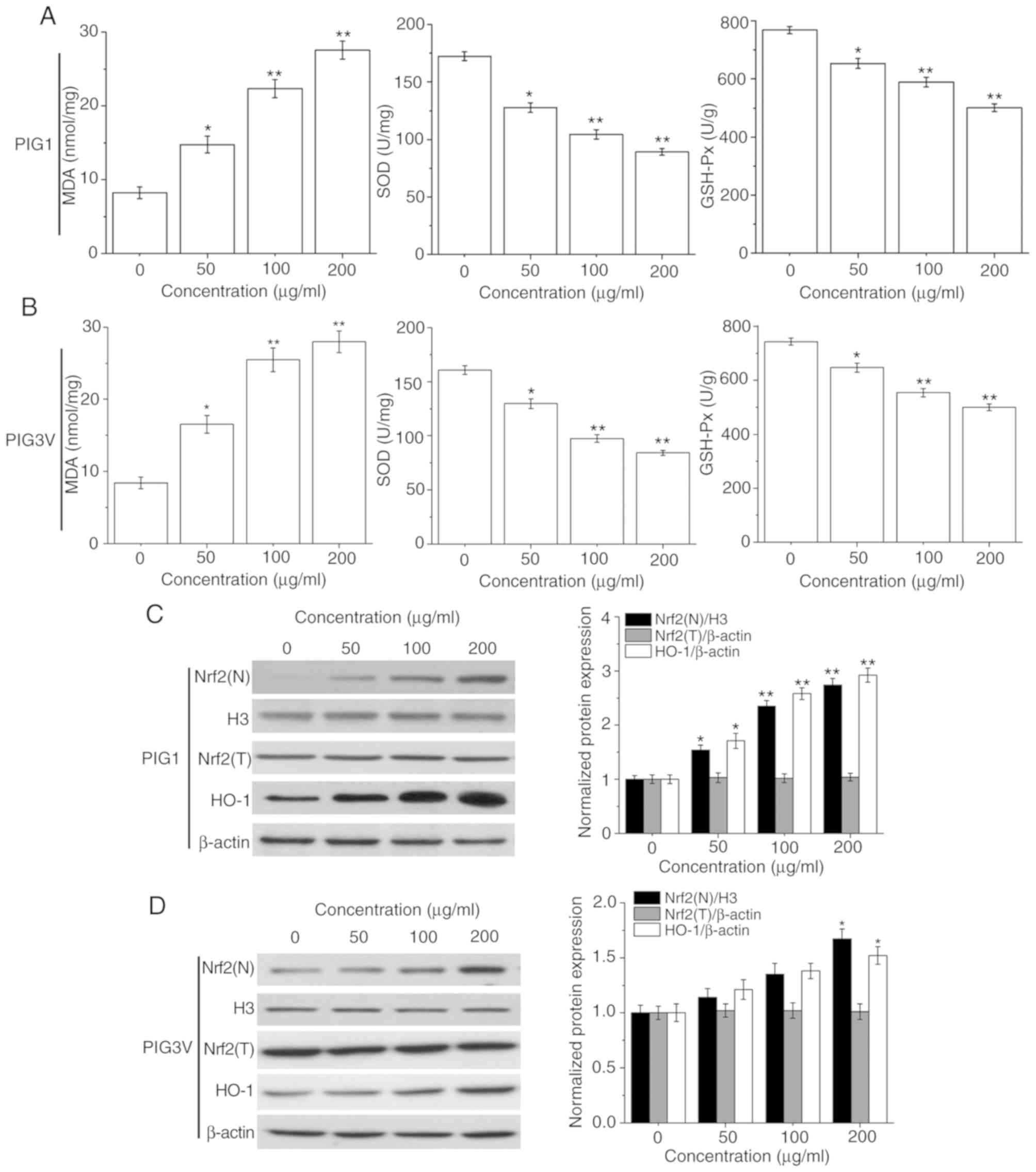
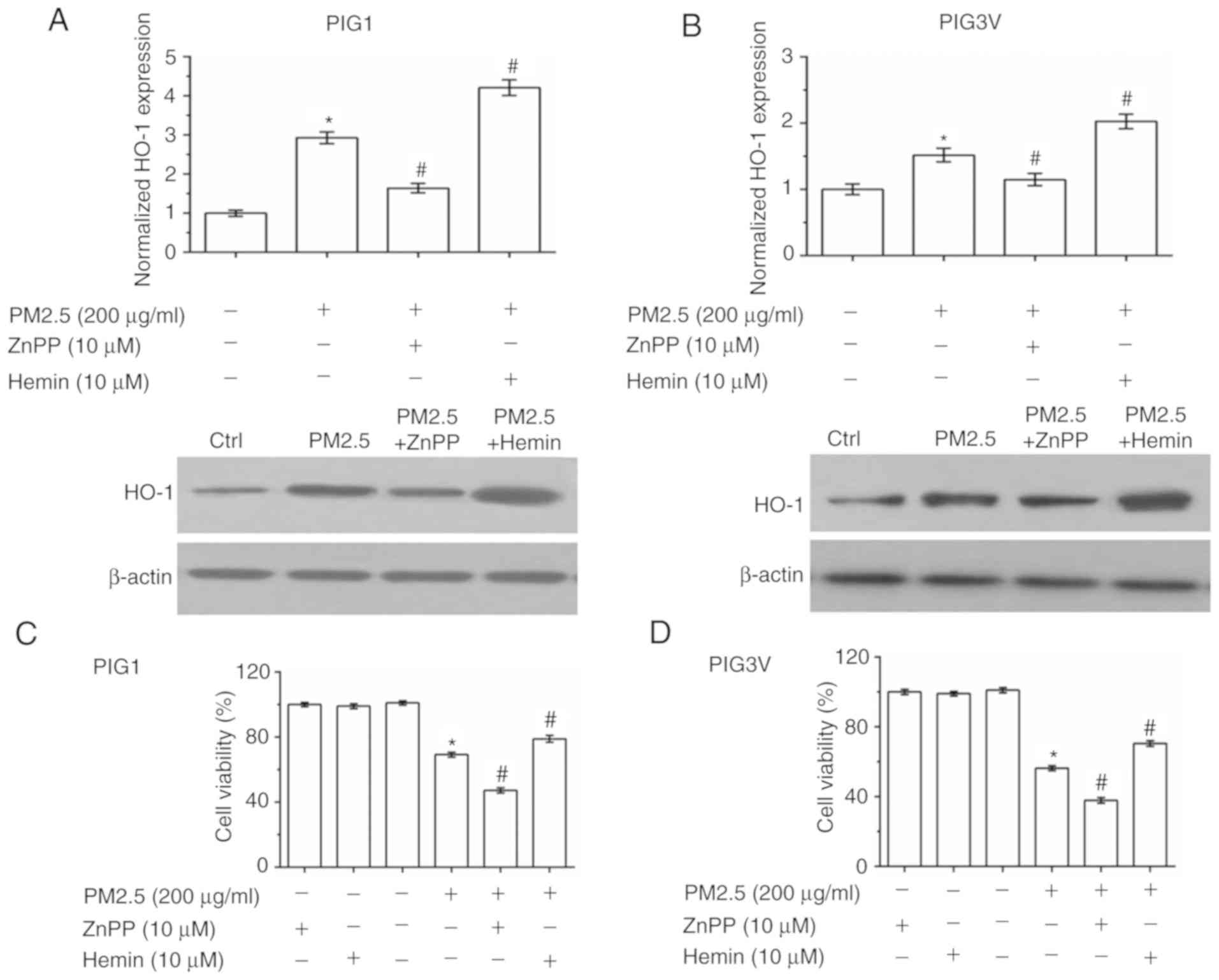
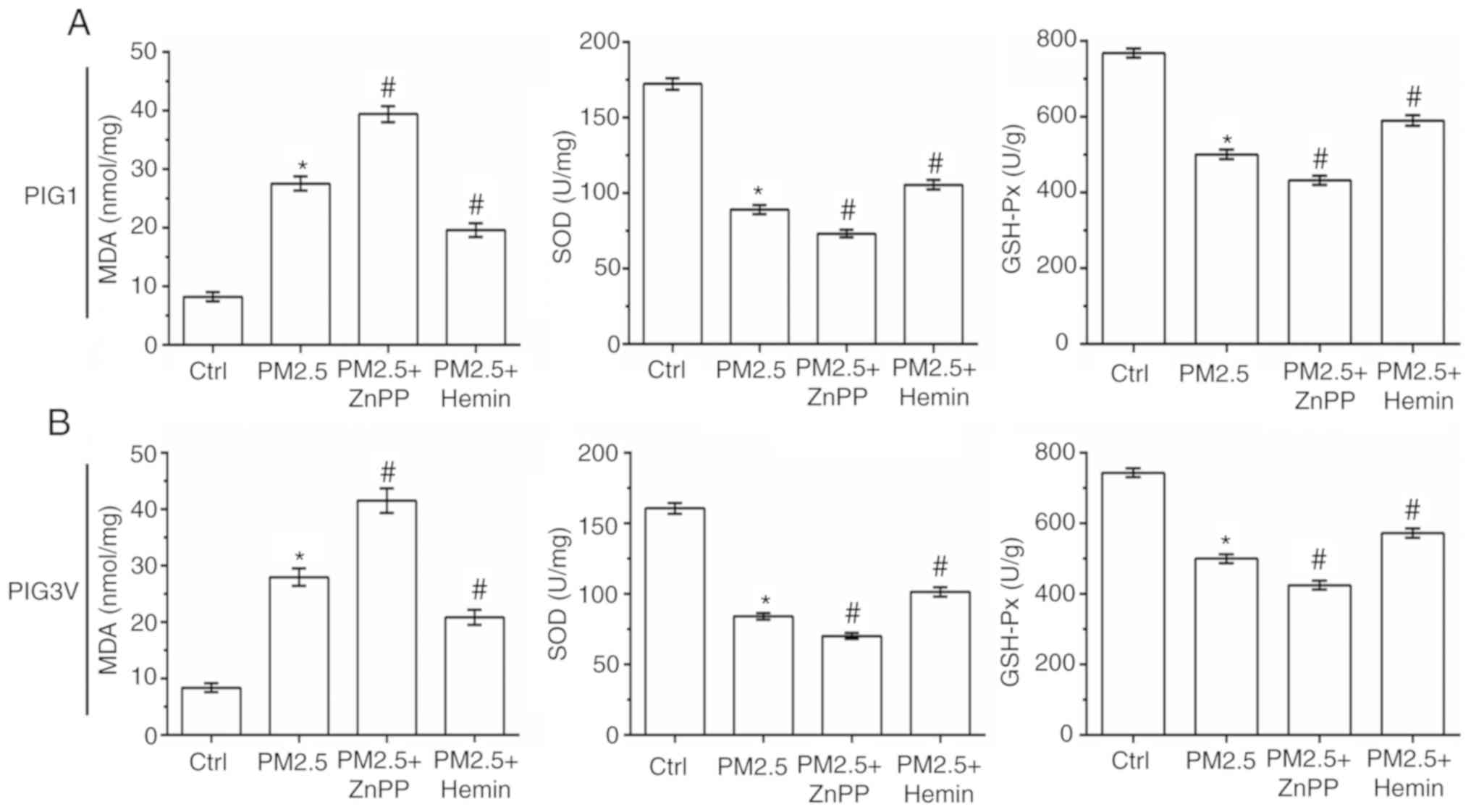
|
1
|
Ezzedine K, Eleftheriadou V, Whitton M and
van Geel N: Vitiligo. Lancet. 386:74–84. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rodrigues M, Ezzedine K, Hamzavi I, Pandya
AG and Harris JE: Vitiligo Working Group : New discoveries in the
pathogenesis and classification of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol.
77:1–13. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ghafourian A, Ghafourian S, Sadeghifard N,
Mohebi R, Shokoohini Y, Nezamoleslami S and Hamat RA: Vitiligo:
Symptoms, pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.
