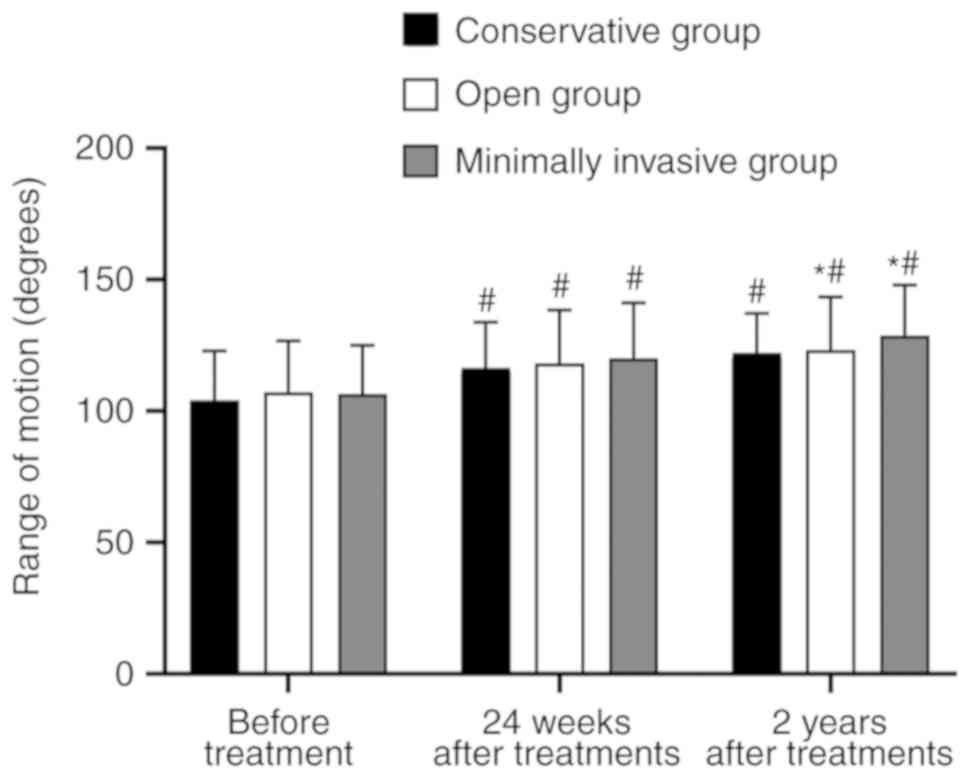
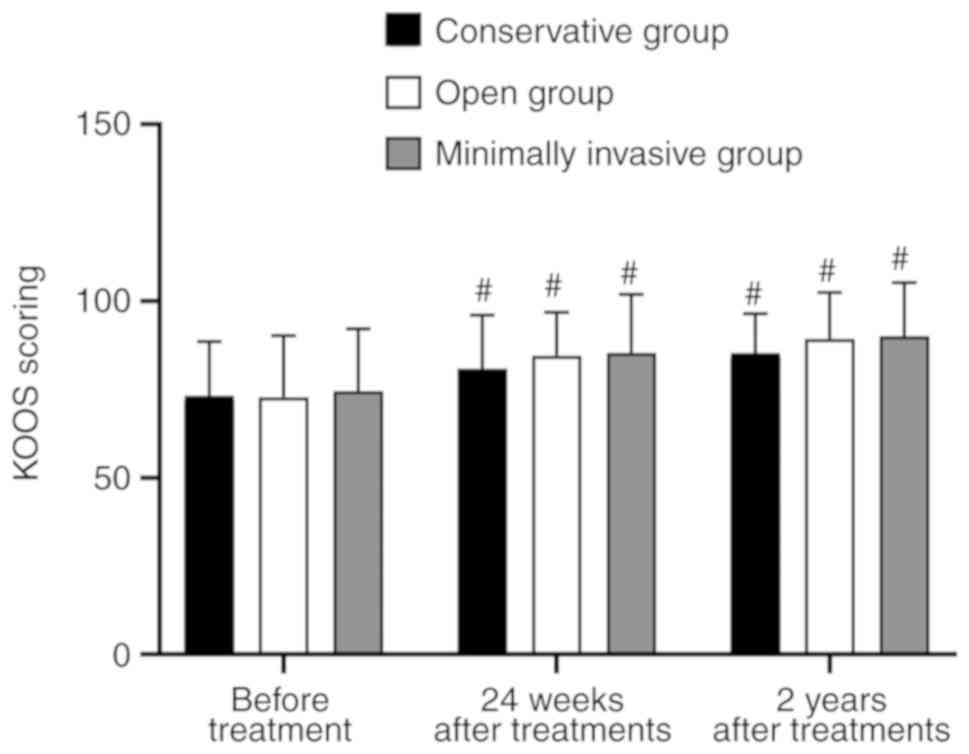
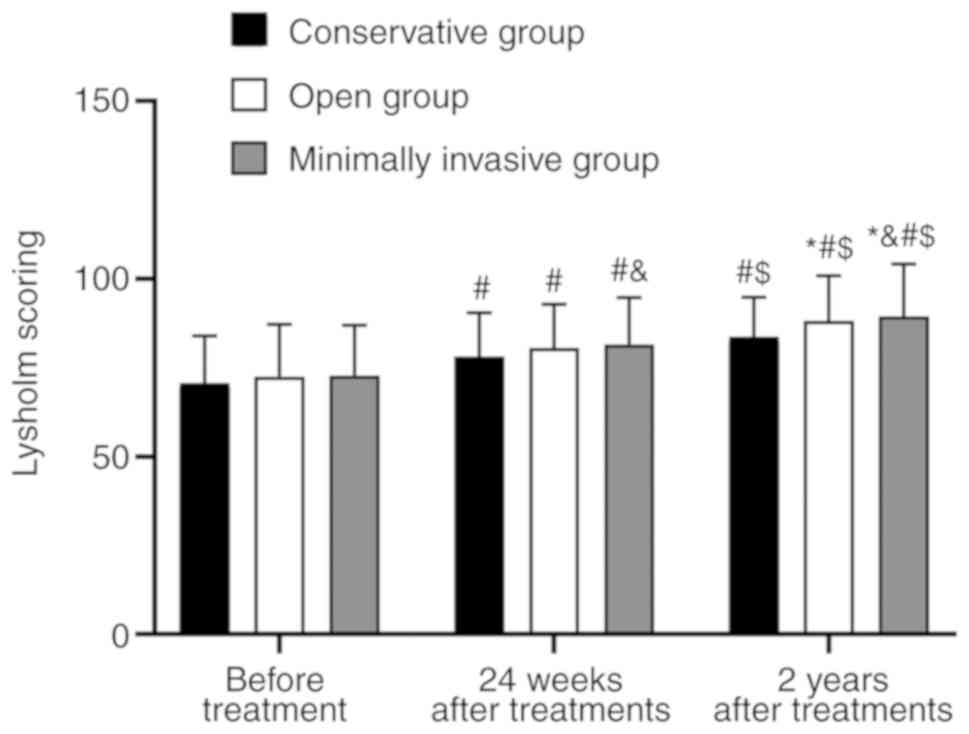
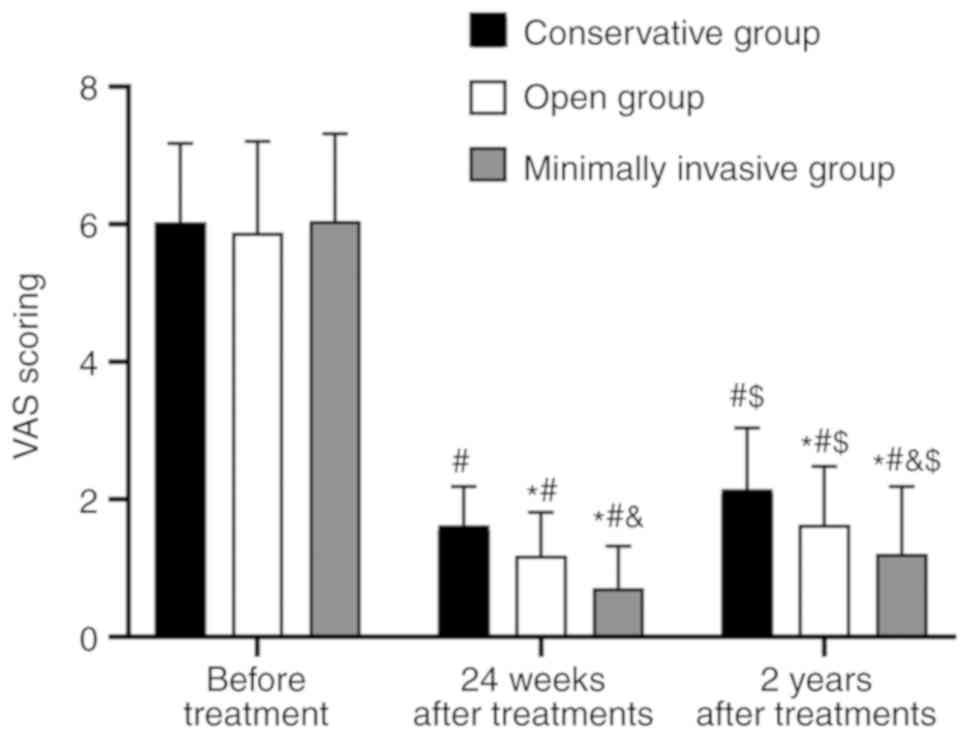
|
1
|
Naimark MB, Kegel G, O'Donnell T, Lavigne
S, Heveran C and Crawford DC: Knee function assessment in patients
with meniscus injury: A preliminary study of reproducibility,
response to treatment, and correlation with patient-reported
questionnaire outcomes. Orthop J Sports Med.
2(2325967114550987)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ebrahimi N, Jalaie S, Salsabili N, Ansari
NN and Naghdi S: Knee injury and osteoarthritis outcome score in
patients with isolated meniscus injury; validity and reliability. J
