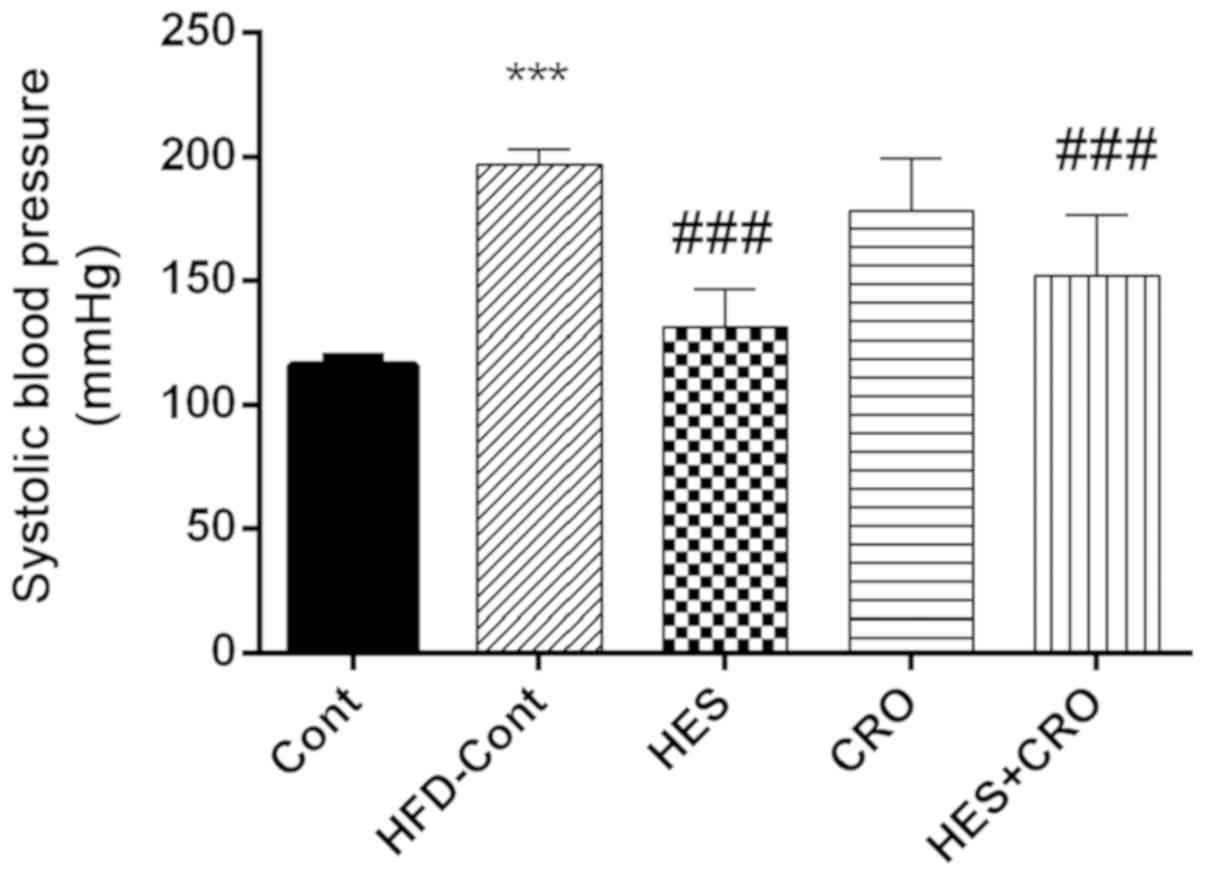
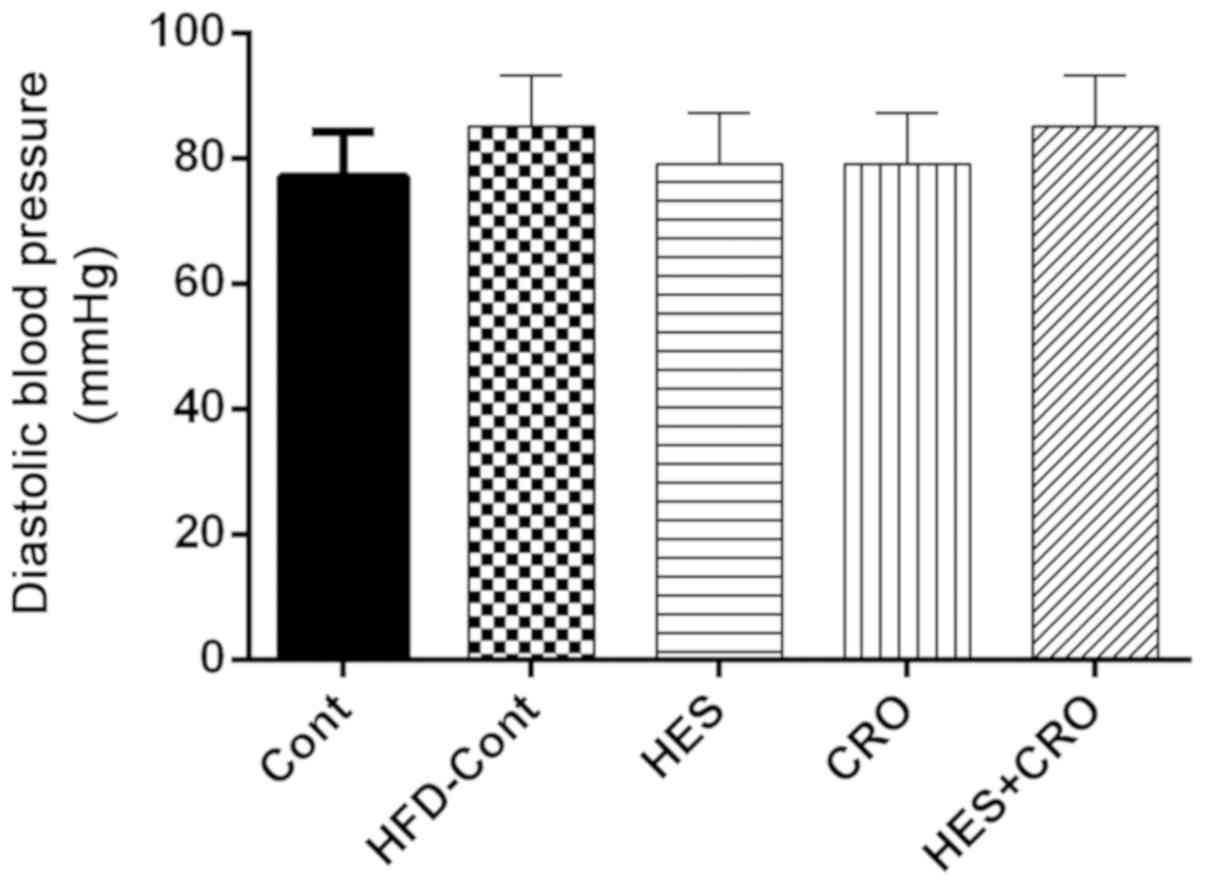
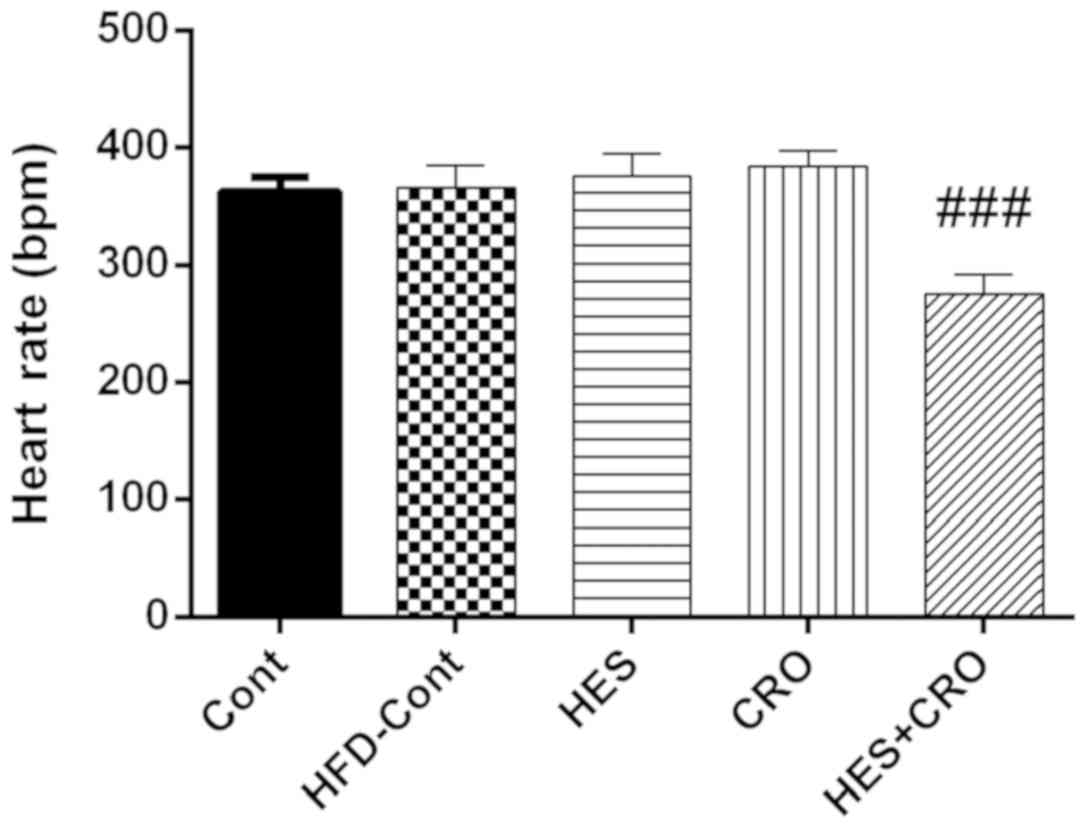
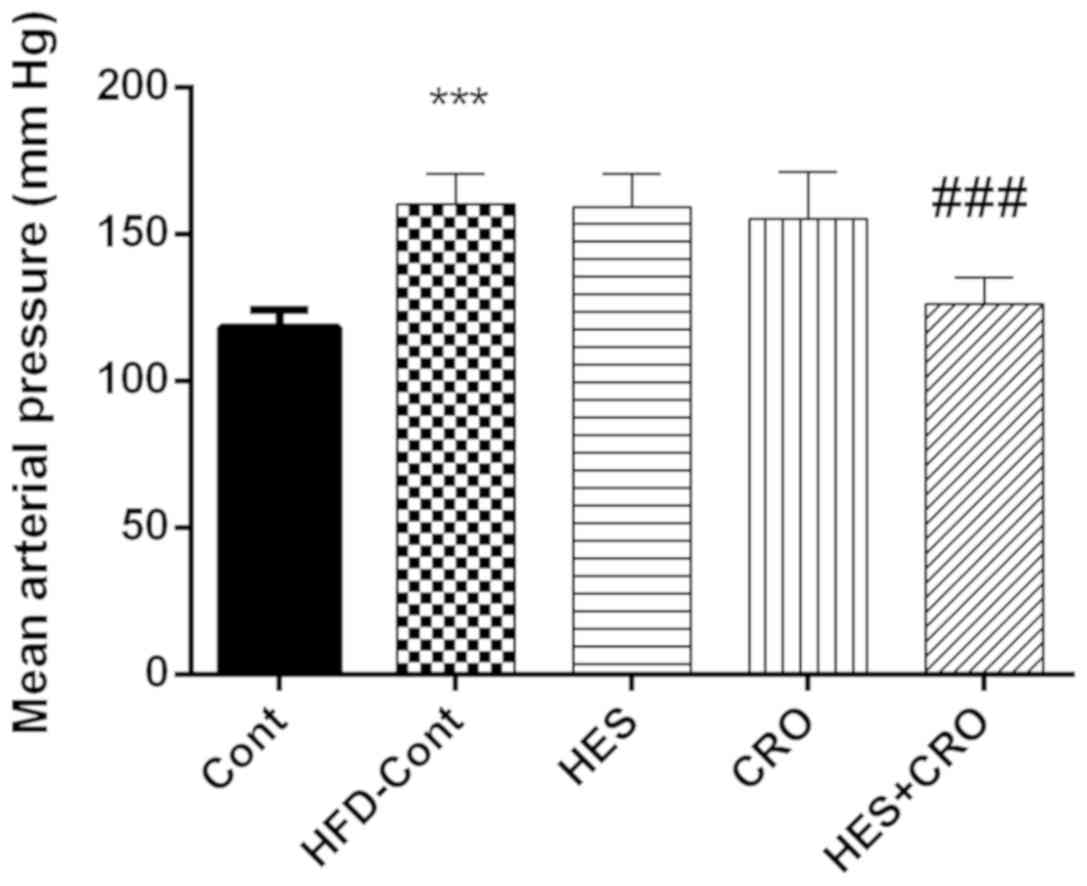
|
1
|
Hashemzaei M, Abdollahzadeh M, Iranshahi
M, Golmakani E, Rezaee R and Tabrizian K: Effects of luteolin and
luteolin-morphine co-administration on acute and chronic pain and
sciatic nerve ligated-induced neuropathy in mice. J Complement
Integr Med. 14(20160066)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hashemzaei M, Imen Shahidi M, Moallem SA,
Abnous K, Ghorbani M and Mohamadpour AH: Modulation of JAK2, STAT3
and Akt1 proteins by granulocyte colony stimulating factor
following carbon monoxide poisoning in male rat. Drug Chem Toxicol.
39:375–379. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hashemzaei M, Karami SP, Delaramifar A,
