|
1
|
Sun HJ, Wu ZY, Cao L, Zhu MY, Liu TT, Guo
L, Lin Y, Nie XW and Bian JS: Hydrogen Sulfide: Recent progression
and perspectives for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy.
Molecules. 24(2857)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, Brophy M,
Conner TA, Duckworth W, Leehey DJ, McCullough PA, O'Connor T,
Palevsky PM, et al: Combined angiotensin inhibition for the
treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 369:1892–1903.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang P, Sun Y, Peng R, Chen W, Fu X,
Zhang L, Peng H and Zhang Z: Long non-coding RNA Rpph1 promotes
inflammation and proliferation of mesangial cells in diabetic
nephropathy via an interaction with Gal-3. Cell Death Dis.
10(526)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Reichelt-Wurm S, Wirtz T, Chittka D,
Lindenmeyer M, Reichelt RM, Beck S, Politis P, Charonis A, Kretz M,
Huber TB, et al: Glomerular expression pattern of long non-coding
RNAs in the type 2 diabetes mellitus BTBR mouse model. Sci Rep.
9(9765)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Moran I, Akerman I, van de Bunt M, Xie R,
Benazra M, Nammo T, Arnes L, Nakić N, García-Hurtado J,
Rodríguez-Seguí S, et al: Human β cell transcriptome analysis
uncovers lncRNAs that are tissue-specific, dynamically regulated,
and abnormally expressed in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab.
