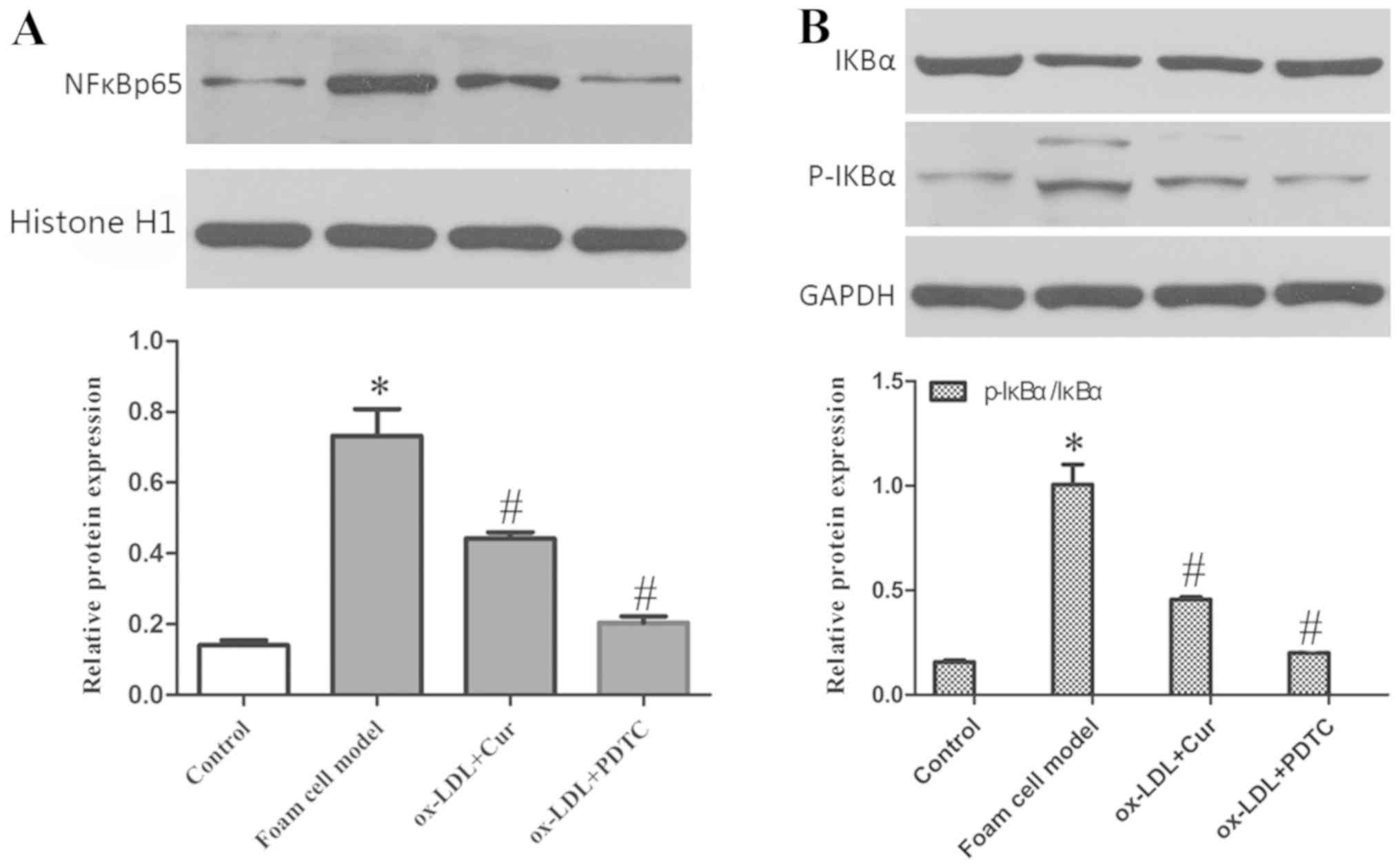
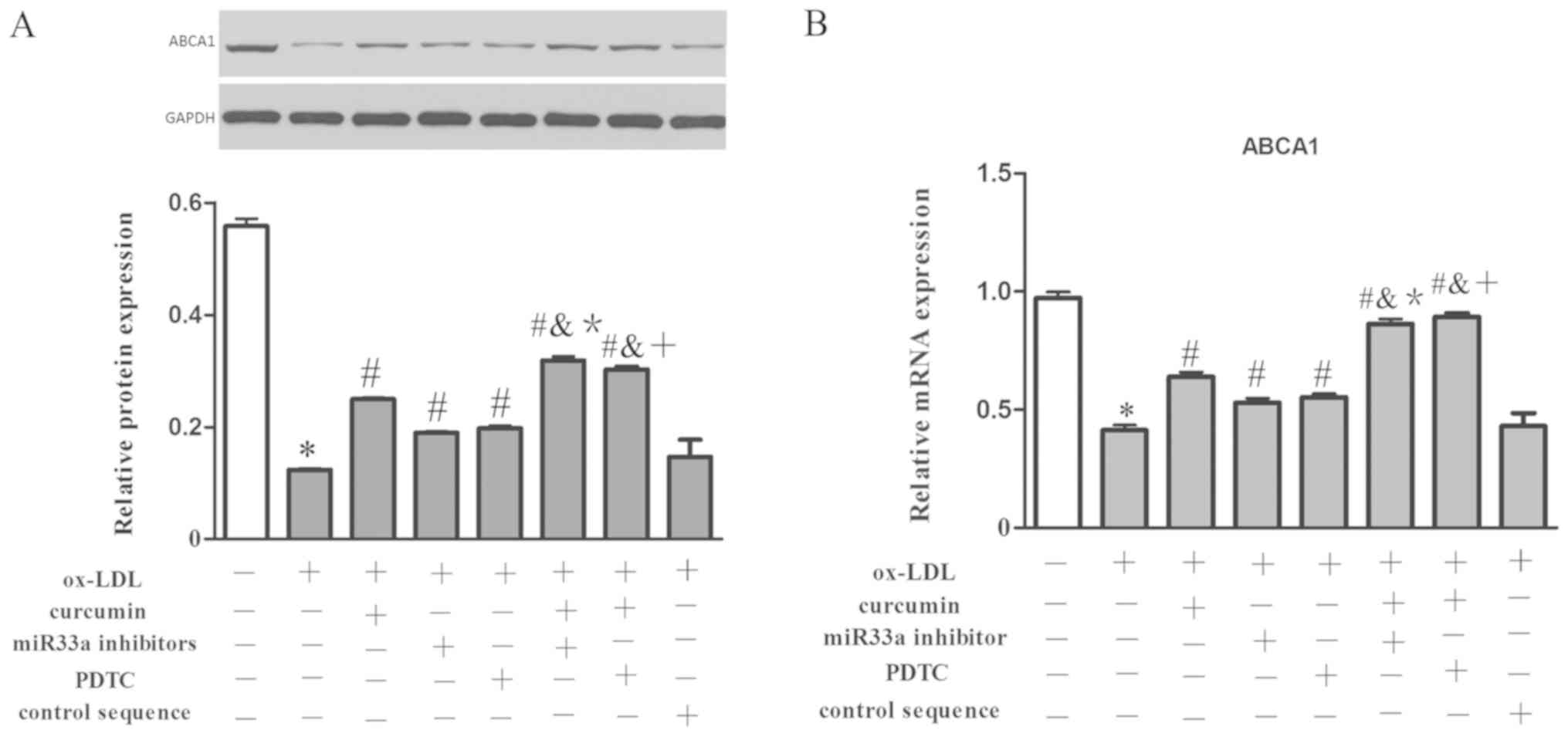
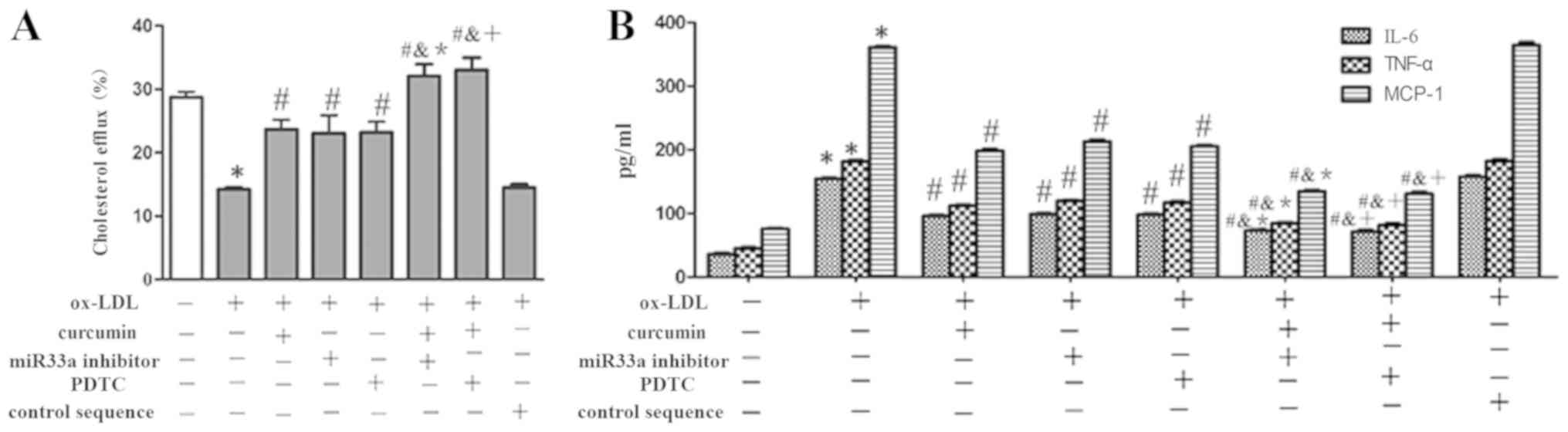
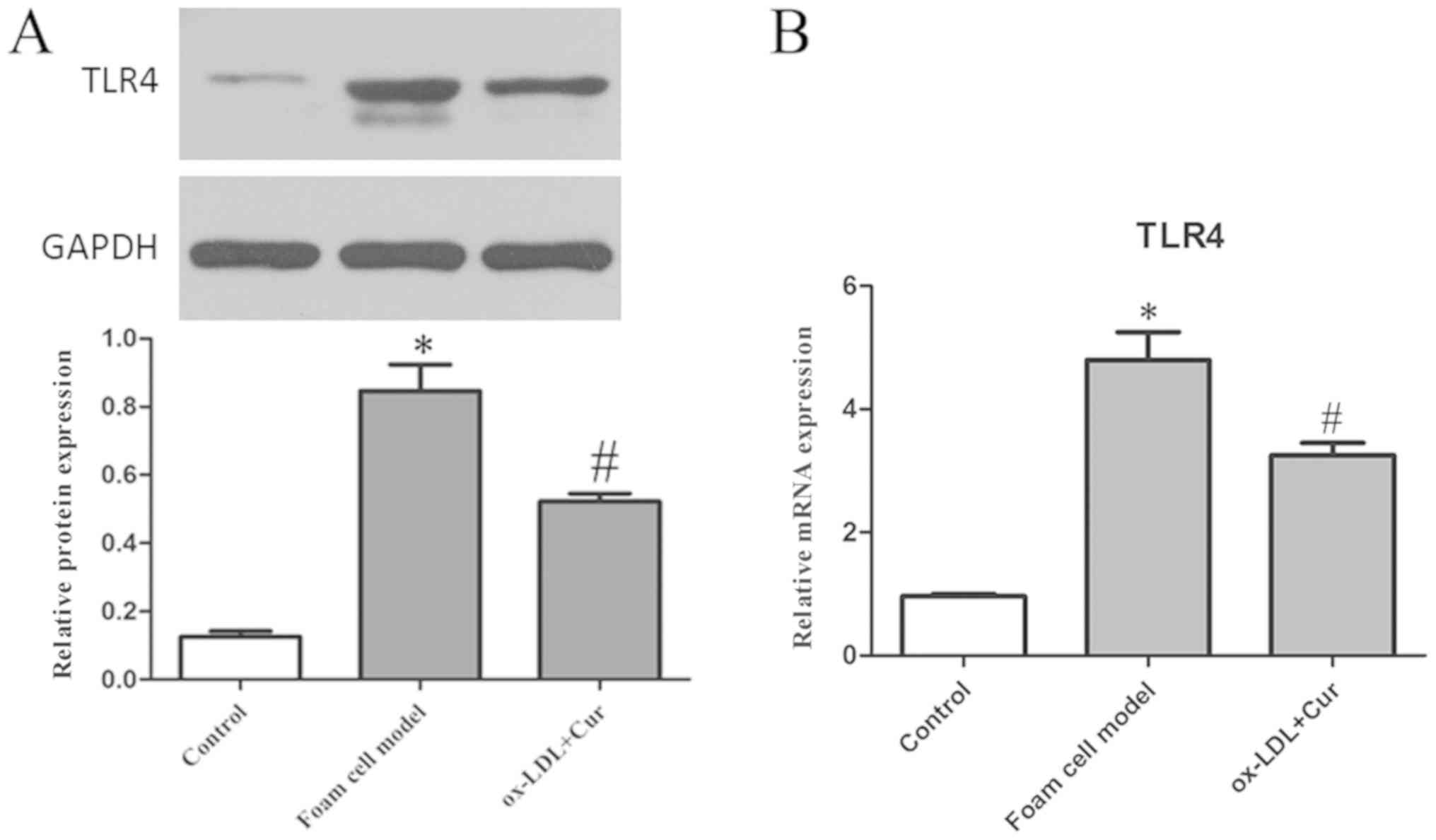
|
1
|
Lancellotti P, Ancion A and Piérard L:
Cardiac rehabilitation, state of the art 2017. Rev Med Liege.
72:481–487. 2017.PubMed/NCBI(In French).
|
|
2
|
Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, Go A,
Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern SM, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, et
al: American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke
Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2008
update: A report from the American Heart Association Statistics
Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation.