Sheidary A, Tabrizian K, Rezaee R, Shahsavand S, Arsene AL,
Tsatsakis AM and Taghdisi SM: Anticancer effects of
co-administration of daunorubicin and resveratrol in MOLT-4, U266
B1 and Raji cell lines. Farmacia. 64:36–42. 2016.
|
|
4
|
Tabeshpour J, Hashemzaei M and Sahebkar A:
The regulatory role of curcumin on platelet functions. J Cell
Biochem. 119:8713–8722. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tabrizian K, Yaghoobi NS, Iranshahi M,
Shahraki J, Rezaee R and Hashemzaei M: Auraptene consolidates
memory, reverses scopolamine-disrupted memory in passive avoidance
task, and ameliorates retention deficits in mice. Iran J Basic Med
Sci. 18:1014–1019. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buijsse B, Weikert C, Drogan D, Bergmann M
and Boeing H: Chocolate consumption in relation to blood pressure
and risk of cardiovascular disease in German adults. Eur Heart J.
31:1616–1623. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Di Castelnuovo A, Rotondo S, Iacoviello L,
Donati MB and De Gaetano G: Meta-analysis of wine and beer
consumption in relation to vascular risk. Circulation.
105:2836–2844. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mink PJ, Scrafford CG, Barraj LM, Harnack
L, Hong CP, Nettleton JA and Jacobs DR Jr: Flavonoid intake and
cardiovascular disease mortality: A prospective study in
postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 85:895–909. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Peters U, Poole C and Arab L: Does tea
affect cardiovascular disease? A meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol.
154:495–503. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Auclair S, Milenkovic D, Besson C, Chauvet
S, Gueux E, Morand C, Mazur A and Scalbert A: Catechin reduces
atherosclerotic lesion development in apo E-deficient mice: A
transcriptomic study. Atherosclerosis. 204:e21–e27. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Norata GD, Marchesi P, Passamonti S,
Pirillo A, Violi F and Catapano AL: Anti-inflammatory and
anti-atherogenic effects of cathechin, caffeic acid and
trans-resveratrol in apolipoprotein E deficient mice.
Atherosclerosis. 191:265–271. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rezaee R, Jamialahmadi K, Riahi Zanjani B,
Mahmoudi M, Abnous K, Zamani Taghizadeh Rabe S, Tabasi N, Zali M,
Rezaee M, Amin B, et al: Crocin effects on human myeloma cells
regarding intracellular redox state, DNA fragmentation, and
apoptosis or necrosis profile. Jundishapur J Nat Pharm Prod.
