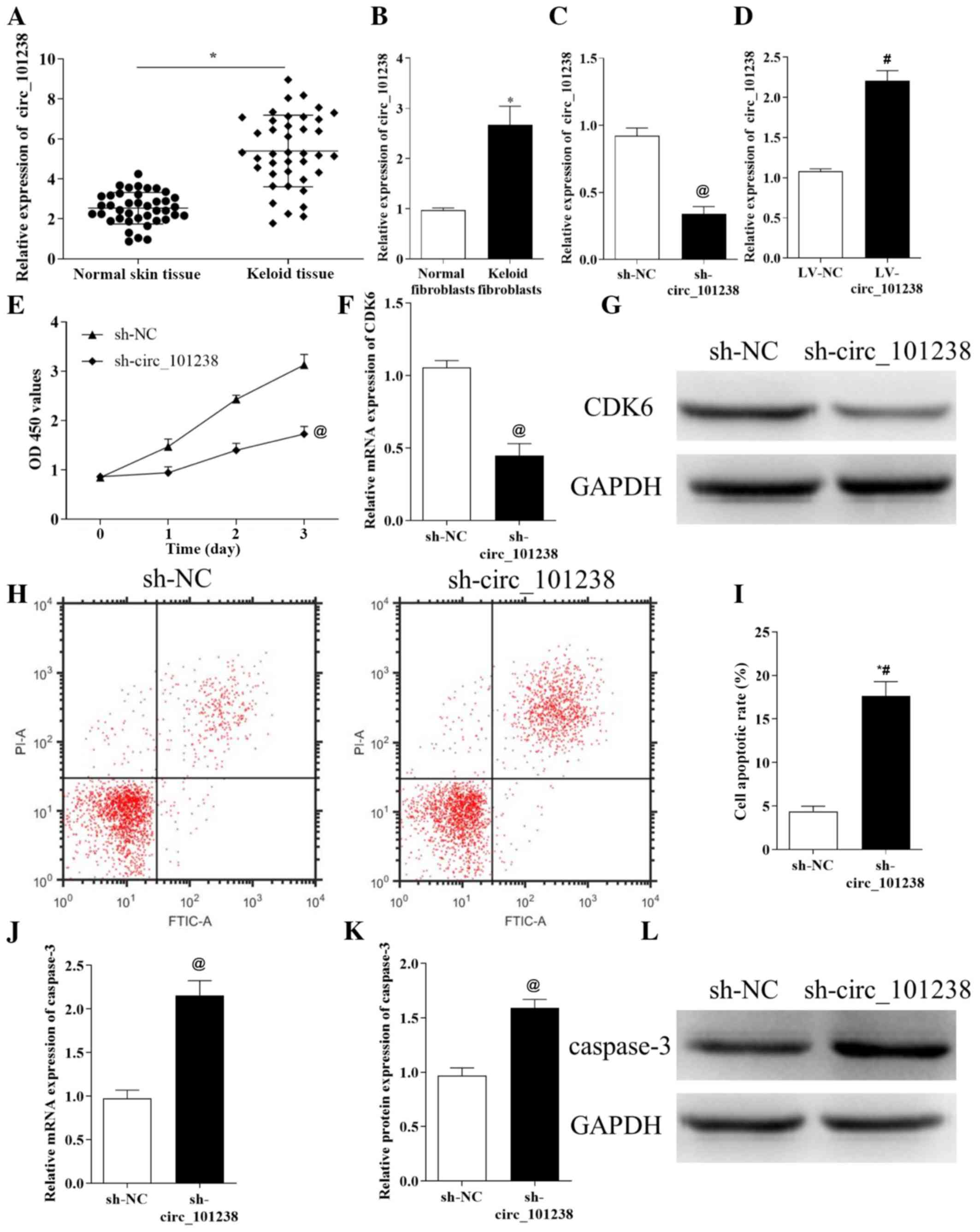
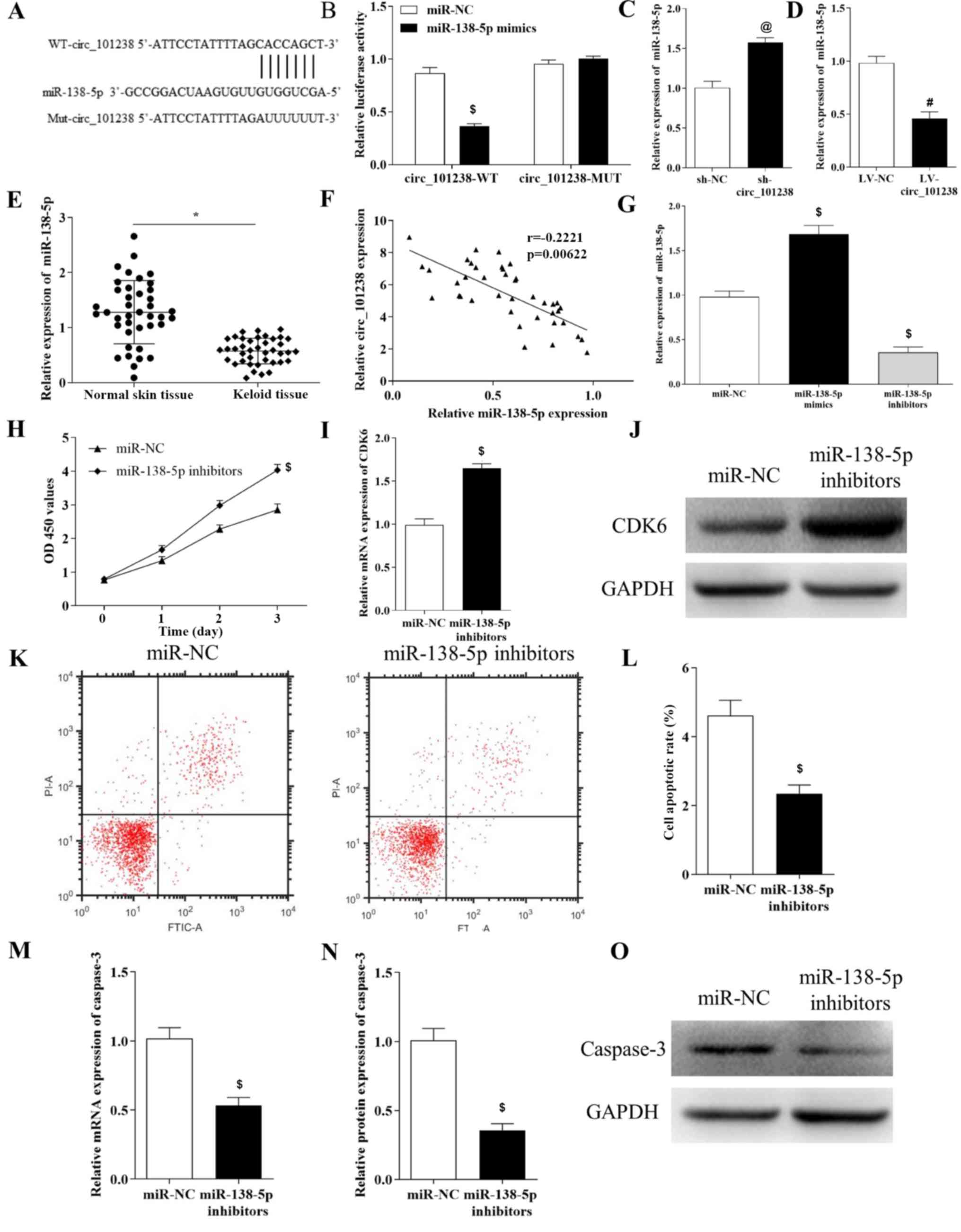
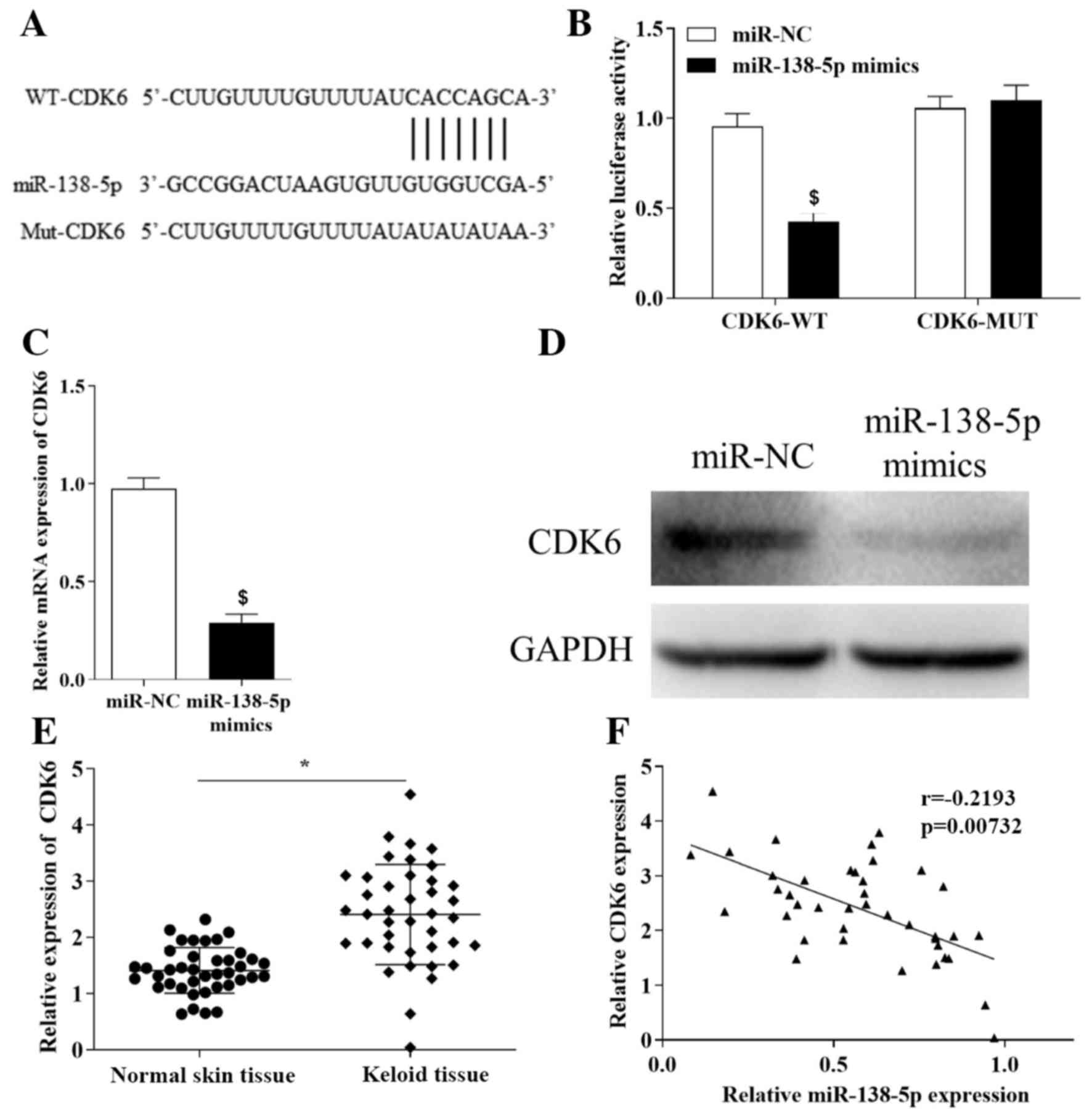
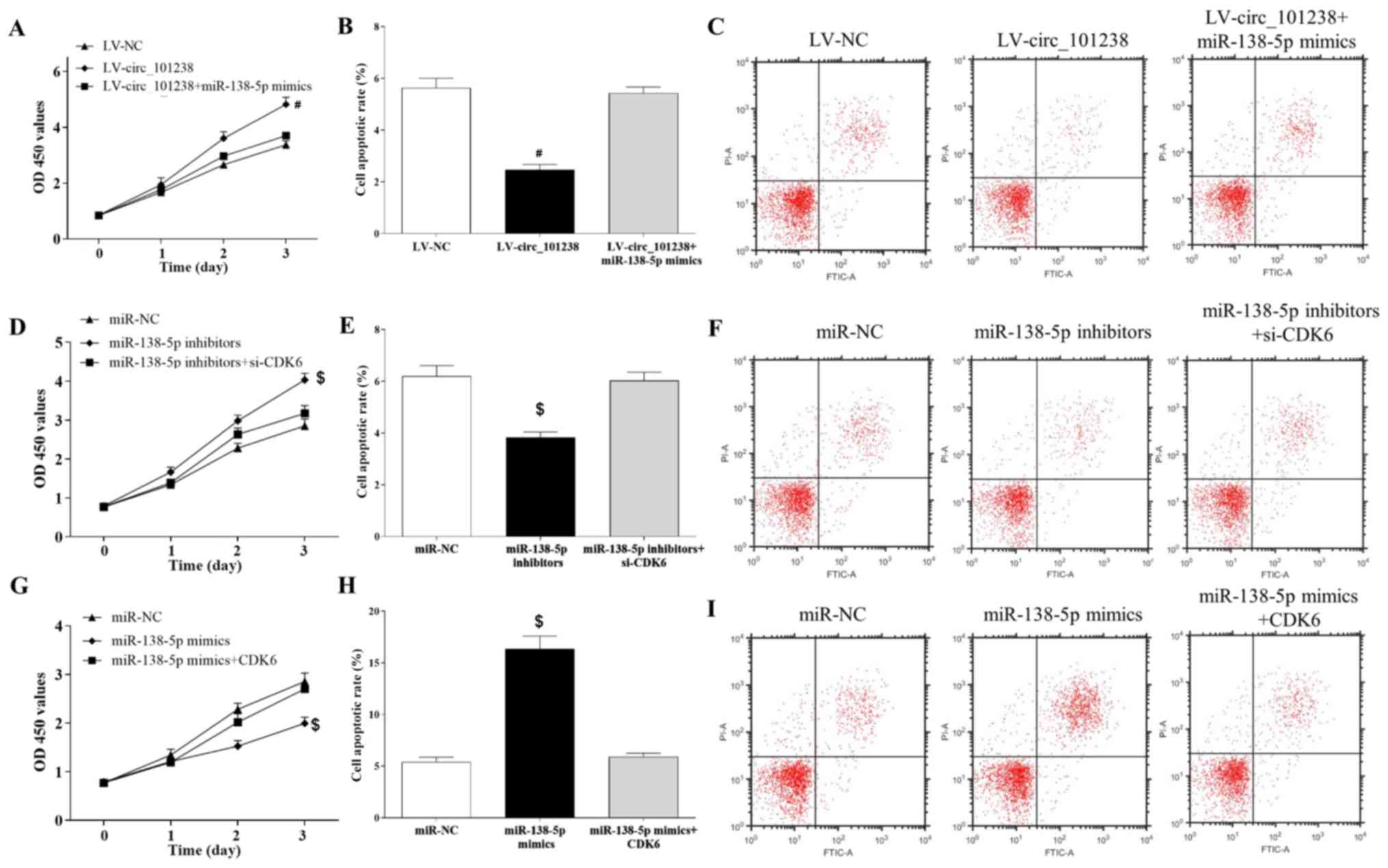
|
1
|
Jfri A, O'Brien E, Alavi A and Goldberg
SR: Association of hidradenitis suppurativa and keloid formation: A
therapeutic challenge. JAAD Case Rep. 5:675–678. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Betarbet U and Blalock T: Keloids: A
review of etiology, prevention, and treatment. J Clin Aesthet