117(e25-e146)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, et al:
American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke
Statistics Subcommittee. Executive summary: heart disease and
stroke statistics--2012 update: a report from the American Heart
Association. Circulation. 125:188–197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Casas R, Castro-Barquero S, Estruch R and
Sacanella E: Nutrition and Cardiovascular Health. Int J Mol Sci.
19(19)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Veitenhansl M, Stegner K, Hierl FX,
Dieterle C, Feldmeier H, et al: 40th EASD Annual Meeting of the
European Association for the Study of Diabetes: Munich, Germany,
5-9 September 2004. Diabetologia. 47 (Suppl
1)(A1-A464)2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang Z and Nakayama T: Inflammation, a
link between obesity and cardiovascular disease. Mediators Inflamm.
2010(535918)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Levi M, van der Poll T and Schultz M:
Infection and inflammation as risk factors for thrombosis and
atherosclerosis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 38:506–514. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nelken NA, Coughlin SR, Gordon D and
Wilcox JN: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in human atheromatous
plaques. J Clin Invest. 88:1121–1127. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Boyle JJ, Weissberg PL and Bennett MR:
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promotes macrophage-induced vascular
smooth muscle cell apoptosis by direct and autocrine mechanisms.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:1553–1558. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jafarzadeh A, Nemati M and Jafarzadeh S:
The important role played by chemokines influence the clinical
outcome of Helicobacter pylori infection. Life Sci.
231(116688)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rull A, Beltrán-Debón R, Aragonès G,
Rodríguez-Sanabria F, Alonso-Villaverde C, Camps J and Joven J:
Expression of cytokine genes in the aorta is altered by the
deficiency in MCP-1: Effect of a high-fat, high-cholesterol diet.