9(e20131)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rezaee R, Mahmoudi M, Abnous K, Zamani
Taghizadeh Rabe S, Tabasi N, Hashemzaei M and Karimi G: Cytotoxic
effects of crocin on MOLT-4 human leukemia cells. J Complement
Integr Med. 10:105–112. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yaribeygi H, Mohammadi MT, Rezaee R and
Sahebkar A: Crocin improves renal function by declining Nox-4,
IL-18, and p53 expression levels in an experimental model of
diabetic nephropathy. J Cell Biochem. 119:6080–6093.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lee IA, Lee JH, Baek NI and Kim DH:
Antihyperlipidemic effect of crocin isolated from the fructus of
Gardenia jasminoides and its metabolite Crocetin. Biol Pharm Bull.
28:2106–2110. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mashmoul M, Azlan A, Mohtarrudin N, Nisak
B, Yusof M and Khaza’ai H: Saffron extract and crocin reduced
biomarkers associated with obesity in rats fed a high-fat diet. Mal
J Nutr. 23:117–127. 2017.
|
|
17
|
Anaeigoudari A, Faramarzi A, Abbasnezhad A
and Shafei M: Effect of intrapertonal injection of crocin on
cardiovascular parameters in Angiotensin II-induced hypertensive
rats. Horizon Med Sci. 24:309–315. 2018.
|
|
18
|
Imenshahidi M, Razavi BM, Faal A,
Gholampoor A, Mousavi SM and Hosseinzadeh H: Effects of chronic
crocin treatment on desoxycorticosterone acetate (doca)-salt
hypertensive rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 17:9–13. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Imenshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H and
Javadpour Y: Hypotensive effect of aqueous saffron extract
(Crocus sativus L.) and its constituents, safranal and
crocin, in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Phytother Res.
24:990–994. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
He SY, Qian ZY and Tang FT: Effect of
crocin on intracellular calcium concentration in cultured bovine
aortic smooth muscle cells. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 39:778–781. 2004.(In
Chinese):PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Williams BA, Liu C, Deyoung L, Brock GB
and Sims SM: Regulation of intracellular Ca2+ release in
corpus cavernosum smooth muscle: Synergism between nitric oxide and
cGMP. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 288:C650–C658. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Iranshahi M, Rezaee R, Parhiz H,
Roohbakhsh A and Soltani F: Protective effects of flavonoids
against microbes and toxins: The cases of hesperidin and
hesperetin. Life Sci. 137:125–132. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Parhiz H, Roohbakhsh A, Soltani F, Rezaee
R and Iranshahi M: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of
the citrus flavonoids hesperidin and hesperetin: An updated review
of their molecular mechanisms and experimental models. Phytother
Res. 29:323–331. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rezaee R, Sheidary A, Jangjoo S, Ekhtiary
S, Bagheri S, Kohkan Z, Dadres M, Oana Docea A, Tsarouhas K,
Sarigiannis DA, et al: Cardioprotective effects of
hesperidin on carbon monoxide poisoned in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol:
Aug 14, 2019 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
25
|
Roohbakhsh A, Parhiz H, Soltani F, Rezaee
R and Iranshahi M: Neuropharmacological properties and
pharmacokinetics of the citrus flavonoids hesperidin and hesperetin
- a mini-review. Life Sci. 113:1–6. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Roohbakhsh A, Parhiz H, Soltani F, Rezaee
R and Iranshahi M: Molecular mechanisms behind the biological
effects of hesperidin and hesperetin for the prevention of cancer
and cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci. 124:64–74. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Haidari F, Heybar H, Jalali MT, Ahmadi
Engali K, Helli B and Shirbeigi E: Hesperidin supplementation
modulates inflammatory responses following myocardial infarction. J
Am Coll Nutr. 34:205–211. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Homayouni F, Haidari F, Hedayati M,
Zakerkish M and Ahmadi K: Blood pressure lowering and
anti-inflammatory effects of hesperidin in type 2 diabetes; a
randomized double-blind controlled clinical trial. Phytother Res.
