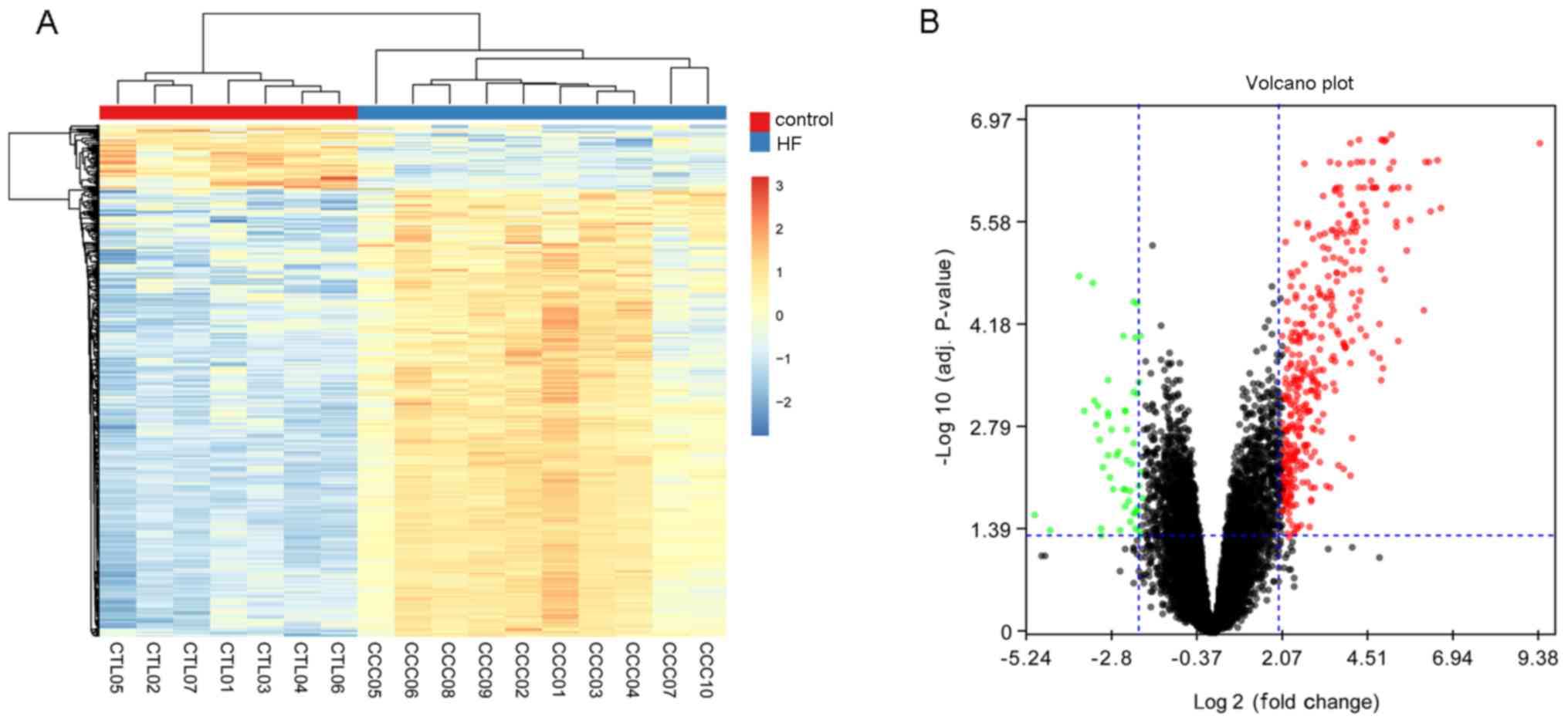
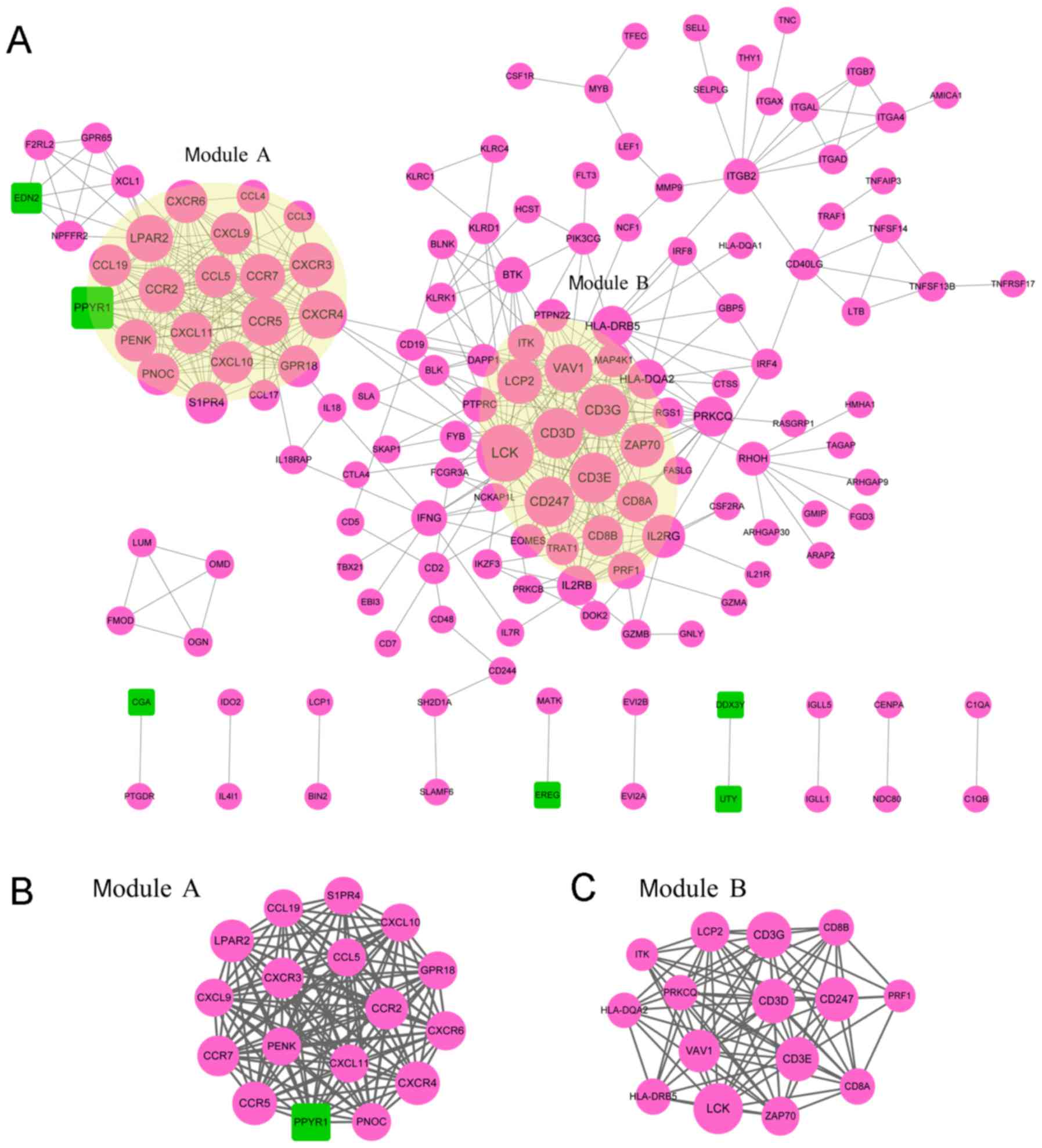
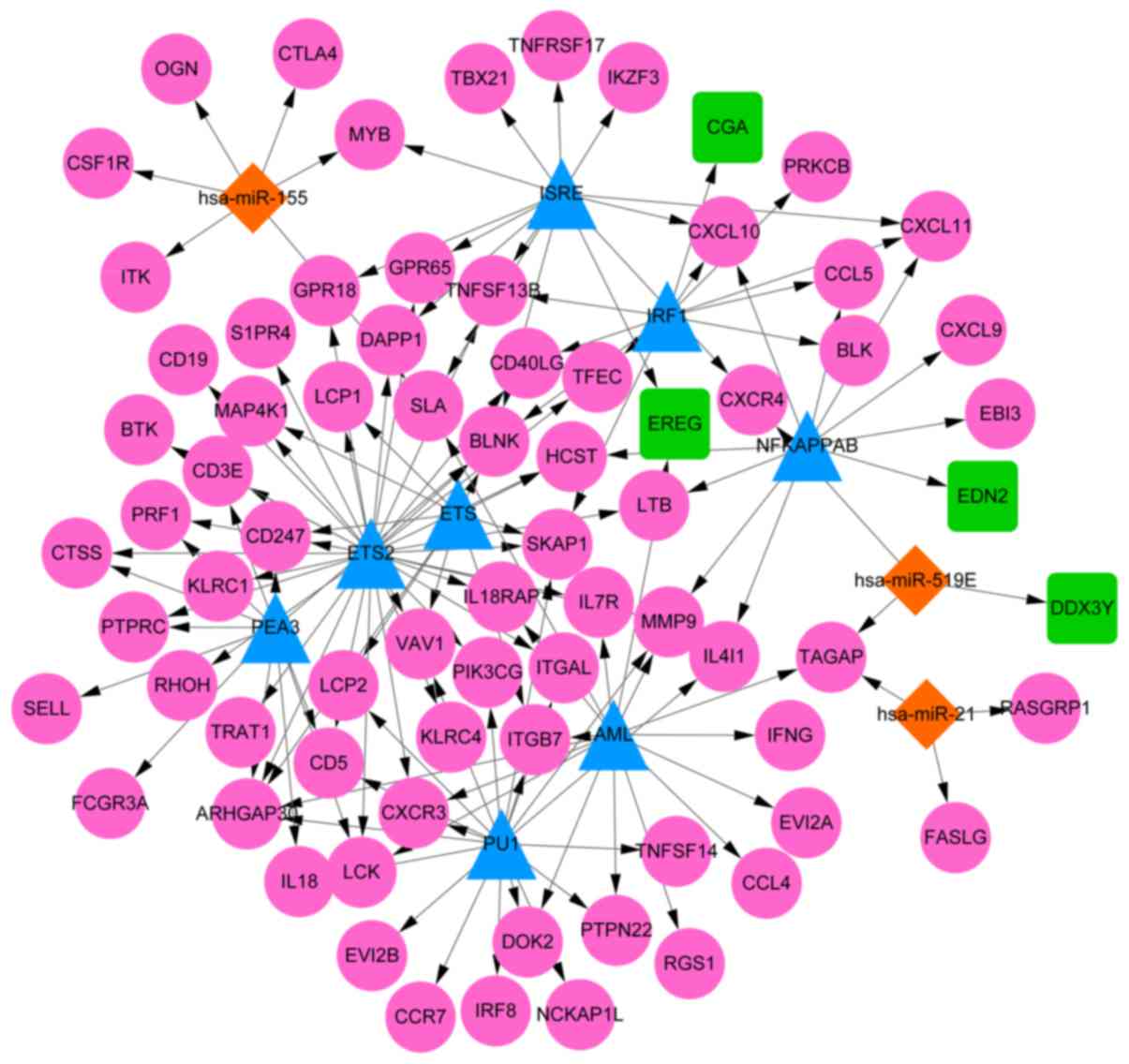
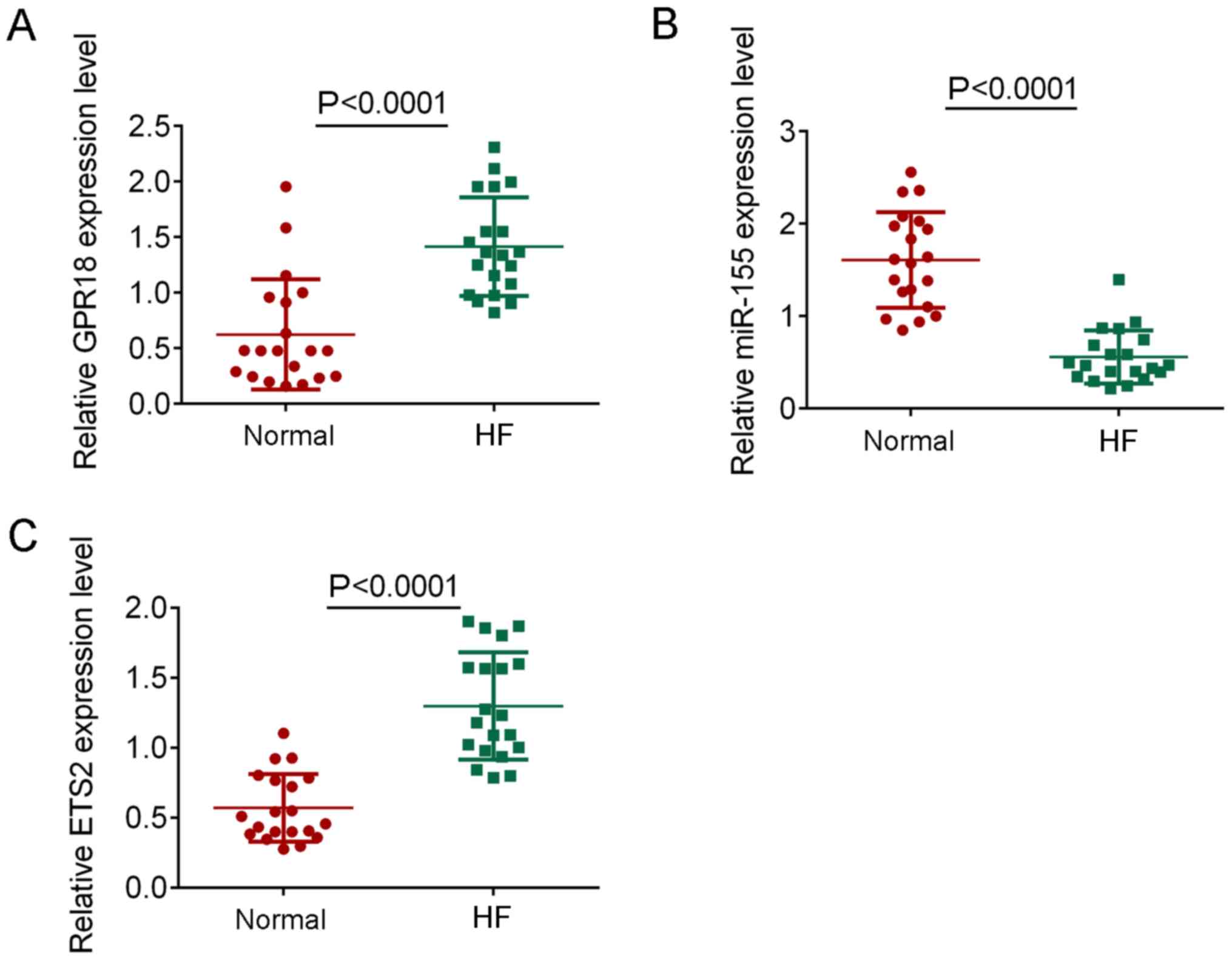
|
1
|
Forouzanfar MH, Moran A, Phillips D,
Mensah GA, Ezzati M, Naghavi M and Murray Christopher JL:
Prevalence of heart failure by cause in 21 regions: global burden
of diseases, injuries and risk factors-2010 study. Journal of the
American College of Cardiology. 61:E786. 2013.
|
|
2
|
Farré N, Vela E, Clèries M, Bustins M,
Cainzos-Achirica M, Enjuanes C, Moliner P, Ruiz S, Verdú-Rotellar
JM and Comín-Colet J: Real world heart failure epidemiology and
outcome: A population-based analysis of 88,195 patients. PLoS One.
