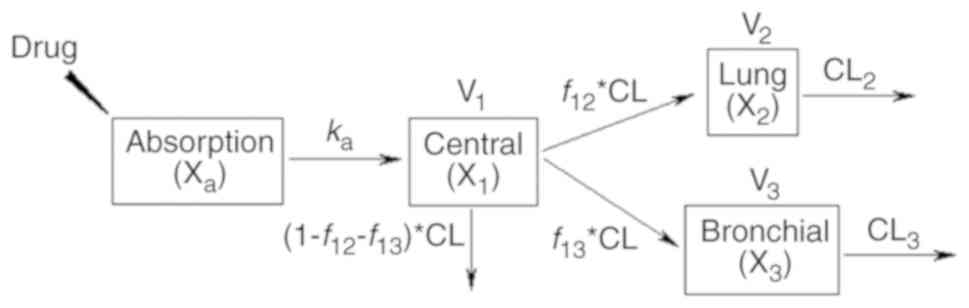
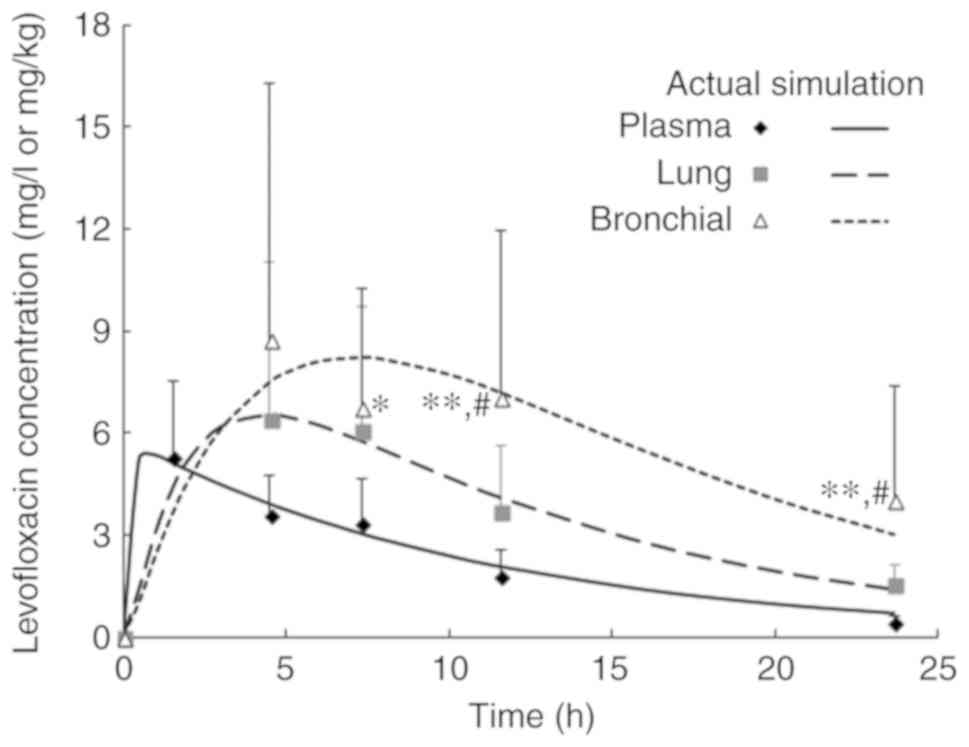
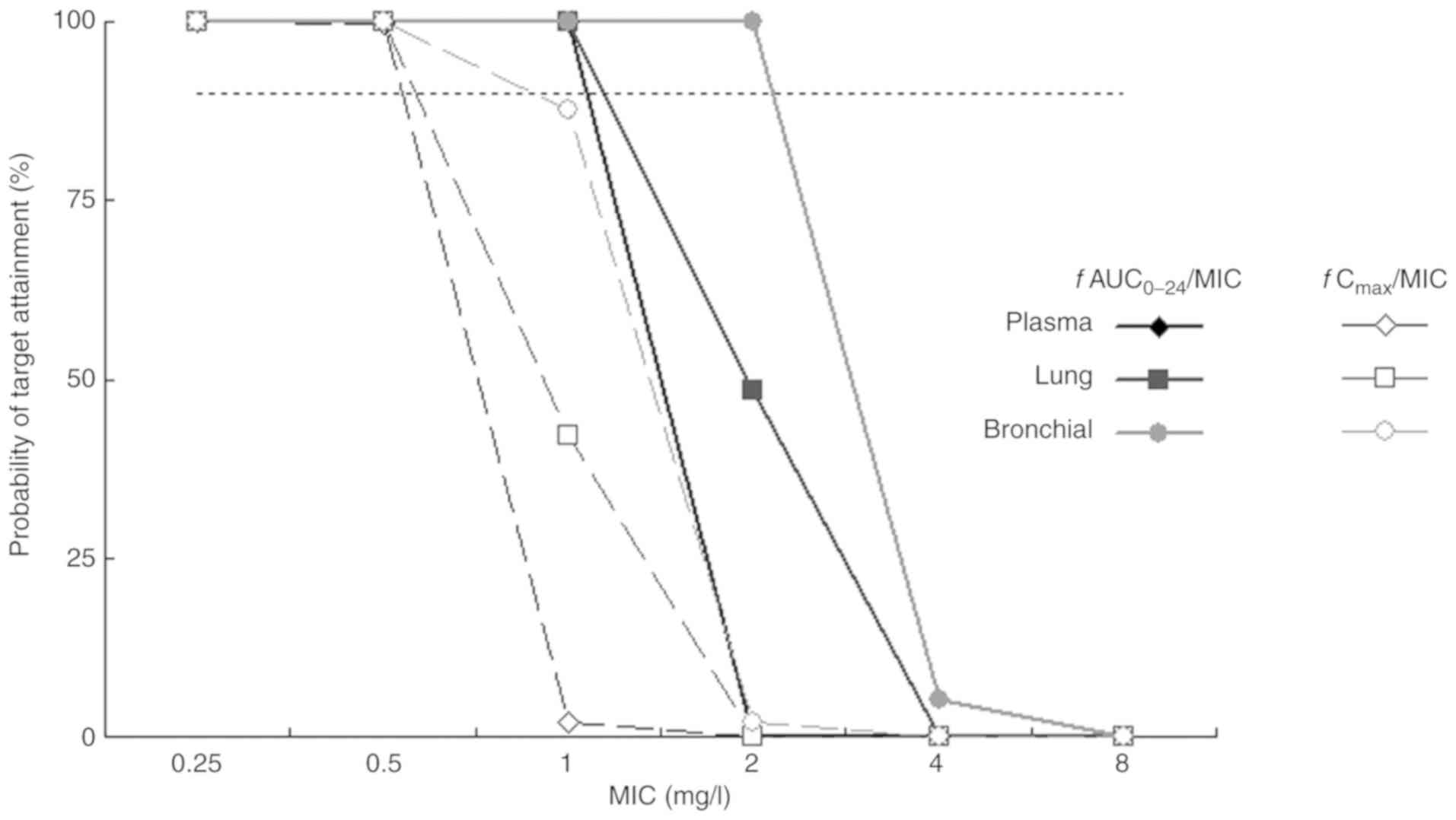
|
1
|
Torres A and Liapikou A: Levofloxacin for
the treatment of respiratory tract infections. Expert Opin
Pharmacother. 13:1203–1212. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhang J, Xie X, Zhou X, Chen YQ, Yu JC,
Cao GY, Wu XJ, Shi YG and Zhang YY: Permeability and concentration
of levofloxacin in epithelial lining fluid in patients with lower
respiratory tract infections. J Clin Pharmacol. 50:922–928.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Nakajima T, Kaji Y and Miyawaki M:
Penetration of single-dose levofloxacin into intestinal tissue. J
Gastroen Hepatol Res. 2:399–402. 2013.
|
|
4
|
Hutschala D, Skhirtladze K, Zuckermann A,
Wisser W, Jaksch P, Mayer-Helm BX, Burgmann H, Wolner E, Müller M
and Tschernko EM: In vivo measurement of levofloxacin penetration
into lung tissue after cardiac surgery. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 49:5107–5111. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Grossman RF, Rotschafer JC and Tan JS:
Antimicrobial treatment of lower respiratory tract infections in
the hospital setting. Am J Med. 118 (Suppl)(29S-38S)2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Andes D and Craig WA: Animal model
pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: A critical review. Int J
Antimicrob Agents. 19:261–268. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Friedman H, Song X, Crespi S and
Navaratnam P: Comparative analysis of length of stay, total costs,
and treatment success between intravenous moxifloxacin 400 mg and
levofloxacin 750 mg among hospitalized patients with
community-acquired pneumonia. Value Health. 12:1135–1143.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Frei CR, Jaso TC, Mortensen EM, Restrepo
MI, Raut MK, Oramasionwu CU, Ruiz AD, Makos BR, Ruiz JL, Attridge
RT, et al: Medical resource utilization among community-acquired
pneumonia patients initially treated with levofloxacin 750 mg daily
versus ceftriaxone 1000 mg plus azithromycin 500 mg daily: A
US-based study. Curr Med Res Opin. 25:859–868. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Schein J, Janagap-Benson C, Grant R,
Sikirica V, Doshi D and Olson W: A comparison of levofloxacin and
moxifloxacin use in hospitalized community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)
patients in the US: Focus on length of stay. Curr Med Res Opin.
