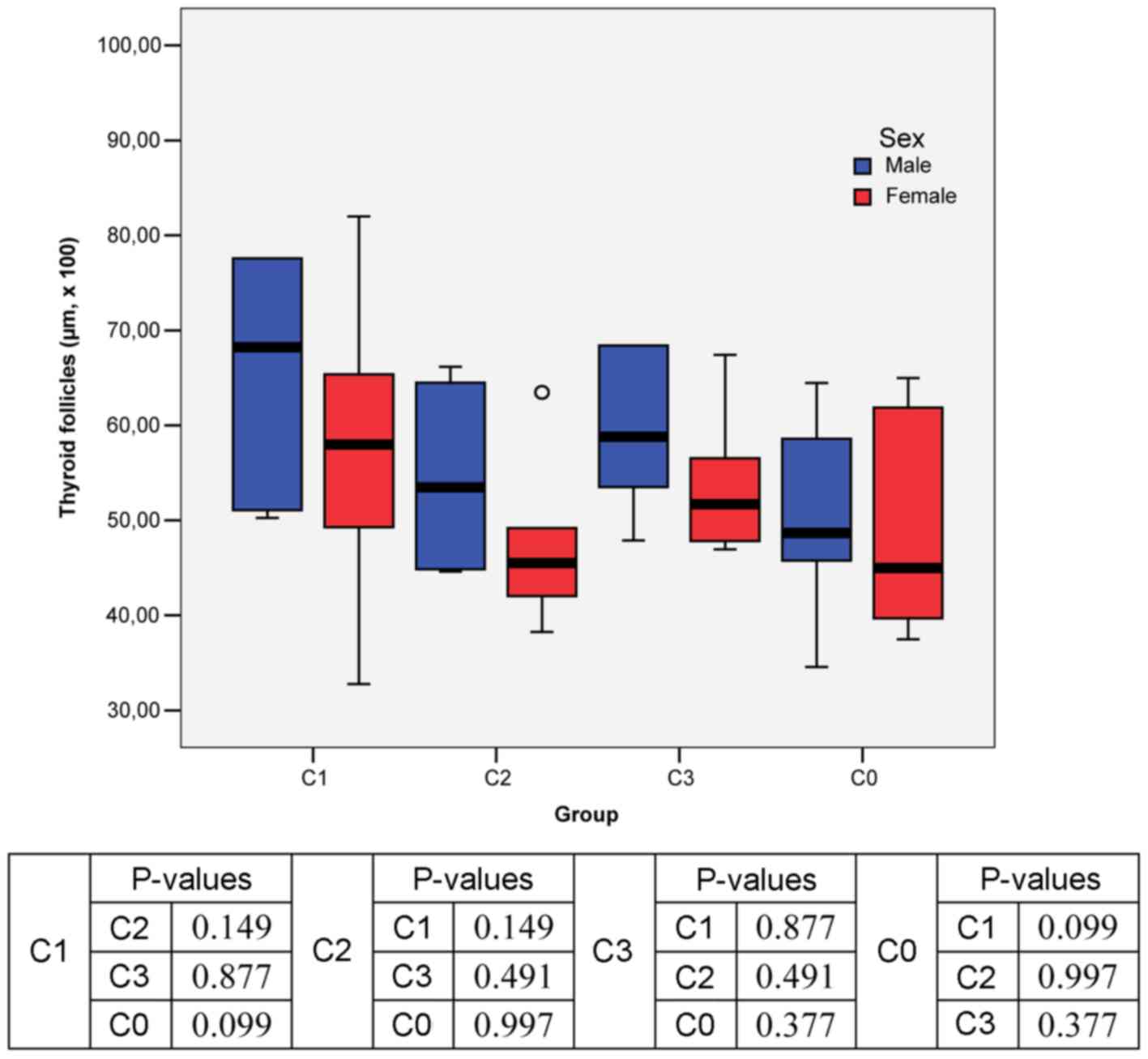
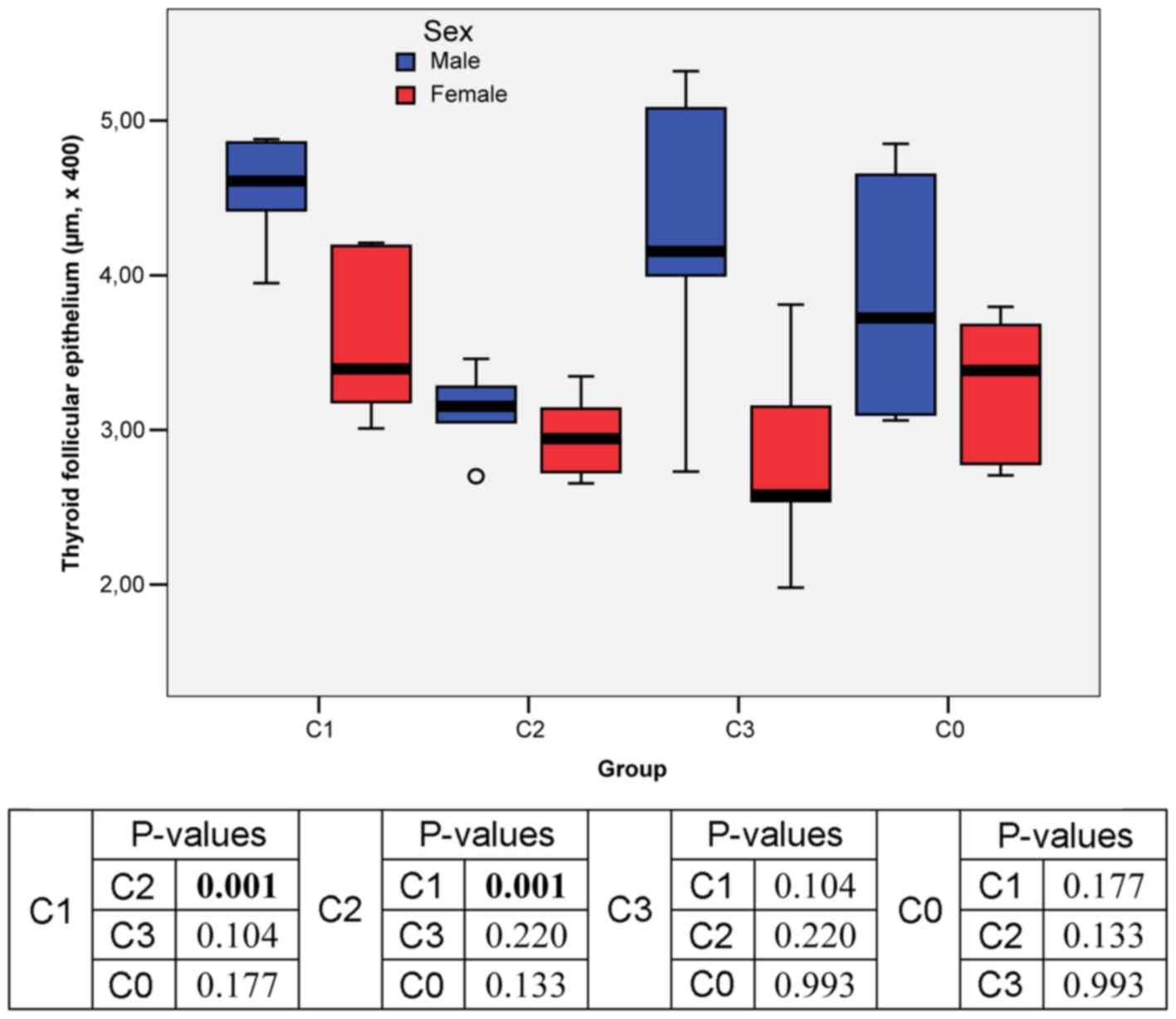
