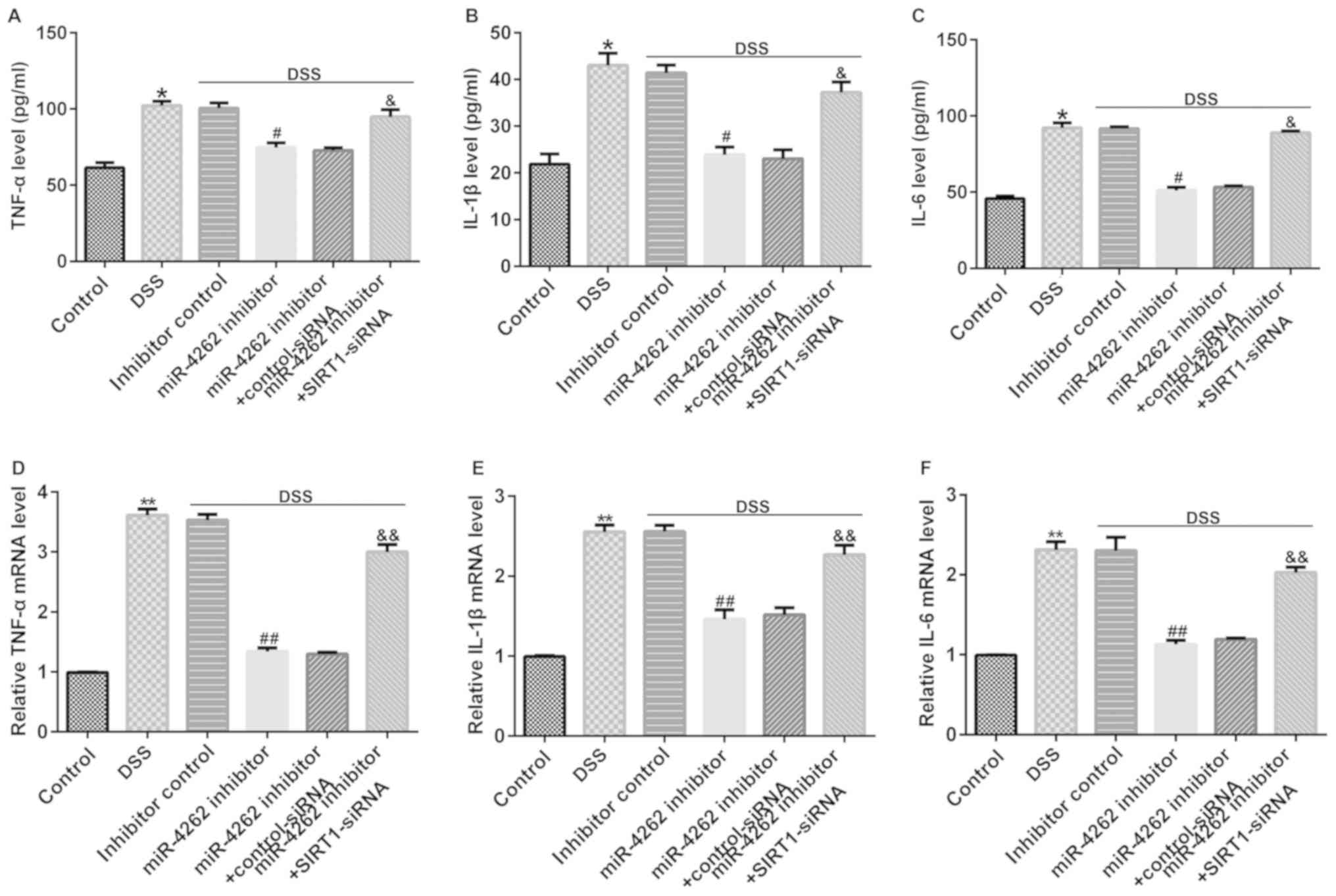
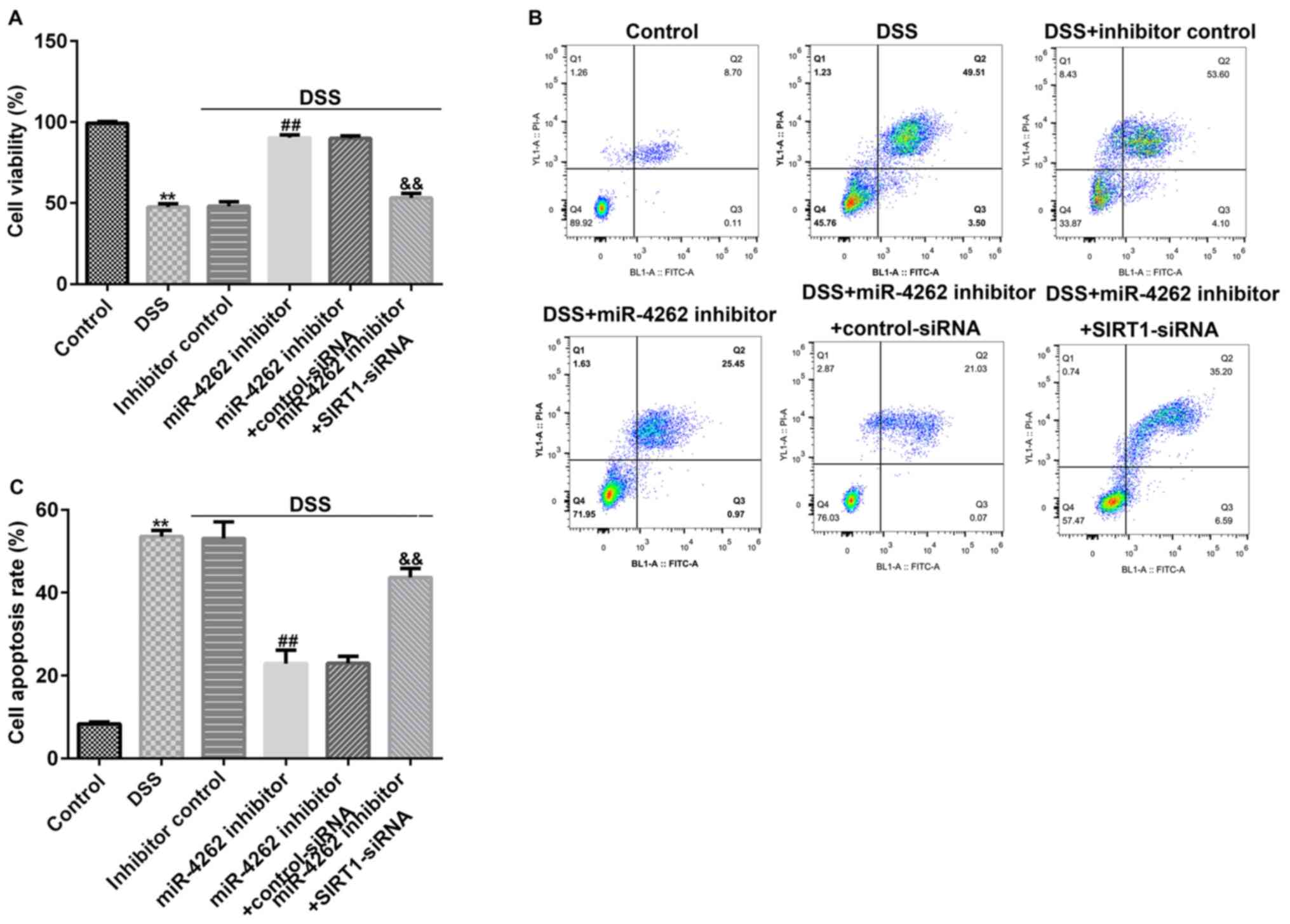
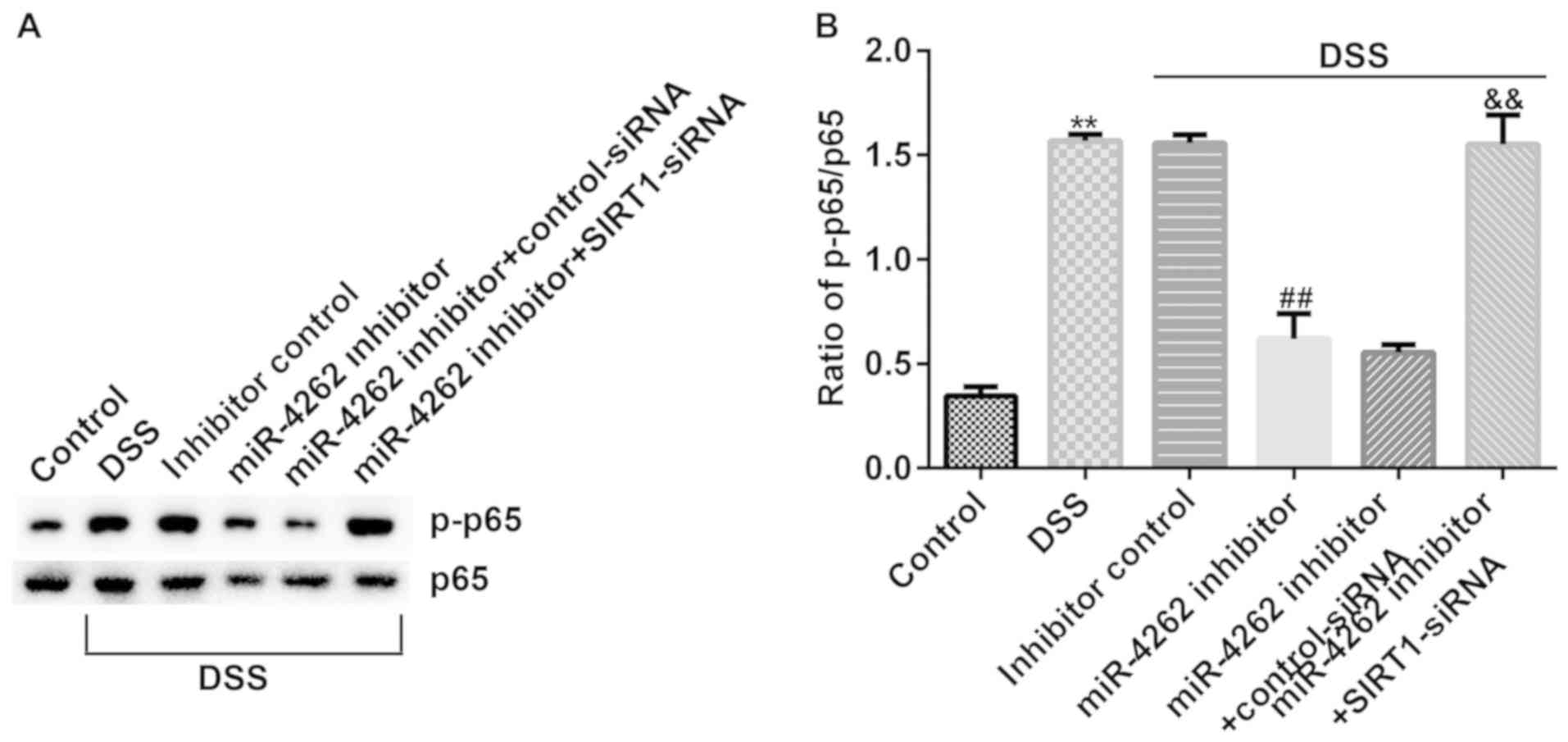
|
1
|
Mogilevski T, Burgell R, Aziz Q and Gibson
PR: Review article: The role of the autonomic nervous system in the
pathogenesis and therapy of IBD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
50:720–737. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hammer T, Lophaven SN, Nielsen KR, von
Euler-Chelpin M, Weihe P, Munkholm P, Burisch J and Lynge E:
Inflammatory bowel diseases in Faroese-born Danish residents and
their offspring: Further evidence of the dominant role of
environmental factors in IBD development. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
45:1107–1114. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wolf DC, Abraham BP, Afzali A, Allegretti
PD and Arai R: Community perspectives: Combining serology,
genetics, and inflammation markers for the diagnosis of IBD and
differentiation between CD and UC. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y).
