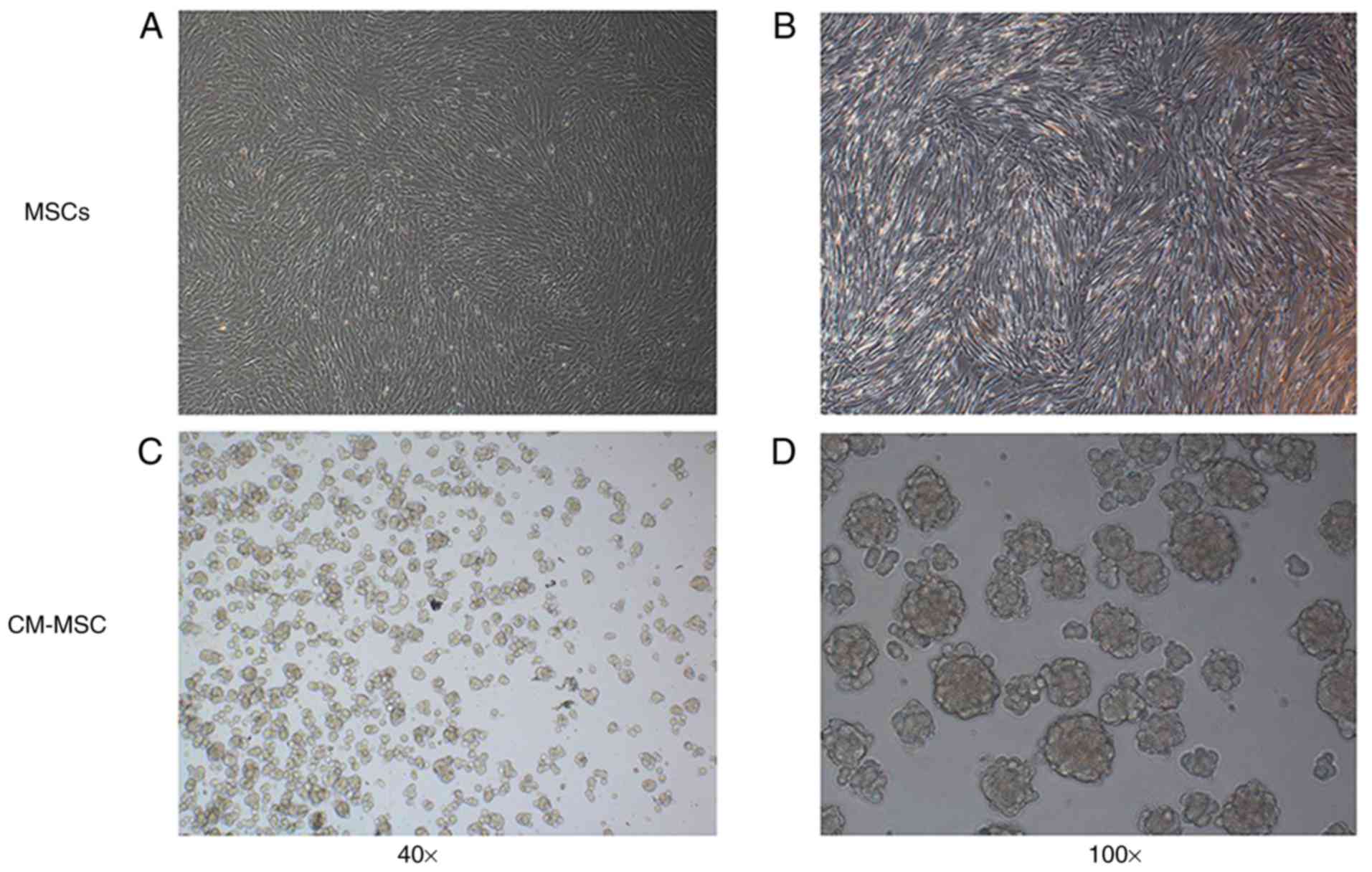
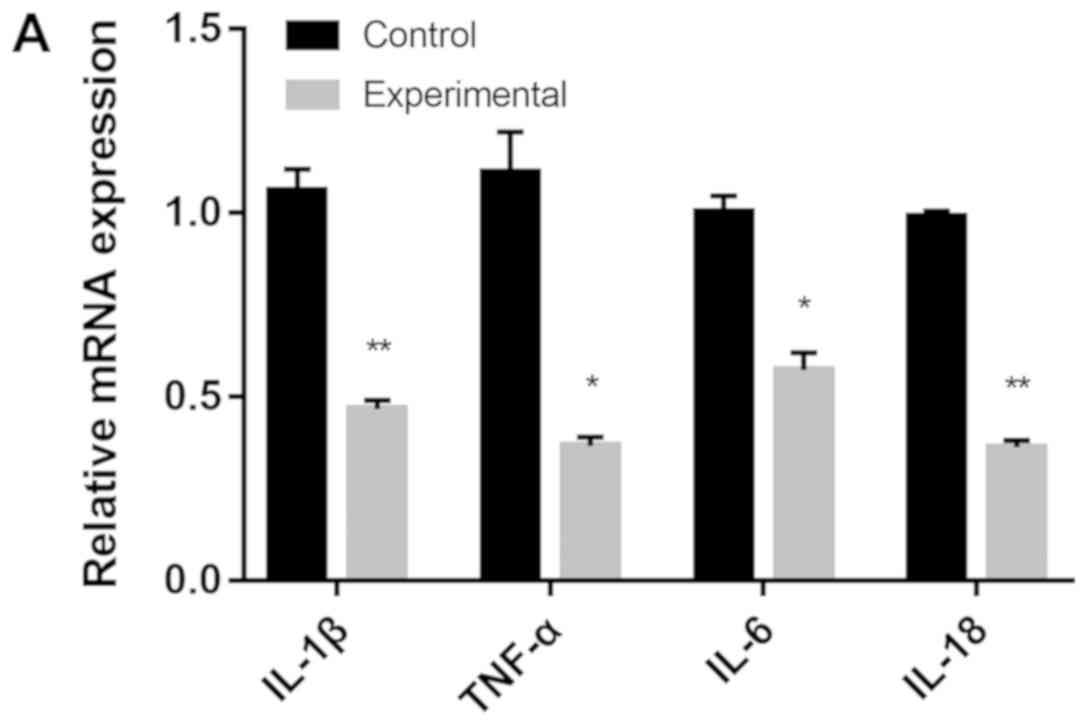
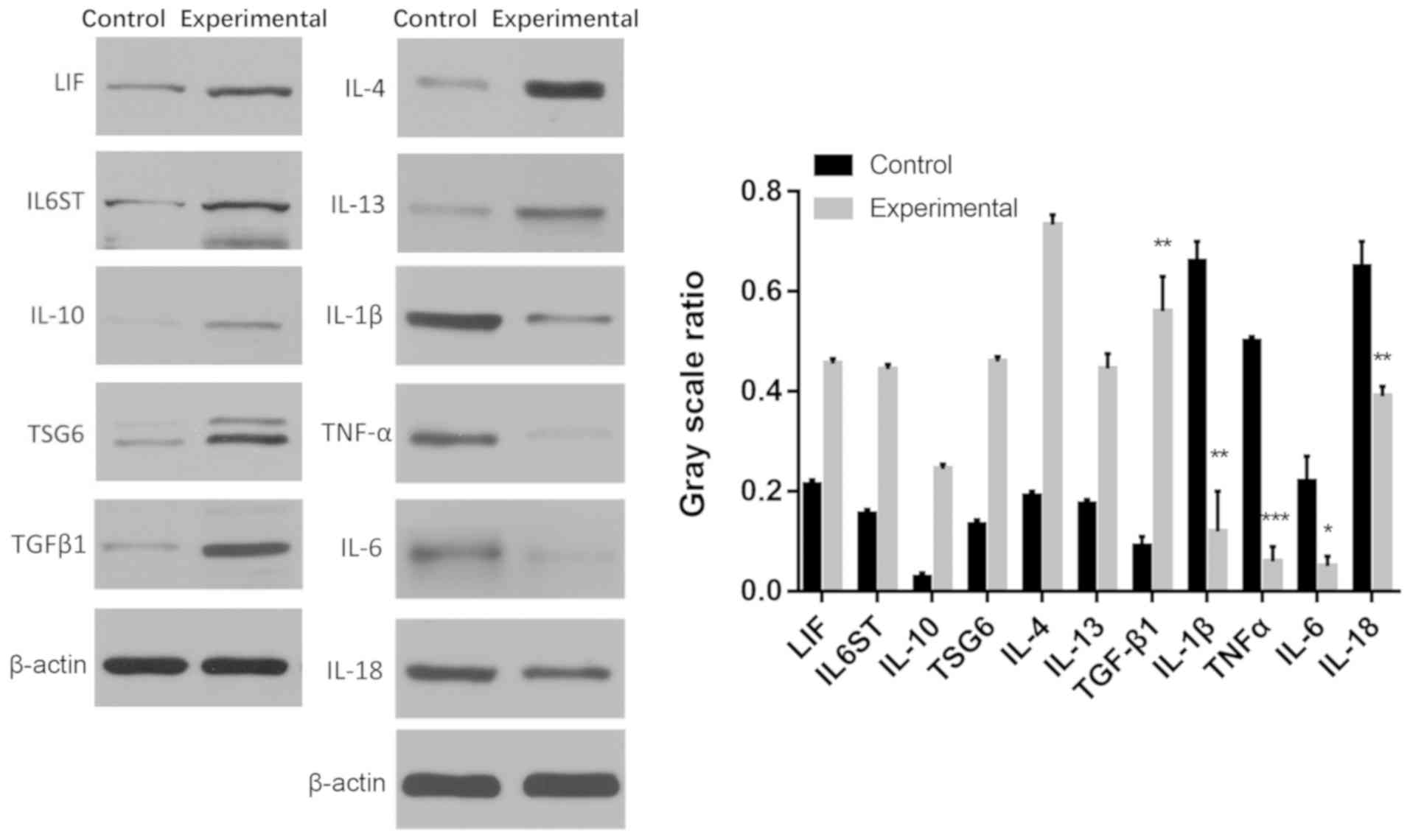
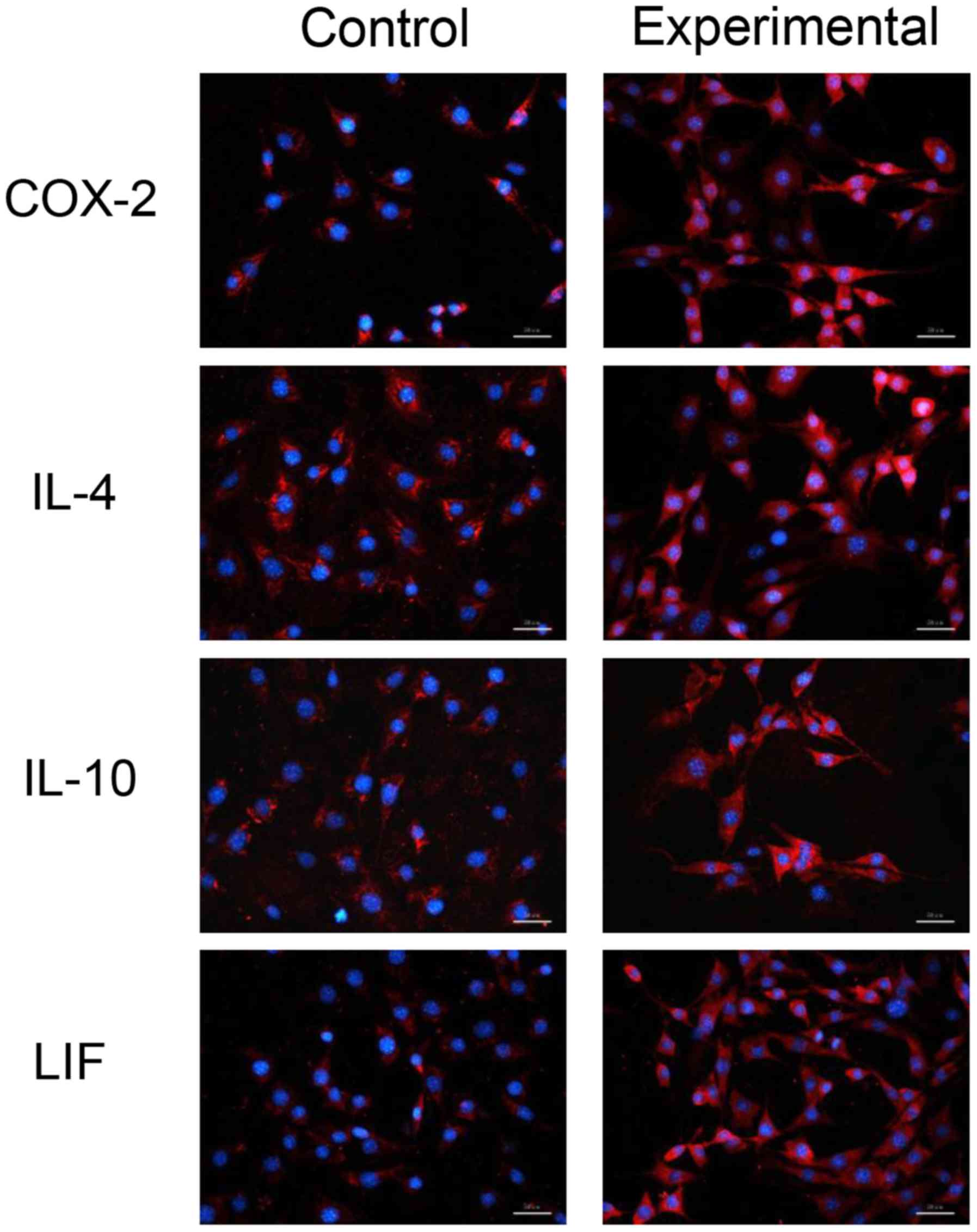
|
1
|
Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, Price
AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H and Carr AJ: Osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis Lancet. 386:376–387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Charlier E, Deroyer C, Ciregia F, Malaise
O, Neuville S, Plener Z, Malaise M and de Seny D: Chondrocyte
dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Biochem Pharmacol.
165:49–65. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski LA and
Szukiewicz D: The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory
cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm.
2014(561459)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vangsness CT Jr, Burke WS, Narvy SJ,
MacPhee RD and Fedenko AN: Human knee synovial fluid cytokines
correlated with grade of knee osteoarthritis - a pilot study. Bull
NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 69:122–127. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mueller MB and Tuan RS: Anabolic/Catabolic
balance in pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Identifying molecular
targets. PM R. 3 (Suppl 1):S3–S11. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Aboushady IM, Salem ZA, Sabry D and
Mohamed A: Comparative study of the osteogenic potential of
mesenchymal stem cells derived from different sources. J Clin Exp
Dent. 10:e7–e13. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gao W, Lin M, Liang A, Zhang L, Chen C,
Liang G, Xu C, Peng Y, Chen C, Huang D, et al: Melatonin enhances
chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J
Pineal Res. 56:62–70. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Du Z, Wei C, Cheng K, Han B, Yan J, Zhang
M, Peng C and Liu Y: Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium
reduces liver injury and enhances regeneration in reduced-size rat
liver transplantation. J Surg Res. 183:907–915. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Delling U, Brehm W, Ludewig E, Winter K
and Jülke H: Longitudinal evaluation of effects of intra-articular
mesenchymal stromal cell administration for the treatment of
osteoarthritis in an ovine model. Cell Transplant. 24:2391–2407.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Saulnier N, Viguier E, Perrier-Groult E,
Chenu C, Pillet E, Roger T, Maddens S and Boulocher C:
Intra-articular administration of xenogeneic neonatal Mesenchymal
Stromal Cells early after meniscal injury down-regulates
metalloproteinase gene expression in synovium and prevents
cartilage degradation in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:122–133. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sun Y, Wang Y, Zhou L, Zou Y, Huang G, Gao
G, Ting S, Lei X and Ding X: Spheroid-cultured human umbilical
cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Sci Rep.
