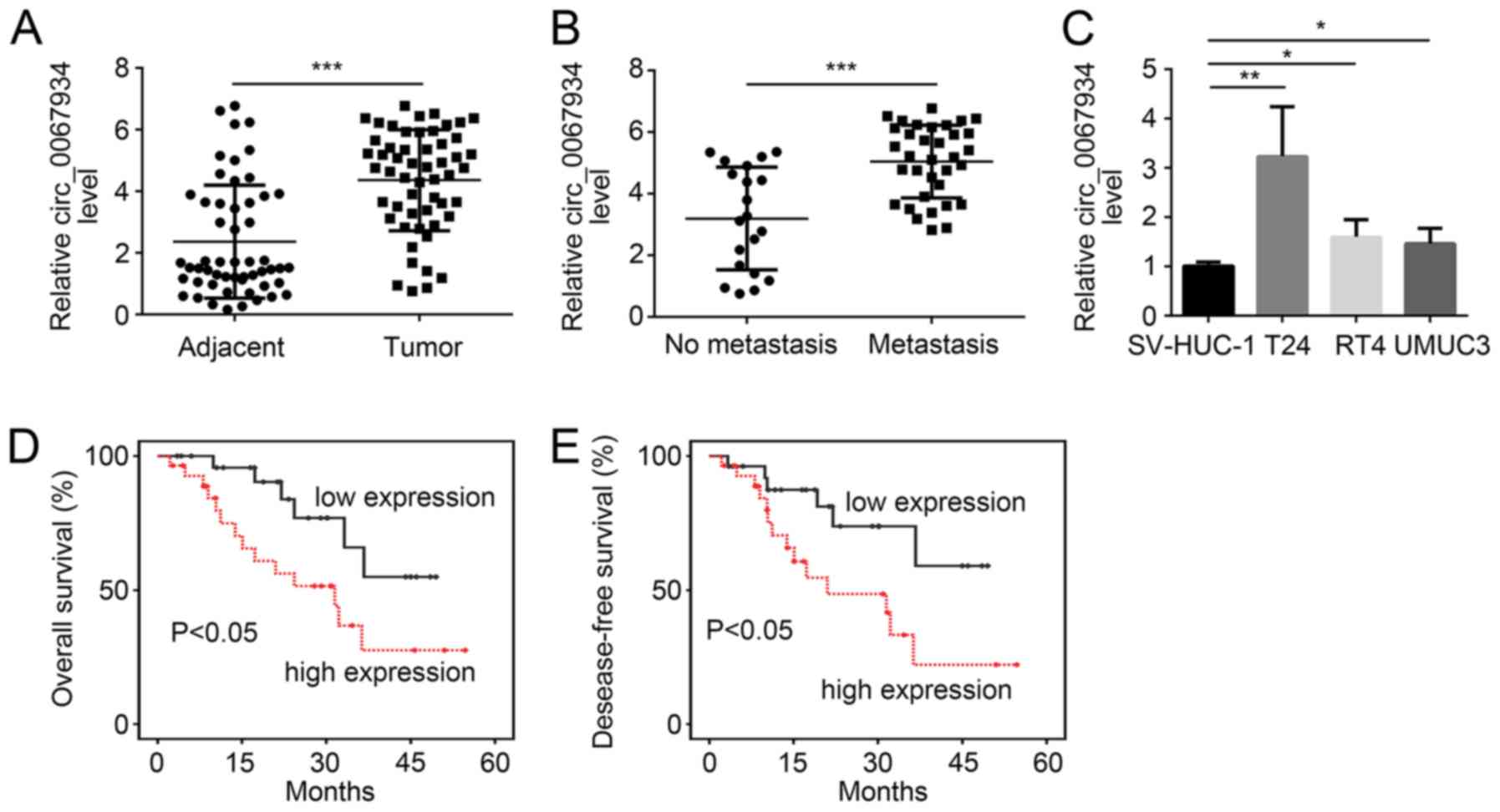
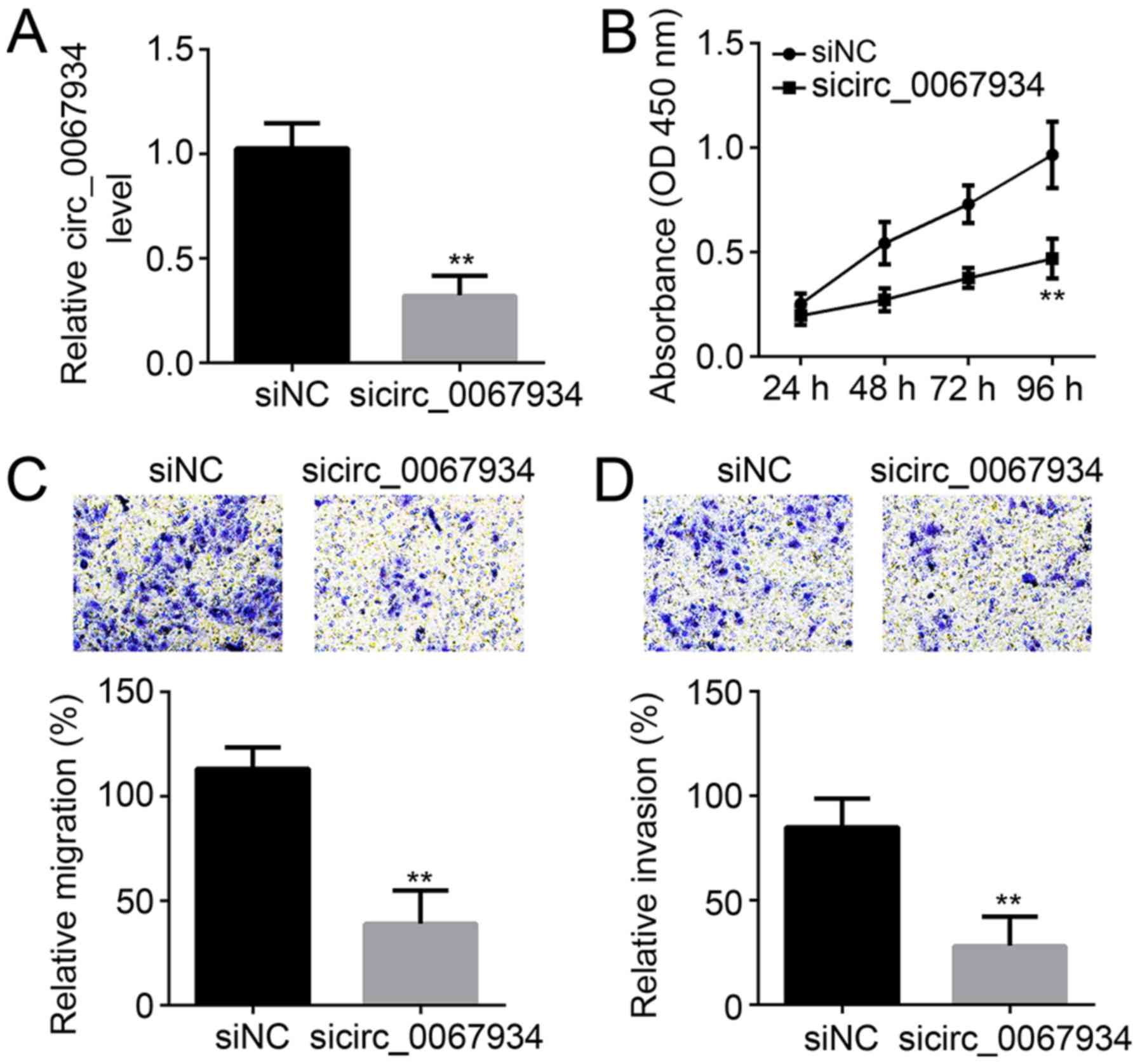
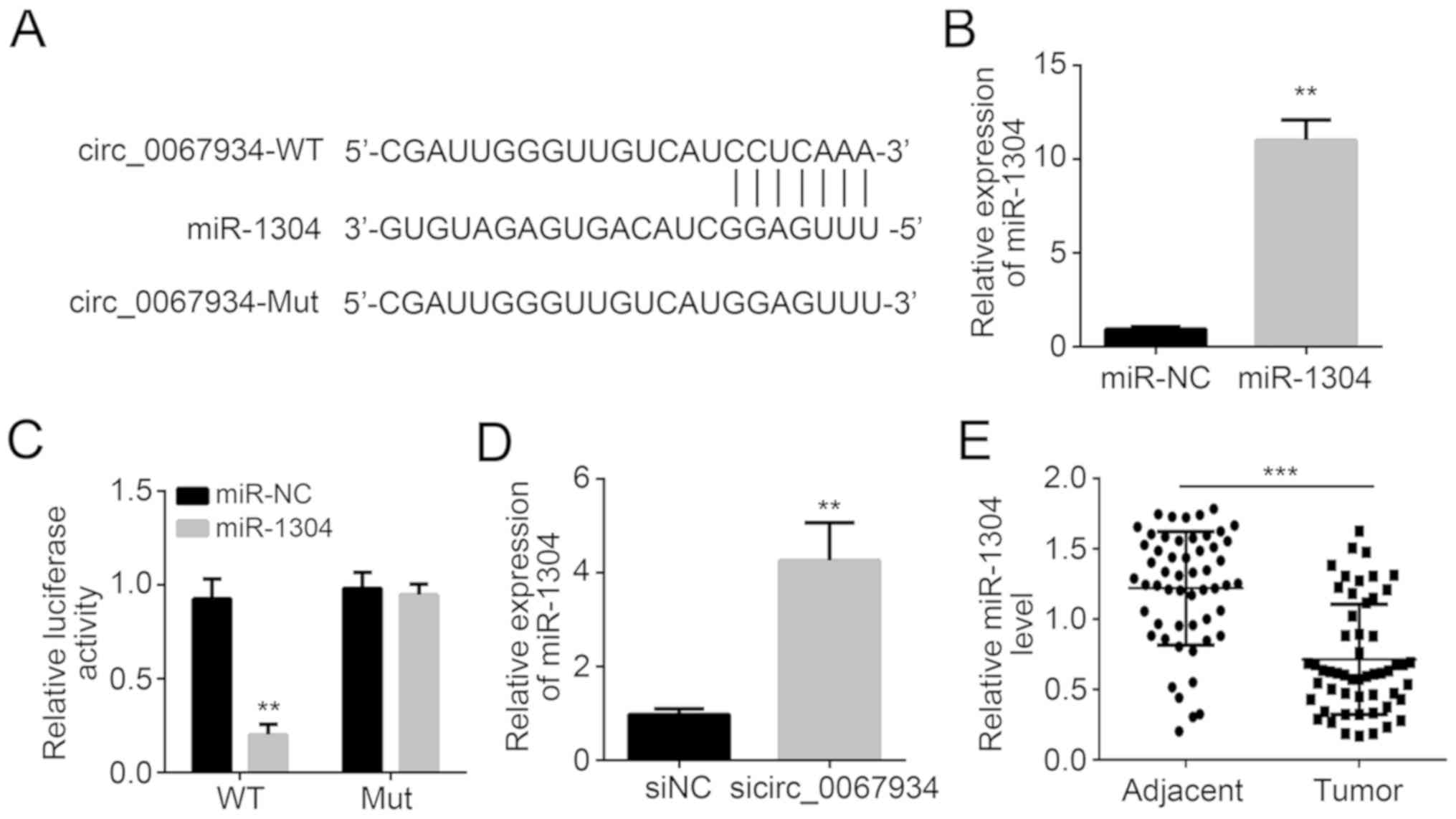
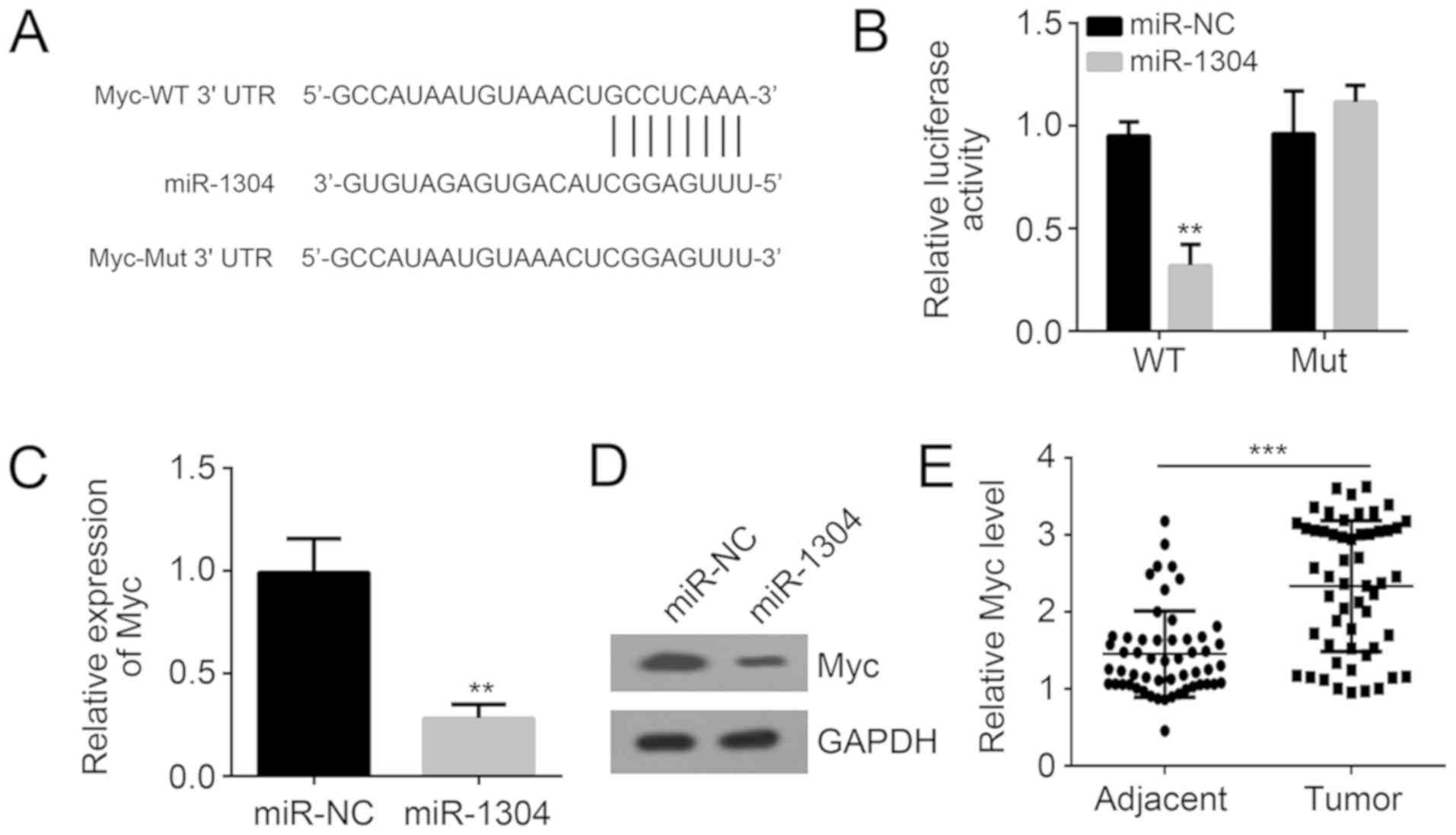
