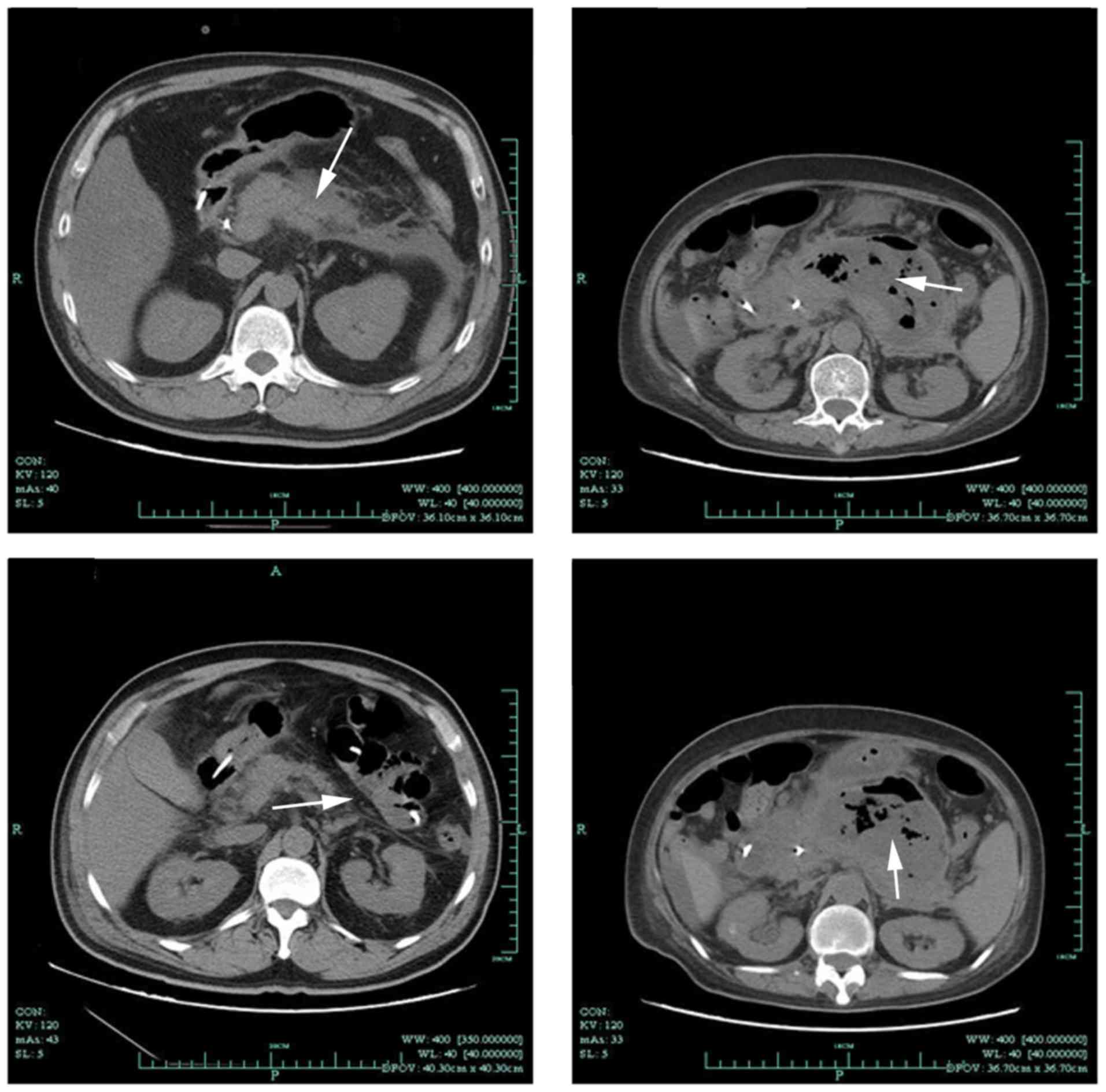
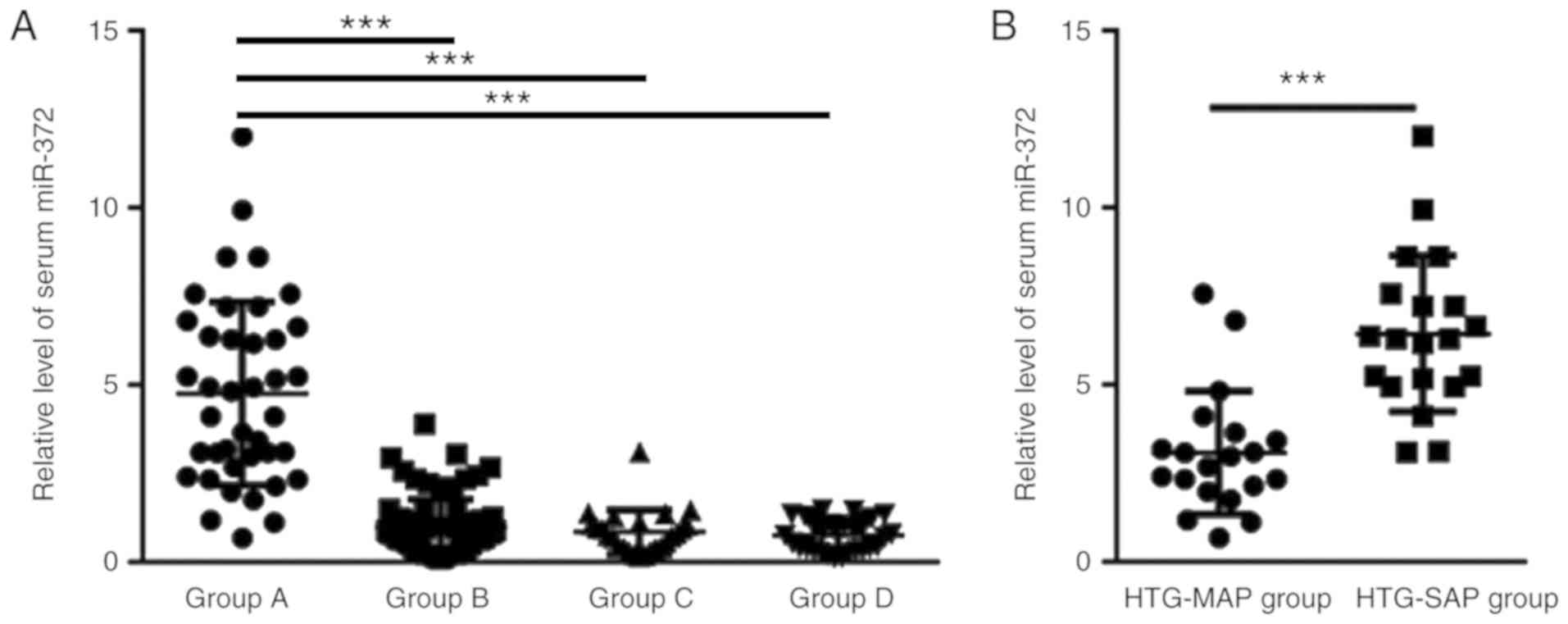
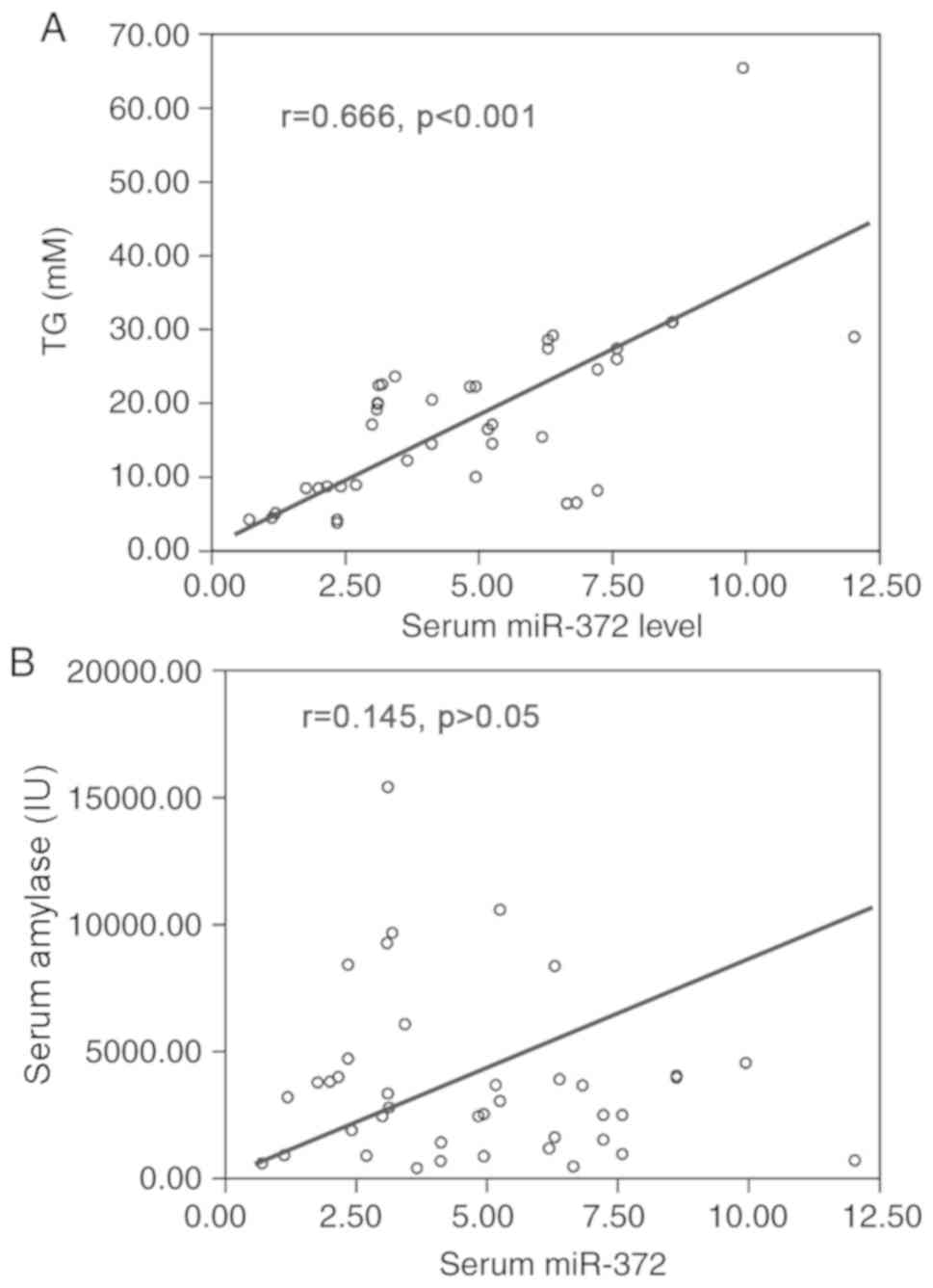
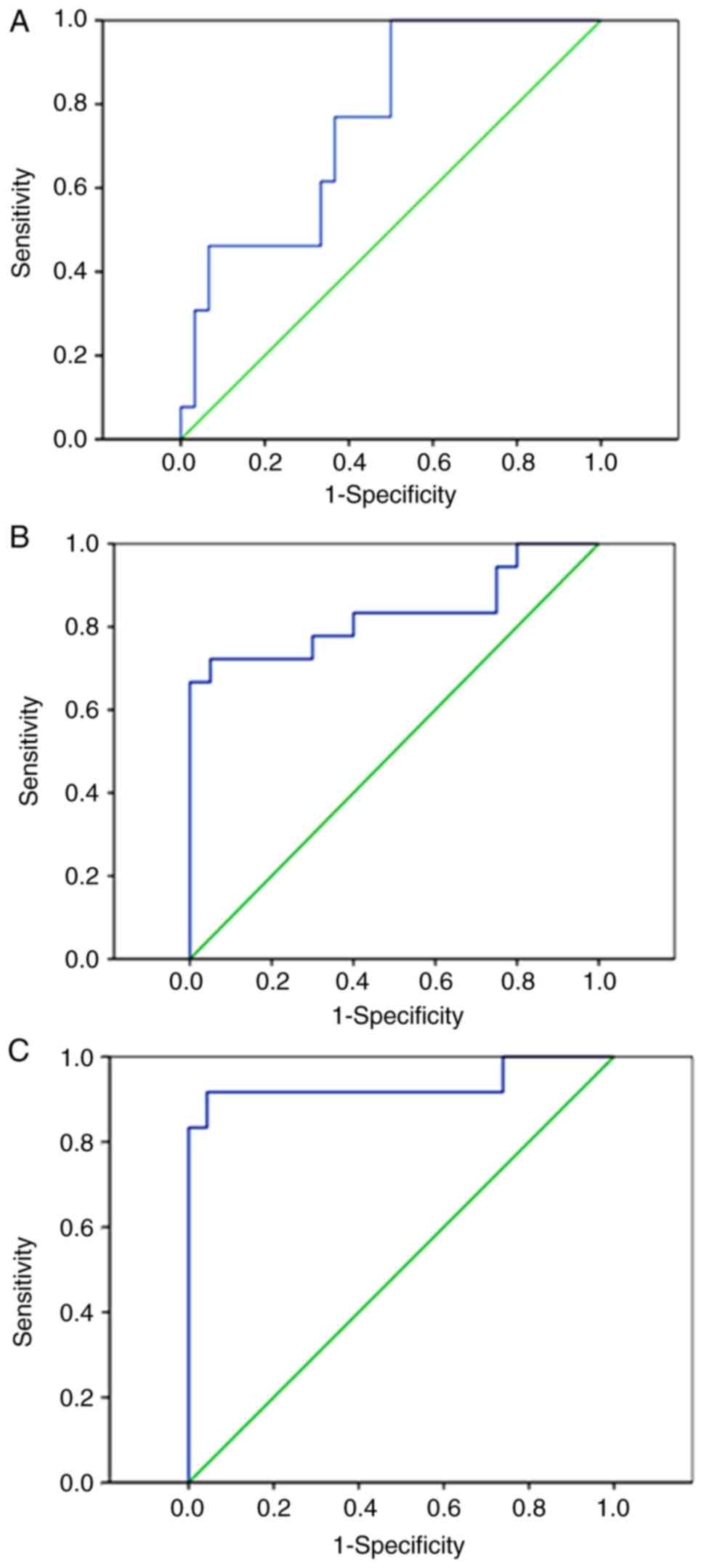
|
1
|
Brown TT and Prahlow JA: Postmortem serum
amylase and lipase analysis in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.
Acad Forensic Pathol. 8:311–323. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cao X, Wang HM, Du H, Chen EX, Yang XF,
Wang SL, Ding Y and She ZF: Early predictors of hyperlipidemic
acute pancreatitis. Exp Ther Med. 16:4232–4238. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dolay K, Hasbahceci M, Hatipoglu E, Ümit
Malya F and Akçakaya A: Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of
biliary obstruction due to acute cholangitis and acute pancreatitis
secondary to Fasciola hepatica infection. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi
Derg. 24:71–73. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Durmaz MS, Arslan S, Özbakır B, Güngör G,
Tolu İ, Arslan FZ, Sivri M and Koplay M: Effectiveness of Shear
Wave Elastography in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis on
admission. Med Ultrason. 20:278–284. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Charlesworth A, Steger A and Crook MA:
Hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis and the Apolipoprotein E4 allele.
Pancreas. 46:e3–e4. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
French JM, Twedt DC, Rao S and Marolf AJ:
Computed tomographic angiography and ultrasonography in the
diagnosis and evaluation of acute pancreatitis in dogs. J Vet
Intern Med. 33:79–88. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Durval A, Zamidei L, Bettocchi D, Luzzio
MG and Consales G: Hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis: A possible
role of antiretroviral therapy with entecavir. Minerva Anestesiol.
77:1018–1021. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Noorolyai S, Baghbani E, Aghebati Maleki
L, Baghbanzadeh Kojabad A, Shanehbansdi D, Khaze Shahgoli V,
Mokhtarzadeh A and Baradaran B: Restoration of miR-193a-5p and
miR-146 a-5p expression induces G1 arrest in colorectal cancer
through targeting of MDM2/p53. Adv Pharm Bull. 10:130–134.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhao C, Fei X, Xu B, Lu Y and Zhang Q:
Long non-coding RNA HEIH contributes to diabetic retinopathy by
regulating miR-939/VEGF axis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 12:2022–2033.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu P, Wang F, Wu J, Wang C, Yan J, Li ZL,
Song JX and Wang JJ: Elevated Serum miR-7, miR-9, miR-122, and
miR-141 are noninvasive biomarkers of acute pancreatitis. Dis
Markers. 2017(7293459)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Miao B, Qi WJ, Zhang SW and Wang H, Wang
C, Hu L, Huang GW, Li SR and Wang H: miR-148a suppresses autophagy
by down-regulation of IL-6/STAT3 signaling in cerulein-induced
acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 19:557–565. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dixit AK, Sarver AE, Yuan Z, George J,
Barlass U, Cheema H, Sareen A, Banerjee S, Dudeja V, Dawra R, et
al: Comprehensive analysis of microRNA signature of mouse
pancreatic acini: Overexpression of miR-21-3p in acute
pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
311:G974–G980. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen H, Zhang Z, Lu Y, Song K, Liu X, Xia
F and Sun W: Downregulation of ULK1 by microRNA-372 inhibits the
survival of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Sci.