Res Med Sci. 22(55)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Matsukura Y, Muneta T, Tsuji K, Koga H and
Sekiya I: Mesenchymal stem cells in synovial fluid increase after
meniscus injury. Orthop Relat Res. 472:1357–1364. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rai MF and McNulty AL: Meniscus beyond
mechanics: Using biology to advance our understanding of meniscus
injury and treatment. Connect Tissue Res. 58:221–224.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Brophy RH, Gefen AM, Matava MJ, Wright RW
and Smith MV: Understanding of meniscus injury and expectations of
meniscus surgery in patients presenting for orthopaedic care.
Arthroscopy. 31:2295–2300.e5. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Salzler MJ, Lin A, Miller CD, Herold S,
Irrgang JJ and Harner CD: Complications after arthroscopic knee
surgery. Am J Sports Med. 42:292–296. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Norton MJ and Ischy ND: Apparatus and
method for minimally invasive surgery. US Patent 9,820,771(P).
Filed on March 3, 2006; issued November 21, 2017.
|
|
8
|
Khan M, Evaniew N, Bedi A, Ayeni OR and
Bhandari M: Arthroscopic surgery for degenerative tears of the
meniscus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ.
186:1057–1064. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Thorlund JB, Juhl CB, Roos EM and
Lohmander LS: Arthroscopic surgery for degenerative knee:
Systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits and harms. BMJ.
