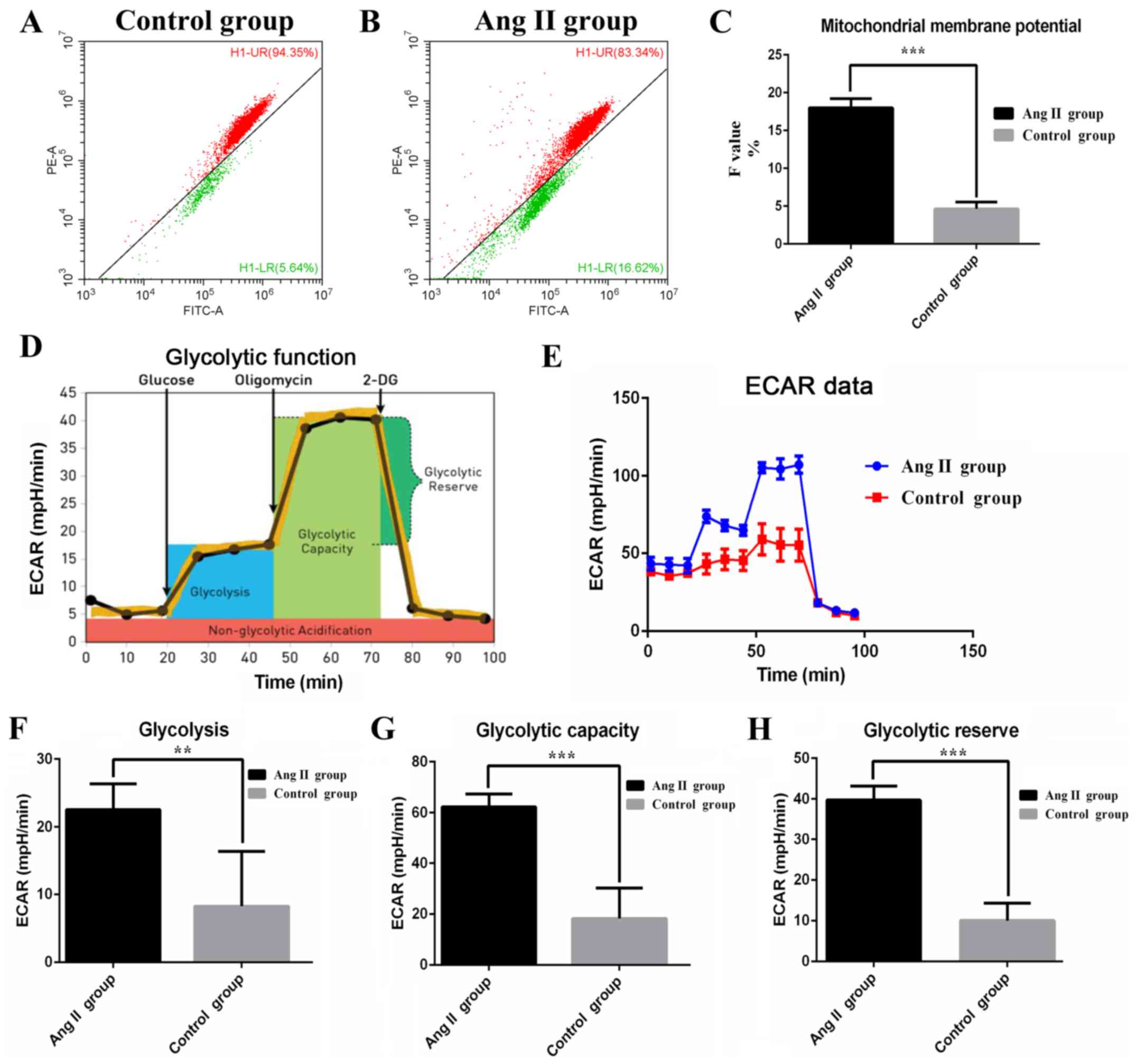
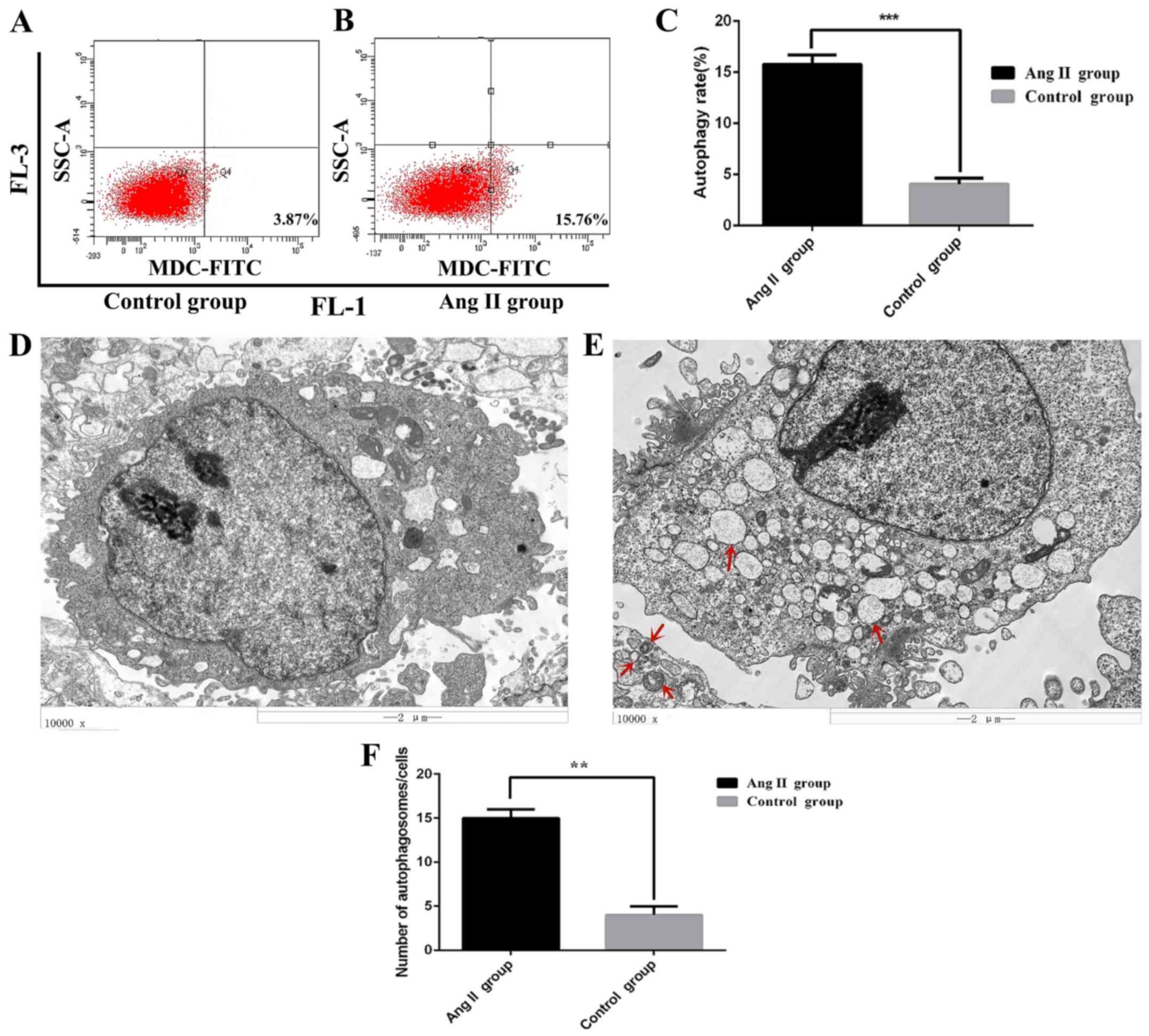
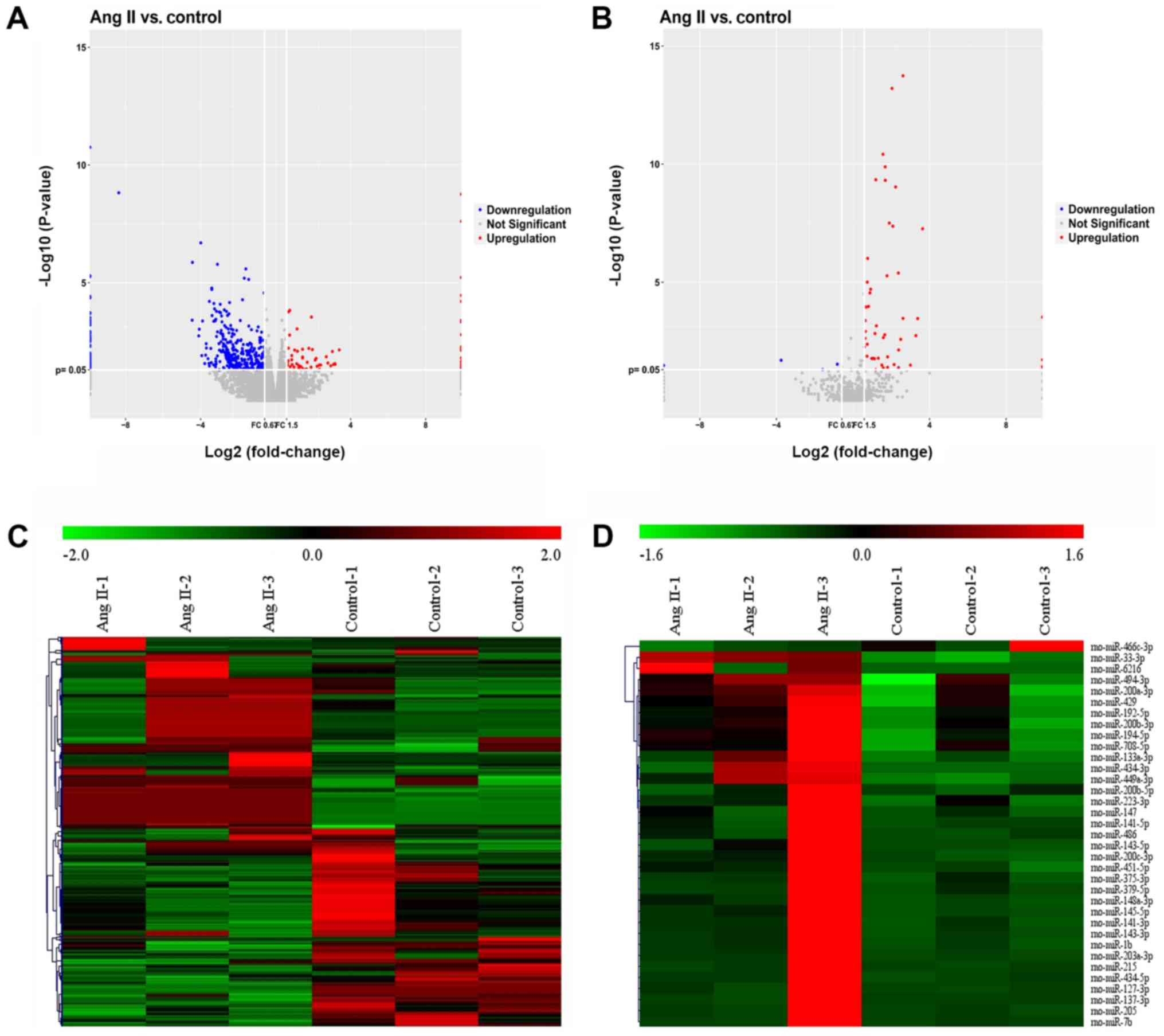
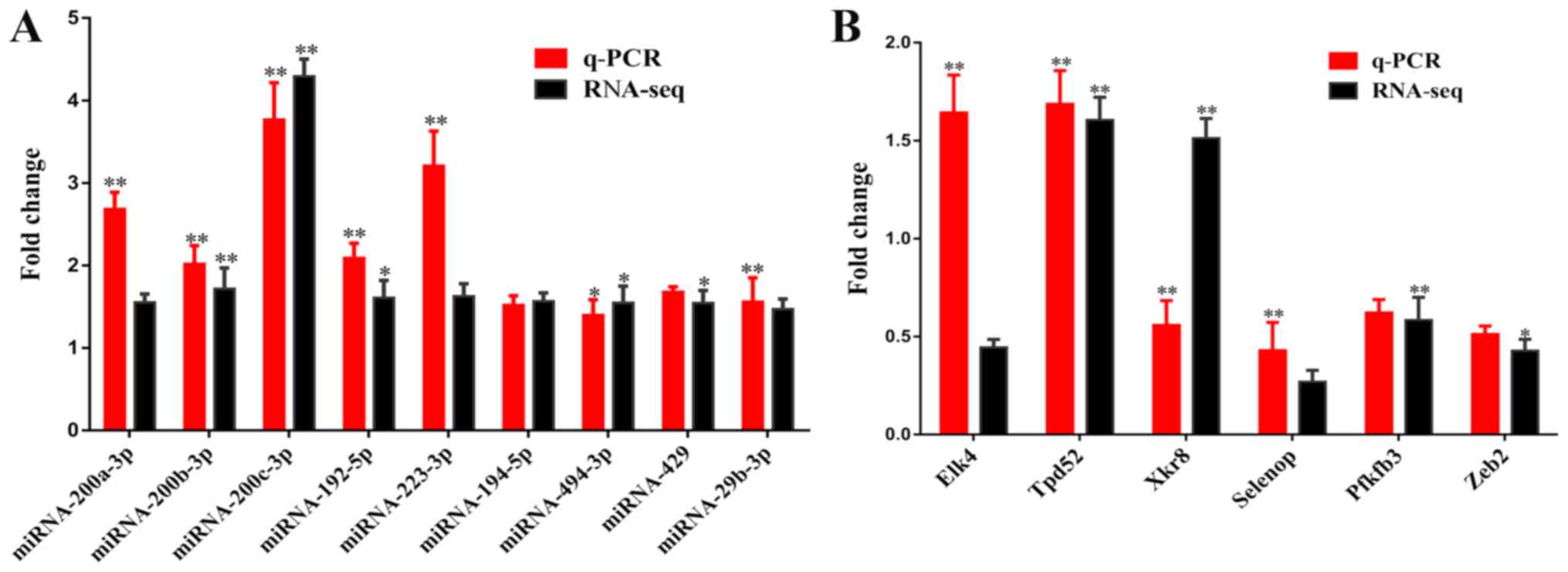
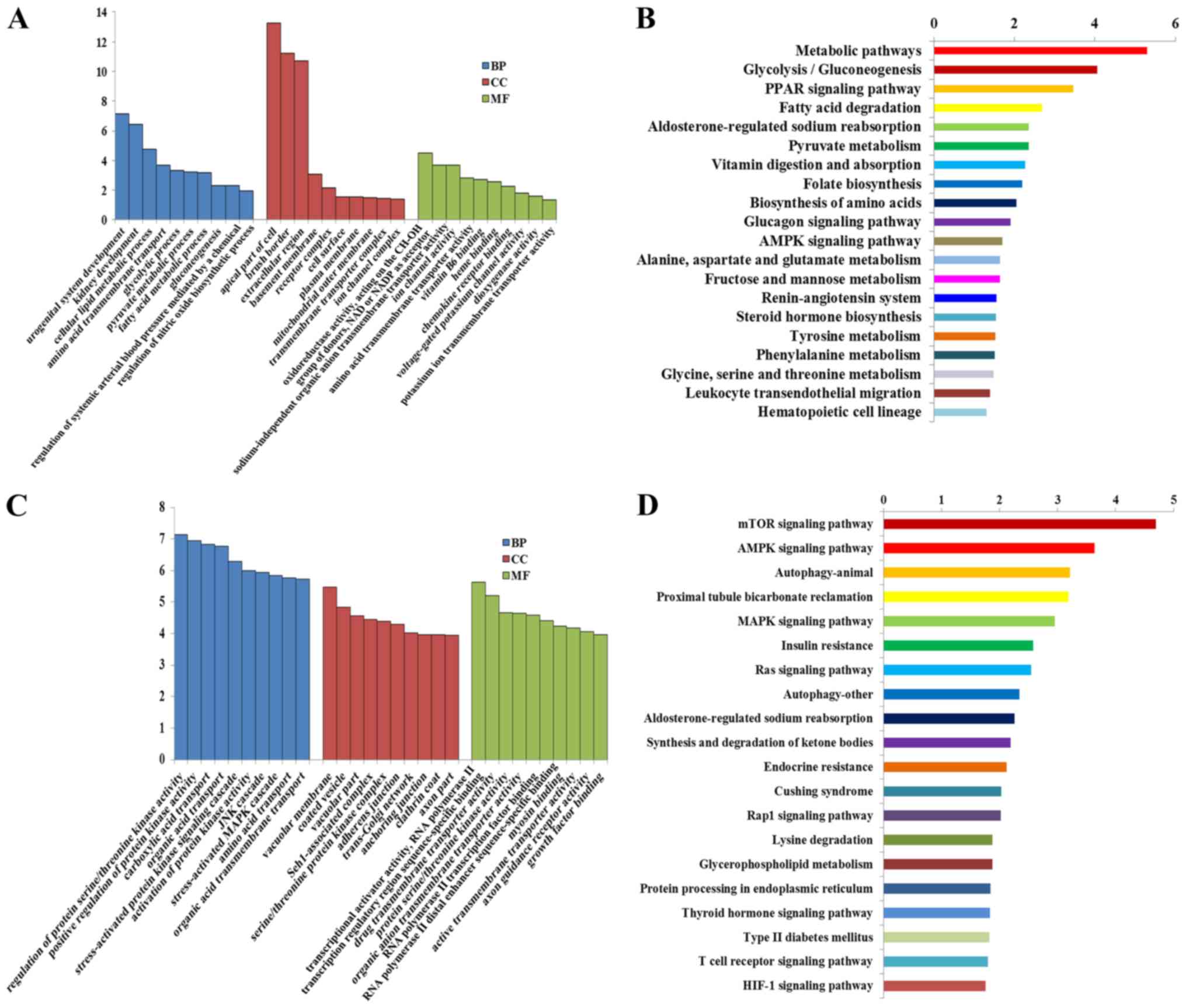
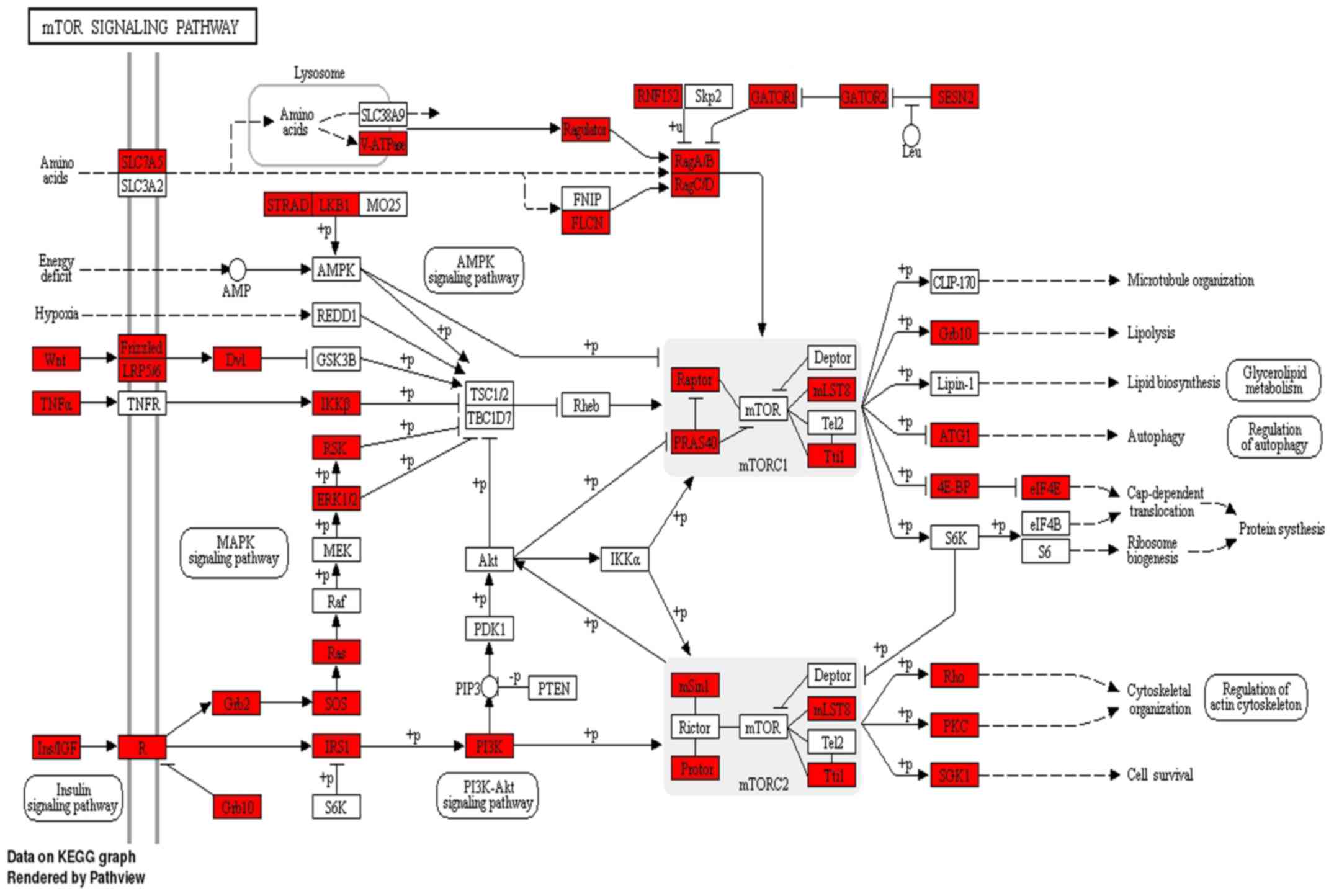
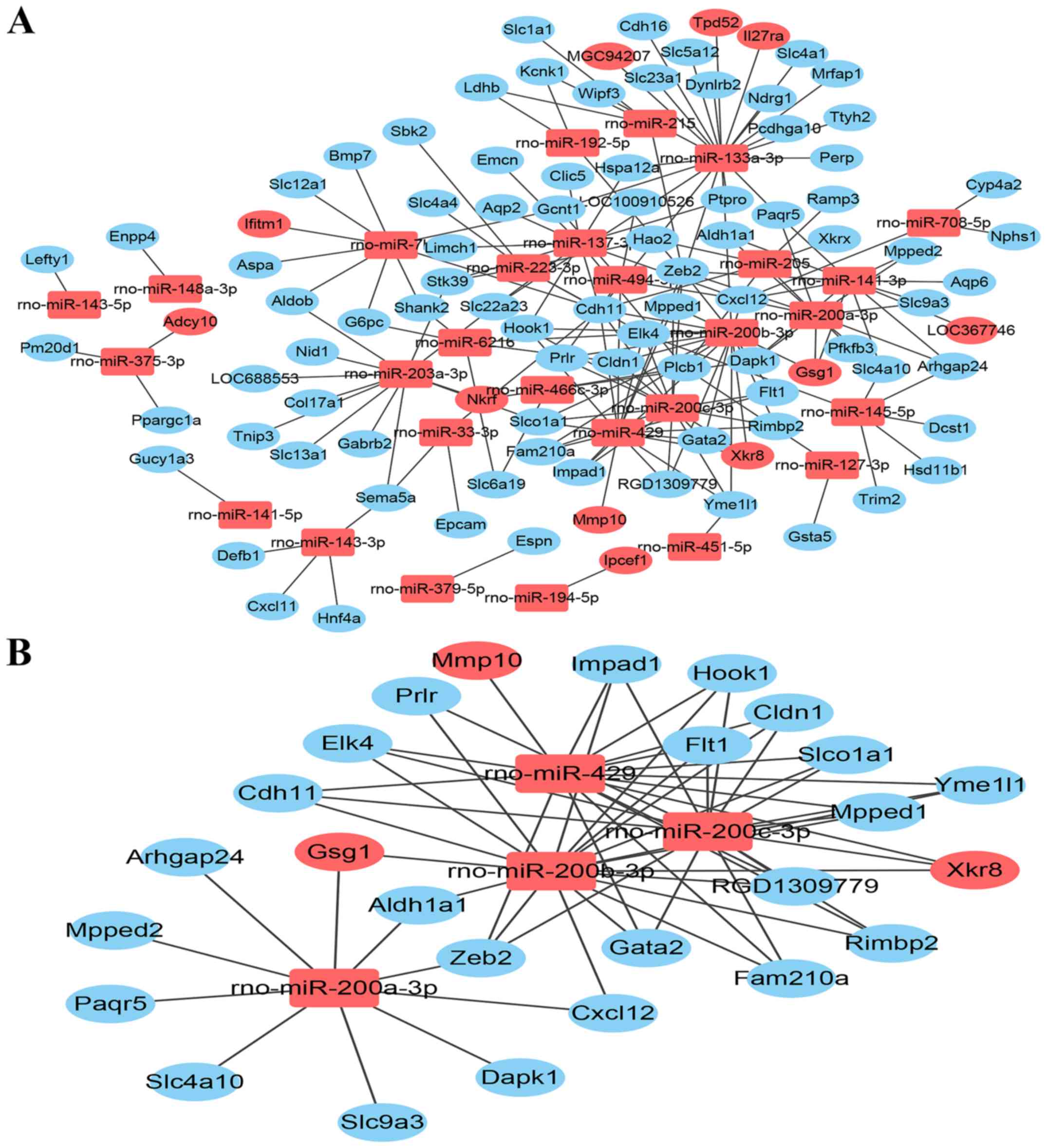
|
1
|
Kashiwagi M, Shinozaki M, Hirakata H,
Tamaki K, Hirano T, Tokumoto M, Goto H, Okuda S and Fujishima M:
Locally activated renin-angiotensin system associated with
TGF-beta1 as a major factor for renal injury induced by chronic
