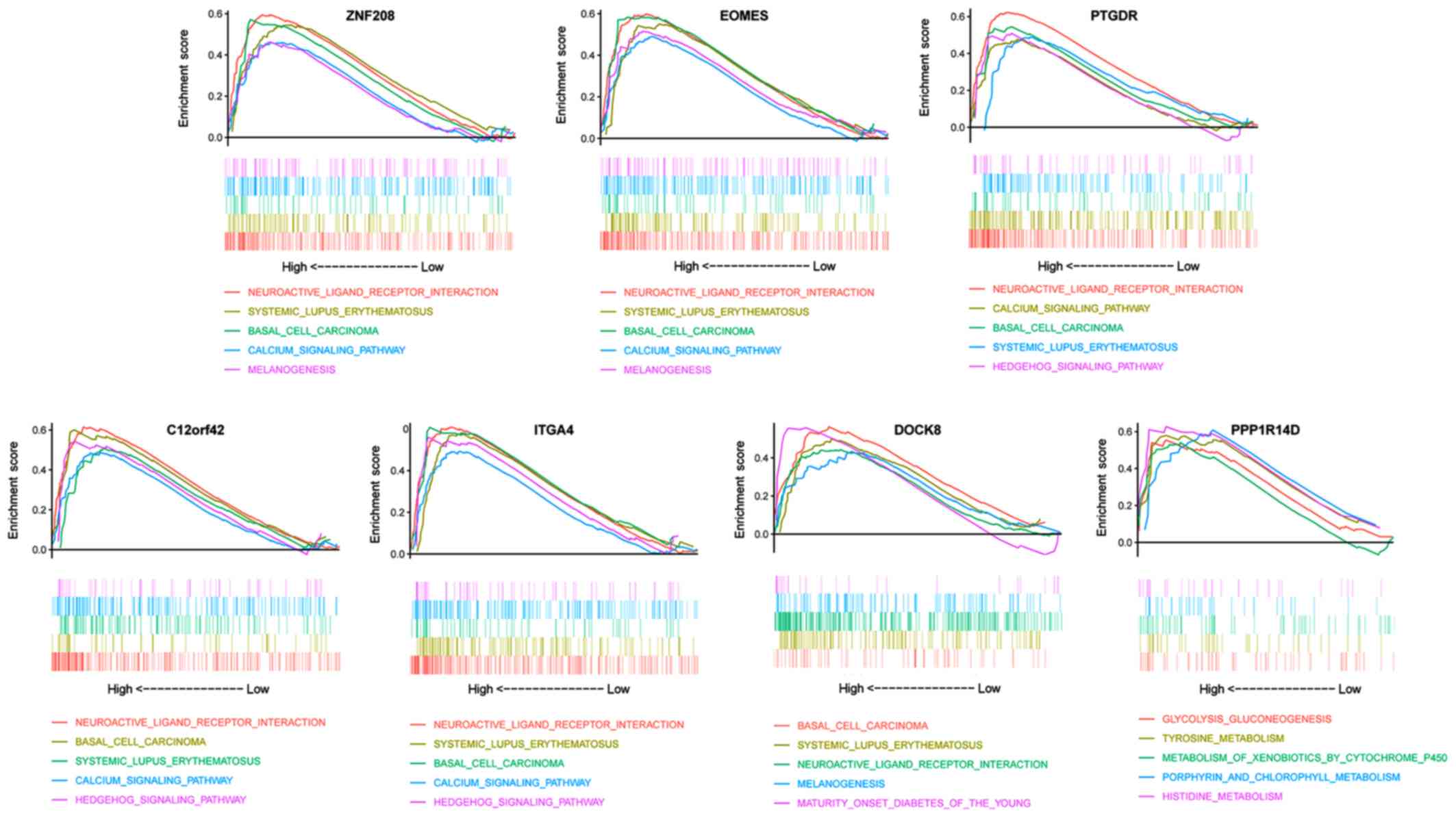
|
1
|
Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig
AB, Fleshman JM and Matrisian LM: Projecting cancer incidence and
deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and
pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 74:2913–2921.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Higuera O, Ghanem I, Nasimi R, Prieto I,
Koren L and Feliu J: Management of pancreatic cancer in the
elderly. World J Gastroenterol. 22:764–775. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Crippa S, Capurso G, Camma C, Fave GD,
Castillo CF and Falconi M: Risk of pancreatic malignancy and
mortality in branch-duct IPMNs undergoing surveillance: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 48:473–479.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chiaravalli M, Reni M and O'Reilly EM:
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: State-of-the-art 2017 and new
therapeutic strategies. Cancer Treat Rev. 60:32–43. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kota J, Hancock J, Kwon J and Korc M:
Pancreatic cancer: Stroma and its current and emerging targeted
therapies. Cancer Lett. 391:38–49. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Giovannetti E, van der Borden CL, Frampton
AE, Ali A, Firuzi O and Peters GJ: Never let it go: Stopping key
mechanisms underlying metastasis to fight pancreatic cancer. Semin
Cancer Biol. 44:43–59. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang ML, Lu S, Zhou L and Zheng SS:
Correlation between ECT2 gene expression and methylation change of
ECT2 promoter region in pancreatic cancer. Hepatobiliary Pancreat
Dis Int. 7:533–538. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jones PA: Functions of DNA methylation:
Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat Rev Genet.