Cytokine. 50:121–128. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen S, Sorrentino R, Shimada K, Bulut Y,
Doherty TM, Crother TR and Arditi M: Chlamydia
pneumoniae-induced foam cell formation requires MyD88-dependent
and -independent signaling and is reciprocally modulated by liver X
receptor activation. J Immunol. 181:7186–7193. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhou Z, Wu Y, Chen L, Liu L, Chen H, Li Z
and Chen C: Heat shock protein 10 of Chlamydophila
pneumoniae induces proinflammatory cytokines through Toll-like
receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 in human monocytes THP-1. In Vitro Cell
Dev Biol Anim. 47:541–549. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Paolillo R, Iovene MR, Romano Carratelli C
and Rizzo A: Induction of VEGF and MMP-9 expression by toll-like
receptor 2/4 in human endothelial cells infected with Chlamydia
pneumoniae. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 25:377–386.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The
C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with
antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nakazeki F, Tsuge I, Horie T, Imamura K,
Tsukita K, Hotta A, Baba O, Kuwabara Y, Nishino T, Nakao T, et al:
miR-33a is a therapeutic target in SPG4-related hereditary spastic
paraplegia human neurons. Clin Sci (Lond). 133:583–595.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lin K, Chen H, Chen X, Qian J, Huang S and
Huang W: Efficacy of Curcumin on Aortic Atherosclerosis: A
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis in Mouse Studies and Insights
into Possible Mechanisms. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2020(1520747)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mohammadian Haftcheshmeh S, Karimzadeh MR,
Azhdari S, Vahedi P, Abdollahi E and Momtazi-Borojeni AA:
Modulatory effects of curcumin on the atherogenic activities of
inflammatory monocytes: Evidence from in vitro and animal models of
human atherosclerosis. Biofactors. Dec 24. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dong SZ, Zhao SP, Wu ZH, Yang J, Xie XZ,
Yu BL and Nie S: Curcumin promotes cholesterol efflux from
adipocytes related to PPARgamma-LXRalpha-ABCA1 passway. Mol Cell
Biochem. 358:281–285. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fogelman AM, Shechter I, Seager J, Hokom
M, Child JS and Edwards PA: Malondialdehyde alteration of low
density lipoproteins leads to cholesteryl ester accumulation in
human monocyte-macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 77:2214–2218.
1980.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Weber C and Noels H: Atherosclerosis:
Current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med.
17:1410–1422. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chiang YM, Lo CP, Chen YP, Wang SY, Yang
NS, Kuo YH and Shyur LF: Ethyl caffeate suppresses NF-kappaB
activation and its downstream inflammatory mediators, iNOS, COX-2,
and PGE2 in vitro or in mouse skin. Br J Pharmacol. 146:352–363.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Coban D, Milenkovic D, Chanet A,
Khallou-Laschet J, Sabbe L, Palagani A, Vanden Berghe W, Mazur A
and Morand C: Dietary curcumin inhibits atherosclerosis by
affecting the expression of genes involved in leukocyte adhesion
and transendothelial migration. Mol Nutr Food Res. 56:1270–1281.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhao GJ, Tang SL, Lv YC, Ouyang XP, He PP,
Yao F, Chen WJ, Lu Q, Tang YY, Zhang M, et al: Antagonism of
betulinic acid on LPS-mediated inhibition of ABCA1 and cholesterol
efflux through inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway
and miR-33 expression. PLoS One. 8(e74782)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Janeesh PA, Sasikala V, Dhanya CR and
Abraham A: Robinin modulates TLR/NF-κB signaling pathway in
oxidized LDL induced human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Int
Immunopharmacol. 18:191–197. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sikora E, Scapagnini G and Barbagallo M:
Curcumin, inflammation, ageing and age-related diseases. Immun
Ageing. 7(1)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Olszanecki R, Jawień J, Gajda M, Mateuszuk
L, Gebska A, Korabiowska M, Chłopicki S and Korbut R: Effect of
curcumin on atherosclerosis in apoE/LDLR-double knockout mice. J
Physiol Pharmacol. 56:627–635. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhong Y, Liu T and Guo Z: Curcumin
inhibits ox-LDL-induced MCP-1 expression by suppressing the p38MAPK
and NF-κB pathways in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Inflamm
Res. 61:61–67. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Steinberg D: Low density lipoprotein
oxidation and its pathobiological significance. J Biol Chem.
