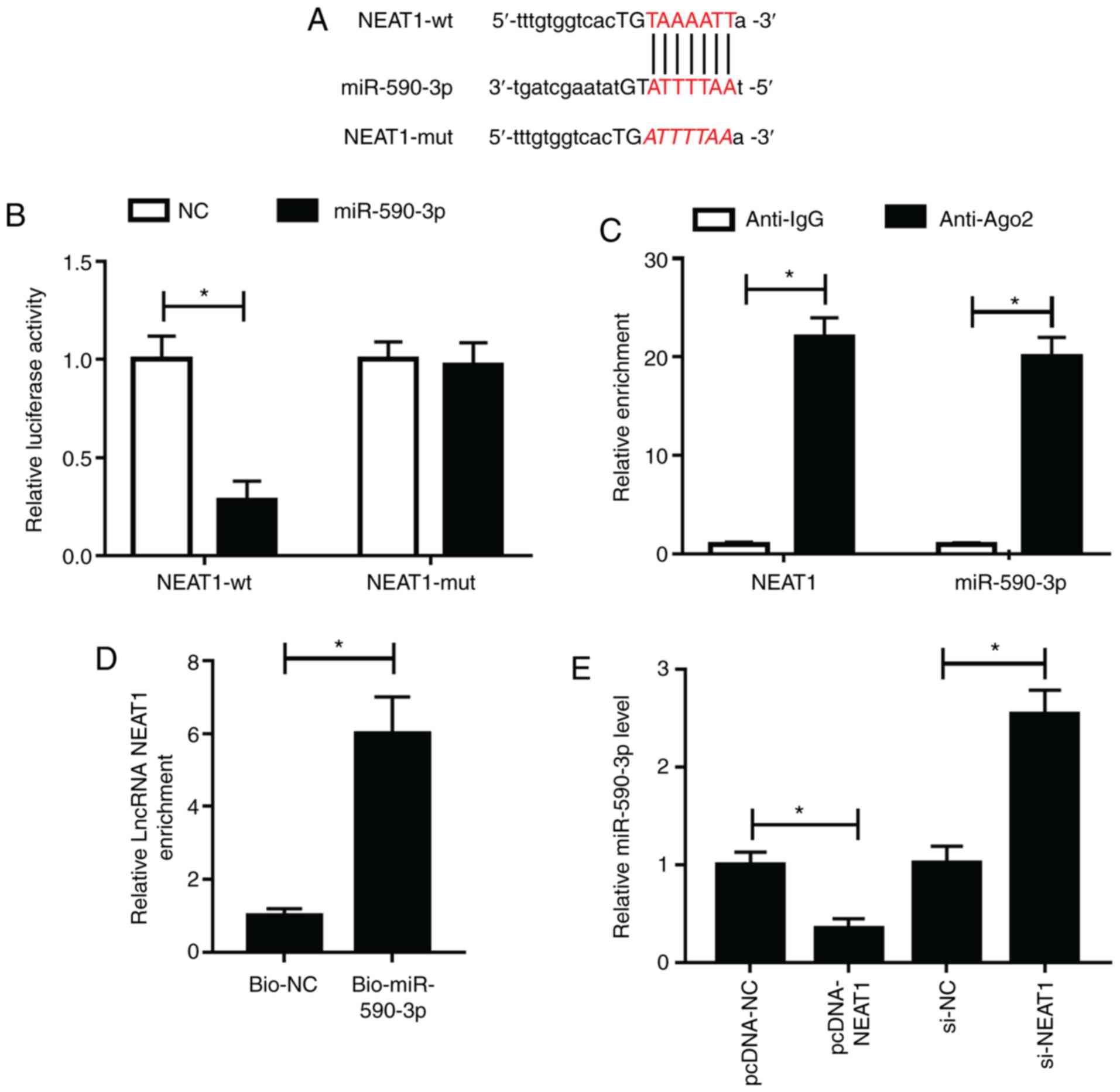
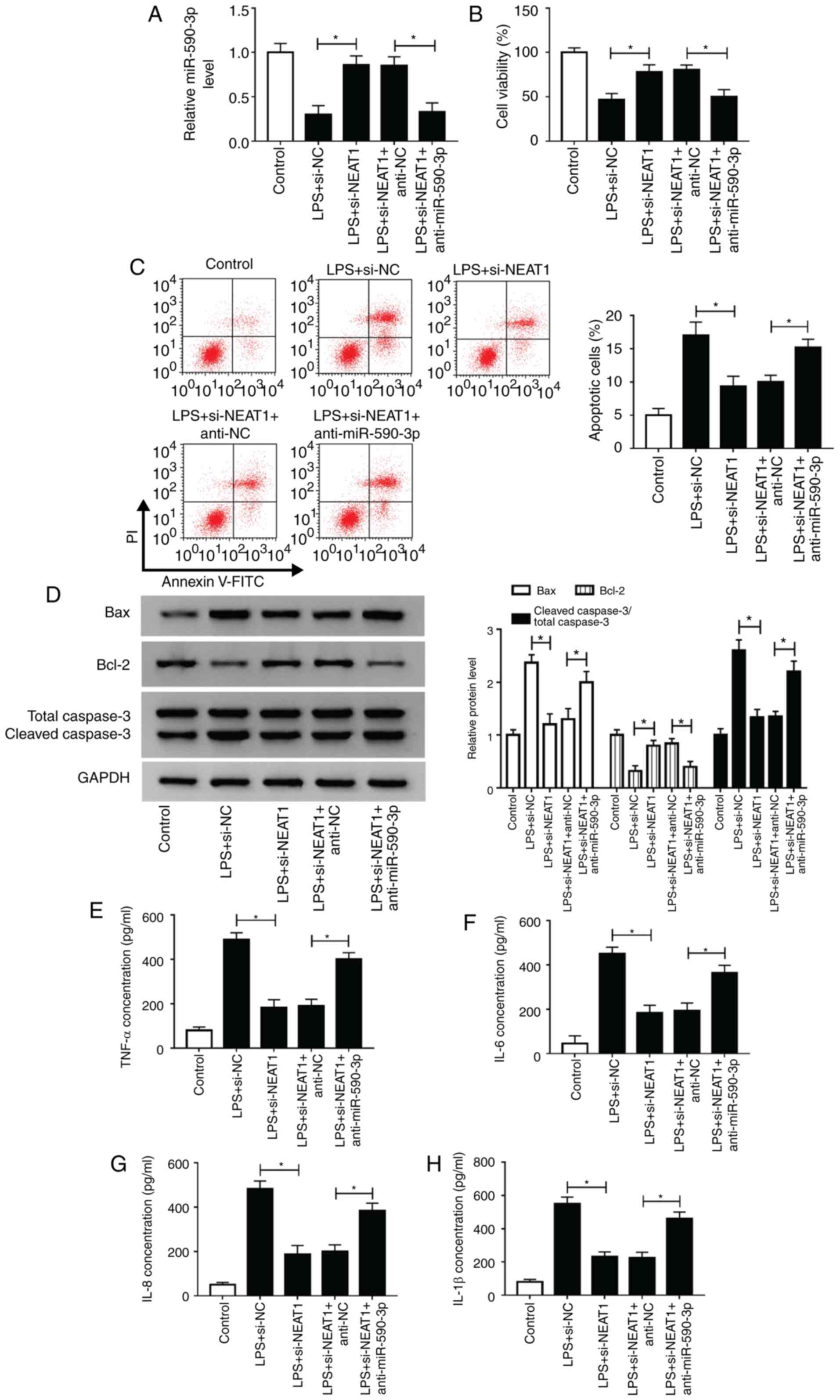
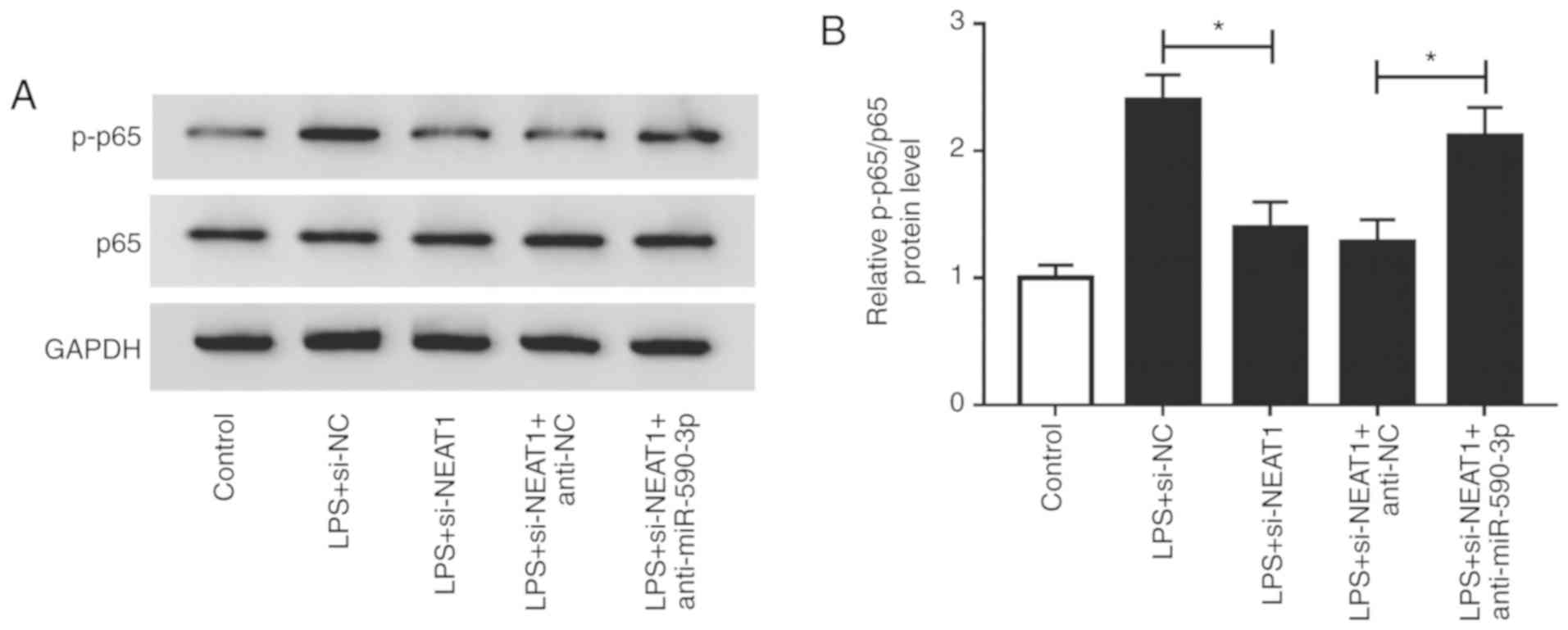
|
1
|
Napolitano LM: Sepsis 2018: Definitions
and Guideline Changes. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 19:117–125.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Delano MJ and Ward PA: Sepsis-induced
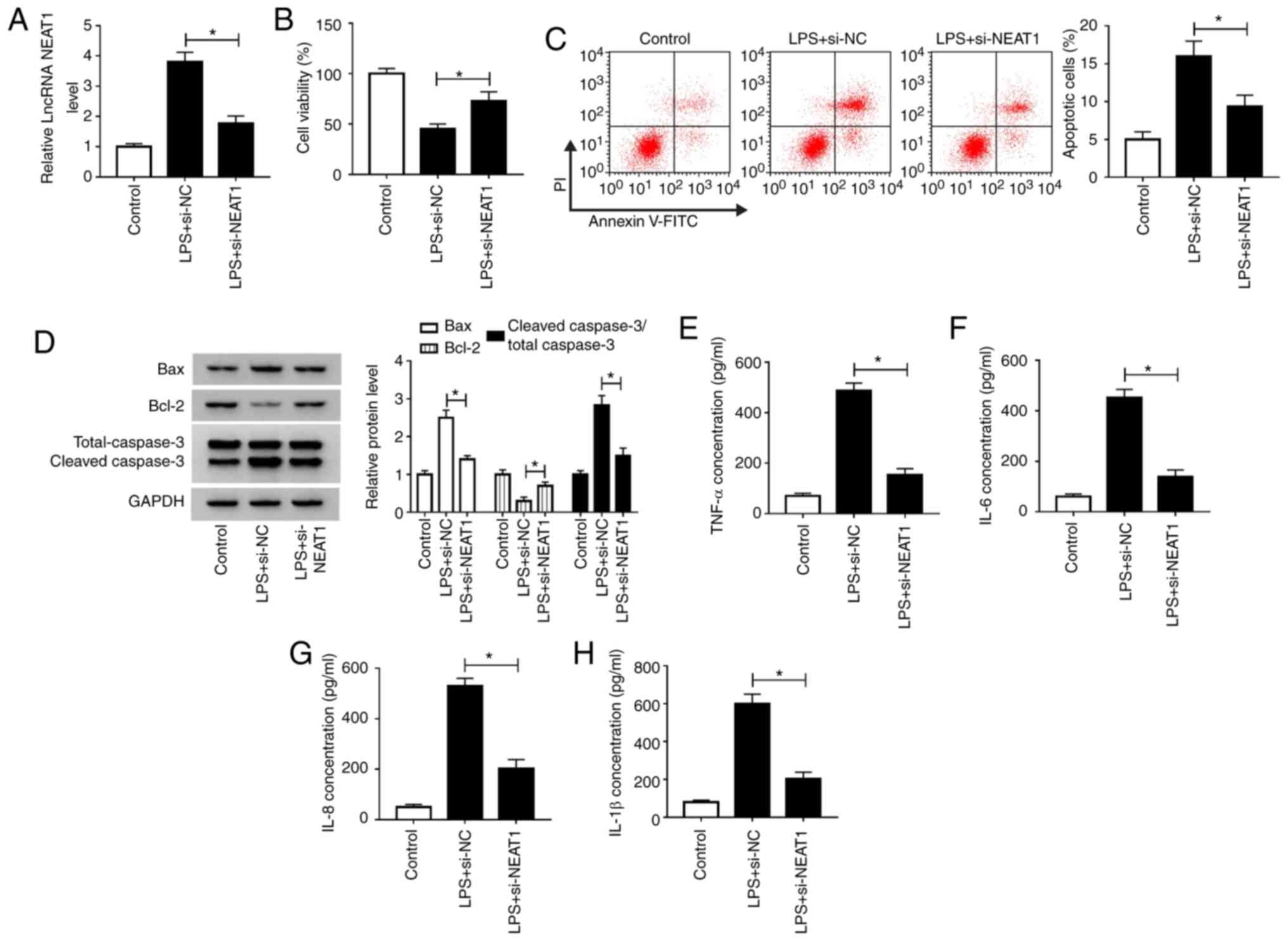
immune dysfunction: Can immune therapies reduce mortality? J Clin
Invest. 126:23–31. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View
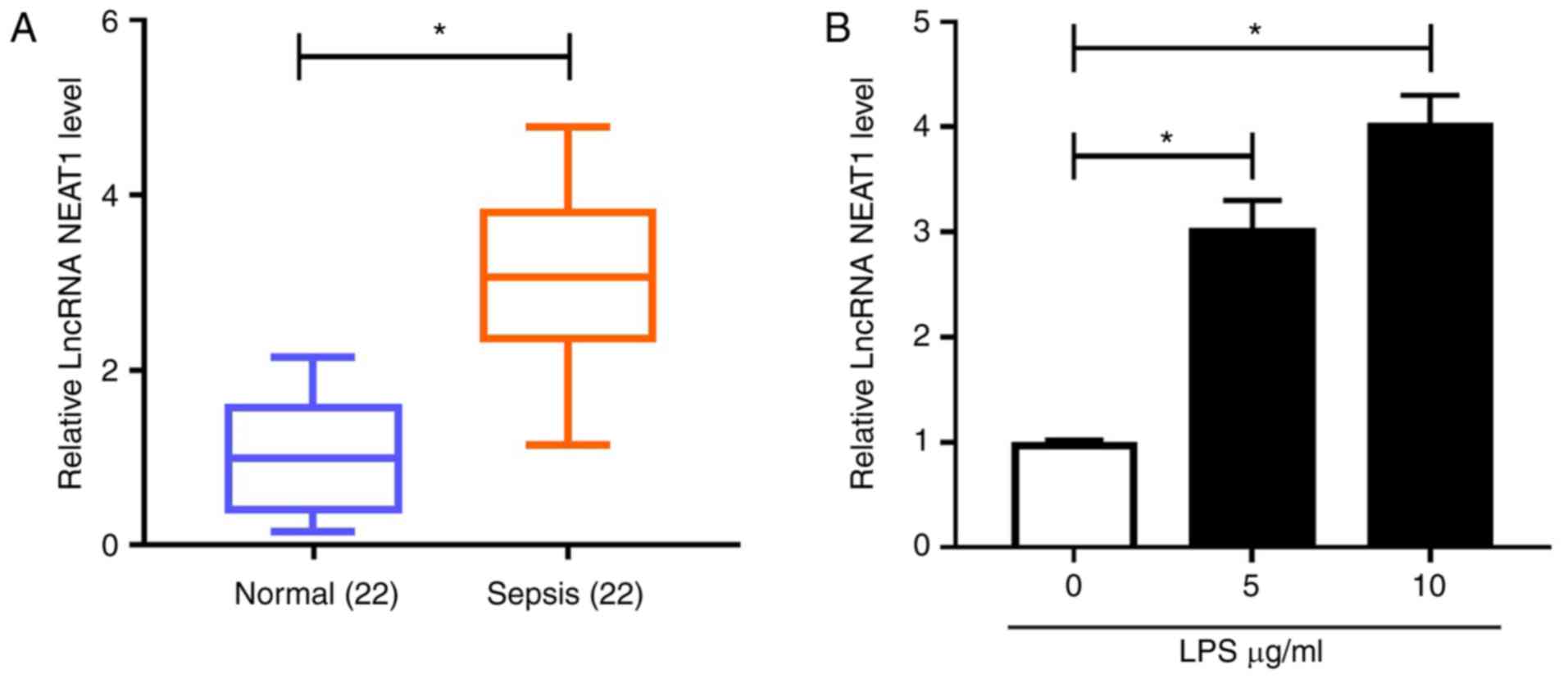
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hotchkiss RS, Moldawer LL, Opal SM,
Reinhart K, Turnbull IR and Vincent JL: Sepsis and septic shock.
Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2(16045)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Stevenson EK, Rubenstein AR, Radin GT,
Wiener RS and Walkey AJ: Two decades of mortality trends among