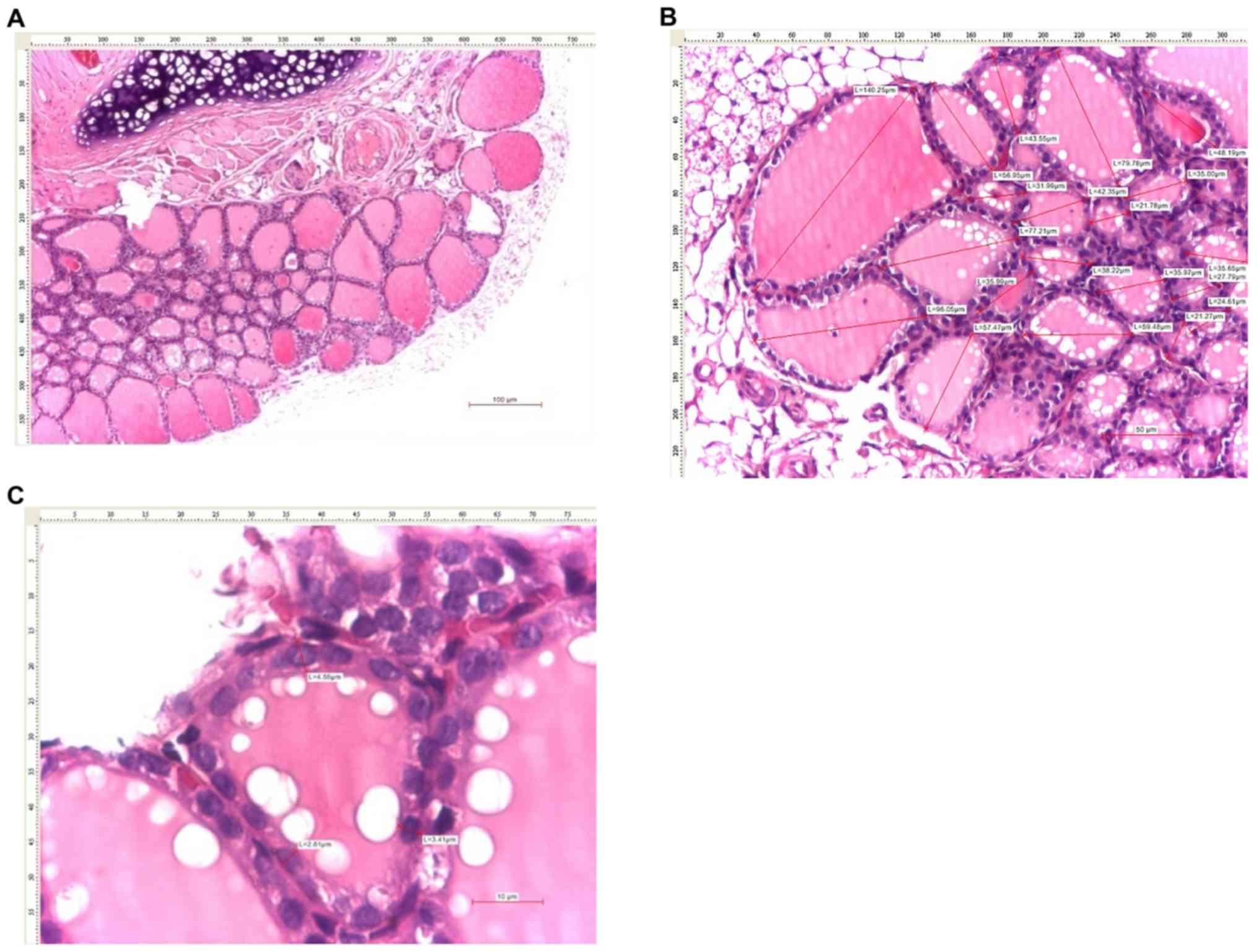
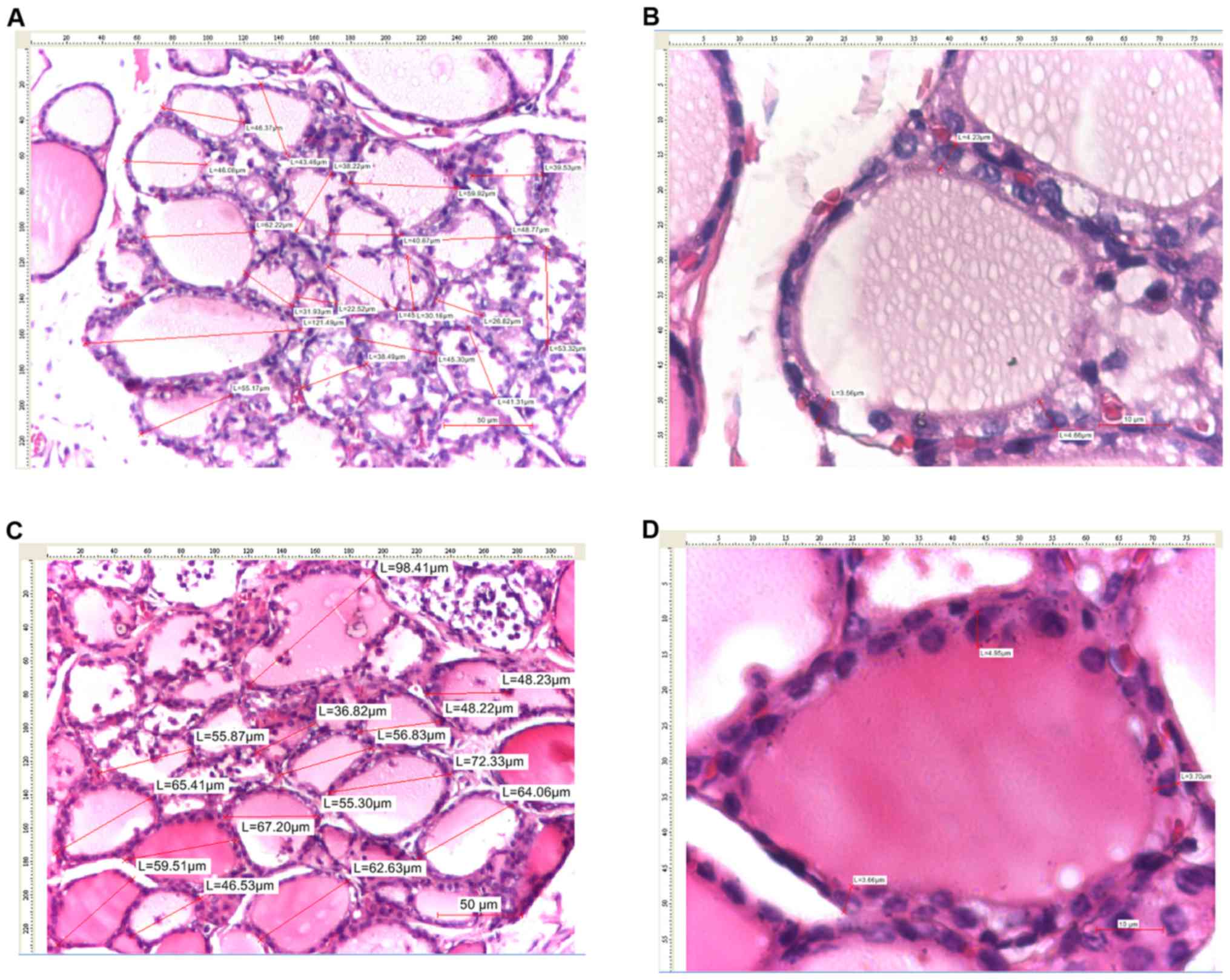
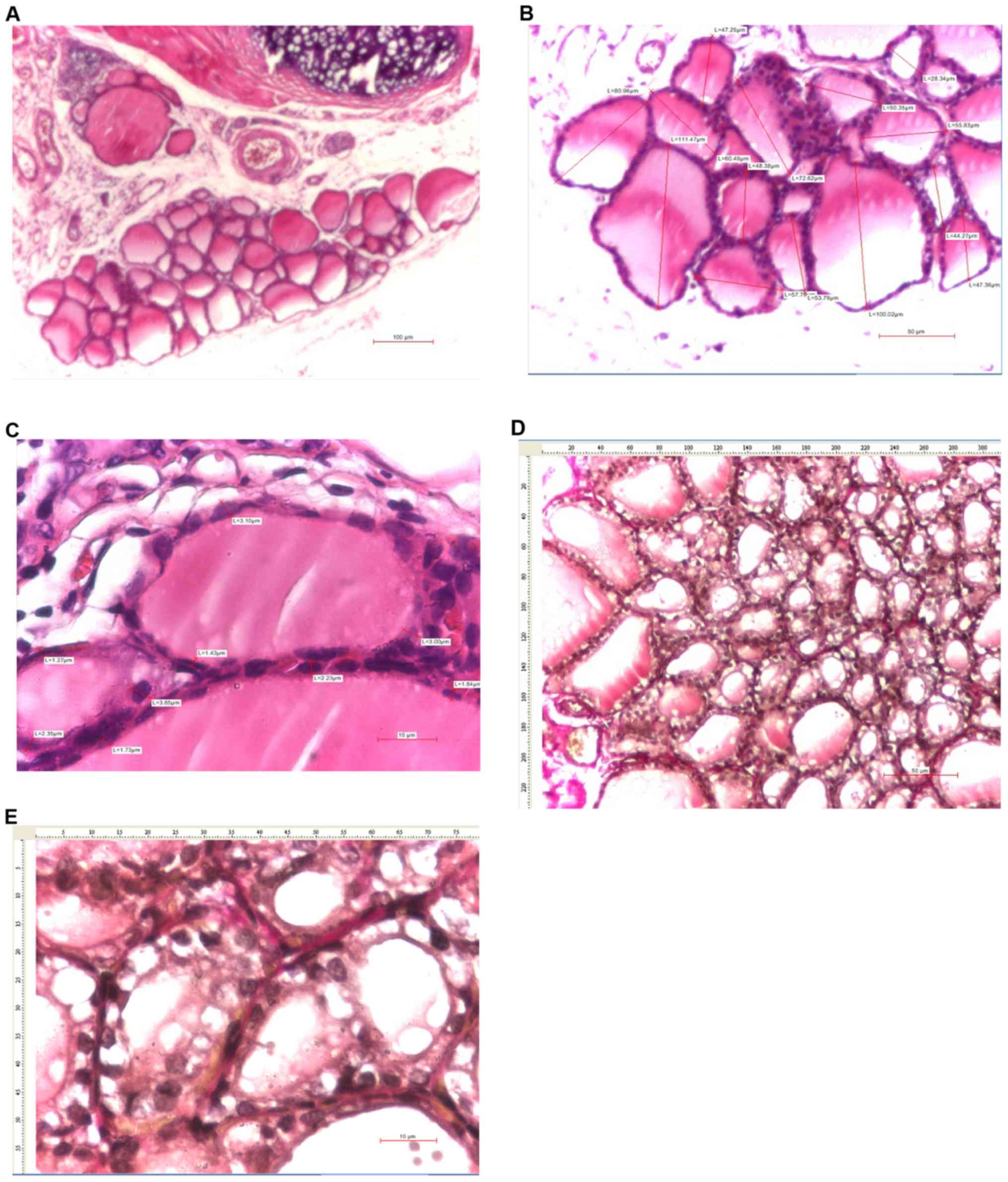