Dermatol. 13:33–43. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lim KH, Itinteang T, Davis PF and Tan ST:
Stem cells in keloid lesions: A review. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob
Open. 7(e2228)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Vicens Q and Westhof E: Biogenesis of
circular RNAs. Cell. 159:13–14. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang J, Wu H, Xiao Z and Dong X:
Expression profiles of lncRNAs and circRNAs in keloid. Plast
Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 7(e2265)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kumar S, Boon RA, Maegdefessel L, Dimmeler
S and Jo H: Role of noncoding RNAs in the pathogenesis of abdominal
aortic aneurysm. Circ Res. 124:619–630. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zou M, Huang C, Li X, He X, Chen Y, Liao
W, Liao Y, Sun J, Liu Z, Zhong L and Bin J: Circular RNA expression
profile and potential function of hsa_circRNA_101238 in human
thoracic aortic dissection. Oncotarget. 8:81825–81837.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Singhvi G, Manchanda P, Krishna Rapalli V,
Kumar Dubey S, Gupta G and Dua K: MicroRNAs as biological
regulators in skin disorders. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:996–1004.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang GY, Wu LC, Liao T, Chen GC, Chen YH,
Zhao YX, Chen SY, Wang AY, Lin K, Lin DM, et al: A novel regulatory
function for miR-29a in keloid fibrogenesis. Clin Exp Dermatol.
