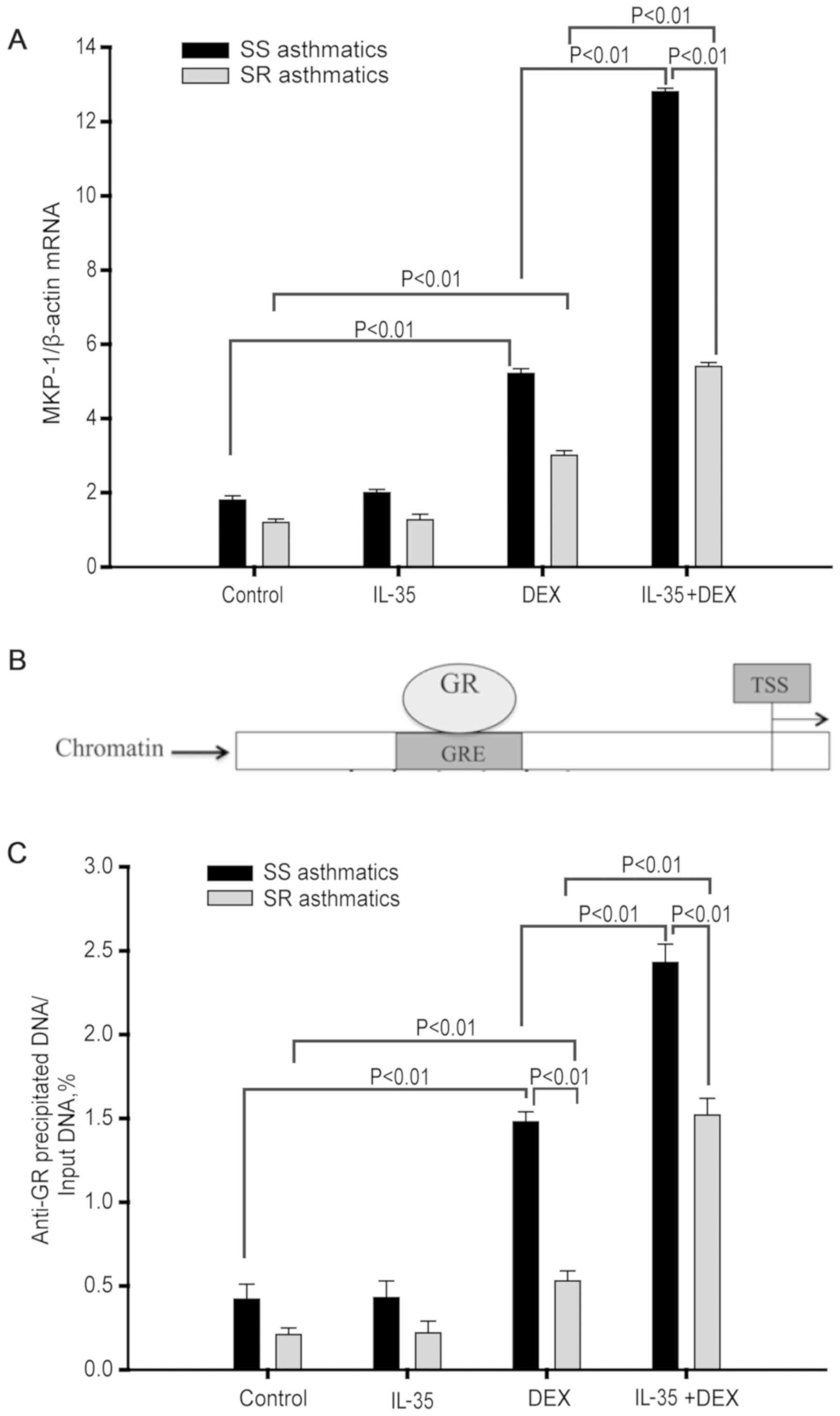
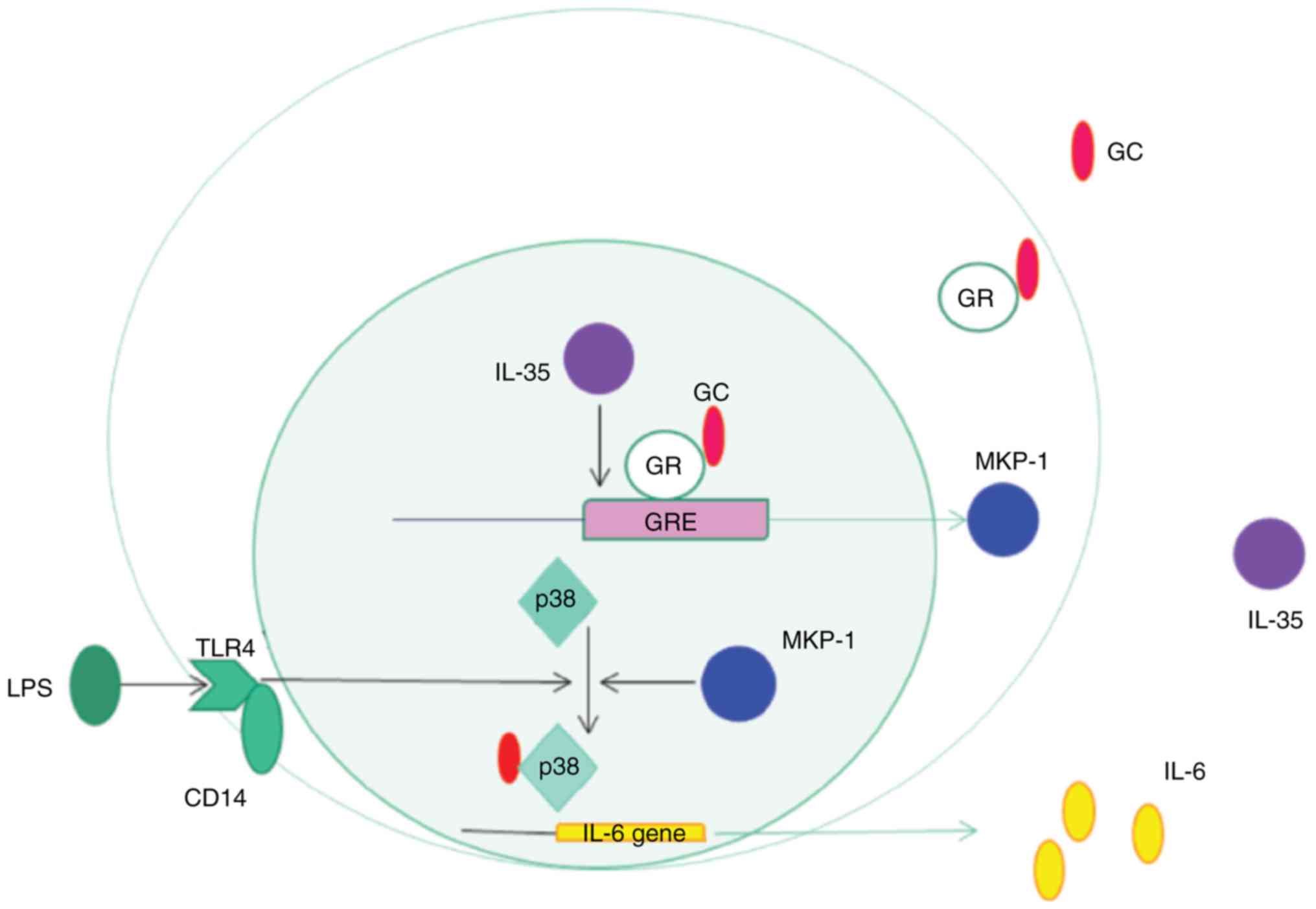
|
1
|
Zervas E, Samitas K, Papaioannou AI,
Bakakos P, Loukides S and Gaga M: An algorithmic approach for the
treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma. ERJ Open Res.