108:1811–1819. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Guan X, Zong ZH, Chen S, Sang XB, Wu DD,
Wang LL, Liu Y and Zhao Y: The role of miR-372 in ovarian carcinoma
cell proliferation. Gene. 624:14–20. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Verdelli C, Forno I, Morotti A, Creo P,
Guarnieri V, Scillitani A, Cetani F, Vicentini L, Balza G, Beretta
E, et al: The aberrantly expressed miR-372 partly impairs
sensitivity to apoptosis in parathyroid tumor cells. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 25:761–771. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yuan S, Gao Y, Ji W, Song J and Mei X: The
evaluation of acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II
score, poisoning severity score, sequential organ failure
assessment score combine with lactate to assess the prognosis of
the patients with acute organophosphate pesticide poisoning.
Medicine (Baltimore). 97(e10862)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang D, Guo C, Kong T, Mi G, Li J and Sun
Y: Serum miR-22 may be a biomarker for papillary thyroid cancer.
Oncol Lett. 17:3355–3361. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jagannath S and Garg PK: Recurrent acute
pancreatitis: Current concepts in the diagnosis and management.
Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 16:449–465. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jin DX, Lacson R, Cochon LR, Alper EC,
McNabb-Baltar J, Banks PA and Khorasani R: A clinical model for the
early diagnosis of acute pancreatitis in the emergency department.
Pancreas. 47:871–879. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hang Y, Chen Y, Lu LX and Zhu CQ: Acute
hyperlipidemic pancreatitis in a pregnant woman. World J Emerg Med.
4:311–313. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kaya M, Değirmenci S, Göya C, Tuncel ET,
Uçmak F and Kaplan MA: The importance of acoustic radiation force
impulse (ARFI) elastography in the diagnosis and clinical course of
acute pancreatitis. Turk J Gastroenterol. 29:342–347.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Huang YX, Jia L, Jiang SM, Wang SB, Li MX
and Yang BH: Incidence and clinical features of hyperlipidemic
acute pancreatitis from Guangdong, China: A retrospective
multicenter study. Pancreas. 43:548–552. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lopes CV, Pereira-Lima J and Hartmann AA:
The role of linear endosonography for the diagnosis of acute
pancreatitis when other methods failed. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 43:98–103. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Senates E: Toward a new ultrasound-based
imaging method for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis: A
preliminary study suggesting that it may be feasible. Turk J
Gastroenterol. 29:256–258. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li MQ, Shi ZX, Xu JY, Lu B, Li JQ, Xu YJ,
Wang XM, Li SM and Mo X: Hemodiafiltration combined with
resin-mediated absorption as a therapy for hyperlipidemic acute
pancreatitis. Cell Biochem Biophys. 69:699–702. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li X, Lin Z, Wang L, Liu Q, Cao Z, Huang
Z, Zhong M, Peng S, Zhang Y, Li Y and Ma X: RNA-Seq analyses of the
role of miR-21 in acute pancreatitis. Cell Physiol Biochem.
51:2198–2211. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y, Yan L and Han W: Elevated level
of miR-551b-5p is associated with inflammation and disease
progression in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Ther Apher
Dial. 22:649–655. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lu J, Xie Y, Du J, Kang M, Jin W, Li Y,
Xie H, Cheng R, Tian R and Wang R: Penta-therapy for severe acute
hyperlipidemic pancreatitis. Am J Emerg Med. 36:1789–1795.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Markota A, Knehtl M, Sinkovic A, Ekart R,
Hojs R and Bevc S: Plasma exchange treatment for acute
hyperlipidemic pancreatitis with falsely low levels of serum
triglycerides-a case report. Transfus Apher Sci. 51:178–180.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yang L, Zhao Z, Zhou K and Zhang Y: Acute
hyperlipidemic pancreatitis accompanied by chylous ascites with
normal amylase and lipase in pregnancy. J Clin Lipidol.
11:1091–1094. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|