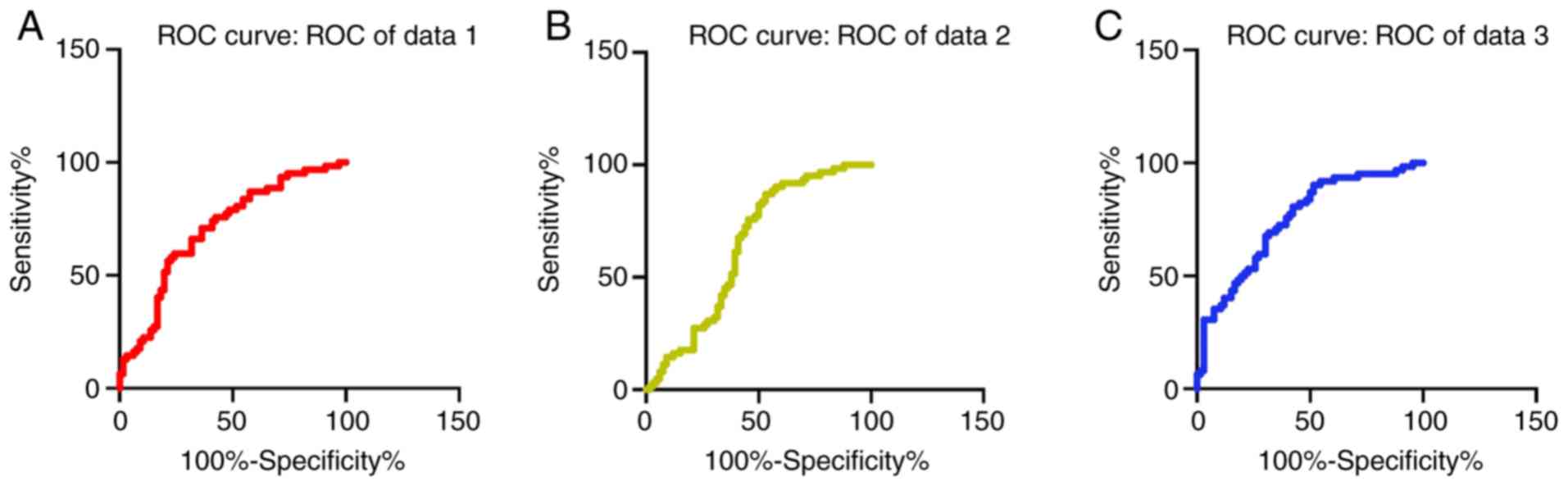
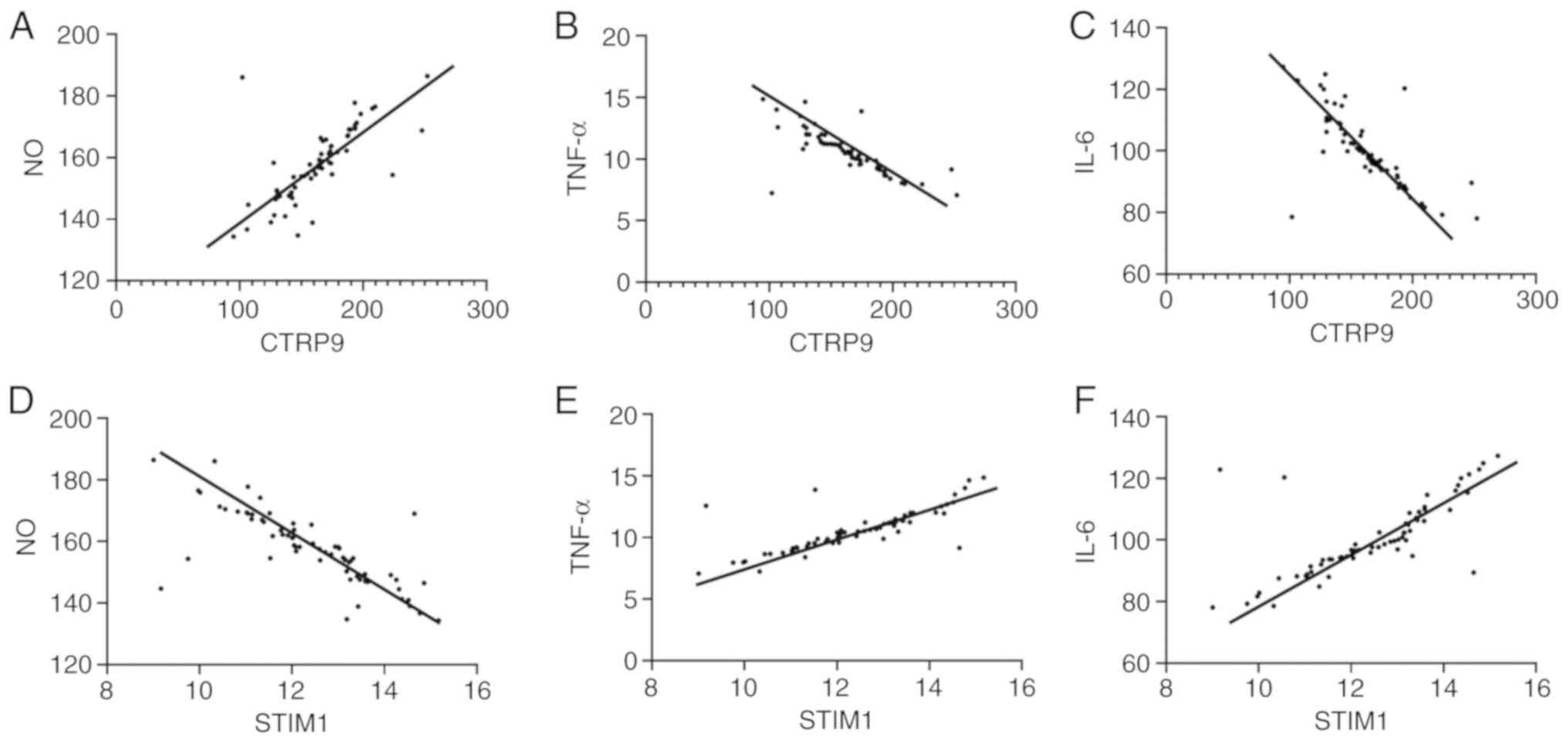
|
1
|
Losito A, Pittavini L, Ferri C and De
Angelis L: Kidney function and mortality in different
cardiovascular diseases: Relationship with age, sex, diabetes and
hypertension. J Nephrol. 24:322–328. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sairanen T, Strbian D, Ruuskanen R,
Silvennoinen H, Salonen O and Lindsberg PJ: Symptomatic
intracranial haemorrhage after thrombolysis with adjuvant
anticoagulation in basilar artery occlusion. Eur J Neurol.
22:493–499. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mintz GS: Intravascular ultrasound and
outcomes after drug- eluting stent implantation. Coron Artery Dis.
28:346–352. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Guan CL, Shi GX, Li Q, Luo YM and Zeng YC:
Prevention of complications following cerebrovascular stent
implantation. J Clin Rehab Tissue Eng Res. 2 (Suppl)(S52)2010.
|
|
5
|
Dinesch V, Dinesch M and Buruian M:
Drug-eluting stent in-stent restenosis and re-restenosis: A hard
time story. J Saudi Heart Assoc. 29:73–74. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ and Walsh K:
Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:85–97. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lago F, Dieguez C, Gómez-Reino J and
Gualillo O: Adipokines as emerging mediators of immune response and
inflammation. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 3:716–724. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Smith CC and Yellon DM: Adipocytokines,
cardiovascular pathophysiology and myocardial protection. Pharmacol
Ther. 129:206–219. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Schäffler A and Buechler C: CTRP family:
Linking immunity to metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
23:194–204. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wong GW, Krawczyk SA, Kitidis-Mitrokostas
C, Ge G, Spooner E, Hug C, Gimeno R and Lodish HF: Identification
and characterization of CTRP9, a novel secreted glycoprotein, from
adipose tissue that reduces serum glucose in mice and forms
heterotrimers with adiponectin. FASEB J. 23:241–258.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liou J, Fivaz M, Inoue T and Meyer T:
Live-cell imaging reveals sequential oligomerization and local
plasma membrane targeting of stromal interaction molecule 1 after
Ca2+ store depletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:9301–9306. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Estrada IA, Donthamsetty R, Debski P, Zhou
MH, Zhang SL, Yuan JX, Han W and Makino A: STIM1 restores coronary
endothelial function in type 1 diabetic mice. Circ Res.