27:485–489. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Huang F, Li X, Wang C, Xu Q, Wang W, Luo
Y, Tao L, Gao Q, Guo J, Chen S, et al: PM2.5 spatiotemporal
variations and the relationship with meteorological factors during
2013-2014 in Beijing, China. PLoS One. 10(e0141642)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kim JY, Lee EY, Choi I, Kim J and Cho KH:
Effects of the particulate matter2.5 (PM2.5)
on lipoprotein metabolism, uptake and degradation, and embryo
toxicity. Mol Cells. 38:1096–1104. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang C, Tu Y, Yu Z and Lu R: PM2.5 and
cardiovascular diseases in the elderly: An overview. Int J Environ
Res Public Health. 12:8187–8197. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hammond D, Croghan C, Shin H, Burnett R,
Bard R, Brook RD and Williams R: Cardiovascular impacts and
micro-environmental exposure factors associated with continuous
personal PM2.5 monitoring. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol.
24:337–345. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Ma Z, Zheng C and Shang Y: Ambient
temperature enhanced acute cardiovascular-respiratory mortality
effects of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Int J Biometeorol.
59:1761–1770. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhao J, Bo L, Gong C, Cheng P, Kan H, Xie
Y and Song W: Preliminary study to explore gene-PM2.5 interactive
effects on respiratory system in traffic policemen. Int J Occup Med
Environ Health. 28:971–983. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li Q, Liu H, Alattar M, Jiang S, Han J, Ma
Y and Jiang C: The preferential accumulation of heavy metals in
different tissues following frequent respiratory exposure to PM2.5
in rats. Sci Rep. 5(16936)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ding A, Yang Y, Zhao Z, Hüls A, Vierkötter
A, Yuan Z, Cai J, Zhang J, Gao W, Li J, et al: Indoor PM2.5
exposure affects skin aging manifestation in a Chinese population.
Sci Rep. 7(15329)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Zheng L, Tuo J, Liu Q, Zhang X,
Xu Z, Liu S and Sui G: Analysis of PM2.5-induced cytotoxicity in
human HaCaT cells based on a microfluidic system. Toxicol In Vitro.
43:1–8. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Deng X, Zhang F, Rui W, Long F, Wang L,
Feng Z, Chen D and Ding W: PM2.5-induced oxidative stress triggers
autophagy in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
27:1762–1770. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bekki K, Ito T, Yoshida Y, He C,
Arashidani K, He M, Sun G, Zeng Y, Sone H, Kunugita N and Ichinose
T: PM2.5 collected in China causes inflammatory and oxidative
stress responses in macrophages through the multiple pathways.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 45:362–369. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chu M, Sun C, Chen W, Jin G, Gong J, Zhu
M, Yuan J, Dai J, Wang M, Pan Y, et al: Personal exposure to PM2.5,
genetic variants and DNA damage: A multi-center population-based
study in Chinese. Toxicol Lett. 235:172–178. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhou W, Yuan X, Zhang L, Su B, Tian D, Li
Y, Zhao J, Wang Y and Peng S: Overexpression of HO-1 assisted
PM2.5-induced apoptosis failure and autophagy-related cell
necrosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 145:605–614. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jian Z, Li K, Song P, Zhu G, Zhu L, Cui T,
Liu B, Tang L, Wang X, Wang G, et al: Impaired activation of the
Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway undermines H2O2-induced oxidative stress
response: A possible mechanism for melanocyte degeneration in
vitiligo. J Invest Dermatol. 134:2221–2230. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jian Z, Tang L, Yi X, Liu B, Zhang Q, Zhu
G, Wang G, Gao T and Li C: Aspirin induces Nrf2-mediated
transcriptional activation of haem oxygenase-1 in protection of
human melanocytes from H2O2-induced oxidative stress. J Cell Mol
Med. 20:1307–1318. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang L, Liu G, Lin Z, Wang Y, He H, Liu T
and Kamp DW: Pro-inflammatory response and oxidative stress induced
by specific components in ambient particulate matter in human
bronchial epithelial cells. Environ Toxicol. 31:923–936.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yu N, Zhu KJ, Ma SJ, Tang Hao and Tan XN:
The total flavonoids of clerodendrum bungei suppress A549 cells
proliferation, migration, and invasion by impacting Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. World J Tradit Chin Med. 4:15–20. 2017.
|
|
21
|
Ichikawa A, Takagi H, Suda K and Yao T:
New methodological approach for the rapid and sensitive detection
of melanocytes and melanocytic tumours. The DOPA-GA method.