13:484–492. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang M, Lv X, Jiang Y, Li G and Qiao Q:
Identification of aberrantly methylated differentially expressed
genes in glioblastoma multiforme and their association with patient
survival. Exp Ther Med. 18:2140–2152. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pan R, Zhou C, Dai J, Ying X, Yu H, Zhong
J, Zhang Y, Wu B, Mao Y, Wu D, et al: Endothelial PAS domain
protein 1 gene hypomethylation is associated with colorectal cancer
in Han Chinese. Exp Ther Med. 16:4983–4990. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kisiel JB, Raimondo M, Taylor WR, Yab TC,
Mahoney DW, Sun Z, Middha S, Baheti S, Zou H, Smyrk TC, et al: New
DNA methylation markers for pancreatic cancer: Discovery, tissue
validation, and pilot testing in pancreatic juice. Clin Cancer Res.
21:4473–4481. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pan FP, Zhou HK, Bu HQ, Chen ZQ, Zhang H,
Xu LP, Tang J, Yu QJ, Chu YQ, Pan J, et al: Emodin enhances the
demethylation by 5-Aza-CdR of pancreatic cancer cell
tumor-suppressor genes P16, RASSF1A and ppENK. Oncol Rep.
35:1941–1949. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Komazaki T, Nagai H, Emi M, Terada Y, Yabe
A, Jin E, Kawanami O, Konishi N, Moriyama Y, Naka T and Kishimoto
T: Hypermethylation-associated inactivation of the SOCS-1 gene, a
JAK/STAT inhibitor, in human pancreatic cancers. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
34:191–194. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang L, Gao J, Li Z and Gong Y: Neuronal
pentraxin II (NPTX2) is frequently down-regulated by promoter
hypermethylation in pancreatic cancers. Dig Dis Sci. 57:2608–2614.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Integrated Genomic Characterization of
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 32: 185-203.e113,
2017.
|
|
16
|
Cedoz PL, Prunello M, Brennan K and
Gevaert O: MethylMix 2.0: An R package for identifying DNA
methylation genes. Bioinformatics. 34:3044–3046. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cleveland P, Gill KR, Coe SG, Woodward TA,
Raimondo M, Jamil L, Gross SA, Heckman MG, Crook JE and Wallace MB:
An evaluation of risk factors for inadequate cytology in EUS-guided
FNA of pancreatic tumors and lymph nodes. Gastrointest Endosc.
71:1194–1199. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li L, Li C, Mao H, Du Z, Chan WY, Murray
P, Luo B, Chan AT, Mok TS, Chan FK, et al: Epigenetic inactivation
of the CpG demethylase TET1 as a DNA methylation feedback loop in
human cancers. Sci Rep. 6(26591)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Reis AH, Vargas FR and Lemos B: Biomarkers
of genome instability and cancer epigenetics. Tumour Biol.
37:13029–13038. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Thomas RK, Baker AC, Debiasi RM, Winckler
W, Laframboise T, Lin WM, Wang M, Feng W, Zander T, MacConaill L,
et al: High-throughput oncogene mutation profiling in human cancer.
Nat Genet. 39:347–351. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Schuebel KE, Chen W, Cope L, Glöckner SC,
Suzuki H, Yi JM, Chan TA, Van Neste L, Van Criekinge W, van den
Bosch S, et al: Comparing the DNA hypermethylome with gene
mutations in human colorectal cancer. PLoS Genet. 3:1709–1723.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Dammann R, Schagdarsurengin U, Liu L, Otto
N, Gimm O, Dralle H, Boehm BO, Pfeifer GP and Hoang-Vu C: Frequent
RASSF1A promoter hypermethylation and K-ras mutations in pancreatic
carcinoma. Oncogene. 22:3806–3812. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sato N, Fukushima N, Maitra A,
Matsubayashi H, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Hruban RH and Goggins M:
Discovery of novel targets for aberrant methylation in pancreatic
carcinoma using high-throughput microarrays. Cancer Res.
