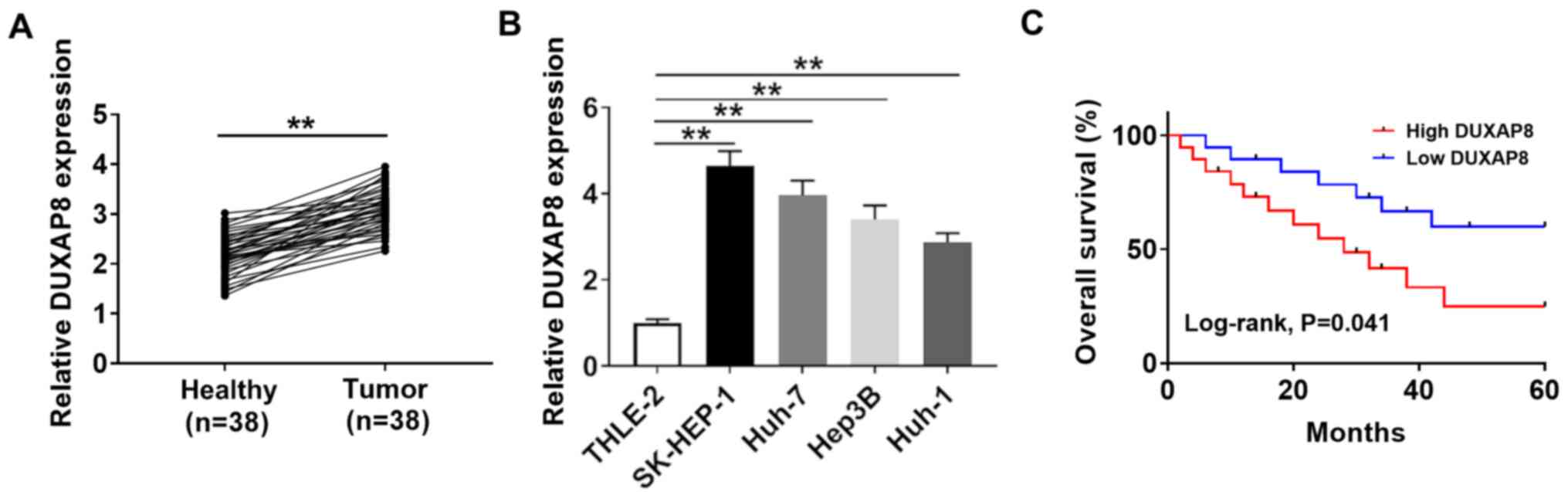
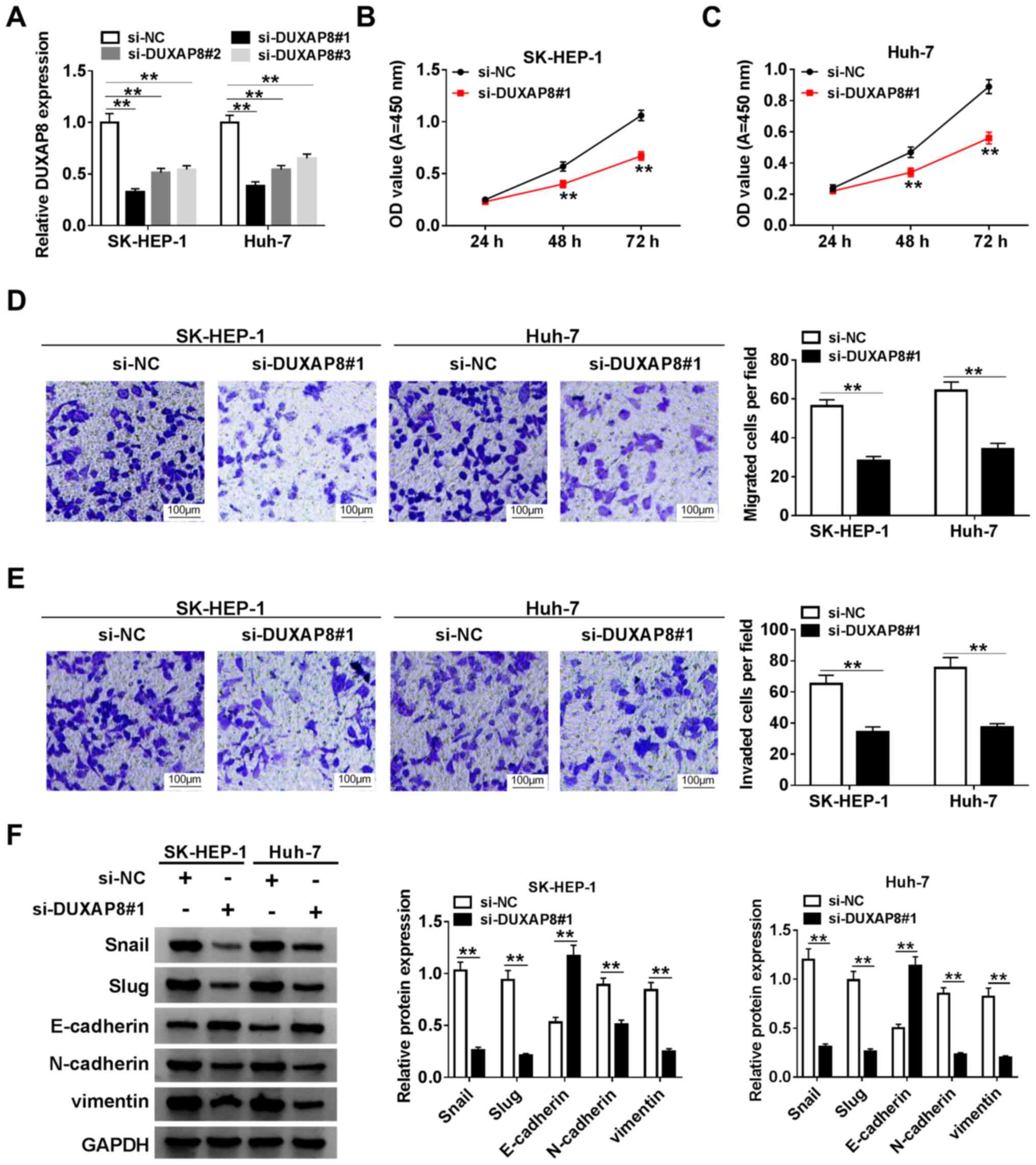
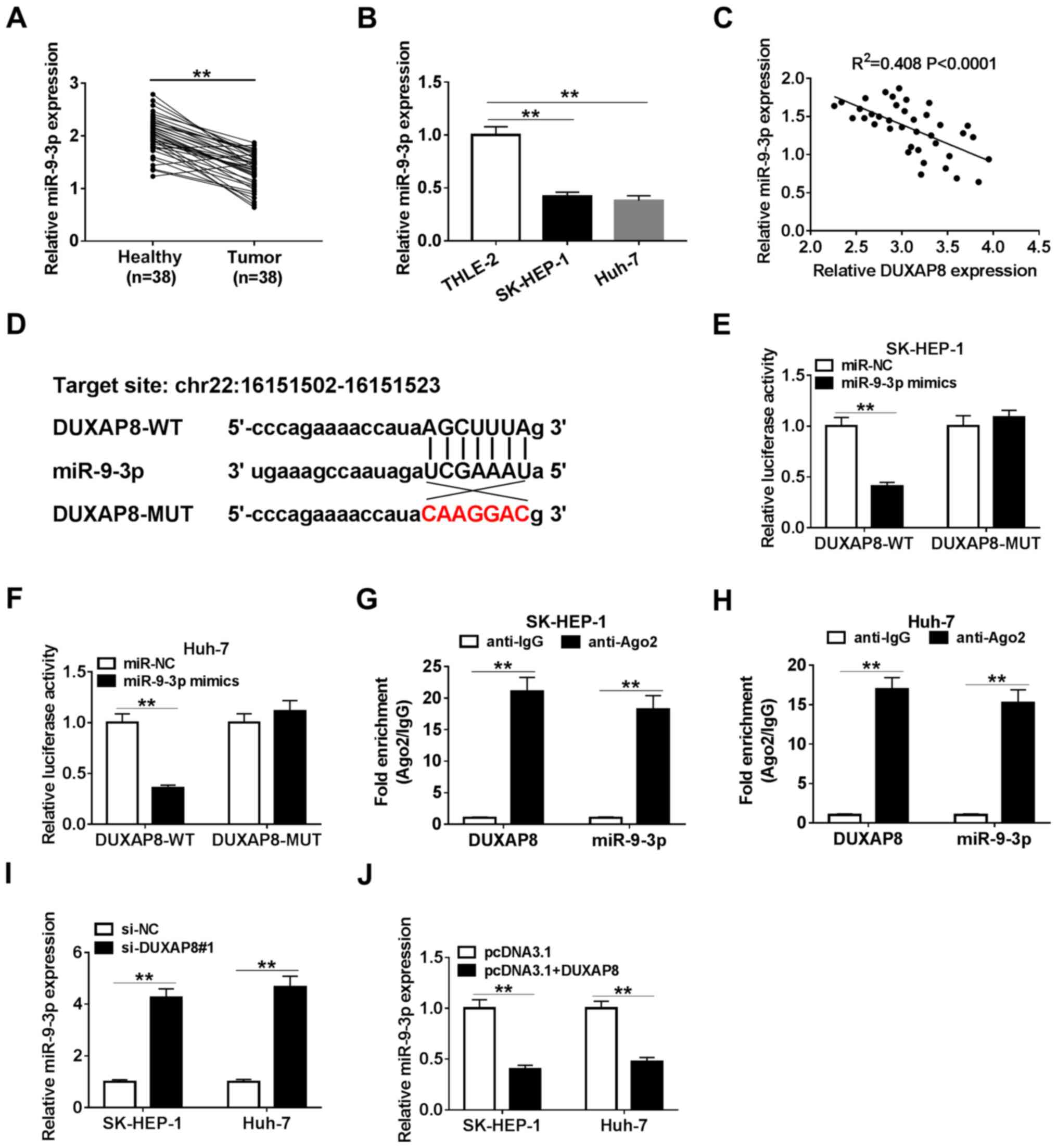
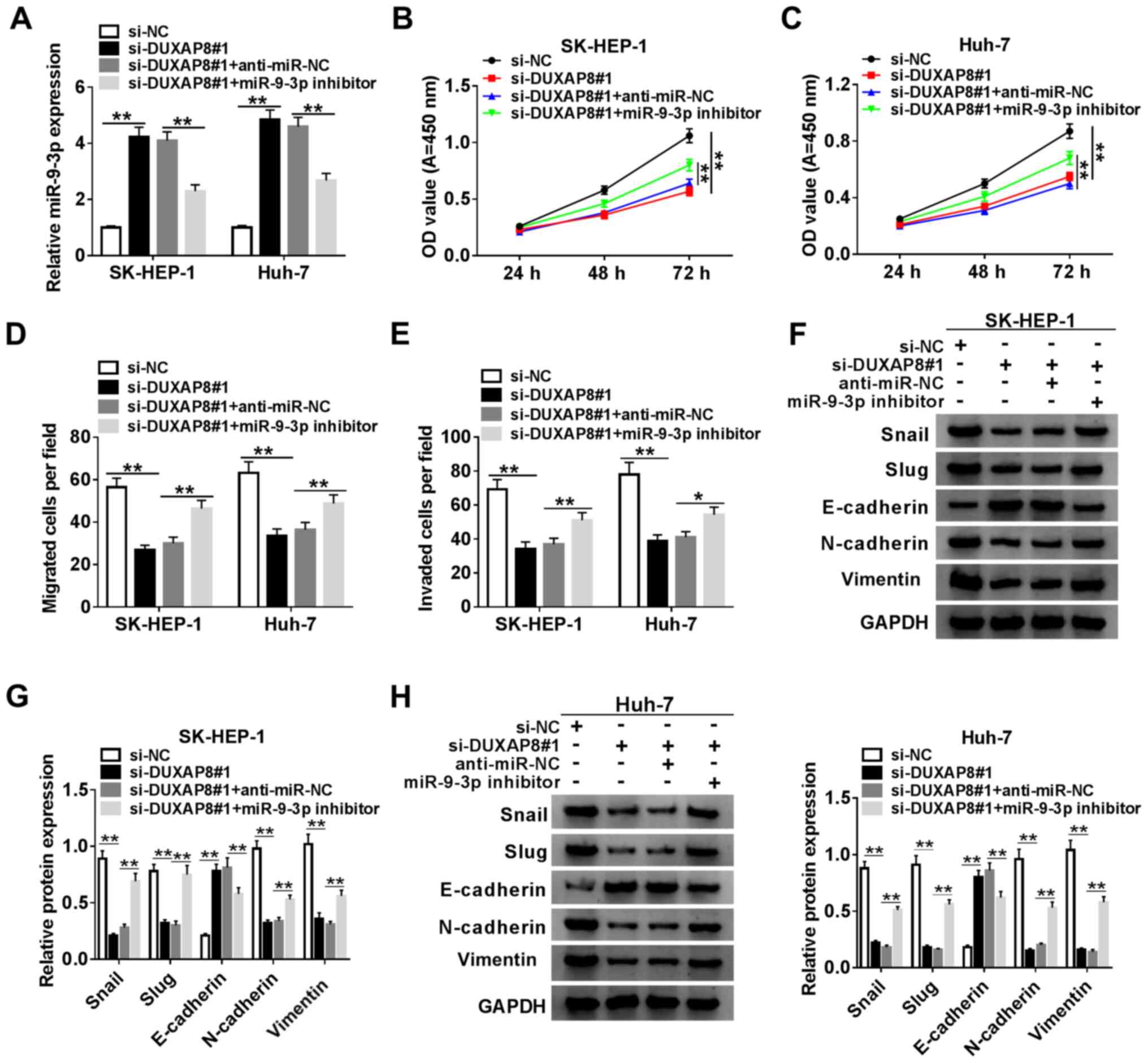
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Erstad DJ and Tanabe KK: Prognostic and
therapeutic implications of microvascular invasion in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 26:1474–1493.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
Non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Marchese FP, Raimondi I and Huarte M: The
multidimensional mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function. Genome