inhibition of nitric oxide synthase in rats. J Am Soc Nephrol.
11:616–624. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kobori H, Nangaku M, Navar LG and
Nishiyama A: The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: From
physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease.
Pharmacol Rev. 59:251–287. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Klingbeil AU, John S, Schneider MP, Jacobi
J, Handrock R and Schmieder RE: Effect of AT1 receptor blockade on
endothelial function in essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens.
16:123–128. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mennuni S, Rubattu S, Pierelli G, Tocci G,
Fofi C and Volpe M: Hypertension and kidneys: Unraveling complex
molecular mechanisms underlying hypertensive renal damage. J Hum
Hypertens. 28:74–79. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Navar LG and Harrison-Bernard LM:
Intrarenal angiotensin II augmentation in angiotensin II dependent
hypertension. Hypertens Res. 23:291–301. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Geraci G, Mulè G, Mogavero M, Geraci C,
D'Ignoti D, Guglielmo C and Cottone S: Renal haemodynamics and
severity of carotid atherosclerosis in hypertensive patients with
and without impaired renal function. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.
25:160–166. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ferraro E, Pulicati A, Cencioni MT,
Cozzolino M, Navoni F, di Martino S, Nardacci R, Carrì MT and
Cecconi F: Apoptosome-deficient cells lose cytochrome c through
proteasomal degradation but survive by autophagy-dependent
glycolysis. Mol Biol Cell. 19:3576–3588. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang R, Su H, Ma X, Xu X, Liang L, Ma G
and Shi L: MiRNA let-7b promotes the development of hypoxic
pulmonary hypertension by targeting ACE2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 316:L547–L557. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Huo KG, Richer C, Berillo O, Mahjoub N,
Fraulob-Aquino JC, Barhoumi T, Ouerd S, Coelho SC, Sinnett D,
Paradis P and Schiffrin EL: MiR-431-5p knockdown protects against
angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular injury.
