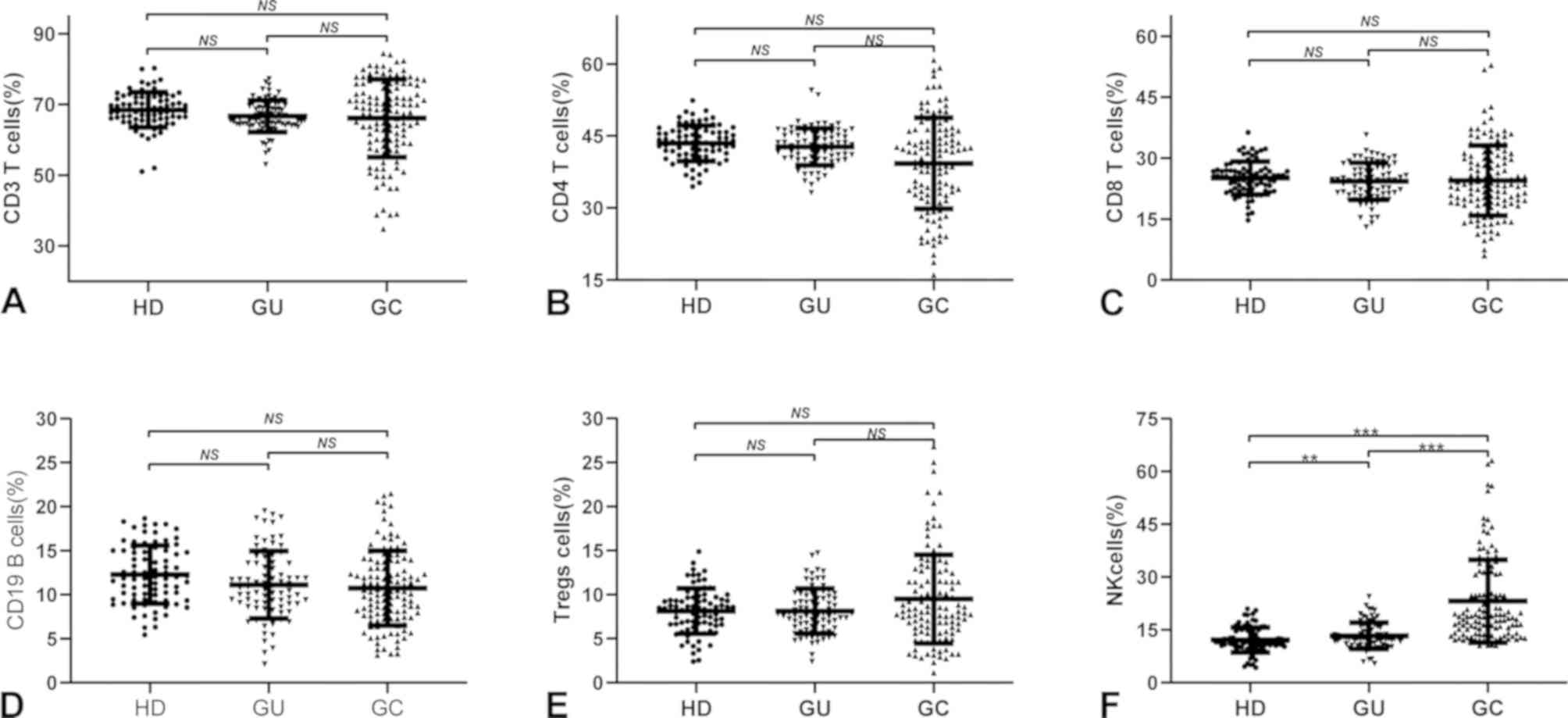
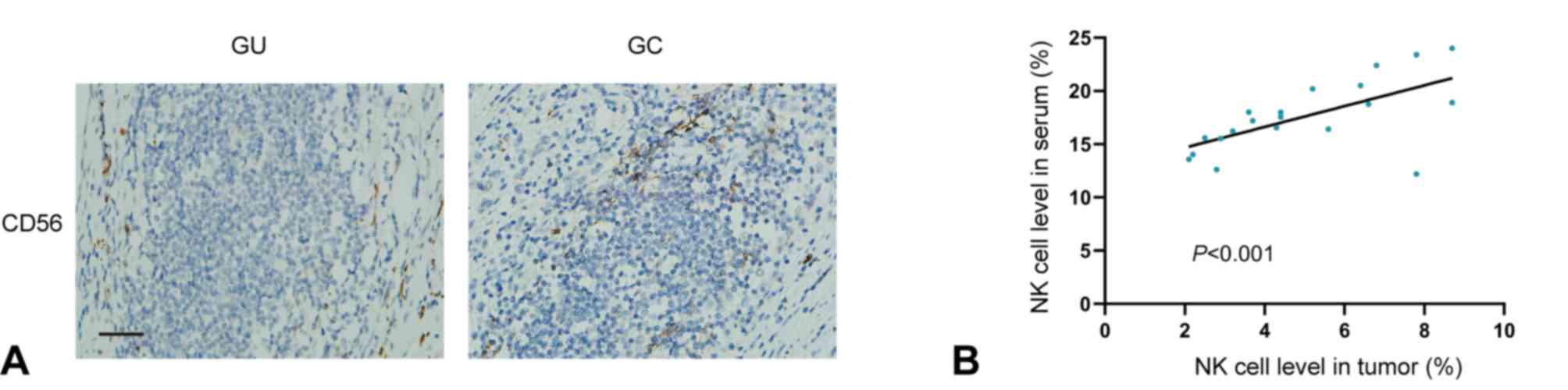
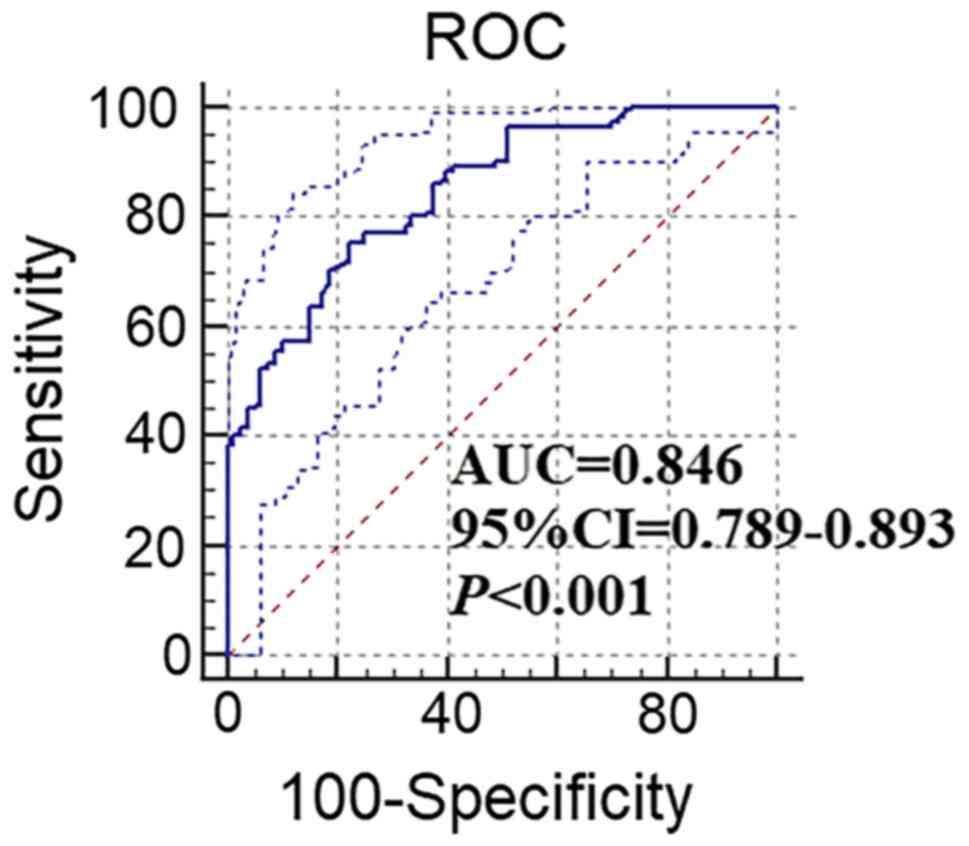
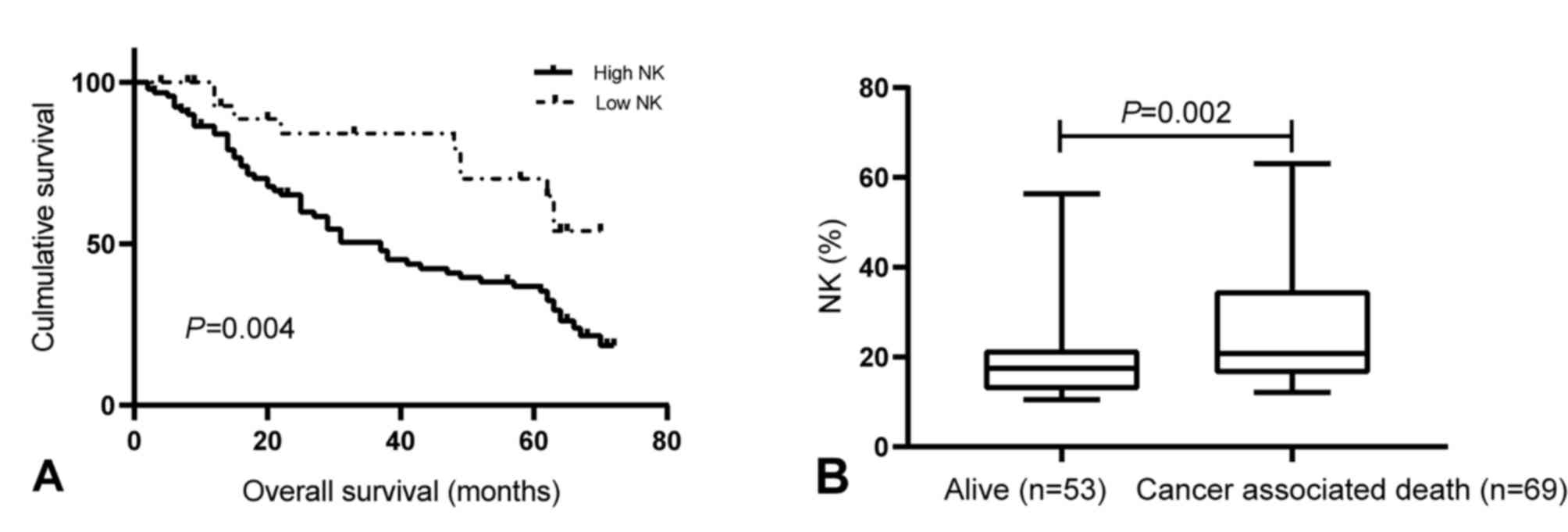
|
1
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang B, Xu D, Yu X, Ding T, Rao H, Zhan Y,
Zheng L and Li L: Association of intra-tumoral infiltrating
macrophages and regulatory T cells is an independent prognostic
factor in gastric cancer after radical resection. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:2585–2593. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chow MT, Möller A and Smyth MJ:
Inflammation and immune surveillance in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
22:23–32. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zarin P, Wong GW, Mohtashami M, Wiest DL
and Zúñiga-Pflücker JC: Enforcement of γδ-lineage commitment by the
pre-T-cell receptor in precursors with weak γδ-TCR signals. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:5658–5663. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Park K, He X, Lee HO, Hua X, Li Y, Wiest D
and Kappes DJ: TCR-mediated ThPOK induction promotes development of
mature (CD24-) gammadelta thymocytes. EMBO J. 29:2329–2341.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bauer S, Groh V, Wu J, Steinle A, Phillips
JH, Lanier LL and Spies T: Pillars article: Activation of NK cells
and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science
1999. 285:727–729, J Immunol 200: 2231-2233. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sardinha LR, Elias RM, Mosca T, Bastos KR,
Marinho CR, D'Império Lima MR and Alvarez JM: Contribution of NK,
NK T, gamma delta T, and alpha beta T cells to the gamma interferon
response required for liver protection against trypanosoma cruzi.