patients with severe sepsis: A comparative
meta-analysis*. Crit Care Med. 42:625–631.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
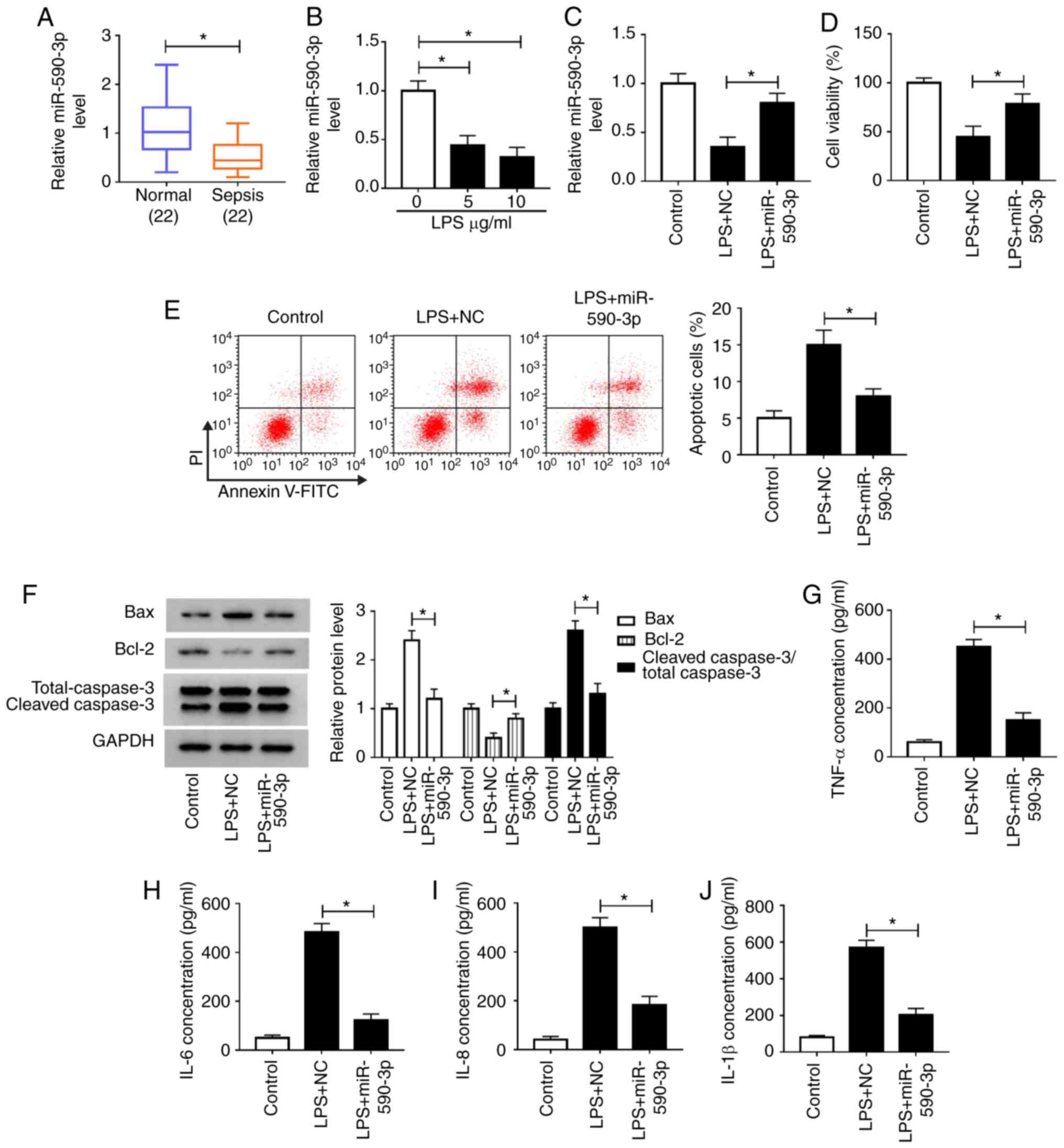
Sheng X, Zuo X, Liu X, Zhou Y and Sun X:
Crosstalk between TLR4 and Notch1 signaling in the IgA nephropathy
during inflammatory response. Int Urol Nephrol. 50:779–785.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang S, Li Z, Chen Q, Wang L, Zheng J, Lin
Z and Li W: NF-kappaB-induced microRNA-211 inhibits interleukin-10
in macrophages of rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:332–342.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Boon RA, Jaé N, Holdt L and Dimmeler S:
Long noncoding RNAs: From clinical genetics to therapeutic targets?
J Am Coll Cardiol. 67:1214–1226. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mohanty V, Gökmen-Polar Y, Badve S and
Janga SC: Role of lncRNAs in health and disease-size and shape