8:S1–S16. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu R, Tang A, Wang X, Chen X, Zhao L,
Xiao Z and Shen S: Inhibition of lncRNA NEAT1 suppresses the
inflammatory response in IBD by modulating the intestinal
epithelial barrier and by exosome-mediated polarization of
macrophages. Int J Mol Med. 42:2903–2913. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pereira TDSF, Brito JAR, Guimarães ALS,
Gomes CC, de Lacerda JCT, de Castro WH, Coimbra RS, Diniz MG and
Gomez RS: MicroRNA profiling reveals dysregulated microRNAs and
their target gene regulatory networks in cemento-ossifying fibroma.
J Oral Pathol Med. 47:78–85. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wu ZW, Liu YF, Wang S and Li B: miRNA-146a
induces vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis in a rat model of
coronary heart disease via NF-κB pathway. Genet Mol Res.
14:18703–18712. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Yin K, Lv X, Yang Q, Shao M, Liu X
and Sun H: MicroRNA-24-3p regulates Hodgkin's lymphoma cell
proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting DEDD. Oncol
Lett. 17:365–371. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen Y, Du J, Zhang Z, Liu T, Shi Y, Ge X
and Li YC: MicroRNA-346 mediates tumor necrosis factor α-induced
downregulation of gut epithelial vitamin D receptor in inflammatory
bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 20:1910–1918. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Huang L, Ma Q, Li Y, Li B and Zhang L:
Inhibition of microRNA-210 suppresses pro-inflammatory response and
reduces acute brain injury of ischemic stroke in mice. Exp Neurol.
300:41–50. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kumar A, Bhatia HS, de Oliveira AC and
Fiebich BL: microRNA-26a modulates inflammatory response induced by
toll-like receptor 4 stimulation in microglia. J Neurochem.
135:1189–1202. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang K, Ren Y, Liu Y, Zhang J and He JJ:
miR-4262 promotes proliferation and invasion of human breast cancer
cells through directly targeting KLF6 and KLF15. Oncol Res.
25:277–283. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Weng L, Ma J, Jia YP, Wu SQ, Liu BY, Cao
Y, Yin X, Shang MY and Mao AW: miR-4262 promotes cell apoptosis and
inhibits proliferation of colon cancer cells: Involvement of
GALNT4. Am J Transl Res. 10:3969–3977. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang D, Li Z, Zhang Y, Tu C, Huo J and
Liu Y: miR-4262 promotes the proliferation of human cutaneous
malignant melanoma cells through KLF6-mediated EGFR inactivation
and p21 upregulation. Oncol Rep. 36:3657–3663. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang L, Duan Z, Liu X and Yuan Y:
N-acetyl-l-cysteine ameliorates the PM2.5-induced oxidative stress
by regulating SIRT-1 in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 57:70–75.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sim WC, Kim DG, Lee W, Sim H, Choi YJ and
Lee BH: Activation of SIRT1 by L-serine increases fatty acid
oxidation and reverses insulin resistance in C2C12 myotubes. Cell
Biol Toxicol. 35:457–470. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pan Q, Lou X, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Li F, Shan
Q, Chen X, Xie Y, Su S, Wei H, et al: Genomic variants in mouse
model induced by azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate improperly
mimic human colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 7(25)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Menconi A, Hernandez-Velasco X, Vicuña EA,
Kuttappan VA, Faulkner OB, Tellez G, Hargis BM and Bielke LR:
Histopathological and morphometric changes induced by a dextran
sodium sulfate (DSS) model in broilers. Poult Sci. 94:906–911.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nighot P, Young K, Nighot M, Rawat M, Sung
EJ, Maharshak N, Plevy SE, Ma T and Blikslager A: Chloride channel
ClC-2 is a key factor in the development of DSS-induced murine
colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 19:2867–2877. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Friedrich M, Pohin M and Powrie F:
Cytokine networks in the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel
disease. Immunity. 50:992–1006. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Rogler G: Resolution of inflammation in
inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol.