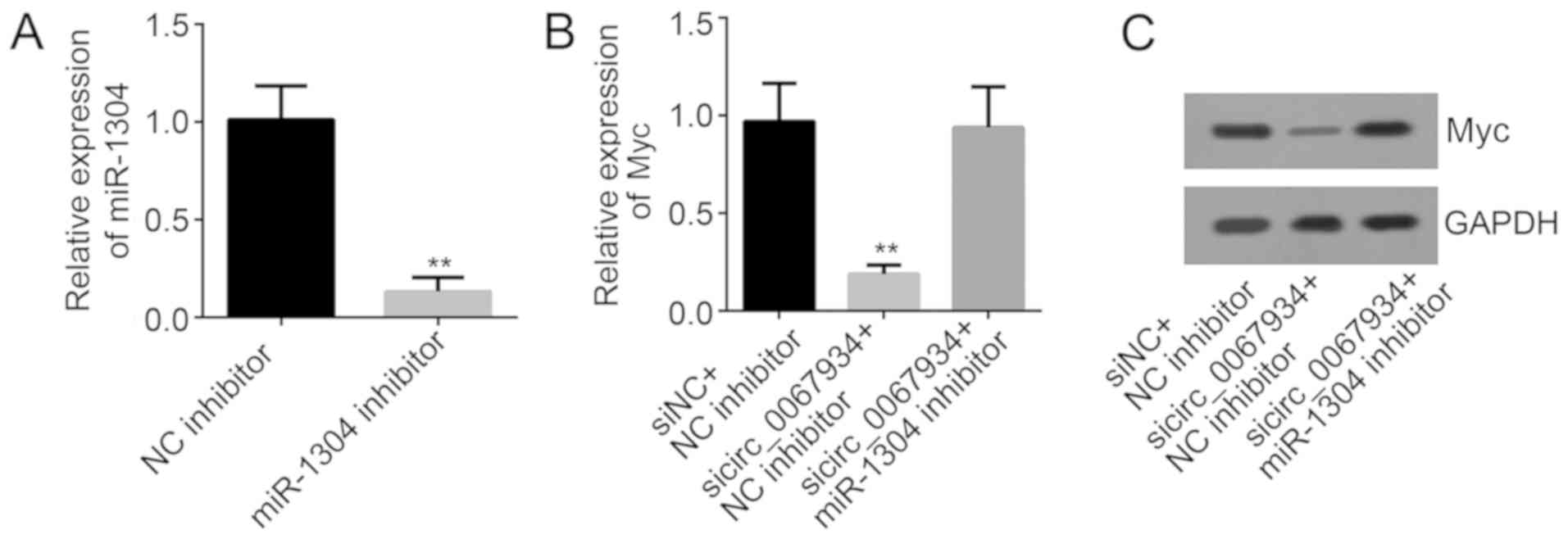
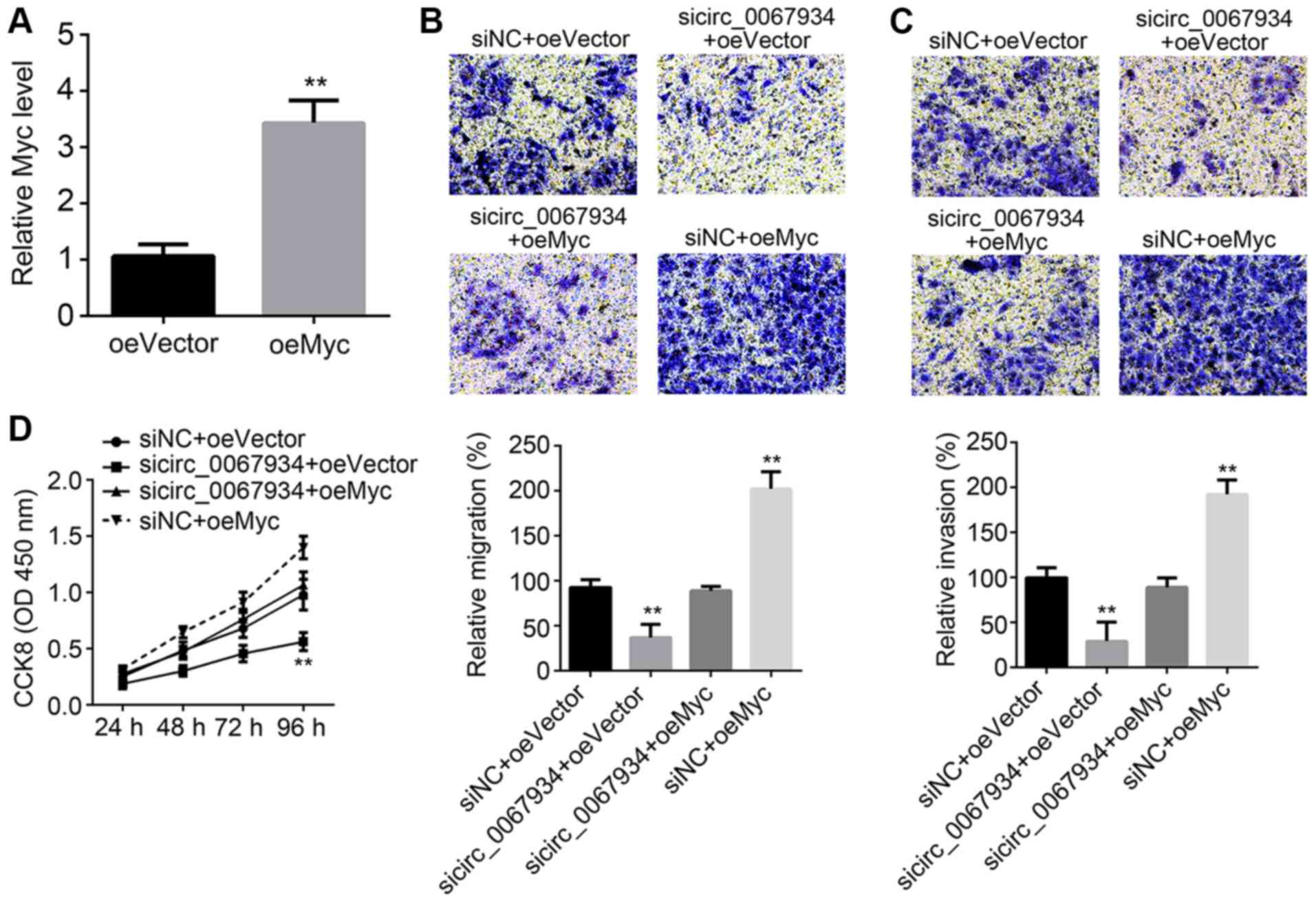
|
1
|
Liu Z and Zhang H: LncRNA plasmacytoma
variant translocation 1 is an oncogene in bladder urothelial
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:64273–64282. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gayyed MF and Tawfiek ER: Utility of SOX2
and livin co-expression in the prognosis of bladder cancer with
bilharzial and non-bilharzial bladder status. World J Oncol.
6:446–455. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U,
Sahu A, Hosono Y, Barrette TR, Prensner JR, Evans JR, Zhao S, et
al: The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human
transcriptome. Nature Genet. 47:199–208. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Xu XW, Zheng BA, Hu ZM, Qian ZY, Huang CJ,
Liu XQ and Wu WD: Circular RNA hsa_circ_000984 promotes colon
cancer growth and metastasis by sponging miR-106b. Oncotarget.
