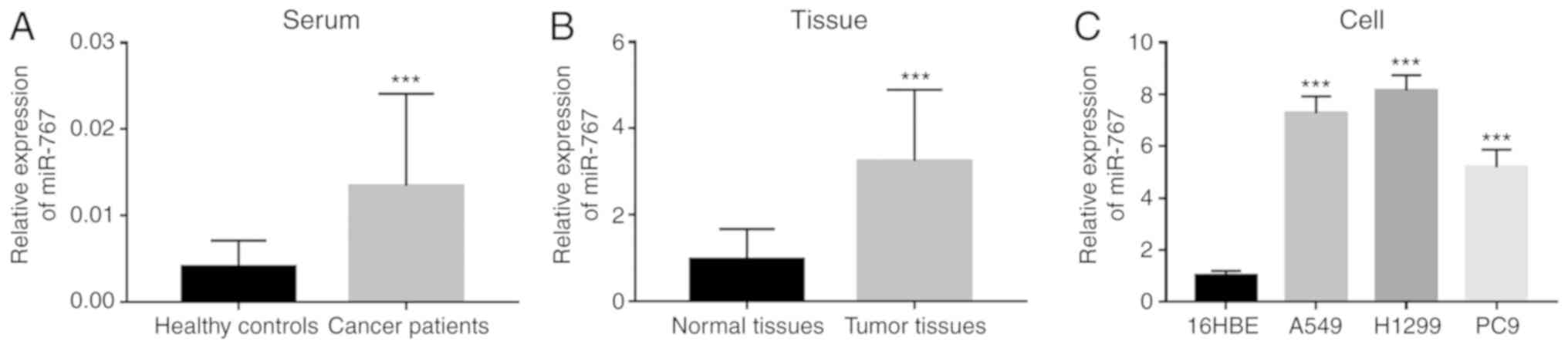
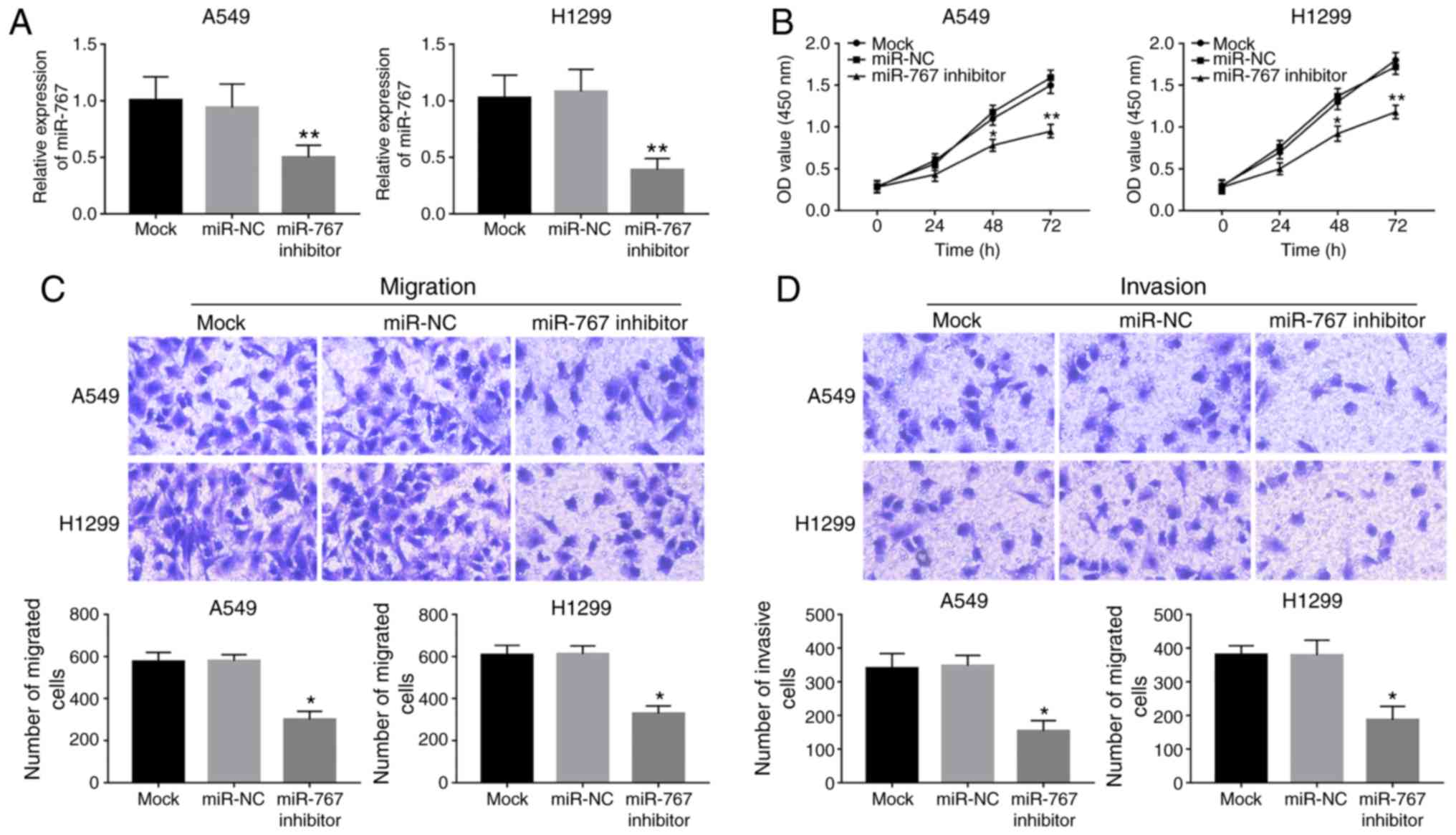
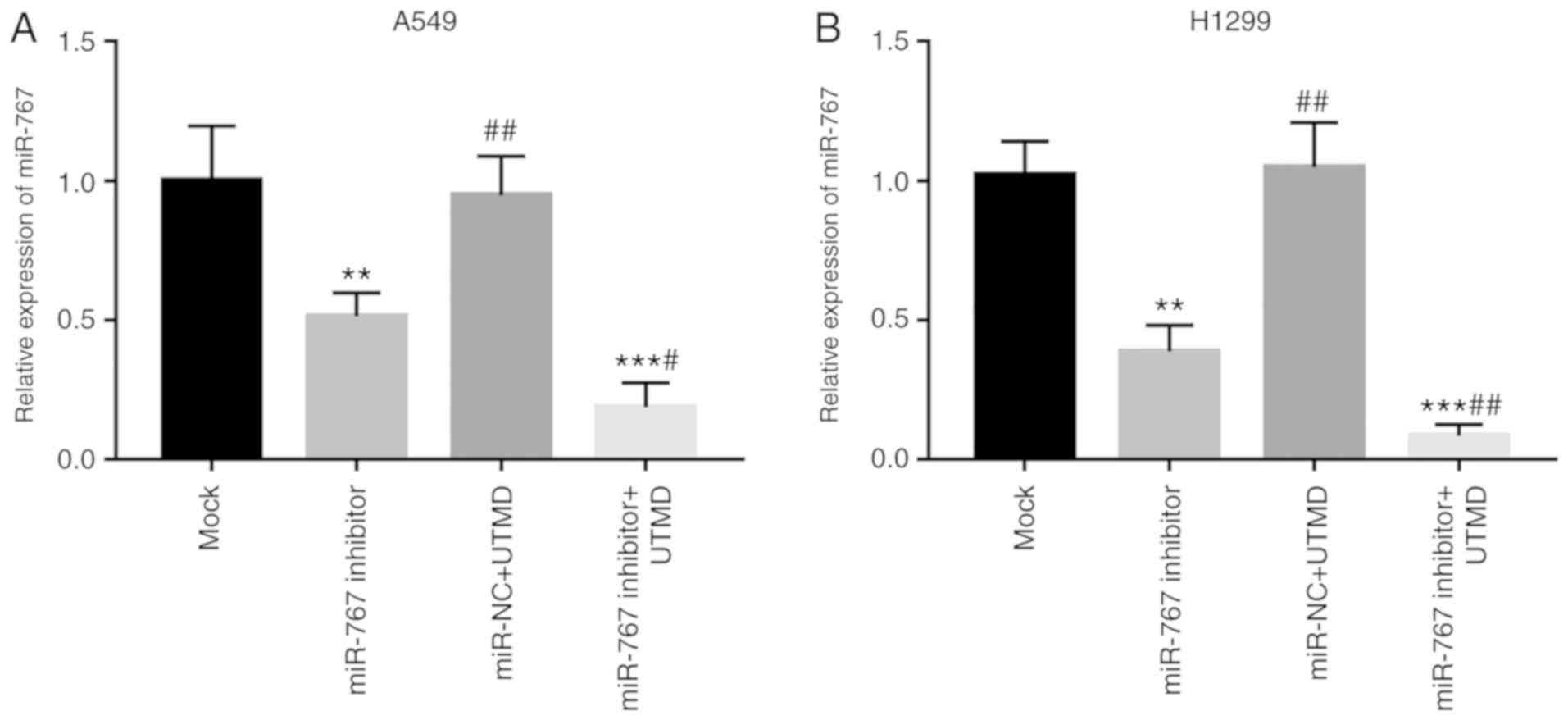
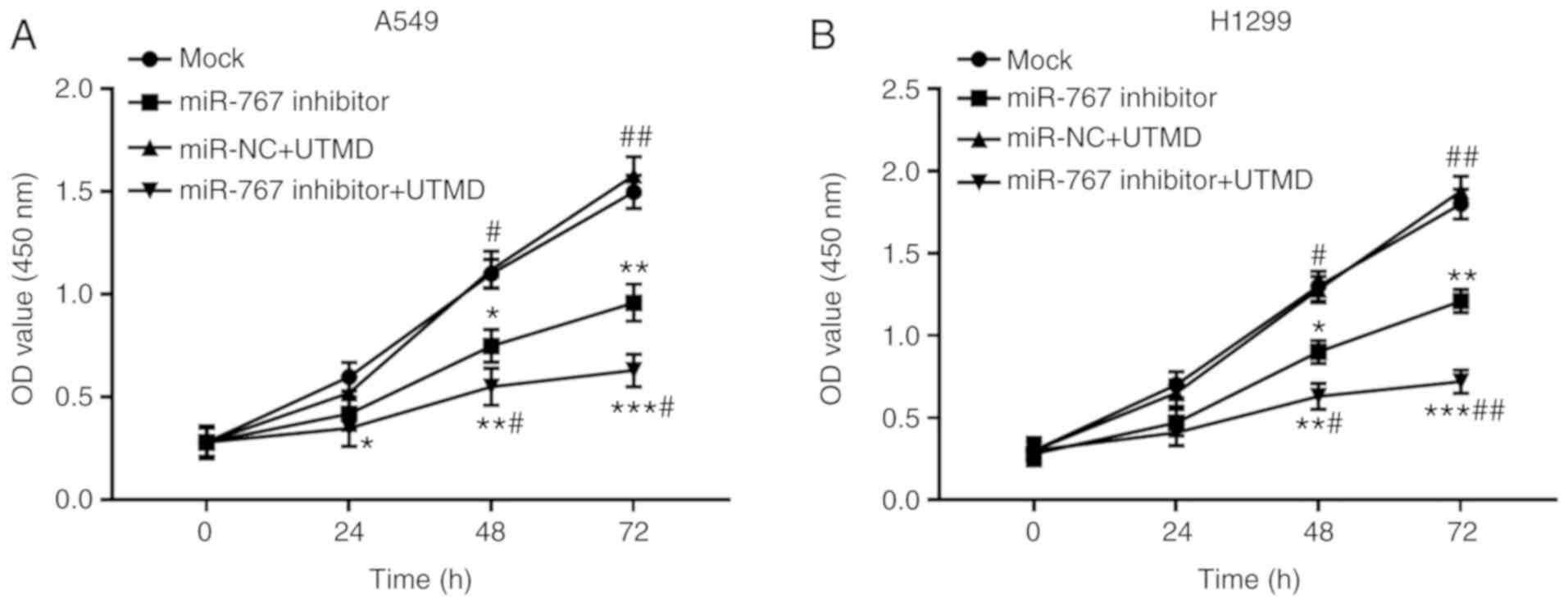
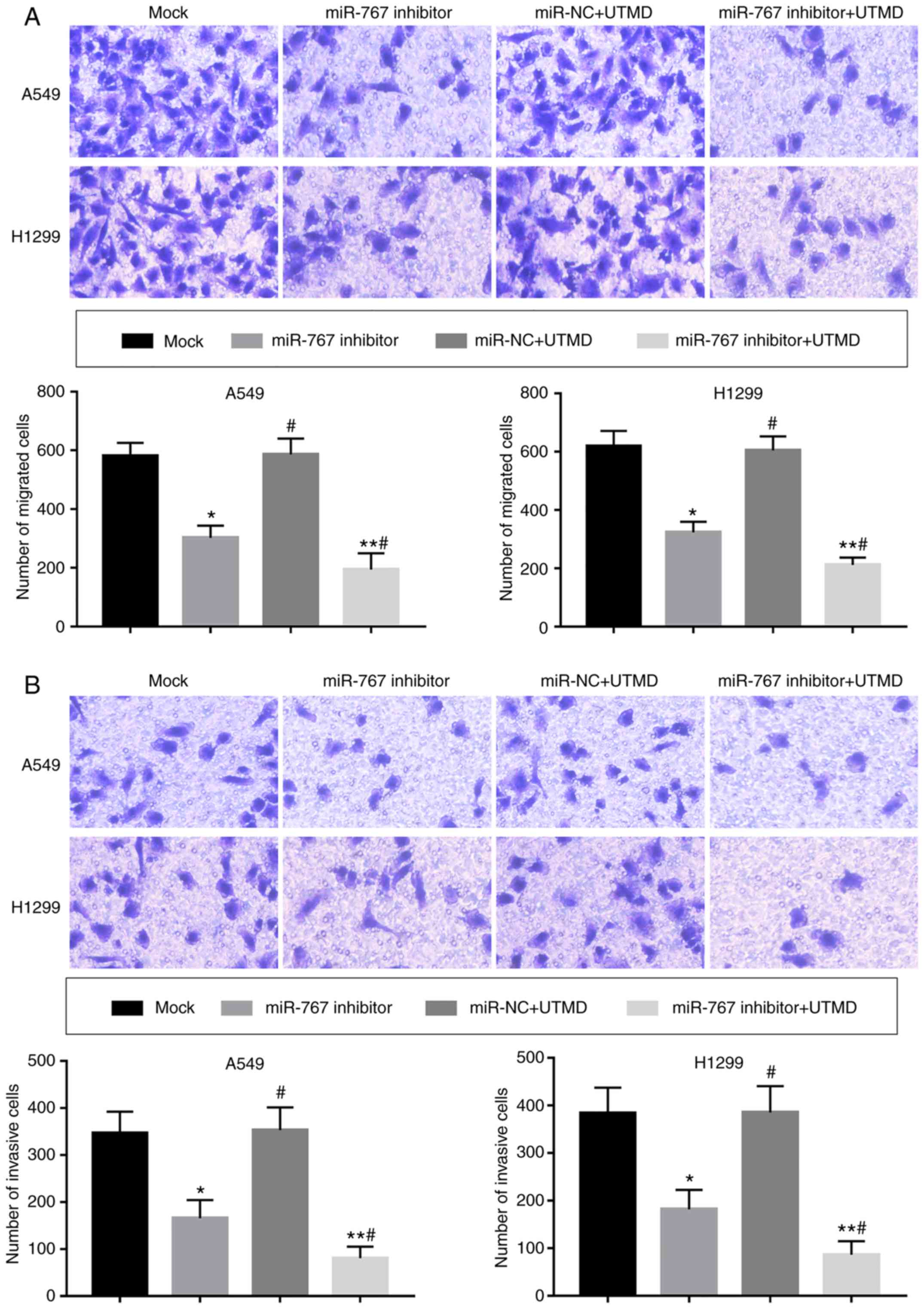
|
1
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Lung
cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:1–19. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Blandin Knight S, Crosbie PA, Balata H,
Chudziak J, Hussell T and Dive C: Progress and prospects of early
detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 7(pii: 170070)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li O, Askin F, Gabrielson E and Li QK:
Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical
markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma
(NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 52:103–109. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dejima H, Iinuma H, Kanaoka R, Matsutani N
and Kawamura M: Exosomal microRNA in plasma as a non-invasive
biomarker for the recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol
Lett. 13:1256–1263. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Verdecchia A, Francisci S, Brenner H,
Gatta G, Micheli A, Mangone L and Kunkler I: EUROCARE-4 Working
Group: Recent cancer survival in Europe: A 2000-02 period analysis
of EUROCARE-4 data. Lancet Oncol. 8:784–796. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Zhang X, Yang Z, Li Y, Han B and
Chen LA: miR-339-5p inhibits metastasis of non-small cell lung
cancer by regulating the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.
