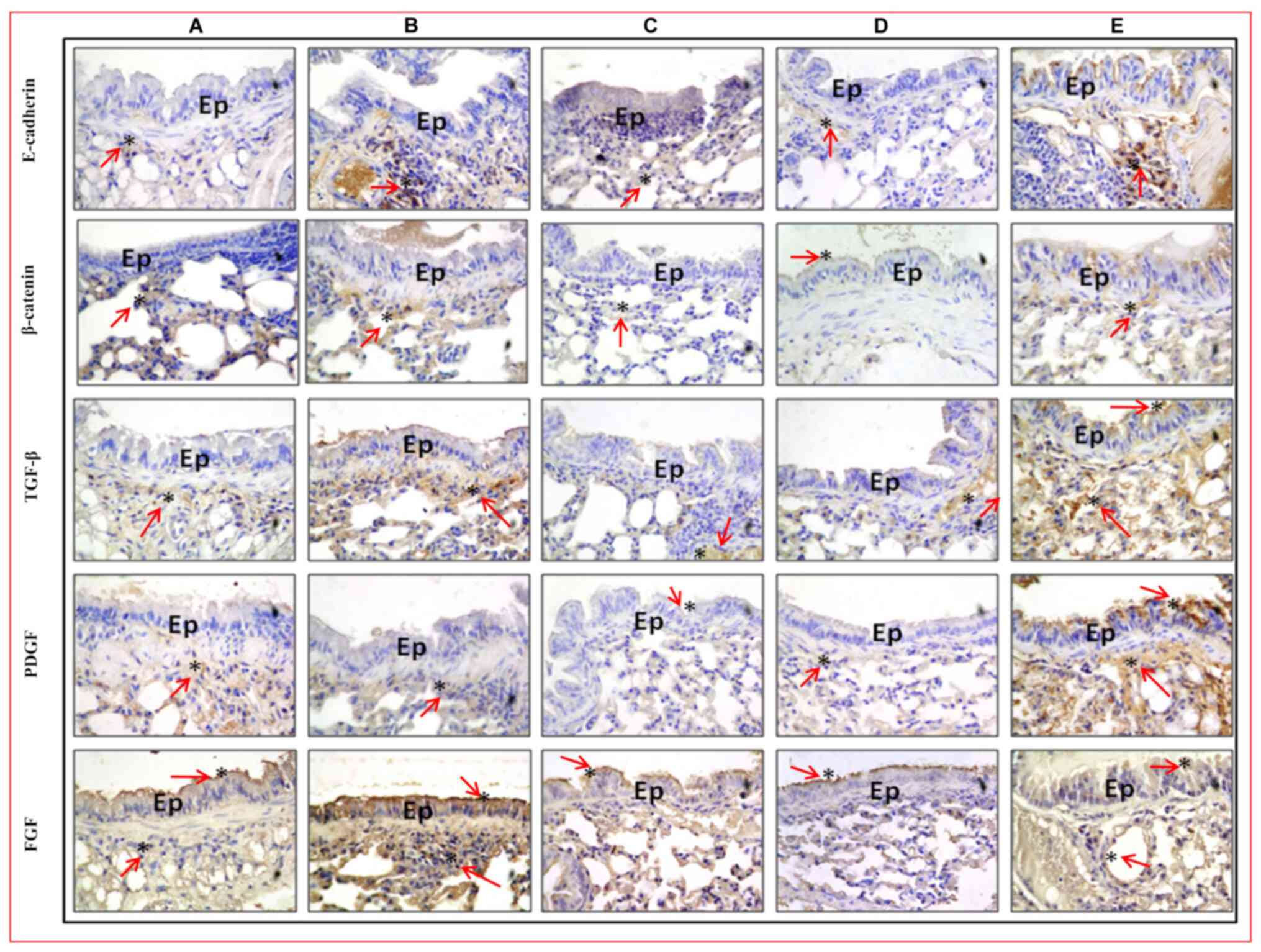
|
1
|
Leynaert B, Le Moual N, Neukirch C, Siroux
V and Varraso R: Environmental risk factors for asthma
developement. Presse Med. 48:262–273. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In French).
|
|
2
|
Goleva E, Berdyshev E and Leung DY:
Epithelial barrier repair and prevention of allergy. J Clin Invest.
129:1463–1474. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lee HY, Hur J, Kim IK, Kang JY, Yoon HK,
Lee SY, Kwon SS, Kim YK and Rhee CK: Effect of nintedanib on airway
inflammation and remodeling in a murine chronic asthma model. Exp
Lung Res. 43:187–196. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kim J and Remick DG: Tumor necrosis factor
inhibitors for the treatment of asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep.