Infect Immun. 74:2031–2042. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xu YF, Lu Y, Cheng H, Shi S, Xu J, Long J,
Liu L, Liu C and Yu X: Abnormal distribution of peripheral
lymphocyte subsets induced by PDAC modulates overall survival.
Pancreatology. 14:295–301. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yu A, Mansure JJ, Solanki S, Siemens DR,
Koti M, Dias ABT, Burnier MM, Brimo F and Kassouf W: Presence of
lymphocytic infiltrate cytotoxic T lymphocyte CD3+, CD8+, and
immunoscore as prognostic marker in patients after radical
cystectomy. PLoS One. 13(e0205746)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Soo RA, Chen Z, Yan Teng RS, Tan HL,
Iacopetta B, Tai BC and Soong R: Prognostic significance of immune
cells in non-small cell lung cancer: meta-analysis. Oncotarget.
9:24801–24820. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zinovkin DA, Pranjol MZI, Bilsky IA and
Zmushko VA: Tumor-associated T-lymphocytes and macrophages are
decreased in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma with MELF-pattern
stromal changes. Cancer Microenviron. 11:107–114. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hagland HR, Lea D, Watson MM and Søreide
K: Correlation of blood T-cells to intratumoural density and
location of CD3+ and CD8+ T-cells in colorectal cancer. Anticancer
Res. 37:675–683. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang K, Shen T, Siegal GP and Wei S: The
CD4/CD8 ratio of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes at the tumor-host
interface has prognostic value in triple-negative breast cancer.
Hum Pathol. 69:110–117. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shah W, Yan X, Jing L, Zhou Y, Chen H and
Wang Y: A reversed CD4/CD8 ratio of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
and a high percentage of CD4(+)FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells are
significantly associated with clinical outcome in squamous cell
carcinoma of the cervix. Cell Mol Immunol. 8:59–66. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yasutomo K: The cellular and molecular
mechanism of CD4/CD8 lineage commitment. J Med Invest. 49:1–6.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hald SM, Bremnes RM, Al-Shibli K, Al-Saad
S, Andersen S, Stenvold H, Busund LT and Donnem T: CD4/CD8
co-expression shows independent prognostic impact in resected
non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with adjuvant
radiotherapy. Lung Cancer. 80:209–215. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xu T, Huang Z, Su B, Wang S, Wang D, Wang
C, Wei W, Jiang J, Zhang G, Yang H and Hu W: Prognostic
significance of circulating CD19+ B lymphocytes in EBV-associated
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Med Oncol. 31(198)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nabeki B, Ishigami S, Uchikado Y, Sasaki
K, Kita Y, Okumura H, Arigami T, Kijima Y, Kurahara H, Maemura K
and Natsugoe S: Interleukin-32 expression and Treg infiltration in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 35:2941–2947.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Salama P, Phillips M, Grieu F, Morris M,
Zeps N, Joseph D, Platell C and Iacopetta B: Tumor-infiltrating
FOXP3+ T regulatory cells show strong prognostic significance in
colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:186–192. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xu B, Chen L, Li J, Zheng X, Shi L, Wu C
and Jiang J: Prognostic value of tumor infiltrating NK cells and
macrophages in stage II+III esophageal cancer patients. Oncotarget.
7:74904–74916. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Karakhanova S, Ryschich E, Mosl B, Harig
S, Jäger D, Schmidt J, Hartwig W, Werner J and Bazhin AV:
Prognostic and predictive value of immunological parameters for
chemoradioimmunotherapy in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Br J Cancer. 112:1027–1036. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Maruyama T, Kono K, Mizukami Y, Kawaguchi
Y, Mimura K, Watanabe M, Izawa S and Fujii H: Distribution of Th17
cells and FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells in tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes, tumor-draining lymph nodes and peripheral blood
lymphocytes in patients with gastric cancer. Cancer Sci.