8:91674–91683. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Xu T, Wu J, Han P, Zhao Z and Song X:
Circular RNA expression profiles and features in human tissues: A
study using RNA-seq data. BMC Genomics. 18
(Suppl)(680)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Quan G and Li J: Circular RNAs:
Biogenesis, expression and their potential roles in reproduction. J
Ovarian Res. 11(9)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lyu D and Huang S: The emerging role and
clinical implication of human exonic circular RNA. Rna Biol. 14:00.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zheng Q, Bao C, Guo W, Li S, Chen J, Chen
B, Luo Y, Lyu D, Li Y, Shi G, et al: Circular RNA profiling reveals
an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging
multiple miRNAs. Nat Commun. 7(11215)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhong Z, Huang M, Lv M, He Y, Duan C,
Zhang L and Chen J: Circular RNA MYLK as a competing endogenous RNA
promotes bladder cancer progression through modulating VEGFA/VEGFR2
signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 403(305)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li P, Yang X, Yuan W, Yang C, Zhang X, Han
J, Wang J, Deng X, Yang H, Li P, et al: CircRNA-cdr1as exerts
anti-oncogenic functions in bladder cancer by sponging
MicroRNA-135a. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:1606–1616. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li Y, Zheng F, Xiao X, Xie F, Tao D, Huang
C, Liu D, Wang M, Wang L, Zeng F and Jiang G: CircHIPK3 sponges
miR-558 to suppress heparanase expression in bladder cancer cells.
EMBO Rep. 18:1646–1659. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xia W, Qiu M, Chen R, Wang S, Leng X, Wang
J, Xu Y, Hu J, Dong G, Xu PL and Yin R: Circular RNA
has_circ_0067934 is upregulated in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma and promoted proliferation. Sci Rep.
6(35576)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhu Q, Lu G, Luo Z, Gui F, Wu J, Zhang D
and Ni Y: CircRNA circ_0067934 promotes tumor growth and metastasis
in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulation of
miR-1324/FZD5/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
497:626–632. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Svatek RS, Hollenbeck BK, Sten HN, Richard
L, Kim SP, Arnulf S and Yair L: The economics of bladder cancer:
Costs and considerations of caring for this disease. Eur Urol.
66:253–262. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jr GRP, Friedell GH, Culp DA, Loening S,
Cummings KB, Cutler SJ, Flanagan MJ, Jr WWK, Pearse H and Merrin C:
Superficial bladder cancer: Progression and recurrence. J Urology.
130:1083–1086. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang T, Yuan J, Feng N, Li Y, Lin Z, Jiang
Z and Gui Y: Hsa-miR-1 downregulates long non-coding RNA urothelial
cancer associated 1 in bladder cancer. Tumor Biol. 35:10075–10084.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rosser CJ, Urquidi V and Goodison S:
Urinary biomarkers of bladder cancer: An update and future
perspectives. Biomark Med. 7:779–790. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang J and Li H: CircRNA circ_0067934
silencing inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of
NSCLC cells and correlates with unfavorable prognosis in NSCLC. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 3053–3060. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mao W, Huang X, Wang L, Zhang Z, Liu M, Li
Y, Luo M, Yao X, Fan J and Geng J: Circular RNA hsa_circ_0068871
regulates FGFR3 expression and activates STAT3 by targeting
miR-181a-5p to promote bladder cancer progression. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 38(169)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lin G, Sheng H, Xie H, Zheng Q, Shen Y,
Shi G and Ye D: circLPAR1 is a novel biomarker of prognosis for
muscle-invasive bladder cancer with invasion and metastasis by
miR-762. Oncol Lett. 17:3537–3547. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kiems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bonizzato A, Gaffo E, Te Kronnie G and
Bortoluzzi S: CircRNAs in hematopoiesis and hematological
malignancies. Blood Cancer J. 6(e483)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li CG, Pu MF, Li CZ, Gao M, Liu MX, Yu CZ,
Yan H, Peng C, Zhao Y, Li Y, et al: MicroRNA-1304 suppresses human
non-small cell lung cancer cell growth in vitro by targeting heme
oxygenase-1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:110–119. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Posternak V and Cole MD: Strategically
targeting MYC in cancer. F1000Res. 5(pii: F408)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Felsher DW: MYC inactivation elicits
oncogene addiction through both tumor cell-intrinsic and
host-dependent mechanisms. Genes Cancer. 1:597–604. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|