7:151–156. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Guntur VP and Reinero CR: The potential
use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in severe asthma. Curr Opin
Allergy Clin Immunol. 12:68–75. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hasan NAHM, Harith HH, Israf DA and Tham
CL: The differential effects of commercial specialized media on
cell growth and transforming growth factor beta 1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bronchial epithelial cells.
Mol Biol Rep. 47:3511–3519. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yuksel H and Türkeli A: Airway epithelial
barrier dysfunction in the pathogenesis and prognosis of
respiratory tract diseases in childhood and adulthood. Tissue
Barriers. 5(e1367458)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chu S, Zhang X, Sun Y, Liang Y, Sun J, Lu
M, Huang J, Jiang M and Ma L: Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of bronchial epithelial
cells through cGMP/PKG signaling by targeting Smad3 in a murine
model of allergic asthma. Exp Lung Res. 45:245–254. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang J and Dong L: Status and prospects:
Personalized treatment and biomarker for airway remodeling in
asthma. J Thorac Dis. 12:6090–6101. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hellings PW and Steelant B: Epithelial
barriers in allergy and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
145:1499–1509. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Post S, Nawijn MC, Jonker MR, Kliphuis N,
van den Berge M, van Oosterhout AJ and Heijink IH: House dust
mite-induced calcium signaling instigates epithelial barrier
dysfunction and CCL20 production. Allergy. 68:1117–1125.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Niessen CM: Tight junctions/adherens
junctions: Basic structure and function. J Invest Dermatol.
127:2525–2532. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Knight DA, Stick SM and Hackett TL:
Defective function at the epithelial junction: A novel therapeutic
frontier in asthma? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 128:557–558.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Heijink IH, Postma DS, Noordhoek JA,
Broekema M and Kapus A: House dust mite-promoted
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human bronchial epithelium.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 42:69–79. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cao N, Wang J, Xu X, Xiang M and Dou J:
PACAP38 improves airway epithelial barrier destruction induced by
house dust mites allergen. Immunobiology. 224:758–764.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yao L, Chen S, Tang H, Huang P, Wei S,
Liang Z, Chen X, Yang H, Tao A, Chen R, et al: Transient receptor
potential ion channels mediate adherens junctions dysfunction in a
toluene diisocyanate-induced murine asthma model. Toxicol Sci.
168:160–170. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : Erratum in Toxicol
Sci 170, 247, 2019.
|
|
17
|
de Boer WI, Sharma HS, Baelemans SM,
Hoogsteden HC, Lambrecht BN and Braunstahl GJ: Altered expression
of epithelial junctional proteins in atopic asthma: Possible role
in inflammation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 86:105–112.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sekiyama A, Gon Y, Terakado M, Takeshita
I, Kozu Y, Maruoka S, Matsumoto K and Hashimoto S: Glucocorticoids
enhance airway epithelial barrier integrity. Int Immunopharmacol.
12:350–357. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
McLellan K, Shields M, Power U and Turner
S: Primary airway epithelial cell culture and asthma in
children-lessons learnt and yet to come. Pediatr Pulmonol.
50:1393–1405. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Takahashi S: Vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF), VEGF receptors and their inhibitors for
antiangiogenic tumor therapy. Biol Pharm Bull.
34(1785e1798)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hur GY and Broide DH: Genes and pathways
regulating decline in lung function and airway remodeling in
asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 11:604–621. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huang C, Dong H, Zou M, Luo L, Hu Y, Xie
Z, Le Y, Liu L, Zou F and Cai S: Bevacizumab reduced
auto-phosphorylation of VEGFR2 to protect HDM-induced
asthma mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 478:181–186.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Herbert C, Hettiaratchi A, Webb DC, Thomas
PS, Foster PS and Kumar RK: Suppression of cytokine expression by
roflumilast and dexamethasone in a model of chronic asthma. Clin
Exp Allergy. 38:847–856. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ghebre MA, Pang PH, Desai D, Hargadon B,
Newby C, Woods J, Rapley L, Cohen SE, Herath A, Gaillard EA, et al:
Severe exacerbations in moderate-to-severe asthmatics are
associated with increased pro-inflammatory and type 1 mediators in
sputum and serum. BMC Pulm Med. 19(144)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Malaviya R, Laskin JD and Laskin DL:
Anti-TNFα therapy in inflammatory lung diseases. Pharmacol Ther.
180:90–98. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mukhopadhyay S, Hoidal JR and Mukherjee
TK: Role of TNFalpha in pulmonary pathophysiology. Respir Res.