101:1947–1954. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Isobe Y, Nashimoto A, Akazawa K, Oda I,
Hayashi K, Miyashiro I, Katai H, Tsujitani S, Kodera Y, Seto Y and
Kaminishi M: Gastric cancer treatment in Japan: 2008 Annual report
of the JGCA nationwide registry. Gastric Cancer. 14:301–316.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ning S, Wei W, Li J, Hou B, Zhong J, Xie
Y, Liu H, Mo X, Chen J and Zhang L: Clinical significance and
diagnostic capacity of serum TK1, CEA, CA 19-9 and CA 72-4 levels
in gastric and colorectal cancer patients. J Cancer. 9:494–501.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Feng F, Tian Y, Xu G, Liu Z, Liu S, Zheng
G, Guo M, Lian X, Fan D and Zhang H: Diagnostic and prognostic
value of CEA, CA19-9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer. BMC
Cancer. 17(737)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shen M, Wang H, Wei K, Zhang J and You C:
Five common tumor biomarkers and CEA for diagnosing early gastric
cancer: A protocol for a network meta-analysis of diagnostic test
accuracy. Medicine (Baltimore). 97(e0577)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yoon JH, Park YG, Nam SW and Park WS: The
diagnostic value of serum gastrokine 1 (GKN1) protein in gastric
cancer. Cancer Med. 8:5507–5514. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lu J, Zhang PY, Xie JW, Wang JB, Lin JX,
Chen QY, Cao LL, Huang CM, Li P and Zheng CH: Hsa_circ_0000467
promotes cancer progression and serves as a diagnostic and
prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer. J Clin Lab Anal.
33(e22726)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xue WJ, Feng Y, Wang F, Li P, Liu YF, Guo
YB, Wang ZW and Mao QS: The value of serum RASSF10 hypermethylation
as a diagnostic and prognostic tool for gastric cancer. Tumour
Biol. 37:11249–11257. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Abbaszadegan MR, Taghehchian N, Aarabi A
and Moghbeli M: MAEL Cancer-testis antigen as a diagnostic marker
in primary stages of gastric cancer with Helicobacter pylori
infection. J Gastrointest Cancer. 51:17–22. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kouzu K, Tsujimoto H, Hiraki S, Nomura S,
Yamamoto J and Ueno H: Diagnostic accuracy of T stage of gastric
cancer from the view point of application of laparoscopic proximal
gastrectomy. Mol Clin Oncol. 8:773–778. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Deng J, Liu J, Wang W, Sun Z, Wang Z, Zhou
Z, Xu H and Liang H: Validation of clinical significance of
examined lymph node count for accurate prognostic evaluation of
gastric cancer for the eighth edition of the American joint
committee on cancer (AJCC) TNM staging system. Chin J Cancer Res.
30:477–491. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wei J, Yao T, Wang Y, Li L, Pan C and
Zhang N: Prognostic analysis of stage III gastric cancer after
curative surgery according to the newest TNM classification. Clin
Transl Oncol. 21:232–238. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xu TP, Wang WY, Ma P, Shuai Y, Zhao K,
Wang YF, Li W, Xia R, Chen WM, Zhang EB and Shu YQ: Upregulation of
the long noncoding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes carcinogenesis by
epigenetically silencing EphB3 through EZH2 and LSD1, and predicts
poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Oncogene. 37:5020–5036.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Moghbeli M, Makhdoumi Y, Soltani Delgosha
M, Aarabi A, Dadkhah E, Memar B, Abdollahi A and Abbaszadegan MR:
ErbB1 and ErbB3 co-over expression as a prognostic factor in
gastric cancer. Biol Res. 52(2)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ji B, Huang Y, Gu T, Zhang L, Li G and
Zhang C: Potential diagnostic and prognostic value of plasma long
noncoding RNA LINC00086 and miR-214 expression in gastric cancer.
Cancer Biomark. 24:249–255. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|