matter. Brief Funct Genomics. 14:115–129. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Qian K, Liu G, Tang Z, Hu Y, Fang Y, Chen
Z and Xu X: The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 interacted with miR-101
modulates breast cancer growth by targeting EZH2. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 615:1–9. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chakravarty D, Sboner A, Nair SS,
Giannopoulou E, Li R, Hennig S, Mosquera JM, Pauwels J, Park K,
Kossai M, et al: The oestrogen receptor alpha-regulated lncRNA
NEAT1 is a critical modulator of prostate cancer. Nat Commun.
5(5383)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen JX, Xu X and Zhang S: Silence of long
noncoding RNA NEAT1 exerts suppressive effects on immunity during
sepsis by promoting microRNA-125-dependent MCEMP1 downregulation.
IUBMB Life. 71:956–968. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu WQ, Wang YJ, Zheng Y and Chen X:
Effects of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 on sepsis-induced brain injury
in mice via NF-κB. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:3933–3939.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Huang Q, Huang C, Luo Y, He F and Zhang R:
Circulating lncRNA NEAT1 correlates with increased risk, elevated
severity and unfavorable prognosis in sepsis patients. Am J Emerg
Med. 36:1659–1663. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen Y, Qiu J, Chen B, Lin Y, Chen Y, Xie
G, Qiu J, Tong H and Jiang D: Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 plays an
important role in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by targeting
miR-204 and modulating the NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
59:252–260. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Huang S, Qian K, Zhu Y, Huang Z, Luo Q and