Oncol Lett. 15:2508–2514. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xu J, Pan X and Hu Z: MiR-502 mediates
esophageal cancer cell TE1 proliferation by promoting AKT
phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 501:119–123.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li J, Liang Y, Lv H, Meng H, Xiong G, Guan
X, Chen X, Bai Y and Wang K: miR-26a and miR-26b inhibit esophageal
squamous cancer cell proliferation through suppression of c-MYC
pathway. Gene. 625:1–9. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Qiu Z, Li H, Wang J and Sun C: miR-146a
and miR-146b in the diagnosis and prognosis of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 38:2735–2740. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Song Y, Guo Q, Gao S and Hua K: miR-454-3p
promotes proliferation and induces apoptosis in human cervical
cancer cells by targeting TRIM3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
516:872–879. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jiang K, Zhao T, Shen M, Zhang F, Duan S,
Lei Z and Chen Y: MiR-940 inhibits TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell invasion by targeting
Snail in non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer. 10:2735–2744.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ji Y, Han Z, Shao L and Zhao Y:
Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction of calcium channel
subunit alpha 1D siRNA inhibits breast cancer via G protein-coupled
receptor 30. Oncol Rep. 36:1886–1892. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen H and Hwang JH: Ultrasound-targeted
microbubble destruction for chemotherapeutic drug delivery to solid
tumors. J Ther Ultrasound. 1(10)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tinkov S, Bekeredjian R, Winter G and
Coester C: Microbubbles as ultrasound triggered drug carriers. J
Pharm Sci. 98:1935–1961. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tu J, Zhang H, Yu J, Liufu C and Chen Z:
Ultrasound-mediated microbubble destruction: A new method in cancer
immunotherapy. Onco Targets Ther. 11:5763–5775. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wu J and Li RK: Ultrasound-targeted
microbubble destruction in gene therapy: A new tool to cure human
diseases. Genes Dis. 4:64–74. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Loriot A, Van Tongelen A, Blanco J,
Klaessens S, Cannuyer J, van Baren N, Decottignies A and De Smet C:
A novel cancer-germline transcript carrying pro-metastatic miR-105
and TET-targeting miR-767 induced by DNA hypomethylation in tumors.
Epigenetics. 9:1163–1171. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Thienpont B, Galle E and Lambrechts D: TET
enzymes as oxygen-dependent tumor suppressors: Exciting new avenues
for cancer management. Epigenomics. 8:1445–1448. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang K and Guo L: MiR-767 promoted cell
proliferation in human melanoma by suppressing CYLD expression.
Gene. 641:272–278. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang J, Xu S, Xu J, Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang
J and Lu X: miR7675p inhibits glioma proliferation and metastasis
by targeting SUZ12. Oncol Rep. 42:55–66. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Leong-Poi H, Kuliszewski MA, Lekas M,
Sibbald M, Teichert-Kuliszewska K, Klibanov AL, Stewart DJ and
Lindner JR: Therapeutic arteriogenesis by ultrasound-mediated
VEGF165 plasmid gene delivery to chronically ischemic skeletal
muscle. Circ Res. 101:295–303. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yang L, Dou Y, Sui Z, Cheng H, Liu X, Wang
Q, Gao P, Qu Y and Xu M: Upregulated miRNA-182-5p expression in
tumor tissue and peripheral blood samples from patients with
non-small cell lung cancer is associated with downregulated Caspase
2 expression. Exp Ther Med. 19:603–610. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Huang L, Tang X, Shi X and Su L:
miR-532-5p promotes breast cancer proliferation and migration by
targeting RERG. Exp Ther Med. 19:400–408. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang J, Kong X, Shi Q and Zhao B:
MicroRNA-383-5p acts as a potential prognostic biomarker and an
inhibitor of tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in
breast cancer. Cancer Biomark: Dec. 24:2019.doi: 10.3233/CBM-190704
(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Biswas S: MicroRNAs as therapeutic agents:
The future of the battle against cancer. Curr Top Med Chem.