7(125)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animal: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US), Washington, DC, 2011.
|
|
28
|
Temelkovski J, Hogan SP, Shepherd DP,
Foster PS and Kumar RK: An improved murine model of asthma:
Selective airway inflammation, epithelial lesions and increased
methacholine responsiveness following chronic exposure to
aerosolised allergen. Thorax. 53:849–856. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cardiff RD, Miller CH and Munn RJ: Manual
hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold
Spring Harb Protoc. 2014:655–658. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yuksel H, Yilmaz O, Baytur YB and Ozbilgin
K: Prenatal administration of granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor increases mesenchymal vascular
endothelial growth factor expression and maturation in fetal rat
lung. Exp Lung Res. 34:550–558. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang T, Zhou Q and Shang Y: MiRNA-451a
inhibits airway remodeling by targeting Cadherin 11 in an allergic
asthma model of neonatal mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
83(106440)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gong JH, Cho IH, Shin D, Han SY, Park SH
and Kang YH: Inhibition of airway epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and fibrosis by kaempferol in endotoxin-induced
epithelial cells and ovalbumin-sensitized mice. Lab Invest.
94:297–308. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Makinde T, Murphy RF and Agrawal DK:
Immunomodulatory role of vascular endothelial growth factor and
angiopoietin-1 in airway remodeling. Curr Mol Med. 6:831–841.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hough KP, Curtiss ML, Blain TJ, Liu RM,
Trevor J, Deshane JS and Thannickal VJ: Airway remodeling in
asthma. Front Med (Lausanne). 7(191)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hasan NAHM, Harith HH, Israf DA and Tham
CL: The differential effects of commercial specialized media on
cell growth and transforming growth factor beta 1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bronchial epithelial cells.
Mol Biol Rep. 47:3511–3519. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Frey A, Lunding LP, Ehlers JC, Weckmann M,
Zissler UM and Wegmann M: More than just a barrier: The immune
functions of the airway epithelium in asthma pathogenesis. Front
Immunol. 11(761)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Post S, Heijink IH, Hesse L, Koo HK,
Shaheen F, Fouadi M, Kuchibhotla VNS, Lambrecht BN, Van Oosterhout
AJM, Hackett TL, et al: Characterization of a lung epithelium
specific E-cadherin knock-out model: Implications for obstructive
lung pathology. Sci Rep. 8(13275)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cai J, Culley MK, Zhao Y and Zhao J: The
role of ubiquitination and deubiquitination in the regulation of
cell junctions. Protein Cell. 9:754–769. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Goto Y, Uchida Y, Nomura A, Sakamoto T,
Ishii Y, Morishima Y, Masuyama K and Sekizawa K: Dislocation of
E-cadherin in the airway epithelium during an antigen-induced
asthmatic response. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 23:712–718.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Baarsma HA, Menzen MH, Halayko AJ, Meurs
H, Kerstjens HA and Gosens R: β-catenin signaling is required for
TGF-β1-induced extracellular matrix production by airway smooth
muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 301:L956–L965.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kim HT, Yin W, Nakamichi Y, Panza P,
Grohmann B, Buettner C, Guenther S, Ruppert C, Kobayashi Y,
Guenther A, et al: WNT/RYK signaling restricts goblet cell
differentiation during lung development and repair. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 116:25697–25706. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Jia XX, Zhu TT, Huang Y, Zeng XX, Zhang H
and Zhang WX: Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway regulates asthma
airway remodeling by influencing the expression of c-Myc and cyclin
D1 via the p38 MAPK-dependent pathway. Exp Ther Med. 18:3431–3438.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Evans SM, Blyth DI, Wong T, Sanjar S and
West MR: Decreased distribution of lung epithelial junction
proteins after intratracheal antigen or lipopolysaccharide
challenge: Correlation with neutrophil influx and levels of BALF
sE-cadherin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 27:446–454. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Xiao C, Puddicombe SM, Field S, Haywood J,
Broughton-Head V, Puxeddu I, Haitchi HM, Vernon-Wilson E, Sammut D,
Bedke N, et al: Defective epithelial barrier function in asthma. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 128:549–56.e1-12. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Trautmann A, Kruger K, Akdis M,
Muller-Wening D, Akkaya A, Brocker EB, Blaser K and Akdis CA:
Apoptosis and loss of adhesion of bronchial epithelial cells in
asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 138:142–150. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yuksel H, Türkeli A, Taneli F, Horasan GD,
Kanik ET, Kizilkaya M, Gözükara C and Yilmaz O: E-cadherin as an
epithelial barrier protein in exhaled breath condensate. J Breath
Res. 8(046006)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Willems-Widyastuti A, Vanaudenaerde BM,
Vos R, Dilisen E, Verleden SE, De Vleeschauwer SI, Vaneylen A, Mooi
WJ, de Boer WI, Sharma HS, et al: Azithromycin attenuates
fibroblast growth factors induced vascular endothelial growth
factor via p38(MAPK) signaling in human airway smooth muscle cells.