63:3735–3742. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ueki T, Walter KM, Skinner H, Jaffee E,
Hruban RH and Goggins M: Aberrant CpG island methylation in cancer
cell lines arises in the primary cancers from which they were
derived. Oncogene. 21:2114–2117. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fukushima N, Sato N, Ueki T, Rosty C,
Walter KM, Wilentz RE, Yeo CJ, Hruban RH and Goggins M: Aberrant
methylation of preproenkephalin and p16 genes in pancreatic
intraepithelial neoplasia and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Am
J Pathol. 160:1573–1581. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kumari A, Srinivasan R and Wig JD: Effect
of c-MYC and E2F1 gene silencing and of 5-azacytidine treatment on
telomerase activity in pancreatic cancer-derived cell lines.
Pancreatology. 9:360–368. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Nakamura TM, Morin GB, Chapman KB,
Weinrich SL, Andrews WH, Lingner J, Harley CB and Cech TR:
Telomerase catalytic subunit homologs from fission yeast and human.
Science. 277:955–959. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ojha J, Codd V, Nelson CP, Samani NJ,
Smirnov IV, Madsen NR, Hansen HM, de Smith AJ, Bracci PM, Wiencke
JK, et al: Genetic variation associated with longer telomere length
increases risk of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 25:1043–1049. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Codd V, Nelson CP, Albrecht E, Mangino M,
Deelen J, Buxton JL, Hottenga JJ, Fischer K, Esko T, Surakka I, et
al: Identification of seven loci affecting mean telomere length and
their association with disease. Nat Genet. 45422–427.
(427e1-2)2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Walsh KM, Codd V, Rice T, Nelson CP,
Smirnov IV, McCoy LS, Hansen HM, Elhauge E, Ojha J, Francis SS, et
al: Longer genotypically-estimated leukocyte telomere length is
associated with increased adult glioma risk. Oncotarget.
6:42468–42477. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Iles MM, Bishop DT, Taylor JC, Hayward NK,
Brossard M, Cust AE, Dunning AM, Lee JE, Moses EK, Akslen LA, et
al: The effect on melanoma risk of genes previously associated with
telomere length. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106(pii:
dju267)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang C, Doherty JA, Burgess S, Hung RJ,
Lindström S, Kraft P, Gong J, Amos CI, Sellers TA, Monteiro AN, et
al: Genetic determinants of telomere length and risk of common
cancers: A Mendelian randomization study. Hum Mol Genet.
24:5356–5366. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang J, Huang JY, Chen YN, Yuan F, Zhang
H, Yan FH, Wang MJ, Wang G, Su M, Lu G, et al: Whole genome and
transcriptome sequencing of matched primary and peritoneal
metastatic gastric carcinoma. Sci Rep. 5(13750)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fernandez-Zapico ME, Gonzalez-Paz NC,
Weiss E, Savoy DN, Molina JR, Fonseca R, Smyrk TC, Chari ST,
Urrutia R and Billadeau DD: Ectopic expression of VAV1 reveals an
unexpected role in pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell.
7:39–49. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Karthik D and Ravikumar S:
Characterization of the brain proteome of rats with diabetes
mellitus through two-dimensional electrophoresis and mass
spectrometry. Brain Res. 1371:171–179. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Rahn S, Zimmermann V, Viol F, Knaack H,
Stemmer K, Peters L, Lenk L, Ungefroren H, Saur D, Schäfer H and
Helm O: Diabetes as risk factor for pancreatic cancer:
Hyperglycemia promotes epithelial-mesenchymal-transition and stem
cell properties in pancreatic ductal epithelial cells. Cancer Lett.