2:521–530. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
McDaniel DK, Eden K, Ringel VM and Allen
IC: Emerging roles for noncanonical NF-κB signaling in the
modulation of inflammatory bowel disease pathobiology. Inflamm
Bowel Dis. 22:2265–2279. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Soufflet F, Biraud M, Rolli-Derkinderen M,
Lardeux B, Trang C, Coron E, Bruley des Varannes S, Bourreille A
and Neunlist M: Modulation of VIPergic phenotype of enteric neurons
by colonic biopsy supernatants from patients with inflammatory
bowel diseases: Involvement of IL-6 in Crohn's disease.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 30:2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Schenk M, Bouchon A, Seibold F and Mueller
C: TREM-1-expressing intestinal macrophages crucially amplify
chronic inflammation in experimental colitis and inflammatory bowel
diseases. J Clin Invest. 117:3097–3106. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhao Q, Liu Y, Tan L, Yan L and Zuo X:
Adiponectin administration alleviates DSS-induced colonic
inflammation in Caco-2 cells and mice. Inflamm Res. 67:663–670.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wirtz S, Neufert C, Weigmann B and Neurath
MF: Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nat
Protoc. 2:541–546. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu X, Chen J, Guan T, Yao H, Zhang W,
Guan Z and Wang Y: Correction to: miRNAs and target genes in the
blood as biomarkers for the early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease.
BMC Syst Biol. 13(20)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang J, Lian B, Shang Y, Li C and Meng Q:
miR-135a protects dextran sodium sulfate-induced inflammation in
human colorectal cell lines by activating STAT3 signal. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 51:1001–1012. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang H, Jiang H, Zhang H, Liu J, Hu X and
Chen L: miR-4262, low level of which predicts poor prognosis,
targets proto-oncogene CD163 to suppress cell proliferation and
invasion in gastric cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 12:599–607.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sun H, Zhou X, Bao Y, Xiong G, Cui Y and
Zhou H: Involvement of miR-4262 in paclitaxel resistance through
the regulation of PTEN in non-small cell lung cancer. Open Biol.
9(180227)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Song K, Liu N, Yang Y and Qiu X:
Regulation of osteosarcoma cell invasion through osteopontin
modification by miR-4262. Tumour Biol. 37:6493–6499.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gerasimidis K, Edwards C, Stefanowicz F,
Galloway P, McGrogan P, Duncan A and Talwar D: Micronutrient status
in children with IBD: True deficiencies or epiphenomenon of the
systemic inflammatory response. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.
56:e50–e51. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Eichele DD and Kharbanda KK: Dextran
sodium sulfate colitis murine model: An indispensable tool for
advancing our understanding of inflammatory bowel diseases
pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 23:6016–6029. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sun W, Li Y and Wei S: miR-4262 regulates
chondrocyte viability, apoptosis, autophagy by targeting SIRT1 and
activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in rats with
osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 15:1119–1128. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Schuliga M: NF-kappaB signaling in chronic
inflammatory airway disease. Biomolecules. 5:1266–1283.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lin TH, Pajarinen J, Lu L, Nabeshima A,
Cordova LA, Yao Z and Goodman SB: NF-κB as a therapeutic target in
inflammatory-associated bone diseases. Adv Protein Chem Struct
Biol. 107:117–154. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hill JM, Clement C, Zhao Y and Lukiw WJ:
Induction of the pro-inflammatory NF-kB-sensitive miRNA-146a by
human neurotrophic viruses. Front Microbiol. 6(43)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Pogue AI, Percy ME, Cui JG, Li YY,
Bhattacharjee S, Hill JM, Kruck TP, Zhao Y and Lukiw WJ:
Up-regulation of NF-kB-sensitive miRNA-125b and miRNA-146a in metal
sulfate-stressed human astroglial (HAG) primary cell cultures. J
Inorg Biochem. 105:1434–1437. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|