8(2518)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bartosh TJ, Ylöstalo JH, Mohammadipoor A,
Bazhanov N, Coble K, Claypool K, Lee RH, Choi H and Prockop DJ:
Aggregation of human mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) into 3D
spheroids enhances their antiinflammatory properties. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 107:13724–13729. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yeh HY, Liu BH, Sieber M and Hsu SH:
Substrate-dependent gene regulation of self-assembled human MSC
spheroids on chitosan membranes. BMC Genomics.
15(10)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Huang GS, Dai LG, Yen BL and Hsu SH:
Spheroid formation of mesenchymal stem cells on chitosan and
chitosan-hyaluronan membranes. Biomaterials. 32:6929–6945.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Shen S, Guo J, Luo Y, Zhang W, Cui Y, Wang
Q, Zhang Z and Wang T: Functional proteomics revealed IL-1β
amplifies TNF downstream protein signals in human synoviocytes in a
TNF-independent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:538–544.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ismail HM, Yamamoto K, Vincent TL, Nagase
h, Troeberg L and Saklatvala J: Interleukin-1 Acts via the JNK-2
Signaling Pathway to Induce Aggrecan Degradation by Human
Chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67:1826–1836. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Osta B, Roux JP, Lavocat F, Pierre M,
Ndongo-Thiam N, Boivin G and Miossec P: Differential Effects of
IL-17A and TNF-α on Osteoblastic Differentiation of Isolated
Synoviocytes and on Bone Explants from Arthritis Patients. Front
Immunol. 6(151)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lawrence JT, Birmingham J and Toth AP:
Emerging ideas: Prevention of posttraumatic arthritis through
interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibition. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 469:3522–3526. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Furman BD, Mangiapani DS, Zeitler E,
Bailey KN, Horne PH, Huebner JL, Kraus VB, Guilak F and Olson SA:
Targeting pro-inflammatory cytokines following joint injury: Acute
intra-articular inhibition of interleukin-1 following knee injury
prevents post-traumatic arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
16(R134)2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mobasheri A, Henrotin Y, Biesalski HK and
Shakibaei M: Scientific evidence and rationale for the development
of curcumin and resveratrol as nutraceutricals for joint health.
Int J Mol Sci. 13:4202–4232. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang T and He C: Pro-inflammatory
cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 44:38–50. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Assirelli E, Pulsatelli L, Dolzani P,
Platano D, Olivotto E, Filardo G, Trisolino G, Facchini A, Borzì RM
and Meliconi R: Human osteoarthritic cartilage shows reduced in
vivo expression of IL-4, a chondroprotective cytokine that
differentially modulates IL-1β-stimulated production of chemokines
and matrix-degrading enzymes in vitro. PLoS One.
9(e96925)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Uchimura T, Foote AT, Smith EL, Matzkin EG
and Zeng L: Insulin-Like Growth Factor II (IGF-II) Inhibits
IL-1β-Induced Cartilage Matrix Loss and Promotes Cartilage
Integrity in Experimental Osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem.