12(e0172745)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cook C, Cole G, Asaria P, Jabbour R and
Francis DP: The annual global economic burden of heart failure. Int
J Cardiol. 171:368–376. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Inglis SC, Clark RA, Dierckx R,
Prieto-Merino D and Cleland JGF: Structured telephone support or
non-invasive telemonitoring for patients with heart failure.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 10(CD007228)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pinti MV, Hathaway QA and Hollander JM:
Role of microRNA in metabolic shift during heart failure. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 312:H33–H45. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Duan Q, Yang L, Gong W, Chaugai S, Wang F,
Chen C, Wang P, Zou MH and Wang DW: MicroRNA-214 is upregulated in
heart failure patients and suppresses XBP1-mediated endothelial
cells angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 230:1964–1973. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Duan Q, Chen C, Yang L, Li N, Gong W, Li S
and Wang DW: MicroRNA regulation of unfolded protein response
transcription factor XBP1 in the progression of cardiac hypertrophy
and heart failure in vivo. J Transl Med. 13(363)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Masson S, Batkai S, Beermann J, Bär C,
Pfanne A, Thum S, Magnoli M, Balconi G, Nicolosi GL, Tavazzi L, et
al: Circulating microRNA-132 levels improve risk prediction for
heart failure hospitalization in patients with chronic heart
failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 20:78–85. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li S, Fan Q, He S, Tang T, Liao Y and Xie
J: MicroRNA-21 negatively regulates Treg cells through a
TGF-β1/Smad-independent pathway in patients with coronary heart
disease. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:866–878. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mcculley DJ and Black BL: Chapter
nine-Transcription Factor Pathways and Congenital Heart Disease.
In: Current Topics in Developmental Biology. Vol 100. Elsevier
Inc., 2012.
|
|
11
|
Bakker ML, Boink GJJ, Boukens BJ, Verkerk
AO, Malou VDB, Den Haan AD, Hoogaars WM, Buermans HP, de Bakker JM,
Seppen J, et al: T-box transcription factor TBX3 reprogrammes
mature cardiac myocytes into pacemaker-like cells. Cardiovasc Res.
94:439–449. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Courties G, Heidt T, Sebas M, Iwamoto Y,
Jeon D, Truelove J, Tricot B, Wojtkiewicz G, Dutta P, Sager HB, et
al: In vivo silencing of the transcription factor IRF5 reprograms
the macrophage phenotype and improves infarct healing. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 63:1556–1566. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Maier HJ, Schips TG, Wietelmann A, Krüger
M, Brunner C, Sauter M, Klingel K, Böttger T, Braun T and Wirth T:
Cardiomyocyte-specific IκB kinase (IKK)/NF-κB activation induces
reversible inflammatory cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 109:11794–11799. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear Models for
Microarray Data. In: Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
Solutions Using R and Bioconductor. Gentleman R, Carey VJ, Huber W,
Irizarry RA and Dudoit S (eds). Springer, New York, NY, 2005.
|
|
15
|
Phipson B, Lee S, Majewski IJ, Alexander
WS and Symth GK: Empirical Bayes in the presence of exceptional
cases, with application to microarray data. ScienceOpen, Inc.,
Burlington, MA, 2016.
|
|
16
|
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono
H and Kanehisa M: KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 27:29–34. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:D561–D568. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bandettini WP, Kellman P, Mancini C,
Booker OJ, Vasu S, Leung SW, Wilson JR, Shanbhag SM, Chen MY and
Arai AE: MultiContrast delayed enhancement (MCODE) improves
detection of subendocardial myocardial infarction by late
gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance: A
clinical validation study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson.