Cell Biochem Biophys. 67:331–339. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Carayol N, Campbell A, Vachier I,
Mainprice B, Bousquet J, Godard P and Chanez P: Modulation of
cadherin and catenins expression by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and
dexamethasone in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 26:341–347. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Moheimani F, Roth HM, Cross J, Reid AT,
Shaheen F, Warner SM, Hirota JA, Kicic A, Hallstrand TS, Kahn M, et
al: Disruption of β-catenin/CBP signaling inhibits human airway
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and repair. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 68:59–69. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Winton HL, Wan H, Cannell MB, Thompson PJ,
Garrod DR, Stewart GA and Robinson C: Class specific inhibition of
house dust mite proteinases which cleave cell adhesion, induce cell
death and which increase the permeability of lung epithelium. Br J
Pharmacol. 124:1048–1059. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Park HY, Kim JH and Park CK: VEGF induces
TGF-β1 expression and myofibroblast transformation after glaucoma
surgery. Am J Pathol. 182:2147–2154. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Chatterjee S, Wang Y, Duncan MK and Naik
UP: Junctional adhesion molecule-A regulates vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor-2 signaling-dependent mouse corneal wound
healing. PLoS One. 8(e63674)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wallez Y and Huber P: Endothelial adherens
and tight junctions in vascular homeostasis, inflammation and
angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1778:794–809. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Díaz-Coránguez M, Lin CM, Liebner S and
Antonetti DA: Norrin restores blood-retinal barrier properties
after vascular endothelial growth factor-induced permeability. J
Biol Chem. 295:4647–4660. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
He J, Wang H, Liu Y, Li W, Kim D and Huang
H: Blockade of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1
prevents inflammation and vascular leakage in diabetic retinopathy.
J Ophthalmol. 2015(605946)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wisniewska-Kruk J, Hoeben KA, Vogels IM,
Gaillard PJ, Van Noorden CJ, Schlingemann RO and Klaassen I: A
novel co-culture model of the blood-retinal barrier based on
primary retinal endothelial cells, pericytes and astrocytes. Exp
Eye Res. 96:181–190. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : Erratum in Exp Eye
Res 138, 167, 2015.
|
|
57
|
Harhaj NS, Felinski EA, Wolpert EB,
Sundstrom JM, Gardner TW and Antonetti DA: VEGF activation of
protein kinase C stimulates occludin phosphorylation and
contributes to endothelial permeability. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
47:5106–5115. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Sullivan DE, Ferris M, Nguyen H, Abboud E
and Brody AR: TNF-alpha induces TGF-beta1 expression in lung
fibroblasts at the transcriptional level via AP-1 activation. J
Cell Mol Med. 13:1866–1876. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Brightling C, Berry M and Amrani Y:
Targeting TNF-alpha: A novel therapeutic approach for asthma. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 121:5–10; quiz 11-12. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Câmara J and Jarai G: .
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in primary human bronchial
epithelial cells is Smad-dependent and enhanced by fibronectin and
TNF-alpha. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 3(2)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Hardyman MA, Wilkinson E, Martin E,
Jayasekera NP, Blume C, Swindle EJ, Gozzard N, Holgate ST, Howarth
PH, Davies DE, et al: TNF-α-mediated bronchial barrier disruption
and regulation by src-family kinase activation. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 132:665–675.e8. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Coyne CB, Vanhook MK, Gambling TM, Carson
JL, Boucher RC and Johnson LG: Regulation of airway tight junctions
by proinflammatory cytokines. Mol Biol Cell. 13:3218–3234.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Pohl C, Hermanns MI, Uboldi C, Bock M,
Fuchs S, Dei-Anang J, Mayer E, Kehe K, Kummer W and Kirkpatrick CJ:
Barrier functions and paracellular integrity in human cell culture
models of the proximal respiratory unit. Eur J Pharm Biopharm.
72:339–349. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Doherty T and Broide D: Cytokines and
growth factors in airway remodeling in asthma. Curr Opin Immunol.
19:676–680. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Wang Z, Li W, Guo Q, Wang Y, Ma L and
Zhang X: Insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling in lung development
and inflammatory lung diseases. BioMed Res Int.
2018(6057589)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Dekkers BG, Pehlic A, Mariani R, Bos IS,
Meurs H and Zaagsma J: Glucocorticosteroids and
β2-adrenoceptor agonists synergize to inhibit airway
smooth muscle remodeling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 342:780–787.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Song J, Zhao H, Dong H, Zhang D, Zou M,
Tang H, Liu L, Liang Z, Lv Y, Zou F, et al: Mechanism of E-cadherin
redistribution in bronchial airway epithelial cells in a
TDI-induced asthma model. Toxicol Lett. 220:8–14. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Doerner AM and Zuraw BL: TGF-β1 induced
epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human bronchial
epithelial cells is enhanced by IL-1β but not abrogated by
corticosteroids. Respir Res. 10(100)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kimura K, Teranishi S, Kawamoto K and
Nishida T: Protective effect of dexamethasone against
hypoxia-induced disruption of barrier function in human corneal
epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 92:388–393. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|