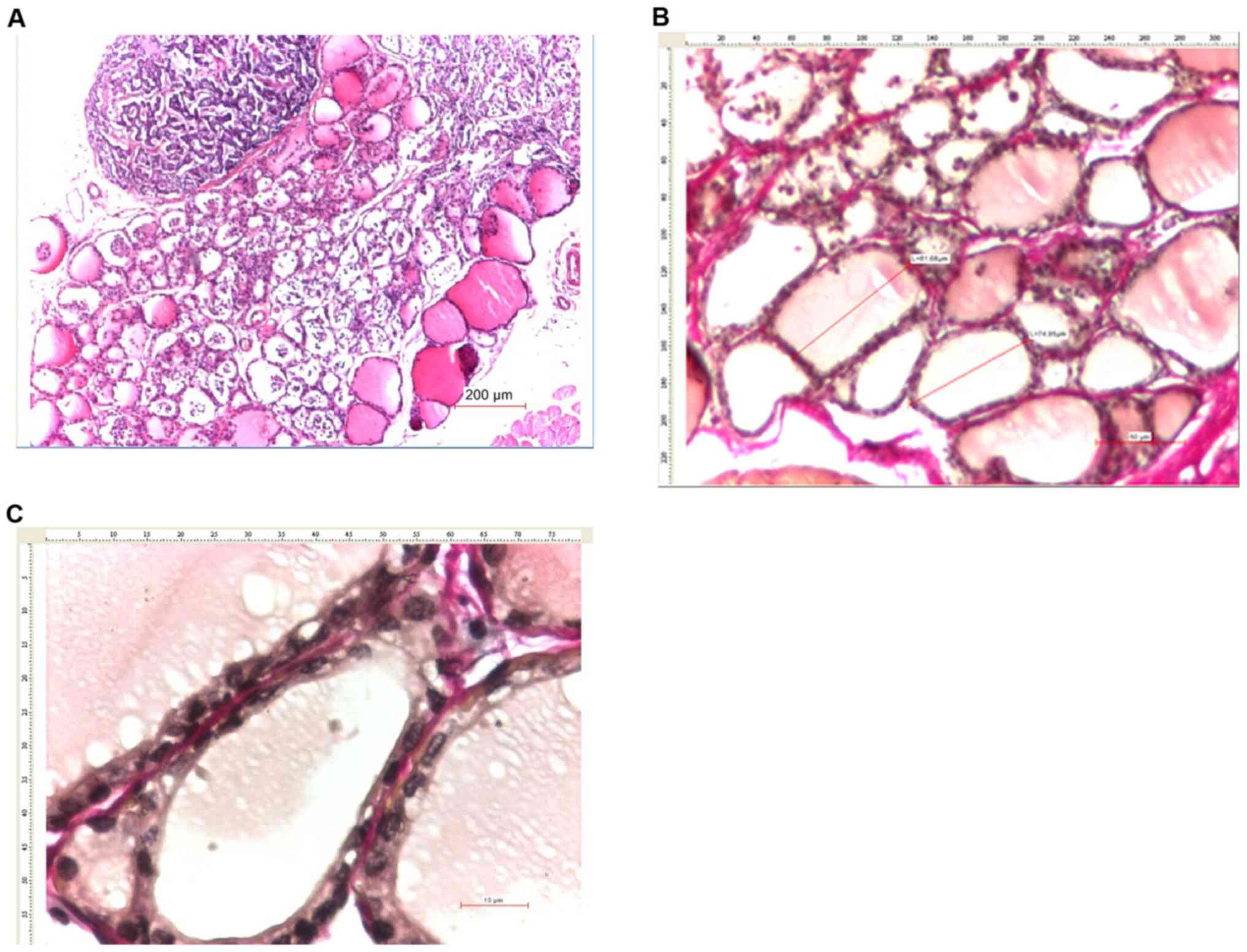
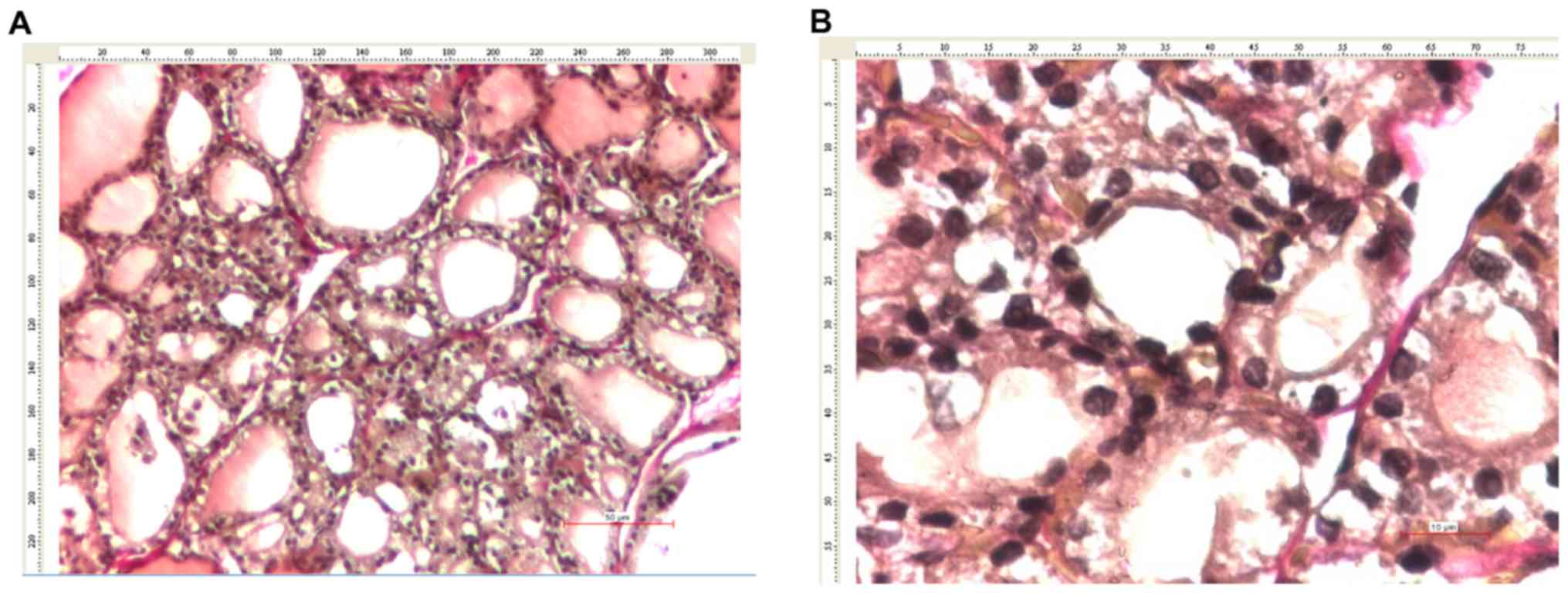