415:129–150. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Jankowska AM, Millward CL and Caldwell CW:
The potential of DNA modifications as biomarkers and therapeutic
targets in oncology. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 15:1325–1337.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Heyn H and Esteller M: DNA methylation
profiling in the clinic: Applications and challenges. Nat Rev
Genet. 13:679–692. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Olkhov-Mitsel E and Bapat B: Strategies
for discovery and validation of methylated and hydroxymethylated
DNA biomarkers. Cancer Med. 1:237–260. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rivera CM and Ren B: Mapping human
epigenomes. Cell. 155:39–55. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bird A: DNA methylation patterns and
epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 16:6–21. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Razin A and Riggs AD: DNA methylation and
gene function. Science. 210:604–610. 1980.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tan K, Kajino K, Momose S, Masaoka A,
Sasahara K, Shiomi K, Izumi H, Abe M, Ohtsuji N, Wang T, et al:
Mesothelin (MSLN) promoter is hypomethylated in malignant
mesothelioma, but its expression is not associated with methylation
status of the promoter. Hum Pathol. 41:1330–1338. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Daskalos A, Nikolaidis G, Xinarianos G,
Savvari P, Cassidy A, Zakopoulou R, Kotsinas A, Gorgoulis V, Field
JK and Liloglou T: Hypomethylation of retrotransposable elements
correlates with genomic instability in non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Cancer. 124:81–87. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hama R, Watanabe Y, Shinada K, Yamada Y,
Ogata Y, Yoshida Y, Tamura T, Hiraishi T, Oikawa R, Sakurai J, et
al: Characterization of DNA hypermethylation in two cases of
peritoneal mesothelioma. Tumour Biol. 33:2031–2040. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Matsubayashi H, Canto M, Sato N, Klein A,
Abe T, Yamashita K, Yeo CJ, Kalloo A, Hruban R and Goggins M: DNA
methylation alterations in the pancreatic juice of patients with
suspected pancreatic disease. Cancer Res. 66:1208–1217.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Missiaglia E, Donadelli M, Palmieri M,
Crnogorac-Jurcevic T, Scarpa A and Lemoine NR: Growth delay of
human pancreatic cancer cells by methylase inhibitor
5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine treatment is associated with activation of
the interferon signalling pathway. Oncogene. 24:199–211.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Fenaux P, Mufti GJ, Hellstrom-Lindberg E,
Santini V, Finelli C, Giagounidis A, Schoch R, Gattermann N, Sanz
G, List A, et al: Efficacy of azacitidine compared with that of
conventional care regimens in the treatment of higher-risk
myelodysplastic syndromes: A randomised, open-label, phase III
study. Lancet Oncol. 10:223–232. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Silverman LR, McKenzie DR, Peterson BL,
Holland JF, Backstrom JT, Beach CL and Larson RA: Cancer and
Leukemia Group B: Further analysis of trials with azacitidine in
patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: Studies 8421, 8921, and
9221 by the Cancer and Leukemia Group B. J Clin Oncol.
24:3895–3903. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hirbe AC, Dahiya S, Miller CA, Li T,
Fulton RS, Zhang X, McDonald S, DeSchryver K, Duncavage EJ, Walrath
J, et al: Whole exome sequencing reveals the order of genetic
changes during malignant transformation and metastasis in a single
patient with NF1-plexiform neurofibroma. Clin Cancer Res.
21:4201–4211. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Walsh KM, Whitehead TP, de Smith AJ,
Smirnov IV, Park M, Endicott AA, Francis SS, Codd V, ENGAGE
Consortium Telomere Group , Samani NJ, et al: Common genetic
variants associated with telomere length confer risk for
neuroblastoma and other childhood cancers. Carcinogenesis.
37:576–582. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
O'Brien SM, Klampatsa A, Thompson JC,
Martinez MC, Hwang WT, Rao AS, Standalick JE, Kim S, Cantu E,
Litzky LA, et al: Function of human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res.
7:896–909. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Chang CC, Wang HC, Liao YP, Chen YC, Weng
YC, Yu MH and Lai HC: The feasibility of detecting endometrial and
ovarian cancer using DNA methylation biomarkers in cervical
scrapings. J Gynecol Oncol. 29(e17)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Przybylski GK, Dittmann K, Grabarczyk P,
Dölken G, Gesk S, Harder L, Landmann E, Siebert R and Schmidt CA:
Molecular characterization of a novel chromosomal translocation
t(12;14)(q23;q11.2) in T-lymphoblastic lymphoma between the T-cell
receptor delta-deleting elements (TRDREC and TRAJ61) and the
hypothetical gene C12orf42. Eur J Haematol. 85:452–456.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Duffy DL, Zhu G, Li X, Sanna M, Iles MM,
Jacobs LC, Evans DM, Yazar S, Beesley J, Law MH, et al: Novel
pleiotropic risk loci for melanoma and nevus density implicate
multiple biological pathways. Nat Commun. 9(4774)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Morandi L, Gissi D, Tarsitano A, Asioli S,
Gabusi A, Marchetti C, Montebugnoli L and Foschini MP: CpG location
and methylation level are crucial factors for the early detection
of oral squamous cell carcinoma in brushing samples using bisulfite
sequencing of a 13-gene panel. Clin Epigenetics.
9(85)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Lokk K, Vooder T, Kolde R, Välk K, Võsa U,
Roosipuu R, Milani L, Fischer K, Koltsina M, Urgard E, et al:
Methylation markers of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS
One. 7(e39813)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|