Hypertension. 73:1007–1017. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang Y, Tang S, Huang C, Chen J, Li J,
Cai A and Feng Y: Circulating miRNA-29 family expression levels in
patients with essential hypertension as potential markers for left
ventricular hypertrophy. Clin Exp Hypertens. 39:119–125.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xu Z, Zou C, Yu W, Xu S, Huang L, Khan Z,
Wang J, Liang G and Wang Y: Inhibition of STAT3 activation mediated
by toll-like receptor 4 attenuates angiotensin II-induced renal
fibrosis and dysfunction. Br J Pharmacol. 176:2627–2641.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Reers M, Smiley ST, Mottola-Hartshorn C,
Chen A, Lin M and Chen LB: Mitochondrial membrane potential
monitored by JC-1 dye. Methods Enzymol. 260:406–417.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Biederbick A, Kern HF and Elsässer HP:
Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) is a specific in vivo marker for
autophagic vacuoles. Eur J Cell Biol. 66:3–14. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kovács AL and Klionsky DJ: A pioneer in
the field of autophagy microscopy: Attila L Kovács. Autophagy.
9:1908–1921. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu P, Tseng G, Wang Z, Huang Y and
Randhawa P: Diagnosis of T-cell mediated kidney rejection in
formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissues using RNA-Seq based
machine learning algorithms. Hum Pathol. 84:283–290.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gu L, Yu J, Wang Q, Xu B, Ji L, Yu L,
Zhang X and Cai H: Identification of a 5-lncRNA signature-based
risk scoring system for survival prediction in colorectal cancer.
Mol Med Rep. 18:279–291. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol.
5(R1)2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Popescu M, Keller JM and Mitchell JA:
Fuzzy measures on the gene ontology for gene product similarity.
IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 3:263–274. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yu J, Li J, Chen Y, Cao W, Lu Y, Yang J
and Xing E: Snail enhances glycolysis in the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition process by targeting FBP1 in gastric cancer. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 43:31–38. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cui J, Quan M, Jiang W, Hu H, Jiao F, Li
N, Jin Z and Wang L, Wang Y and Wang L: Suppressed expression of
LDHB promotes pancreatic cancer progression via inducing glycolytic
phenotype. Med Oncol. 32(143)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tang Y, Zhang Y, Wang C, Sun Z, Li L,
Cheng S and Zhou W: Overexpression of PCK1 gene antagonizes
hepatocellular carcinoma through the activation of gluconeogenesis
and suppression of glycolysis pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.
47:344–355. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Guo T, Chen T, Gu C, Li B and Xu C:
Genetic and molecular analyses reveal G6PC as a key element
connecting glucose metabolism and cell cycle control in ovarian
cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:7649–7658. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Peng SY, Lai PL, Pan HW, Hsiao LP and Hsu
HC: Aberrant expression of the glycolytic enzymes aldolase B and
type II hexokinase in hepatocellular carcinoma are predictive
markers for advanced stage, early recurrence and poor prognosis.
Oncol Rep. 19:1045–1053. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
van Bruggen R, Gualtieri C, Iliescu A,
Louicharoen Cheepsunthorn C, Mungkalasut P, Trape JF, Modiano D,
Sirima BS, Singhasivanon P, Lathrop M, et al: Modulation of malaria
phenotypes by pyruvate kinase (PKLR) variants in a thai population.
PLoS One. 10(e0144555)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu CC, Wang H, Wang WD, Wang L, Liu WJ,
Wang JH, Geng QR and Lu Y: ENO2 promotes cell proliferation,
glycolysis, and glucocorticoid-resistance in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:1525–1535. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li X, Jiang Y, Meisenhelder J, Yang W,
Hawke DH, Zheng Y, Xia Y, Aldape K, He J, Hunter T, et al:
Mitochondria-translocated phosphoglycerate PGK1 functions as a
protein kinase to coordinate glycolysis and TCA cycle in
tumorigenesis. Mol Cell. 61:705–719. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kim NH, Cha YH, Lee J, Lee SH, Yang JH,
Yun JS, Cho ES, Zhang X, Nam M, Kim N, et al: Snail reprograms
glucose metabolism by repressing phosphofructokinase PFKP allowing
cancer cell survival under metabolic stress. Nat Commun.
8(14374)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
He J, Jin Y, Chen Y, Yao HB, Xia YJ, Ma
YY, Wang W and Shao QS: Downregulation of ALDOB is associated with
poor prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. OncoTargets Ther.
9:6099–6109. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu L, Cai S, Han C, Banerjee A, Wu D, Cui
T, Xie G, Zhang J, Zhang X, McLaughlin E, et al: ALDH1A1
contributes to PARP inhibitor resistance via enhancing DNA repair
in BRCA2-/- ovarian cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
19:199–210. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Singh P, Ravanan P and Talwar P: Death
associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1): A regulator of apoptosis and
autophagy. Front Mol Neurosci. 9(46)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Riehle C, Wende AR, Sena S, Pires KM,
Pereira RO, Zhu Y, Bugger H, Frank D, Bevins J, Chen D, et al:
Insulin receptor substrate signaling suppresses neonatal autophagy
in the heart. J Clin Invest. 123:5319–5333. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hou C, Zhu M, Sun M and Lin Y: MicroRNA
let-7i induced autophagy to protect T cell from apoptosis by
targeting IGF1R. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 453:728–734.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Russell RC, Tian Y, Yuan H, Park HW, Chang
YY, Kim J, Kim H, Neufeld TP, Dillin A and Guan KL: ULK1 induces
autophagy by phosphorylating Beclin-1 and activating VPS34 lipid
kinase. Nat Cell Biol. 15:741–750. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pham HQ, Yoshioka K, Mohri H, Nakata H,
Aki S, Ishimaru K, Takuwa N and Takuwa Y: MTMR4, a
phosphoinositide-specific 3'-phosphatase, regulates TFEB activity
and the endocytic and autophagic pathways. Genes Cells: Jul 2, 2018
(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
37
|
Diao J, Liu R, Rong Y, Zhao M, Zhang J,
Lai Y, Zhou Q, Wilz LM, Li J, Vivona S, et al: ATG14 promotes
membrane tethering and fusion of autophagosomes to endolysosomes.