24:895–906. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lynch-JP III, File-TM Jr and Zhanel GG:
Levofloxacin for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia.
Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 4:725–742. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
DiPiro JT: Short-term prophylaxis in
clean-contaminated surgery. J Chemother. 11:551–555.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Radu DM, Jauréguy F, Seguin A, Foulon C,
Destable MD, Azorin J and Martinod E: Postoperative pneumonia after
major pulmonary resections: An unsolved problem in thoracic
surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 84:1669–1673. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Schussler O, Alifano M, Dermine H, Strano
S, Casetta A, Sepulveda S, Chafik A, Coignard S, Rabbat A and
Regnard JF: Postoperative pneumonia after major lung resection. Am
J Respir Crit Care Med. 173:1161–1169. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Belda J, Cavalcanti M, Ferrer M, Serra M,
Puig de la Bellacasa J, Canalis E and Torres A: Bronchial
colonization and postoperative respiratory infections in patients
undergoing lung cancer surgery. Chest. 128:1571–1579.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bratzler DW and Houck PM: Antimicrobial
prophylaxis for surgery: An advisory statement from the National
Surgical infection prevention project. Am J Surg. 189:395–404.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gupta R, Sinnett D, Carpenter R, Preece PE
and Royle GT: Antibiotic prophylaxis for post-operative wound
infection in clean elective breast surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol.
26:363–366. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bratzler DW, Houck PM, Richards C, Steele
L, Dellinger EP, Fry DE, Wright C, Ma A, Carr K and Red L: Use of
antimicrobial prophylaxis for major surgery: Baseline results from
the National Surgical Infection Prevention Project. Arch Surg.
140:174–182. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Malone DL, Genuit T, Tracy JK, Gannon C
and Napolitano LM: Surgical site infections: Reanalysis of risk
factors. J Surg Res. 103:89–95. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Von Baum H, Böttcher S, Hoffmann H and
Sonntag HG: Tissue penetration of a single dose of levofloxacin
intravenously for antibiotic prophylaxis in lung surgery. J
Antimicrob Chemother. 47:729–730. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Swoboda S, Oberdorfer K, Klee F,
Hoppe-Tichy T, von Baum H and Geiss HK: Tissue and serum
concentrations of levofloxacin 500 mg administered intravenously or
orally for antibiotic prophylaxis in biliary surgery. J Antimicrob
Chemother. 51:459–462. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cockcroft DW and Gault MH: Prediction of
creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 16:31–41.
1976.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xie X, Zhang J, Yu JC, Shi YG and Zhang
YY: HPLC assay of levofloxacin concentration in plasma, lung
tissue, and body fluids. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 17:158–162.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Cao Y, Zhou J and Liu X:
Mechanism-based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of
bidirectional effect of danshensu on plasma homocysteine in rats.
Pharm Res. 26:1863–1673. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Askenazi SS and Perlman M: Pulmonary
hypoplasia: Lung weight and radial alveolar count as criteria of
diagnosis. Arch Dis Child. 54:614–618. 1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Qi XL, Bo AH and Xia L: Determination of
cerebral and lung weight of fetus. Chin J Birth Health Heredity.
65(65)1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jaruratanasirikul S, Jaspattananon A,
Wongpoowarak W, Nawakitrangsan M, Thengyai S and Samaeng M:
Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics modeling of oral
levofloxacin. J Med Assoc Thai. 99:886–892. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cojutti PG, Ramos-Martin V, Schiavon I,
Rossi P, Baraldo M, Hope W and Pea F: Population pharmacokinetics
and pharmacodynamics of levofloxacin in acutely hospitalized older
patients with various degrees of renal function. Antimicrob Agents
Chemothe. 61(e02134-16)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Scaglione F, Mouton JW, Mattina R and
Fraschini F: Pharmacodynamics of levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in
a murine pneumonia model: Peak concentration/MIC versus area under
the curve/MIC ratios. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 47:2749–2755.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang YY, Huang HH and Ren ZY: Clinical
evaluation of oral levofloxacin 500 mg once-daily dosage for
treatment of lower respiratory tract infections and urinary tract
infections: A prospective multicenter study in China. J Infect
Chemother. 15:301–311. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cao G, Zhang J, Wu X, Yu J, Chen Y, Ye X,
Zhu D, Zhang Y, Guo B and Shi Y: Pharmacokinetics and
pharmacodynamics of levofloxacin injection in healthy Chinese
volunteers and dosing regimen optimization. J Clin Pharm Ther.