Dermatology. 219:195–201. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mohamad N, Gutiérrez A, Núñez M, Cocca C,
Martín G, Cricco G, Medina V, Rivera E and Bergoc R: Mitochondrial
apoptotic pathways. Biocell. 29:149–161. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pisoschi AM and Pop A: The role of
antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur J
Med Chem. 97:55–74. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lee C: Collaborative power of Nrf2 and
PPARγ activators against metabolic and drug-induced oxidative
injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017(1378175)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Colucci R, Dragoni F and Moretti S:
Oxidative stress and immune system in vitiligo and thyroid
diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015(631927)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Repnik U, Česen MH and Turk B: The
endolysosomal system in cell death and survival. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 5(a008755)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Estaquier J, Vallette F, Vayssiere JL and
Mignotte B: The mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 942:157–183. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Shalini S, Dorstyn L, Dawar S and Kumar S:
Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ.
22:526–539. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Slimen IB, Najar T, Ghram A, Dabbebi H,
Ben Mrad M and Abdrabbah M: Reactive oxygen species, heat stress
and oxidative-induced mitochondrial damage. A review. Int J
Hyperthermia. 30:513–523. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kupsco A and Schlenk D: Oxidative stress,
unfolded protein response and apoptosis in developmental toxicity.
Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 317:1–66. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shi Q, Zhang W, Guo S, Jian Z, Li S, Li K,
Ge R, Dai W, Wang G, Gao T and Li C: Oxidative stress-induced
overexpression of miR-25: the mechanism underlying the degeneration
of melanocytes in vitiligo. Cell Death Differ. 23:496–508.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hu R, Xie XY, Xu SK, Wang YN, Jiang M, Wen
LR, Lai W and Guan L: PM2.5 exposure elicits oxidative stress
responses and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway activation in HaCaT
keratinocytes. Chin Med J (Engl). 130:2205–2214. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shi MH, Wu Y, Li L, Cai YF, Liu M, Gao XH
and Chen HD: Meta-analysis of the association between vitiligo and
the level of superoxide dismutase or malondialdehyde. Clin Exp
Dermatol. 42:21–29. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li QL, Wu YH, Niu M, Lu XJ, Huang YH and
He DH: Protective effects of tacalcitol against oxidative damage in
human epidermal melanocytes. Int J Dermatol. 56:232–238.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Karsli N, Akcali C, Ozgoztasi O, Kirtak N
and Inaloz S: Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of
vitiligo with special emphasis on the antioxidant action of
narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy. J Int Med Res. 42:799–805.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Bao L, Li J, Zha D, Zhang L, Gao P, Yao T
and Wu X: Chlorogenic acid prevents diabetic nephropathy by
inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation through modulation of
the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-ĸB pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 54:245–253.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Goldstein NB, Koster MI, Hoaglin LG,
Spoelstra NS, Kechris KJ, Robinson SE, Robinson WA, Roop DR, Norris
DA and Birlea SA: Narrow band ultraviolet B treatment for human
vitiligo is associated with proliferation, migration, and
differentiation of melanocyte precursors. J Invest Dermatol.
135:2068–2076. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yang L, Wei Y, Sun Y, Shi W, Yang J, Zhu L
and Li M: Interferon-gamma inhibits melanogenesis and induces
apoptosis in melanocytes: A pivotal role of CD8+ cytotoxic T
lymphocytes in vitiligo. Acta Derm Venereol. 95:664–670.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kim HJ, Bae IH, Son ED, Park J, Cha N, Na
HW, Jung C, Go YS, Kim DY, Lee TR and Shin DW: Transcriptome
analysis of airborne PM2.5-induced detrimental effects on human
keratinocytes. Toxicol Lett. 273:26–35. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Videira IF, Moura DF and Magina S:
Mechanisms regulating melanogenesis. An Bras Dermatol. 88:76–83.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lo Cicero A, Delevoye C, Gilles-Marsens F,
Loew D, Dingli F, Guéré C, André N, Vié K, van Niel G and Raposo G:
Exosomes released by keratinocytes modulate melanocyte
pigmentation. Nat Commun. 6(7506)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|