Nature. 520:563–566. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang D, Xu X and Dong Z: PRKCD/PKCδ
contributes to nephrotoxicity during cisplatin chemotherapy by
suppressing autophagy. Autophagy. 13:631–632. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Pascall JC, Rotondo S, Mukadam AS, Oxley
D, Webster J, Walker SA, Piron J, Carter C, Ktistakis NT and
Butcher GW: The immune system GTPase GIMAP6 interacts with the Atg8
homologue GABARAPL2 and is recruited to autophagosomes. PLoS One.
8(e77782)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liu H, Mi S, Li Z, Hua F and Hu ZW:
Interleukin 17A inhibits autophagy through activation of PIK3CA to
interrupt the GSK3B-mediated degradation of BCL2 in lung epithelial
cells. Autophagy. 9:730–742. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Jung CH, Jun CB, Ro SH, Kim YM, Otto NM,
Cao J, Kundu M and Kim DH: ULK-Atg13-FIP200 complexes mediate mTOR
signaling to the autophagy machinery. Mol Biol Cell. 20:1992–2003.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Efeyan A, Zoncu R, Chang S, Gumper I,
Snitkin H, Wolfson RL, Kirak O, Sabatini DD and Sabatini DM:
Regulation of mTORC1 by the Rag GTPases is necessary for neonatal
autophagy and survival. Nature. 493:679–683. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Jung CH, Ro SH, Cao J, Otto NM and Kim DH:
mTOR regulation of autophagy. FEBS Lett. 584:1287–1295.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Sakamaki JI and Ryan KM: Autophagy
determines the path on the TRAIL to death. Dev Cell. 37:291–293.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Guo Y: Role of HIF-1a in regulating
autophagic cell survival during cerebral ischemia reperfusion in
rats. Oncotarget. 8:98482–98494. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bin BH, Bhin J, Yang SH, Choi DH, Park K,
Shin DW, Lee AY, Hwang D, Cho EG and Lee TR: Hyperosmotic stress
reduces melanin production by altering melanosome formation. PLoS
One. 9(e105965)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
He C, Zhu H, Zhang W, Okon I, Wang Q, Li
H, Le YZ and Xie Z: 7-Ketocholesterol induces autophagy in vascular
smooth muscle cells through Nox4 and Atg4B. Am J Pathol.
183:626–637. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Yuan J, Zhang Y, Sheng Y, Fu X, Cheng H
and Zhou R: MYBL2 guides autophagy suppressor VDAC2 in the
developing ovary to inhibit autophagy through a complex of
VDAC2-BECN1-BCL2L1 in mammals. Autophagy. 11:1081–1098.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wu M, Neilson A, Swift AL, Moran R,
Tamagnine J, Parslow D, Armistead S, Lemire K, Orrell J, Teich J,
et al: Multiparameter metabolic analysis reveals a close link
between attenuated mitochondrial bioenergetic function and enhanced
glycolysis dependency in human tumor cells. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 292:C125–C136. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Androulakis E, Tousoulis D, Papageorgiou
N, Latsios G, Siasos G and Stefanadis C: The role of matrix
metalloproteinases in essential hypertension. Curr Top Med Chem.
12:1149–1158. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Tran ED, DeLano AF and Schmid-Schönbein
GW: Enhanced matrix metalloproteinase activity in the spontaneously
hypertensive rat: VEGFR-2 cleavage endothelial apoptosis, and
capillary rarefaction. J Vasc Res. 47:423–431. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Williams JM, Zhang J, North P, Lacy S,
Yakes M, Dahly-Vernon A and Roman RJ: Evaluation of metalloprotease
inhibitors on hypertension and diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 300:F983–F998. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Allawzi AM, Vang A, Clements RT, Jhun BS,
Kue NR, Mancini TJ, Landi AK, Terentyev D, O-Uchi J, Comhair SA, et
al: Activation of anoctamin-1 limits pulmonary endothelial cell
proliferation via p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent
apoptosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 58:658–667. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Heinze C, Seniuk A, Sokolov MV, Huebner
AK, Klementowicz AE, Szijártó IA, Schleifenbaum J, Vitzthum H,
Gollasch M, Ehmke H, et al: Disruption of vascular
Ca2+-activated chloride currents lowers blood pressure.
J Clin Invest. 124:675–686. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Manoury B, Tamuleviciute A and Tammaro P:
TMEM16A/anoctamin-1 protein mediates calcium-activated chloride
currents in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. J Physiol.