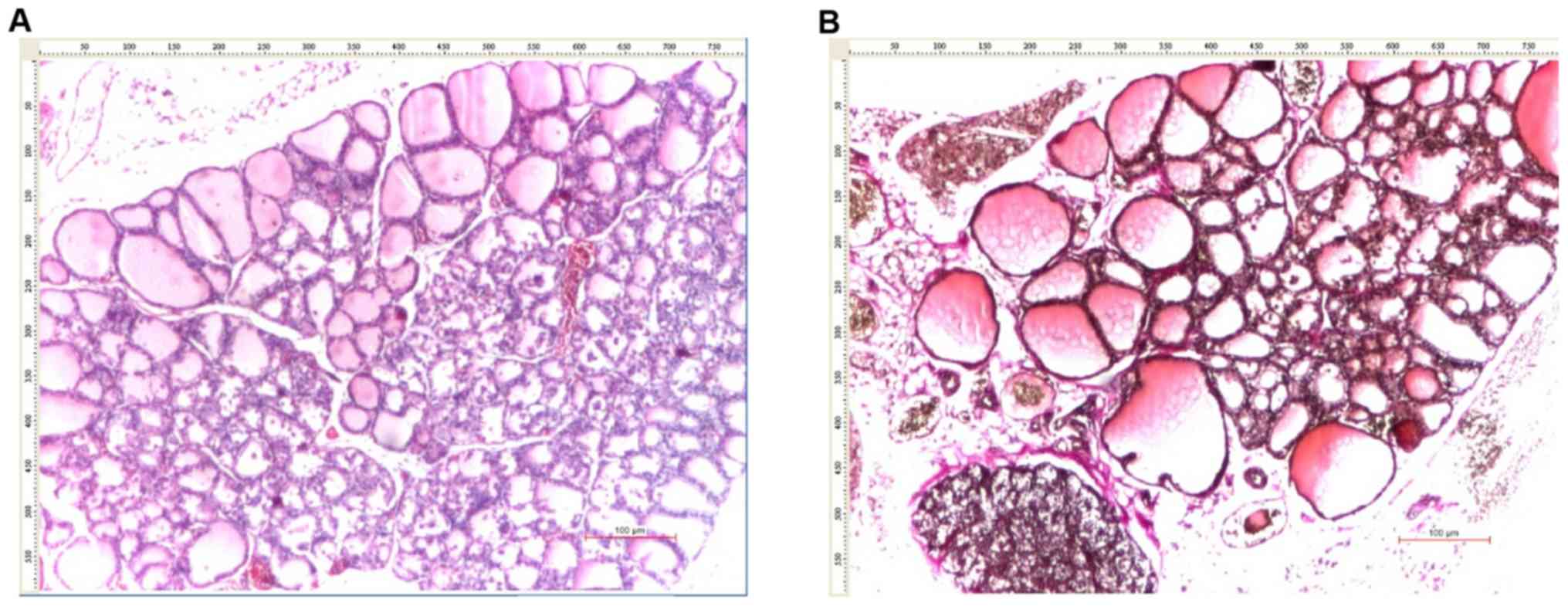
|
1
|
Rose NR, Bonita R and Burek CL: Iodine: An
environmental trigger of thyroiditis. Autoimmun Rev. 1:97–103.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Markou K, Georgopoulos N, Kyriazopoulou V
and Vagenakis AG: Iodine-induced hypothyroidism. Thyroid.