16:435–448. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zha F, Qu X, Tang B, Li J, Wang Y, Zheng
P, Ji T, Zhu C and Bai S: Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes
fibrosis and inflammatory response in diabetic nephropathy via
miR-181a/Egr-1/TLR4 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 11:3716–3730.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang S, Chen X, Wang M, Yao D, Chen T, Yan
Q and Lu W: Long non-coding RNA CYP4B1-PS1-001 inhibits
proliferation and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by interacting
with nucleolin. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:2174–2187. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
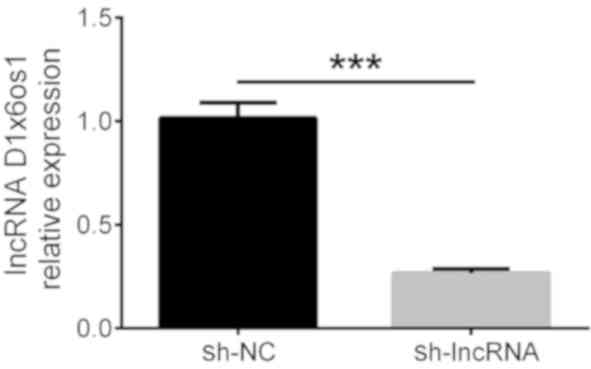
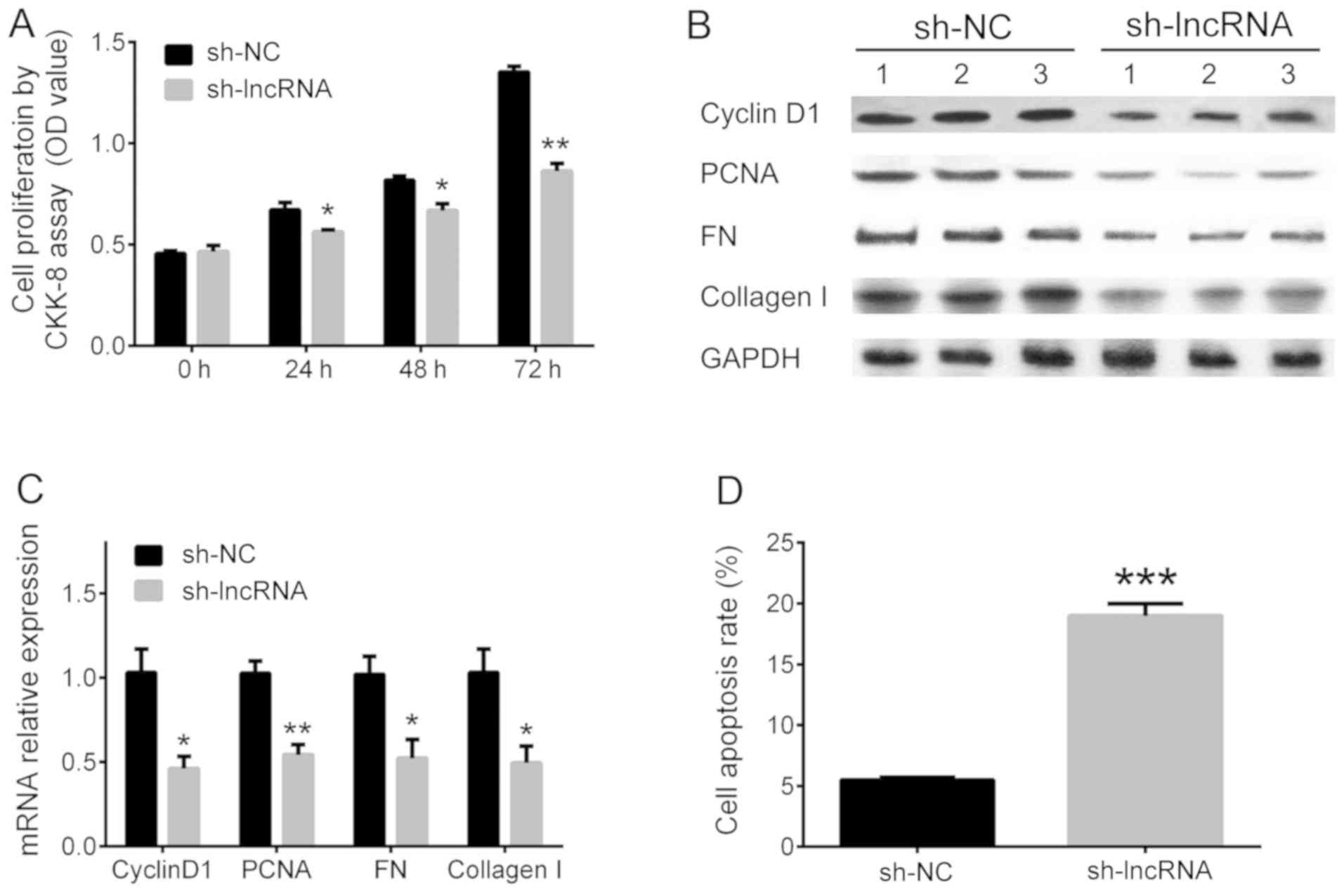
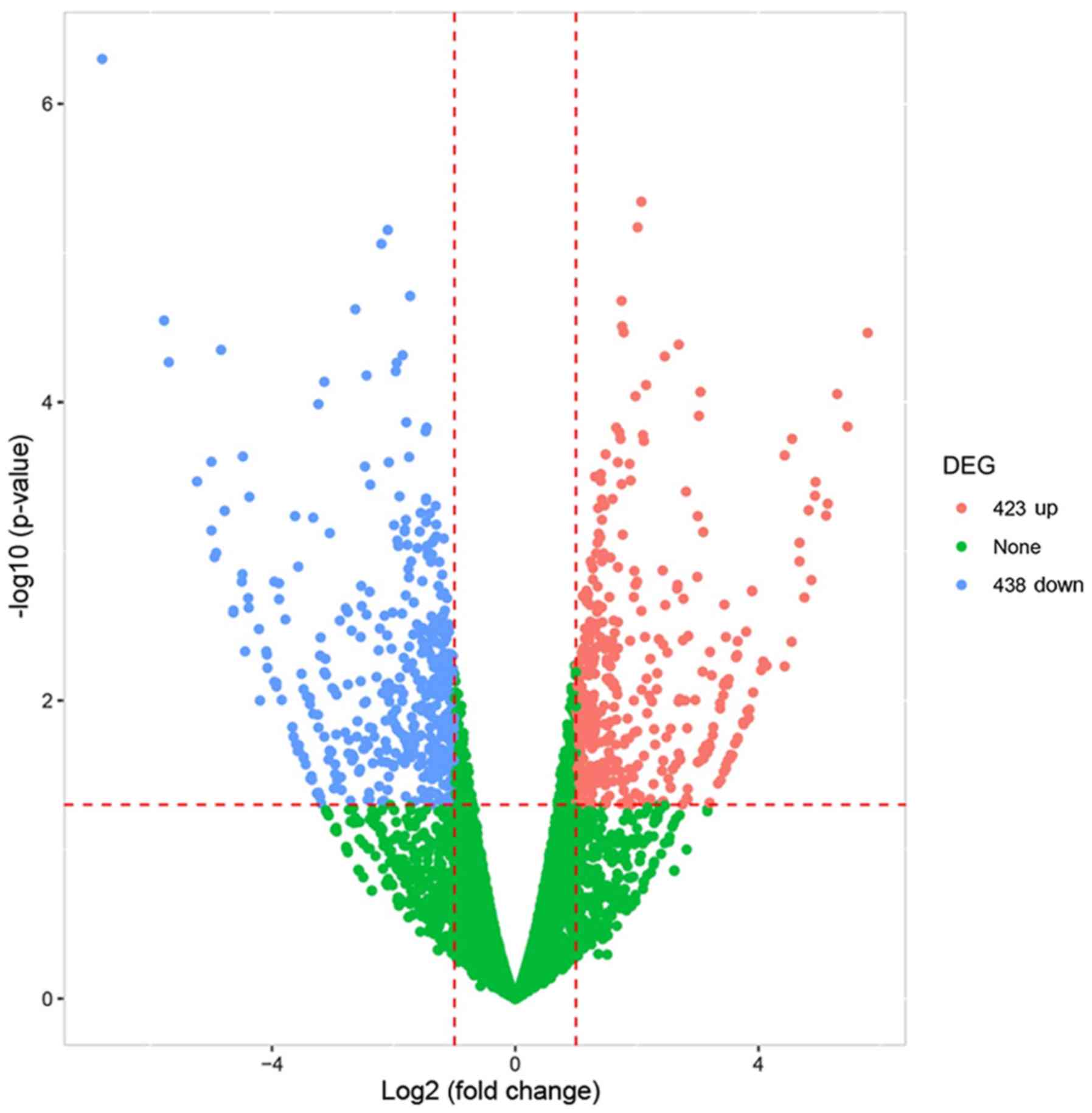
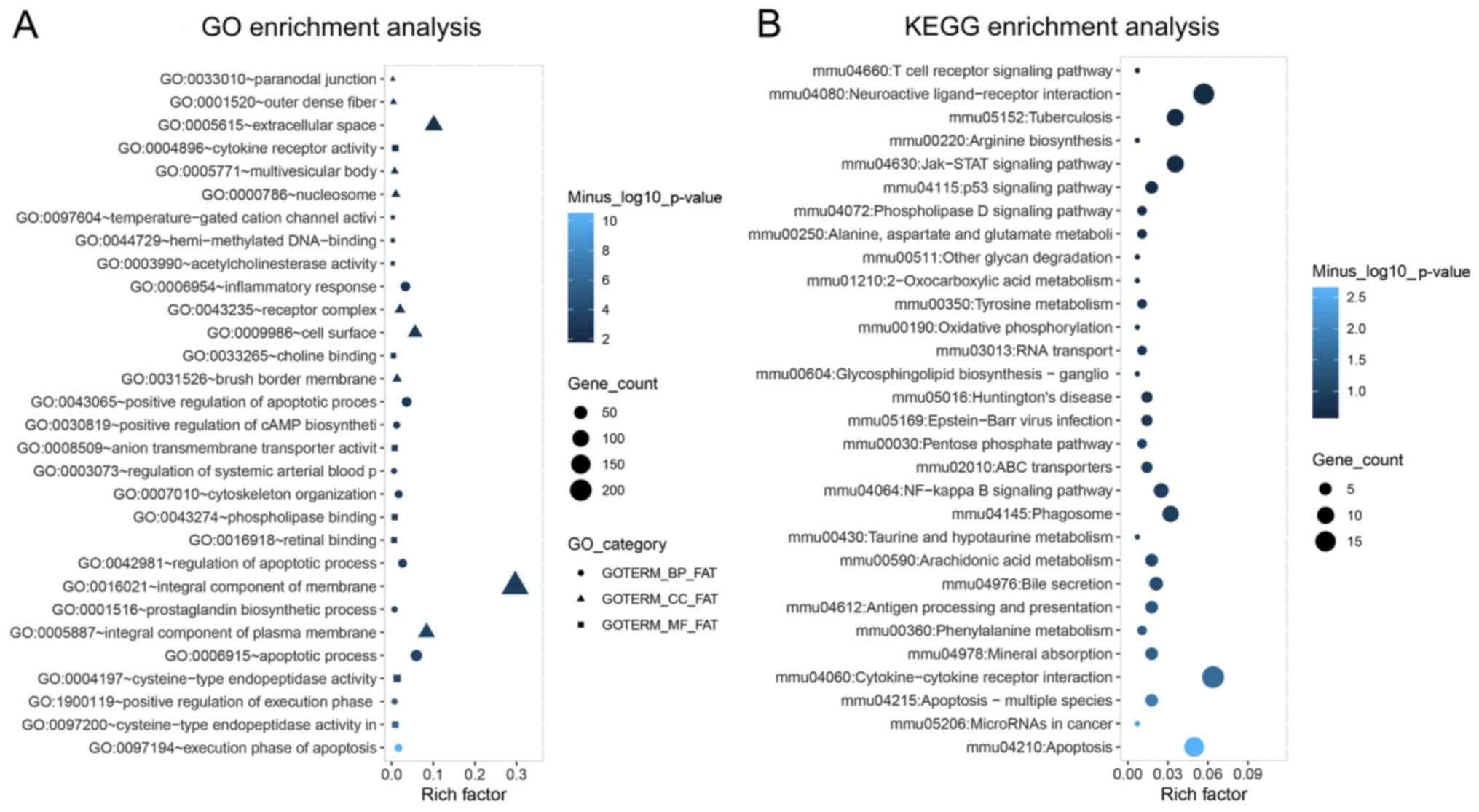
Cheng J, Cheng L, Tang Y, Li H, Peng W and
Huang S: Inhibition of lncRNA Dlx6os1 decreases cell proliferation
and fibrosis and increases cell apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 11:3302–3309. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim D, Paggi JM, Park C, Bennett C and
Salzberg SL: Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with
HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat Biotechnol. 37:907–915.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
The R Foundation for Statistical
Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL http://www.R-project.org.
|
|
11
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zheng M, Lv LL, Cao YH, Liu H, Ni J, Dai
HY, Liu D, Lei XD and Liu BC: A pilot trial assessing urinary gene
expression profiling with an mRNA array for diabetic nephropathy.
PLoS One. 7(e34824)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Barutta F, Bruno G, Grimaldi S and Gruden
G: Inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: Moving toward clinical
biomarkers and targets for treatment. Endocrine. 48:730–742.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Duran-Salgado MB and Rubio-Guerra AF:
Diabetic nephropathy and inflammation. World J Diabetes. 5:393–398.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gao L, Sun N, Xu Q, Jiang Z and Li C:
Comparative analysis of mRNA expression profiles in type 1 and type
2 diabetes mellitus. Epigenomics. 11:685–699. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yi W and OuYang Q: Adiponectin improves
diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting necrotic apoptosis. Arch Med
Sci. 15:1321–1328. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang T, Gao Y, Wang X, Shi Y, Xu J, Wu B,
He J and Li Y: Calpain-10 drives podocyte apoptosis and renal
injury in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes.
12:1811–1820. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tsai YC, Kuo PL, Hung WW, Wu LY, Wu PH,
Chang WA, Kuo MC and Hsu YL: Angpt2 induces mesangial cell
apoptosis through the MicroRNA-33-5p-SOCS5 loop in diabetic
nephropathy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 13:543–555. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yi H, Peng R, Zhang LY, Sun Y, Peng HM,
Liu HD, Yu LJ, Li AL, Zhang YJ, Jiang WH and Zhang Z:
LincRNA-Gm4419 knockdown ameliorates NF-κB/NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. Cell
Death Dis. 8(e2583)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang M, Wang S, Yao D, Yan Q and Lu W: A
novel long non-coding RNA CYP4B1-PS1-001 regulates proliferation
and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
426:136–145. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Han F, Xue M, Chang Y, Li X, Yang Y, Sun B
and Chen L: Triptolide suppresses glomerular mesangial cell
proliferation in diabetic nephropathy is associated with inhibition
of PDK1/Akt/mTOR pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 13:1266–1275.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li W, Wang P, Li Y, Zhang K, Ding F, Nie
T, Yang X, Lv Q and Zhao L: Identification of MicroRNAs in response
to different day lengths in soybean using high-throughput
sequencing and qRT-PCR. PLoS One. 10(e0132621)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|