350(h2747)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Meckes JK, Caramés B, Olmer M, Kiosses WB,
Grogan SP, Lotz MK and D'Lima DD: Compromised autophagy precedes
meniscus degeneration and cartilage damage in mice. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 25:1880–1889. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kloefkorn HE, Jacobs BY, Loye AM and Allen
KD: Spatiotemporal gait compensations following medial collateral
ligament and medial meniscus injury in the rat: Correlating gait
patterns to joint damage. Arthritis Res Ther.
17(287)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Vaquero-Picado A and Rodríguez-Merchán EC:
Arthroscopic repair of the meniscus: Surgical management and
clinical outcomes. EFORT Open Rev. 3:584–594. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Howell R, Kumar NS, Patel N and Tom J:
Degenerative meniscus: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
options. World J Orthop. 5:597–602. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Krause M, Freudenthaler F, Frosch KH,
Achtnich A, Petersen W and Akoto R: Operative versus conservative
treatment of anterior cruciate ligament rupture. Dtsch Arztebl Int.
115:855–862. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Filbay SR, Andersson C, Ardern C, Gauffin
H and Kvist J: Patient-reported outcome 32 to 37 years following
surgically treated or non-surgically treated acute anterior
cruciate ligament injury. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 26 (Suppl
1):S52–S53. 2018.
|
|
16
|
Sihvonen R, Paavola M, Malmivaara A, Itälä
A, Joukainen A, Nurmi H, Kalske J and Järvinen TL: Finnish
degenerative meniscal lesion study (FIDELITY) group. Arthroscopic
partial meniscectomy versus sham surgery for a degenerative
meniscal tear. N Engl J Med. 369:2515–2524. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Herrlin SV, Wange PO, Lapidus G, Hållander
M, Werner S and Weidenhielm L: Is arthroscopic surgery beneficial
in treating non-traumatic, degenerative medial meniscal tears? A
five year follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.
21:358–364. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Katz JN, Brophy RH, Chaisson CE, de Chaves
L, Cole BJ, Dahm DL, Donnell-Fink LA, Guermazi A, Haas AK, Jones
MH, et al: Surgery versus physical therapy for a meniscal tear and
osteoarthritis. N Engl J Med. 368:1675–1684. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Beaufils P, Becker R, Kopf S, Matthieu O
and Pujol N: The knee meniscus: Management of traumatic tears and
degenerative lesions. EFORT Open Rev. 2:195–203. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
De Coninck T, Huysse W, Verdonk R,
Verstraete K and Verdonk P: Open versus arthroscopic meniscus
allograft transplantation: Magnetic resonance imaging study of
meniscal radial displacement. Arthroscopy. 29:514–521.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gu HF, Zhang SJ, Zhao C, Chen Y and Bi Q:
A comparison of open and arthroscopic surgery for treatment of
diffuse pigmented villonodular synovitis of the knee. Knee Surg
Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 22:2830–2836. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Davis TR, Brady O and Dias JJ: Excision of
the trapezium for osteoarthritis of the trapeziometacarpal joint: A
study of the benefit of ligament reconstruction or tendon
interposition. J Hand Surg Am. 29:1069–1077. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fok AW and Yau WP: Delay in ACL
reconstruction is associated with more severe and painful meniscal
and chondral injuries. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.
21:928–933. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Eckstein F, Cotofana S, Wirth W, Nevitt M,
John MR, Dreher D and Frobell BR: Greater rates of cartilage loss
in painful knees than in pain-free knees after adjustment for
radiographic disease stage Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 63:2257–2267. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dunn WR, Spindler KP, Amendola A, Andrish
JT, Kaeding CC, Marx RG, McCarty EC, Parker RD, Harrell FE Jr and
An AQ: Which preoperative factors, including bone bruise, are
associated with knee pain/symptoms at index anterior cruciate
ligament reconstruction (ACLR)? A Multicenter Orthopaedic Outcomes
Network (MOON) ACLR Cohort Study. Am J Sports Med. 38:1778–1787.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|