11:501–510. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Foley TP Jr: The relationship between
autoimmune thyroid disease and iodine intake: A review. Endokrynol
Pol. 43):53–69. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wolff J and Chaikoff IL: Plasma inorganic
iodide as a homeostatic regulator of thyroid function. J Biol Chem.
174:555–564. 1948.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Paul T, Meyers B, Witorsch RJ, Pino S,
Chipkin S, Ingbar SH and Braverman LE: The effect of small
increases in dietary iodine on thyroid function in euthyroid
subjects. Metabolism. 37:121–124. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Denef JF, Many MC and van den Hove MF:
Iodine-induced thyroid inhibition and cell necrosis: Two
consequences of the same free-radical mediated mechanism? Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 121:101–103. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vitale M, Di Matola T, D'Ascoli F, Salzano
S, Bogazzi F, Fenzi G, Martino E and Rossi G: Iodide excess induces
apoptosis in thyroid cells through a p53-independent mechanism
involving oxidative stress. Endocrinology. 141:598–605.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cardoso LC, Martins DCL, Figueiredo MDL,
Rosenthal D, Vaisman M, Violante AHD and Carvalho DP:
Ca(2+)/nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent
H(2)O(2) generation is inhibited by iodide in human thyroids. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86:4339–4343. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mahmoud I, Colin I, Many MC and Denef JF:
Direct toxic effect of iodide in excess on iodine-deficient thyroid
glands: Epithelial necrosis and inflammation associated with
lipofuscin accumulation. Exp Mol Pathol. 44:259–271.
1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Contempre B, Denef JF, Dumont JEMM and
Many MC: Selenium deficiency aggravates the necrotizing effects of
a high iodide dose in iodine deficient rats. Endocrinology.
132:1866–1868. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Contempre B, Le Moine O, Dumont JE, Denef
JF and Many MC: Selenium deficiency and thyroid fibrosis. A key
role for macrophages and transforming growth factor beta
(TGF-beta). Mol Cell Endocrinol. 124:7–15. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chiu-Ugalde J, Wirth EK, Klein MO, Sapin
R, Fradejas-Villar N, Renko K, Schomburg L, Köhrle J and Schweizer
U: Thyroid function is maintained despite increased oxidative
stress in mice lacking selenoprotein biosynthesis in thyroid
epithelial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 17:902–913.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kolypetri P, Noel NA, Carayanniotis KA and
Carayanniotis G: Iodine content of thyroglobulin in
Nod.H2® mice developing iodine-accelerated autoimmune
thyroiditis. Hormones (Athens). 9:151–160. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Arata N, Ando T, Unger P and Davies TF:
By-stander activation in autoimmune thyroiditis: Studies on
experimental autoimmune thyroiditis in the GFP®
fluorescent mouse. Clin Immunol. 121:108–117. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rasooly L, Burek CL and Rose NR:
Iodine-induced autoimmune thyroiditis in NOD-H-2® mice.
Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 81:287–292. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Čiháková D, Sharma RB, Fairweather D,
Afanasyeva M and Rose NR: Animal models for autoimmune myocarditis
and autoimmune thyroiditis. In: Autoimmunity: Methods and
Protocols. Perl A (ed). Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp175-193,
2004.
|
|
17
|
Pitsiavas V, Smerdely P, Li M and Boyages
SC: Amiodarone induces a different pattern of ultrastructural
change in the thyroid to iodine excess alone in both the BB/W rat
and the Wistar rat. Eur J Endocrinol. 137:89–98. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gao J, Lin X, Liu X, Yang Q, Zhang Z,
Jiang Q and Bian J: Effect of combined excess iodine and
low-protein diet on thyroid hormones and ultrastructure in Wistar
rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. 155:416–422. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bagchi N, Brown TR, Urdanivia E and
Sundick RS: Induction of autoimmune thyroiditis in chickens by
dietary iodine. Science. 230:325–327. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hassanin KM, Abd El-Kawi SH and Hashem KS:
The prospective protective effect of selenium nanoparticles against
chromium-induced oxidative and cellular damage in rat thyroid. Int
J Nanomedicine. 8:1713–1720. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Roubaty C, Bedin C and Charreire J:
Prevention of experimental autoimmune thyroiditis through the
anti-idiotypic network. J Immunol. 144:2167–2172. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cui SL, Yu J and Shoujun L: Iodine Intake
Increases IP-10 Expression in the serum and thyroids of rats with
experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. Int J Endocrinol.