588:2305–2314. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Usatyuk PV, Singleton PA, Pendyala S,
Kalari SK, He D, Gorshkova IA, Camp SM, Moitra J, Dudek SM, Garcia
JG and Natarajan V: Novel role for non-muscle myosin light chain
kinase (MLCK) in hyperoxia-induced recruitment of cytoskeletal
proteins, NADPH oxidase activation, and reactive oxygen species
generation in lung endothelium. J Biol Chem. 287:9360–9375.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Rigor RR, Shen Q, Pivetti CD, Wu MH and
Yuan SY: Myosin light chain kinase signaling in endothelial barrier
dysfunction. Med Res Rev. 33:911–933. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Torimoto K, Okada Y and Tanaka Y: Type 2
diabetes and vascular endothelial dysfunction. J UOEH. 40:65–75.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Japanese).
|
|
59
|
Rahman TJ, Mayosi BM, Hall D, Avery PJ,
Stewart PM, Connell JM, Watkins H and Keavney B: Common variation
at the 11-b hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 gene is associated
with left ventricular mass. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 4:156–162.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
White PC, Rogoff D and McMillan DR:
Physiological roles of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1
and hexose-6-phoshate dehydrogenase. Curr Opin Pediatr. 20:453–457.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Spolarics Z, Lang CH, Bagby GJ and Spitzer
JJ: Glutamine and fatty acid oxidation are the main sources of
energy for Kupffer and endothelial cells. Am J Physiol.
261:G185–G190. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Mertens S, Noll T, Spahr R, Krützfeldt A
and Piper HM: Energetic response of coronary endothelial cells to
hypoxia. Am J Physiol. 258:H689–H694. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
De Bock K, Georgiadou M, Schoors S,
Kuchnio A, Wong BW, Cantelmo AR, Quaegebeur A, Ghesquière B,
Cauwenberghs S, Eelen G, et al: Role of PFKFB3-driven glycolysis in
vessel sprouting. Cell. 154:651–663. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Polet F and Feron O: Endothelial cell
metabolism and tumour angiogenesis: Glucose and glutamine as
essential fuels and lactate as the driving force. J Inter Med.
273:156–165. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Schoors S, Bruning U, Missiaen R, Queiroz
KC, Borgers G, Elia I, Zecchin A, Cantelmo AR, Christen S, Goveia
J, et al: Fatty acid carbon is essential for dNTP synthesis in
endothelial cells. Nature. 520:192–197. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Rüster C and Wolf G:
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and progression of renal
disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:2985–2991. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Wolf G, Butzmann U and Wenzel UO: The
renin-angiotensin system and progression of renal disease: From
hemodynamics to cell biology. Nephron Physiol. 93:P3–P13.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Tian Z, Greene AS, Pietrusz JL, Matus IR
and Liang M: MicroRNA-target pairs in the rat kidney identified by
microRNA microarray, proteomic, and bioinformatic analysis. Genome
Res. 18:404–411. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Perdigão-Henriques R, Petrocca F,
Altschuler G, Thomas MP, Le MT, Tan SM, Hide W and Lieberman J:
MiR-200 promotes the mesenchymal to epithelial transition by
suppressing multiple members of the Zeb2 and Snail1 transcriptional
repressor complexes. Oncogene. 35:158–172. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Filios SR, Xu G, Chen J, Hong K, Jing G
and Shalev A: MicroRNA-200 is induced by thioredoxin-interacting
protein and regulates Zeb1 protein signaling and beta cell
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 289:36275–36283. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Pan Y, Liang H, Liu H, Li D, Chen X, Li L,
Zhang C and Zen K: Platelet-secreted microRNA-223 promotes
endothelial cell apoptosis induced by advanced glycation end
products via targeting the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. J
Immunol. 192:437–446. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Meloche J, Le Guen M, Potus F, Vinck J,
Ranchoux B, Johnson I, Antigny F, Tremblay E, Breuils-Bonnet S,
Perros F, et al: MiR-223 reverses experimental pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 309:C363–C372.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Wang X, Zhang X, Ren XP, Chen J, Liu H,
Yang J, Medvedovic M, Hu Z and Fan GC: MicroRNA-494 targeting both
proapoptotic and antiapoptotic proteins protects against
ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury. Circulation.
122:1308–1318. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Shukla GC, Singh J and Barik S: MicroRNAs:
Processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory
functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 3:83–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: MTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Shimobayashi M and Hall MN: Making new
contacts: The mTOR network in metabolism and signaling crosstalk.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:155–162. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Surviladze Z, Sterk RT, DeHaro SA and
Ozbun MA: Cellular entry of human papillomavirus type 16 involves
activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway
and inhibition of autophagy. J Virol. 87:2508–2517. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Jin Y, Liu S, Ma Q, Xiao D and Chen L:
Berberine enhances the AMPK activation and autophagy and mitigates
high glucose-induced apoptosis of mouse podocytes. Eur J Pharmacol.
794:106–114. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Bruckova L, Soukup T, Visek B, Moos J,
Moosova M, Pavelkova J, Rezabek K, Kucerova L, Micuda S, Brcakova E
and Mokry J: Proliferative potential and phenotypic analysis of
long-term cultivated human granulosa cells initiated by addition of
follicular fluid. J Assist Reprod Genet. 28:939–950.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Rabelink TJ and Carmeliet P: Renal
metabolism in 2017: Glycolytic adaptation and progression of kidney
disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 14:75–76. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Garcia D and Shaw RJ: AMPK: Mechanisms of
cellular energy sensing and restoration of metabolic balance. Mol
Cell. 66:789–800. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Robey RB and Hay N: Akt, hexokinase, mTOR:
Targeting cellular energy metabolism for cancer therapy. Drug
Discov Today Dis Mech. 2:239–246. 2005.
|
|
83
|
Jiao L, Zhang HL, Li DD, Yang KL, Tang J,
Li X, Ji J, Yu Y, Wu RY, Ravichandran S, et al: Regulation of
glycolytic metabolism by autophagy in liver cancer involves
selective autophagic degradation of HK2 (hexokinase 2). Autophagy.
14:671–684. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Duan L, Perez RE, Davaadelger B, Dedkova
EN, Blatter LA and Maki CG: p53-regulated autophagy is controlled
by glycolysis and determines cell fate. Oncotarget. 6:23135–23156.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|