Qing C: Diagnostic value of the lncRNA NEAT1 in peripheral blood
mononuclear cells of patients with sepsis. Dis Markers.
2017(7962836)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Stefani G and Slack FJ: Small non-coding
RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:219–230.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cao X, Zhang C, Zhang X, Chen Y and Zhang
H: miR-145 negatively regulates TGFBR2 signaling responsible for
sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 111:852–858.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ma Y, Liu Y, Hou H, Yao Y and Meng H:
miR-150 predicts survival in patients with sepsis and inhibits
LPS-induced inflammatory factors and apoptosis by targeting NF-κB1
in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 500:828–837. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yao Y, Sun F and Lei M: miR-25 inhibits
sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targetting PTEN. Biosci
Rep. 38(38)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Salem M, O'Brien JA, Bernaudo S, Shawer H,
Ye G, Brkić J, Amleh A, Vanderhyden BC, Refky B, Yang BB, et al:
miR-590-3p promotes ovarian cancer growth and metastasis via a
novel FOXA2-versican pathway. Cancer Res. 78:4175–4190.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Rohini M, Gokulnath M, Miranda PJ and
Selvamurugan N: miR-590-3p inhibits proliferation and promotes
apoptosis by targeting activating transcription factor 3 in human
breast cancer cells. Biochimie. 154:10–18. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Du B, Wang T, Yang X, Wang J, Shi X, Wang
X, Wu D, Feng L, Chen L and Zhang W: SOX9, miR-495, miR-590-3p, and
miR-320d were identified as chemoradiotherapy-sensitive genes and
miRNAs in colorectal cancer patients based on a microarray dataset.