2014(581069)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Risher J (ed): Toxicological Profile for
Selenium (Update). DIANE Publishing, Darby, PA, 2011. https://books.google.com/books?id=AEVdvRbs6xEC&pgis=1.
|
|
24
|
Solcan C, Ciobanu C and Cuciureanu R:
Dose-dependent subacute toxicity of sodium selenite in male Wistar
rats. Jökull J. 63:57–69. 2013.
|
|
25
|
Effraimidis G and Wiersinga WM: Mechanisms
in endocrinology: autoimmune thyroid disease: old and new players.
Eur J Endocrinol. 170:R241–R252. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Vanderpump MP, Tunbridge WM, French JM,
Appleton D, Bates D, Clark F, Evans JG, Hasan DM, Rodgers H,
Tunbridge F, et al: The incidence of thyroid disorders in the
community: A twenty-year follow-up of the Whickham Survey. Clin
Endocrinol (Oxf). 43:55–68. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Laurberg P, Pedersen KM, Hreidarsson A,
Sigfusson N, Iversen E and Knudsen PR: Iodine intake and the
pattern of thyroid disorders: A comparative epidemiological study
of thyroid abnormalities in the elderly in Iceland and in Jutland,
Denmark. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 83:765–769. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fountoulakis S, Philippou G and Tsatsoulis
A: The role of iodine in the evolution of thyroid disease in
Greece: From endemic goiter to thyroid autoimmunity. Hormones
(Athens). 6:25–35. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nielsen E, Greve K, Larsen JC, Meyer O,
Krogholm K and Hansen M: Iodine, Inorganic and Soluble Salts. The
Danish Environmental Protection Agency, Copenhagen K, Denmark,
2014. https://www2.mst.dk/Udgiv/publications/2014/01/978-87-93026-87-2.pdf.
|
|
30
|
Yanagisawa M, Hara Y, Satoh K, Tanikawa T,
Sakatsume Y, Katayama S, Kawazu S, Ishii J and Komeda K:
Spontaneous Autoimmune Bio Breeding/Worcester Thyroiditis in
(BB/W). Rat. 33:851–861. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li M, Eastman CJ and Boyages SC: Iodine
induced lymphocytic thyroiditis in the BB/W rat: Early and late
immune phenomena. Autoimmunity. 14:181–187. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Barin JG, Talor MV, Sharma RB, Rose NR and
Burek CL: Iodination of murine thyroglobulin enhances autoimmune
reactivity in the NOD.H2 mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 142:251–259.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhu YP, Bilous M and Boyages SC: Excess
iodine induces the expression of thyroid solid cell nests in
lymphocytic thyroiditis-prone BB/W rats. Autoimmunity. 20:201–206.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lupachik SV, Nadol'nik LI, Netsetskaya ZV
and Vinogradov VV: Effect of long-term injection of high doses of
potassium iodide on iodine metabolism in rat thyroid gland. Biochem
Suppl Ser B: Biomed Chem. 1:53–57. 2007.
|
|
35
|
Ruwhof C and Drexhage HA: Iodine and
thyroid autoimmune disease in animal models. Thyroid. 11:427–436.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Amara IB, Bouaziz H, Guermazi F and Zeghal
N: Effect of selenium on hypothyroidism induced by methimazole
(MMI) in lactating rats and their pups. Acta Biol Hung. 61:145–157.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jacobson DL, Gange SJ, Rose NR and Graham
NMH: Epidemiology and estimated population burden of selected
autoimmune diseases in the United States. Clin Immunol
Immunopathol. 84:223–243. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xiang Y, Jin Q, Li L, Yang Y, Zhang H, Liu
M, Fan C, Li J, Shan Z and Teng W: Physiological low-dose oestrogen
promotes the development of experimental autoimmune thyroiditis
through the up-regulation of Th1/Th17 responses. J Reprod Immunol.
126:23–31. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kincade PW, Medina KL, Smithson G and
Scott DC: Pregnancy: A clue to normal regulation of B
lymphopoiesis. Immunol Today. 15:539–544. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yin X, Latif R, Tomer Y and Davies TF:
Thyroid epigenetics: X chromosome inactivation in patients with
autoimmune thyroid disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1110:193–200.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chailurkit LO, Aekplakorn W and
Ongphiphadhanakul B: The relationship between circulating estradiol
and thyroid autoimmunity in males. Eur J Endocrinol. 170:63–67.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chen Y, Chen Y, Xia F, Wang N, Chen C, Nie
X, Li Q, Han B, Zhai H, Jiang B, et al: A higher ratio of estradiol
to testosterone is associated with autoimmune thyroid disease in
males. Thyroid. 27:960–966. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Falgarone G, Heshmati HM, Cohen R and
Reach G: Mechanisms in endocrinology. Role of emotional stress in
the pathophysiology of Graves' disease. Eur J Endocrinol.
168:R13–R18. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|