4:00125–2017. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fang SB, Zhang HY, Jiang AY, Fan XL, Lin
YD, Li CL, Wang C, Meng XC and Fu QL: Human iPSC-MSCs prevent
steroid-resistant neutrophilic airway inflammation via modulating
Th17 phenotypes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9(147)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lea S, Harbron C, Khan N, Booth G,
Armstrong J and Singh D: Corticosteroid insensitive alveolar
macrophages from asthma patients; synergistic interaction with a
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 79:756–766. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li JJ, Wang W, Baines KJ, Bowden NA,
Hansbro PM, Gibson PG, Kumar RK, Foster PS and Yang M: IL-27/IFN-γ
induce MyD88-dependent steroid-resistant airway hyperresponsiveness
by inhibiting glucocorticoid signaling in macrophages. J Immunol.
185:4401–4409. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Baines KJ, Backer V, Gibson PG, Powel H
and Porsbjerg CM: Impaired lung function is associated with
systemic inflammation and macrophage activation. Eur Respir J.
45:557–559. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yuryeva K, Saltykova I, Ogorodova L,
Kirillova N, Kulikov E, Korotkaya E, Iakovleva Y, Feoktistov I,
Sazonov A and Ryzhov S: Expression of adenosine receptors in
monocytes from patients with bronchial asthma. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:1314–1320. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Plantinga M, Guilliams M, Vanheerswynghels
M, Deswarte K, Branco-Madeira F, Toussaint W, Vanhoutte L, Neyt K,
Killeen N, Malissen B, et al: Conventional and monocyte-derived
CD11b(+) dendritic cells initiate and Maintain T helper
2cell-mediated immunity to house dust mite allergen. Immunity.
38:322–335. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li LB, Leung DY and Goleva E: Activated
p38 MAPK in peripheral blood monocytes of steroid resistant
asthmatic patients. PLoS One. 10(e0141909)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nixon M, Andrew R and Chapman KE: It takes
two to tango: Dimerisation of glucocorticoid receptor and its
anti-inflammatory functions. Steroids. 78:59–68. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kassel O, Sancono A, Krätzschmar J, Kreft
B, Stassen M and Cato AC: Glucocorticoids inhibit MAP kinase via
increased expression and decreased degradation of MKP-1. EMBO J.
20:7108–7116. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Owens DM and Keyse SM: Differential
regulation of MAP kinase signalling by dual-specificity protein
phosphatases. Oncogene. 26:3203–3213. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bhavsar P, Khorasani N, Hew M, Johnson M
and Chung KF: Effect of p38 MAPK Inhibition on corticosteroid
suppression of cytokine release in severe asthma. Eur Respir J.
35:750–756. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mercado N, Hakim A, Kobayashi Y, Meah S,
Usmani OS, Chung KF, Barnes PJ and Ito K: Restoration of
corticosteroid sensitivity by p38 mitogen activated protein kinase
inhibition in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from severe
asthma. PLoS One. 7(e41582)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ma Y, Chen L, Xie G, Zhou Y, Yue C, Yuan
X, Zheng Y, Wang W, Deng L and Shen L: Elevated level of
interleukin-35 in colorectal cancer induces conversion of T cells
into iTr35 by activating STAT1/STAT3. Oncotarget. 7:73003–73015.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Whitehead GS, Wilson RH, Nakano K, Burch
LH, Nakano H and Cook DN: IL-35 production by inducible
costimulator (ICOS)-positive regulatory T cells reverses
established IL-17-dependent allergic airways disease. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 129:207–215.e1-e5. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhao H, Liao XL and Kang Y: Tregs: Where
we are and what comes next? Front Immunol. 8(1578)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Pan X, Peng X, Li S, Zhou Y, Zheng X
and Li M: Adenovirus-mediated interleukin-35 gene transfer
suppresses allergic airway inflammation in a murine model of
asthma. Inflamm Res. 64:767–774. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dong J, Wong CK, Cai Z, Jiao D, Chu M and
Lam CW: Amelioration of allergic airway inflammation in mice by
regulatory IL-35 through dampening inflammatory dendritic cells.