111:1166–1175. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Edgell RC, Zaidat OO, Gupta R, Abou-Chebl
A, Linfante I, Xavier A, Nogueira R, Alshekhlee A, Kalia J, Etezadi
V, et al: Multicenter study of safety in stenting for symptomatic
vertebral artery origin stenosis: Results from the Society of
Vascular and Interventional Neurology Research Consortium. J
Neuroimaging. 23:170–174. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Albuquerque FC, Fiorella D, Han P,
Spetzler RF and Mc Dougall CG: A reappraisal of angioplasty and
stenting for the treatment of vertebral origin stenosis.
Neurosurgery. 53:607–616. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kang SJ, Mintz GS, Park DW, Lee SW, Kim
YH, Lee CW, Han KH, Kim JJ, Park SW and Park SJ: Mechanisms of
in-stent restenosis after drug-eluting stent implantation:
Intravascular ultrasound analysis. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 4:9–14.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Virmani R, Liistro F, Stankovic G, Di
Mario C, Montorfano M, Farb A, Kolodgie FD and Colombo A: Mechanism
of late in-stent restenosis after implantation of a paclitaxel
derivate-eluting polymer stent system in humans. Circulation.
106:2649–2651. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Peel SE, Liu B and Hall IP: A key role for
STIM1 in store operated calcium channel activation in airway smooth
muscle. Respir Res. 7(119)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zheng Q, Yuan Y, Yi W, Lau WB, Wang Y,
Wang X, Sun Y, Lopez BL, Christopher TA, Peterson JM, et al:
Clq/TNF-related proteins, a family of novel adipokines, induce
vascular relaxation through the adiponectin receptor-1/AMPK/e
NOS/nitric oxide signaling pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
31:2616–2623. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Takeuchi S, Wada K, Uozumi Y, Otani N,
Osada H, Nagatani K and Mori K: Adiponectin receptor 1 expression
is associated with carotid plaque stability. Neurol India.
61:249–253. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jing XD, Wei XM, Deng SB, Du JL, Liu YJ
and She Q: The relationship between the high-density lipoprotein
(HDL)-associated sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) and coronary
in-stent restenosis. Clin Chim Acta. 15:248–252. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kambara T, Ohashi K, Shibata R, Ogura Y,
Maruyama S, Enomoto T, Uemura Y, Shimizu Y, Yuasa D, Matsuo K, et
al: CTRP9 protein protects against myocardial injury following
ischemia-reperfusion through AMP-activated protein kinase
(AMPK)-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 287:18965–18973.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Elnaggar MA, Seo SH, Gobaa S, Lim KS, Bae
IH, Jeong MH, Han DK and Joung YK: Nitric oxide releasing coronary
stent: A new approach using layer-by-layer coating and liposomal
encapsulation. Small. 12:6012–6023. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhang H, Park Y, Wu J, Chen XP, Lee S,
Yang J, Dellsperger KC and Zhang C: Role of TNF-alpha in vascular
dysfunction. Clin Sci (Lond). 116:219–230. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Picchi A, Gao X, Belmadani S, Potter BJ,
Focardi M, Chilian WM and Zhang C: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
induces endothelial dysfunction in Lepr (dp) mice. Circulation.
115:245–254. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Booth AJ, Csencsits-Smith K, Wood SC, Lu
G, Lipson KE and Bishop DK: Connective tissue growth factor
promotes fibrosis downstream of TGFbeta and IL-6 in chronic cardiac
allograft rejection. Am J Transplant. 10:220–230. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|