272:20963–20966. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhao GJ, Yin K, Fu YC and Tang CK: The
interaction of ApoA-I and ABCA1 triggers signal transduction
pathways to mediate efflux of cellular lipids. Mol Med. 18:149–158.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lee J, Park Y and Koo SI: ATP-binding
cassette transporter A1 and HDL metabolism: Effects of fatty acids.
J Nutr Biochem. 23:1–7. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yin K, Liao DF and Tang CK: ATP-binding
membrane cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1): A possible link between
inflammation and reverse cholesterol transport. Mol Med.
16:438–449. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Moore KJ, Rayner KJ, Suárez Y and
Fernández-Hernando C: The role of microRNAs in cholesterol efflux
and hepatic lipid metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 31:49–63.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Moore KJ: microRNAs: Small regulators with
a big impact on lipid metabolism. J Lipid Res. 54:1159–1160.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Rakcheev AP, Chistiakova IA and Kamennykh
PV: [The successful treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis with an
argon laser]. Vestn Dermatol Venerol. 12:53–55. 1989.PubMed/NCBI(In Russian).
|
|
38
|
Rayner KJ, Suárez Y, Dávalos A, Parathath
S, Fitzgerald ML, Tamehiro N, Fisher EA, Moore KJ and
Fernández-Hernando C: miR-33 contributes to the regulation of
cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 328:1570–1573. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhou C, Lei H, Chen Y, Liu Q, Li LC,
Moorhead JF, Varghese Z and Ruan XZ: Enhanced SCAP glycosylation by
inflammation induces macrophage foam cell formation. PLoS One.
8(e75650)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Rayner KJ, Sheedy FJ, Esau CC, Hussain FN,
Temel RE, Parathath S, van Gils JM, Rayner AJ, Chang AN, Suarez Y,
et al: Antagonism of miR-33 in mice promotes reverse cholesterol
transport and regression of atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest.
121:2921–2931. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ho PC, Chang KC, Chuang YS and Wei LN:
Cholesterol regulation of receptor-interacting protein 140 via
microRNA-33 in inflammatory cytokine production. FASEB J.
25:1758–1766. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
de Beer MC, Ji A, Jahangiri A, Vaughan AM,
de Beer FC, van der Westhuyzen DR and Webb NR: ATP binding cassette
G1-dependent cholesterol efflux during inflammation. J Lipid Res.
52:345–353. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Shih VF, Tsui R, Caldwell A and Hoffmann
A: A single NFκB system for both canonical and non-canonical
signaling. Cell Res. 21:86–102. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Li Z, Wang S, Zhao W, Sun Z, Yan H and Zhu
J: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein upregulates microRNA-146a via
JNK and NF-κB signaling. Mol Med Rep. 13:1709–1716. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
den Dekker WK, Cheng C, Pasterkamp G and
Duckers HJ: Toll like receptor 4 in atherosclerosis and plaque
destabilization. Atherosclerosis. 209:314–320. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Edfeldt K, Swedenborg J, Hansson GK and
Yan ZQ: Expression of toll-like receptors in human atherosclerotic
lesions: A possible pathway for plaque activation. Circulation.
105:1158–1161. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Michelsen KS, Wong MH, Shah PK, Zhang W,
Yano J, Doherty TM, Akira S, Rajavashisth TB and Arditi M: Lack of
Toll-like receptor 4 or myeloid differentiation factor 88 reduces
atherosclerosis and alters plaque phenotype in mice deficient in
apolipoprotein E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:10679–10684.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Baker RG, Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB,
inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 13:11–22.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|