14(83)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang J, Duncan D, Shi Z and Zhang B:
WEB-based GEne SeT AnaLysis Toolkit (WebGestalt): Update 2013.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41:W77–W83. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Method. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Franics GS and Tang WH: Pathophysiology of
congestive heart failure. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 4 (Suppl 2):S14–S20.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ziaeian B and Fonarow GC: Epidemiology and
aetiology of heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. 13:368–378.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Marrouche NF, Brachmann J, Andresen D,
Siebles J, Boersma L, Jordaens L, Merkely B, Pokushalov E, Sanders
P, Proff J, et al: Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation with
heart failure. N Engl J Med. 378:417–427. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Velazquez EJ, Morrow DA, DeVore AD, Duffy
CI, Ambrosy AP, McCague K, Rocha R and Braunwald E: PIONEER-HF
Investigators. Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition in acute
decompensated heart failure. N Engl J Med. 380:539–548.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Caldwell MD, Hu SJ, Viswanathan S,
Bradshaw H, Kelly ME and Straiker A: A GPR18-based signalling
system regulates IOP in murine eye. Br J Pharmacol. 169:834–843.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Alexander SP: So what do we call GPR18
now? Br J Pharmacol. 165:2411–2413. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Penumarti A and Abdel-Rahman AA: Role of
central atypical cannabinoid receptor GPR18 in modulating
cardiovascular function. FASEB J. 26: (Suppl 1)(663.10)2012.
|
|
30
|
Penumarti A and Abdel-Rahman AA: Abstract
17612: Central GPR18 mediates hypotension via enhanced
PI3K/AKT-ERK1/2-nNOS signaling and inhibition of cAMP in the
rostral ventrolateral medulla of conscious normotensive rats.
Circulation. 128:A17612. 2013.
|
|
31
|
Sheydina A, Volkova M, Jiang L, Juhasz O,
Zhang J, Tae HJ, Perino MG, Wang M, Zhu Y, Lakatta EG and Boheler
KR: Linkage of cardiac gene expression profiles and ETS2 with
lifespan variability in rats. Aging Cell. 11:350–359.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Islas JF, Liu Y, Weng KC, Robertson MJ,
Zhang S, Prejusa A, Harger J, Tikhomirova D, Chopra M, Iyer D, et
al: Transcription factors ETS2 and MESP1 transdifferentiate human
dermal fibroblasts into cardiac progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 109:13016–13021. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Schwartz RJ, Potaman VN and Francisco IJ:
Ets2 and Mesp1 generate cardiac progenitors from fibroblasts. US
Patent 9109232. Filed June 12, 2013; issued August 18, 2015.
|
|
34
|
Rowell J, Koitabashi N, Kass DA and Barth
AS: Dynamic gene expression patterns in animal models of early and
late heart failure reveal biphasic-bidirectional transcriptional
activation of signaling pathways. Physiol Genomics. 46:779–787.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Czyzyk-Krzeska MF and Zhang X: MiR-155 at
the heart of oncogenic pathways. Oncogene. 33:677–678.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Bao JL and Lin L: MiR-155 and miR-148a
reduce cardiac injury by inhibiting NF-κB pathway during acute
viral myocarditis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:2349–2356.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Blanco RR, Austin H, Vest RN III, Valadri
R, Li W, Lassegue B, Song Q, London B, Dudley SC, Bloom HL, et al:
Angiotensin receptor type 1 single nucleotide polymorphism A1166C
is associated with malignant arrhythmias and altered circulating
miR-155 levels in patients with chronic heart failure. J Card Fail.
18:717–723. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Matsumoto S, Sakata Y, Nakatani D, Suna S,
Mizuno H, Shimizu M, Usami M, Sasaki T, Sato H, Kawahara Y, et al:
A subset of circulating microRNAs are predictive for cardiac death
after discharge for acute myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 427:280–284. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|