116:2858–2869. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Fytili P, Giannatou E, Karachalios T,
Malizos K and Tsezou A: Interleukin-10G and interleukin-10R
microsatellite polymorphisms and osteoarthritis of the knee. Clin
Exp Rheumatol. 23:621–627. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Coricor G and Serra R: TGF-β regulates
phosphorylation and stabilization of Sox9 protein in chondrocytes
through p38 and Smad dependent mechanisms. Sci Rep.
6(38616)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Huang W, Mabrouk ME, Sylvester J, Dehnade
F and Zafarullah M: Enhanced expression of tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases-4 gene in human osteoarthritic synovial
membranes and its differential regulation by cytokines in
chondrocytes. Open Rheumatol J. 5:81–87. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang X, Dong C, Li N, Ma Q, Yun Z, Cai C,
An M and Ma B: Modulation of TGF β activity by latent TGF β binding
protein 1 in human osteoarthritis fibroblast like synoviocytes. Mol
Med Rep. 17:1893–1900. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mueller MB, Fischer M, Zellner J, Berner
A, Dienstknecht T, Prantl L, Kujat R, Nerlich M, Tuan RS and Angele
P: Hypertrophy in mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis: Effect of
TGF-beta isoforms and chondrogenic conditioning. Cells Tissues
Organs. 192:158–166. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Spees JL, Lee RH and Gregory CA:
Mechanisms of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell function. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 7(125)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang S, Tong M, Hu S and Chen X: The
Bioactive Substance Secreted by MSC Retards Mouse Aortic Vascular
Smooth Muscle Cells Calcification. BioMed Res Int.
2018(6053567)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ichiseki T, Shimasaki M, Ueda Y, Ueda S,
Tsuchiya M, Souma D, Kaneuji A and Kawahara N:
Intraarticularly-Injected Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulate
Anti-Inflammatory Molecules and Inhibit Pain Related Protein and
Chondrolytic Enzymes in a Monoiodoacetate-Induced Rat Arthritis
Model. Int J Mol Sci. 19(203)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Emadedin M, Ghorbani Liastani M, Fazeli R,
Mohseni F, Moghadasali R, Mardpour S, Hosseini SE, Niknejadi M,
Moeininia F, Aghahossein Fanni A, et al: Long-Term Follow-up of
Intra-articular Injection of Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cells in
Patients with Knee, Ankle, or Hip Osteoarthritis. Arch Iran Med.
18:336–344. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Chen B, Yan F and Yang W: The
Influence of Inflammatory Cytokines on the Proliferation and
Osteoblastic Differentiation of MSCs. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.
12:401–408. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mehta G, Hsiao AY, Ingram M, Luker GD and
Takayama S: Opportunities and challenges for use of tumor spheroids
as models to test drug delivery and efficacy. J Control Release.
164:192–204. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Huang BW and Gao JQ: Application of 3D
cultured multicellular spheroid tumor models in tumor-targeted drug
delivery system research. J Control Release. 270:246–259.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Xu Y, Shi T, Xu A and Zhang L: 3D spheroid
culture enhances survival and therapeutic capacities of MSCs
injected into ischemic kidney. J Cell Mol Med. 20:1203–1213.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ahsan SM, Thomas M, Reddy KK, Sooraparaju
SG, Asthana A and Bhatnagar I: Chitosan as biomaterial in drug
delivery and tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 110:97–109.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Cheng NC, Wang S and Young TH: The
influence of spheroid formation of human adipose-derived stem cells
on chitosan films on stemness and differentiation capabilities.
Biomaterials. 33:1748–1758. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hsu SH, Huang GS and Feng F: Isolation of
the multipotent MSC subpopulation from human gingival fibroblasts
by culturing on chitosan membranes. Biomaterials. 33:2642–2655.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yeh HY, Liu BH and Hsu SH: The
calcium-dependent regulation of spheroid formation and
cardiomyogenic differentiation for MSCs on chitosan membranes.
Biomaterials. 33:8943–8954. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|