Neoplasma. 66:8–19. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhao S, Yang G, Liu PN, Deng YY, Zhao Z,
Sun T, Zhuo XZ, Liu JH, Tian Y, Zhou J, et al: miR-590-3p Is a
novel microRNA in myocarditis by targeting nuclear factor kappa-b
in vivo. Cardiology. 132:182–188. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhao C, Jiang J, Wang YL and Wu YQ:
Overexpression of microRNA-590-3p promotes the proliferation of and
inhibits the apoptosis of myocardial cells through inhibition of
the NF-κB signaling pathway by binding to RIPK1. J Cell Biochem.
120:3559–3573. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xu L, Wu Q, Zhou X, Wu Q and Fang M:
TRIM13 inhibited cell proliferation and induced cell apoptosis by
regulating NF-κB pathway in non-small-cell lung carcinoma cells.
Gene. 715(144015)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Qi R, Huang J, Wang Q, Liu H, Wang R, Wang
J and Yang F: MicroRNA-224-5p regulates adipocyte apoptosis induced
by TNFα via controlling NF-κB activation. J Cell Physiol.
233:1236–1246. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang H, Li H, Ge A, Guo E, Liu S and
Zhang L: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 inhibits apoptosis and
inflammatory response in LPS-treated H9c2 cells by down-regulation
of miR-29b. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:663–669. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yao Y, Xu K, Sun Y, Tian T, Shen W, Sun F,
Yuan W, Wu H, Chen G, Yuan L, et al: MiR-215-5p inhibits the
inflammation injury in septic H9c2 by regulating ILF3 and LRRFIP1.
Int Immunopharmacol. 78(106000)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Song B, Wang Z, Liu Y, Xu S, Huang G,
Xiong Y, Zhang S, Xu L, Deng X and Guan S: Immunosuppressive
activity of daphnetin, one of coumarin derivatives, is mediated
through suppression of NF-κB and NFAT signaling pathways in mouse T
cells. PLoS One. 9(e96502)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
He PP, Ouyang XP, Tang YY, Liao L, Wang
ZB, Lv YC, Tian GP, Zhao GJ, Huang L, Yao F, et al: MicroRNA-590
attenuates lipid accumulation and pro-inflammatory cytokine
secretion by targeting lipoprotein lipase gene in human THP-1
macrophages. Biochimie. 106:81–90. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li TM, Liu SC, Huang YH, Huang CC, Hsu CJ,
Tsai CH, Wang SW and Tang CH: YKL-40-Induced Inhibition of
miR-590-3p promotes interleukin-18 expression and angiogenesis of
endothelial progenitor cells. Int J Mol Sci. 18(18)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ma J, Li YT, Zhang SX, Fu SZ and Ye XZ:
miR-590-3p attenuates acute kidney injury by inhibiting tumor
necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 in septic mice.
Inflammation. 42:637–649. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Karin M: NF-kappaB as a critical link
between inflammation and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1(a000141)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Rossi MN and Antonangeli F: LncRNAs: New
players in spoptosis control. Int J Cell Biol.
2014(473857)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mirza AH, Berthelsen CH, Seemann SE, Pan
X, Frederiksen KS, Vilien M, Gorodkin J and Pociot F:
Transcriptomic landscape of lncRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease.
Genome Med. 7(39)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Fatica A and Bozzoni I: Long non-coding
RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev
Genet. 15:7–21. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Geng F, Liu W and Yu L: Potential role of
circulating long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in predicting disease risk,
severity, and patients' survival in sepsis. J Clin Lab Anal.
33(e22968)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen Y, Fu Y, Song YF and Li N: Increased
expression of lncRNA UCA1 and HULC is required for pro-inflammatory
response during LPS induced sepsis in endothelial cells. Front
Physiol. 10(608)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|