41:341–345. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhu D, Gu L, Li Z, Jin W, Lu Q and Ren T:
MiR-138-5p suppresses lung adenocarcinoma cell
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, proliferation and metastasis by
targeting ZEB2. Pathol Res Pract. 215:861–872. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Romero-Pozuelo J, Figlia G, Kaya O,
Martin-Villalba A and Teleman AA: CDK4 and CDK6 couple the
cell-cycle machinery to cell growth via mTORC1. Cell Rep.
31(107504)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liang X, Ma L, Long X and Wang X: LncRNA
expression profiles and validation in keloid and normal skin
tissue. Int J Oncol. 47:1829–1838. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang Z, Yu K, Liu O, Xiong Y, Yang X,
Wang S, Zhang S, Feng Y and Peng Y: Expression profile and
bioinformatics analyses of circular RNAs in keloid and normal
dermal fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 388(111799)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kashiyama K, Mitsutake N, Matsuse M, Ogi
T, Saenko VA, Ujifuku K, Utani A, Hirano A and Yamashita S:
miR-196a downregulation increases the expression of type I and III
collagens in keloid fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 132:1597–1604.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang R, Bai Z, Wen X, Du H, Zhou L, Tang
Z, Yang Z and Ma W: MiR-152-3p regulates cell proliferation,
invasion and extracellular matrix expression through by targeting
FOXF1 in keloid fibroblasts. Life Sci. 234(116779)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shi K, Qiu X, Zheng W, Yan D and Peng W:
MiR-203 regulates keloid fibroblast proliferation, invasion, and
extracellular matrix expression by targeting EGR1 and FGF2. Biomed
Pharmacother. 108:1282–1288. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu J, Fang L, Cen Y, Qing Y, Chen J and Li
Z: MiR-21 regulates keloid formation by downregulating Smad7 via
the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. J Burn Care Res. 40:809–817.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jin J, Zhai HF, Jia ZH and Luo XH: Long
non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS induces type I collagen synthesis to
stimulate keloid formation via sponging miR-124-3p and activation
of Smad5 signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 317:C1001–C1010.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shi J, Yao S, Chen P, Yang Y, Qian M, Han
Y, Wang N, Zhao Y, He Y, Lyu L and Lu D: The integrative regulatory
network of circRNA and microRNA in keloid scarring. Mol Biol Rep.
47:201–209. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cai Y, Zhu S, Yang W, Pan M, Wang C and Wu
W: Downregulation of β-catenin blocks fibrosis via Wnt2 signaling
in human keloid fibroblasts. Tumour Biol.
39(1010428317707423)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Harmanci D, Erkan EP, Kocak A and Akdogan
GG: Role of the microRNA-29 family in fibrotic skin diseases.
Biomed Rep. 6:599–604. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Limandjaja GC, Belien JM, Scheper RJ,
Niessen FB and Gibbs S: Hypertrophic and keloid scars fail to
progress from the CD34-/α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA)+ immature
scar phenotype and show gradient differences in α-SMA and p16
expression. Br J Dermatol. 182:974–986. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sherr CJ, Beach D and Shapiro GI:
Targeting CDK4 and CDK6: From discovery to therapy. Cancer Discov.
6:353–367. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|