32:1073–1079. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Morand C, Dubray C, Milenkovic D, Lioger
D, Martin JF, Scalbert A and Mazur A: Hesperidin contributes to the
vascular protective effects of orange juice: A randomized crossover
study in healthy volunteers. Am J Clin Nutr. 93:73–80.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Demonty I, Lin Y, Zebregs YE, Vermeer MA,
van der Knaap HC, Jäkel M and Trautwein EA: The citrus flavonoids
hesperidin and naringin do not affect serum cholesterol in
moderately hypercholesterolemic men and women. J Nutr.
140:1615–1620. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rizza S, Muniyappa R, Iantorno M, Kim JA,
Chen H, Pullikotil P, Senese N, Tesauro M, Lauro D, Cardillo C, et
al: Citrus polyphenol hesperidin stimulates production of nitric
oxide in endothelial cells while improving endothelial function and
reducing inflammatory markers in patients with metabolic syndrome.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:E782–E792. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ohtsuki K, Abe A, Mitsuzuwi H, Kondo M,
Uemura K, Iwasaki Y and Kondo Y: Effects of long-term
administration of hesperidin and glucosyl hesperidin to
spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo).
48:420–422. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yamamoto M, Suzuki A and Hase T:
Short-term effects of glucosyl hesperidin and hesperetin on blood
pressure and vascular endothelial function in spontaneously
hypertensive rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 54:95–98.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Asgharpour A, Cazanave SC, Pacana T,
Seneshaw M, Vincent R, Banini BA, Kumar DP, Daita K, Min H-K,
Mirshahi F, et al: A diet-induced animal model of non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease and hepatocellular cancer. J Hepatol.
65:579–588. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lin HT, Shiou YL, Jhuang WJ and Lee HC:
Simultaneous electrocardiography recording and invasive blood
pressure measurement in rats. J Vis Exp. 143(e59115)2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Parasuraman S and Raveendran R:
Measurement of invasive blood pressure in rats. J Pharmacol
Pharmacother. 3:172–177. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Dobrian AD, Davies MJ, Prewitt RL and
Lauterio TJ: Development of hypertension in a rat model of
diet-induced obesity. Hypertension. 35:1009–1015. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ikemura M, Sasaki Y, Giddings JC and
Yamamoto J: Preventive effects of hesperidin, glucosyl hesperidin
and naringin on hypertension and cerebral thrombosis in
stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Phytother Res.
26:1272–1277. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wunpathe C, Potue P, Maneesai P, Bunbupha
S, Prachaney P, Kukongviriyapan U, Kukongviriyapan V and
Pakdeechote P: Hesperidin suppresses renin-angiotensin system
mediated NOX2 over-expression and sympathoexcitation in 2K-1C
hypertensive rats. Am J Chin Med. 46:751–767. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Shafei MN, Faramarzi A, Khajavi Rad A and
Anaeigoudari A: Crocin prevents acute angiotensin II-induced
hypertension in anesthetized rats. Avicenna J Phytomed. 7:345–352.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Imenshahidi M, Razavi BM, Faal A,
Gholampoor A, Mousavi SM and Hosseinzadeh H: The effect of chronic
administration of saffron (Crocus sativus) Stigma aqueous
extract on systolic blood pressure in rats. Jundishapur J Nat Pharm
Prod. 8:175–179. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Llorens S, Mancini A, Serrano-Díaz J,
D'Alessandro AM, Nava E, Alonso GL and Carmona M: Effects of
crocetin esters and crocetin from Crocus sativus L. on
aortic contractility in rat genetic hypertension. Molecules.
20:17570–17584. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Mancini A, Serrano-Díaz J, Nava E,
D'Alessandro AM, Alonso GL, Carmona M and Llorens S: Crocetin, a
carotenoid derived from saffron (Crocus sativus L.),
improves acetylcholine-induced vascular relaxation in hypertension.
J Vasc Res. 51:393–404. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|