Allergy. 70:921–932. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Collison LW, Chaturvedi V, Henderson AL,
Giacomin PR, Guy C, Bankoti J, Finkelstein D, Forbes K, Workman CJ,
Brown SA, et al: IL-35-mediated induction of a potent regulatory T
cell population. Nat Immunol. 11:1093–1101. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jiang H, Chi X, Zhang X and Wang J:
Increased serum VDBP as a risk predictor for steroid resistance in
asthma patients. Respir Med. 114:111–116. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
De Almeida MC, Silva AC, Barral A and
Barral Netto M: A simple method for human peripheral blood monocyte
isolation. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 95:221–223. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tchen CR, Martins JR, Paktiawal N, Perelli
R, Saklatvala J and Clark AR: Glucocorticoid regulation of mouse
and human dual specificity phosphatase 1 (DUSP1) genes: Unusual
cis-acting elements and unexpected evolutionary divergence. J Biol
Chem. 285:2642–2652. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ma Y, Liu X, Wei Z, Wang X, Xu D, Dai S,
Li Y, Gao M, Ji C, Guo C, et al: The expression of a novel
anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-35 and its possible significance in
childhood asthma. Immunol Lett. 162:11–17. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang W, Li P, Chen YF and Yang J: A
potential immunopathogenic role for reduced IL-35 expression in
allergic asthma. J Asthma. 52:763–771. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim RY, Pinkerton JW, Essilfie AT,
Robertson AAB, Baines KJ, Brown AC, Mayall JR, Ali MK, Starkey MR,
Hansbro NG, et al: Role for NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated,
IL-1β-dependent responses in severe, steroid-resistant asthma. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 196:283–297. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Leung DYM and Goleva E:
Anti-inflammatory and corticosteroid-enhancing actions of vitamin D
in monocytes of patients with steroid-resistant and those with
steroid-sensitive asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 133:1744–1752.e1.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lee HJ, Ko HJ, Song DK and Jung YJ:
Lysophosphatidylcholine promotes phagosome maturation and regulates
inflammatory mediator production through the protein kinase
a-phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase-p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase signaling pathway during mycobacterium tuberculosis
infection in mouse macrophages. Front Immunol.
9(920)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sha X, Meng S, Li X, Xi H, Maddaloni M,
Pascual DW, Shan H, Jiang X, Wang H and Yang XF: Interleukin-35
inhibits endothelial cell activation by suppressing MAPK-AP-1
pathway. J Biol Chem. 290:19307–19318. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ramamoorthy S and Cidlowski JA: Exploring
the molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid receptor action from
sensitivity to resistance. Endocr Dev. 24:41–56. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Moosavi SM, Prabhala P and Ammit AJ: Role
and regulation of MKP-1 in airway inflammation. Respir Res.
18(154)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xie SJ, Li JH, Chen HF, Tan YY, Liu SR,
Zhang Y, Xu H, Yang JH, Liu S, Zheng LL, et al: Inhibition of the
JNK/MAPK signaling pathway by myogenesis-associated miRNAs is
required for skeletal muscle development. Cell Death Differ.
25:1581–1597. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang ZK, Dou M, Liu FJ, Jiang P, Ye SL, Ma
L, Cao HJ, Du X, Sun P, Su N, et al: GDF11 induces differentiation
and apoptosis and inhibits migration of C17.2 neural stem cells via
modulating MAPK signaling pathway. PeerJ. 6(e5524)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhao ST and Wang CZ: Regulatory T cells
and asthma. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 19:663–673. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|