18:2544–2554. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Azarbarzin S, Hosseinpour Feizi MA,
Safaralizadeh R, Ravanbakhsh R, Kazemzadeh M, Fateh A, Karimi N and
Moaddab Y: The value of miR-299-5p in diagnosis and prognosis of
Intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma. Biochem Genet. 54:413–420.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zheng W, Zhao J, Tao Y, Guo M, Ya Z, Chen
C, Qin N, Zheng J, Luo J and Xu L: MicroRNA-21: A promising
biomarker for the prognosis and diagnosis of non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncol Lett. 16:2777–2782. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bagheri A, Khorram Khorshid HR, Mowla SJ,
Mohebbi HA, Mohammadian A, Yaseri M, Solaymani-Dodaran M,
Sherafatian M and Tavallaie M: Altered miR-223 expression in sputum
for diagnosis of Non-small cell lung cancer. Avicenna J Med
Biotechnol. 9:189–195. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sromek M, Glogowski M, Chechlinska M,
Kulinczak M, Szafron L, Zakrzewska K, Owczarek J, Wisniewski P,
Wlodarczyk R, Talarek L, et al: Changes in plasma miR-9, miR-16,
miR-205 and miR-486 levels after non-small cell lung cancer
resection. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 40:529–536. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang SY, Li Y, Jiang YS and Li RZ:
Investigation of serum miR-411 as a diagnosis and prognosis
biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 21:4092–4097. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ow SH, Chua PJ and Bay BH: miR-149 as a
potential molecular target for cancer. Curr Med Chem. 25:1046–1054.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kang X, Kong F, Wu S, Liu Q, Yang C, Wu X
and Zhang W: microRNA-612 suppresses the malignant development of
non-small-cell lung cancer by directly targeting
bromodomain-containing protein 4. Onco Targets Ther. 12:4167–4179.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ling C, Wang X, Zhu J, Tang H, Du W, Zeng
Y, Sun L, Huang JA and Liu Z: MicroRNA-4286 promotes cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion via PTEN regulation of the
PI3K/Akt pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Me.
8:3520–3531. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Feng Y, Zhang L, Wu J, Khadka B, Fang Z,
Gu J, Tang B, Xiao R, Pan G and Liu J: CircRNA circ_0000190
inhibits the progression of multiple myeloma through modulating
miR-767-5p/MAPK4 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38(54)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang TY, Choe JW, Pu K, Devulapally R,
Bachawal S, Machtaler S, Chowdhury SM, Luong R, Tian L, Khuri-Yakub
B, et al: Ultrasound-guided delivery of microRNA loaded
nanoparticles into cancer. J Control Release. 203:99–108.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lin L, Fan Y, Gao F, Jin L, Li D, Sun W,
Li F, Qin P, Shi Q, Shi X and Du L: UTMD-promoted Co-delivery of
gemcitabine and miR-21 inhibitor by Dendrimer-entrapped gold
nanoparticles for pancreatic cancer therapy. Theranostics.
8:1923–1939. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ji Y, Han Z, Shao L and Zhao Y: Evaluation
of in vivo antitumor effects of low-frequency ultrasound-mediated
miRNA-133a microbubble delivery in breast cancer. Cancer Med.
5:2534–2543. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Qin D, Li H and Xie H: Ultrasoundtargeted
microbubble destructionmediated miR205 enhances cisplatin
cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 18:3242–3250.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Park SJ, Lee BR, Kim HS, Ji YR, Sung YH,
ShikChoi K, Park HD, Kim SH, Kim MO and Ryoo ZY: Inhibition of
migration and invasion by Tet-1 overexpression in human lung
carcinoma H460 cells. Oncol Res. 23:89–98. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|