38:394–400. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rodvold KA, Danziger LH and Gotfried MH:
Steady-state plasma and bronchopulmonary concentrations of
intravenous levofloxacin and Azithromycin in healthy adults.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 47:2450–2457. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Conte JE Jr, Golden JA, McIver M, Little E
and Zurlinden E: Intrapulmonary pharmacodynamics of high-dose
levofloxacin in subjects with chronic bronchitis or chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 30:422–427.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Preston SL, Drusano GL, Berman AL, Fowler
CL, Chow AT, Dornseif B, Reichl V, Natarajan J and Corrado M:
Pharmacodynamics of levofloxac in: A new paradigm for early
clinical trials. JAMA. 279:125–129. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang J, Yu JC, Shi YG, Zhou L, Ye XY, Zhu
DM and Zhang YY: Study of pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of
levofloxacin. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 85:1926–1932. 2005.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu XJ, Zhang J, Guo BN, Zhang YY, Yu JC,
Cao GY, Chen YC, Zhu DM, Ye XY, Wu JF, et al: Pharmacokinetics and
pharmacodynamics of multiple-dose intravenous nemonoxacin in
healthy Chinese volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
59:1446–1454. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lee LJ, Sha X, Gotfried MH, Howard JR, Dix
RK and Fish DN: Penetration of levofloxacin into lung tissue after
oral administration to subjects undergoing lung biopsy or
lobectomy. Pharmacotherapy. 18:35–41. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang CQ, Wang W, Jin MH, Huang Q and Guan
Q: Pulmonary resections in surgical treatment of lung tuberculosis.
J Clin Pulmonary Med. 14:906–908. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li P, Mao YB and Liu CT: Risk factors for
surgical site infections in patients undergoing pneumonectomy. Chin
J Nosocomiol. 23(5198-5199-5202)2013.
|
|
39
|
Pea F: Intracellular pharmacokinetics of
antibacterials and their clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet.
57:177–189. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Moriarty TF, McElnay JC, Elborn JS and
Tunney MM: Sputum antibiotic concentrations: Implications for
treatment of cystic fibrosis lung infection. Pediatr Pulmonol.
42:1008–1017. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kelly MM, Efthimiadis A and Hargreave FE:
Induced sputum: Selection method. Methods Mol Med. 56:77–91.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Cazzola M, Blasi F, Terzano C, Matera MG
and Marsico SA: Delivering antibacterials to the lungs:
Considerations for optimizing outcomes. Am J Respir Med. 1:261–272.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yu JC, Zhang J and Cao GY: Single-dose and
multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin in Chinese healthy
subjects. J Third Mil Med Univ. 35:2516–2520. 2013.
|
|
44
|
Simon N, Sampol E, Albanese J, Martin C,
Arvis P, Urien S, Lacarelle B and Bruguerolle B: Population
pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in plasma and bronchial secretions
in patients with severe bronchopneumonia. Clin Pharmacol Ther.
74:353–363. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Capitano B, Mattoes HM, Shore E, O'Brien
A, Braman S, Sutherland C and Nicolau DP: Steady-state
intrapulmonary concentrations of moxifloxacin, levofloxacin, and
azithromycin in older adults. Chest. 125:965–973. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hutschala D, Kinstner C, Skhirtladze K,
Mayer-Helm BX, Zeitlinger M, Wisser W, Müller M and Tschernko E:
The impact of perioperative atelectasis on antibiotic penetration
into lung tissue: An in vivo microdialysis study. Intensive Care
Med. 34:1827–1834. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Van't Boveneind-Vrubleuskaya N, Seuruk T,
van Hateren K, van der Laan T, Kosterink JGW, van der Werf TS, van
Soolingen D, van den Hof S, Skrahina A and Alffenaar JC:
Pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin in multidrug- and extensively
drug-resistant tuberculosis patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
61(pii: e00343-17)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Al-Shaer MH, Alghamdi WA, Alsultan A, An
G, Ahmed S, Alkabab Y, Banu S, Barbakadze K, Houpt E, Kipiani M, et
al: Fluoroquinolones in drug-resistant tuberculosis: Culture
conversion and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic target attainment to
guide dose selection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 63(pii:
e00279-19)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
U.S. Department of Health and Human
Services. FDA guidance for industry: Population Pharmacokinetics,
July 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/128793/download.
Accessed October 2019.
|