Biol. 18(206)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kong L and Zhang C: LncRNA DLX6-AS1
aggravates the development of ovarian cancer via modulating FHL2 by
sponging miR-195-5p. Cancer Cell Int. 20(370)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yang Q, Wan Q, Zhang L, Li Y, Zhang P, Li
D, Feng C, Yi F, Zhang L, Ding X, et al: Analysis of LncRNA
expression in cell differentiation. RNA Biol. 15:413–422.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wu Y and Qian Z: Long non-coding RNAs
(lncRNAs) and microRNAs regulatory pathways in the tumorigenesis
and pathogenesis of glioma. Discov Med. 28:129–138. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang Y, Chen L, Gu J, Zhang H, Yuan J,
Lian Q, Lv G, Wang S, Wu Y, Yang YT, et al: Recurrently deregulated
lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun.
8(14421)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li B, Mao R, Liu C, Zhang W, Tang Y and
Guo Z: LncRNA FAL1 promotes cell proliferation and migration by
acting as a CeRNA of miR-1236 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Life Sci. 197:122–129. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ma J, Li T and Han X: Knockdown of LncRNA
ANRIL suppresses cell proliferation, metastasis, and invasion via
regulating miR-122-5p expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:205–214. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhao X, Hao S, Wang M, Xing D and Wang C:
Knockdown of pseudogene DUXAP8 expression in glioma suppresses
tumor cell proliferation. Oncol Lett. 17:3511–3516. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jiang B, Hailong S, Yuan J, Zhao H, Xia W,
Zha Z, Bin W and Liu Z: Identification of oncogenic long noncoding
RNA SNHG12 and DUXAP8 in human bladder cancer through a
comprehensive profiling analysis. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:500–507.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Huang T, Wang X, Yang X, Ji J, Wang Q, Yue
X and Dong Z: Long non-coding RNA DUXAP8 enhances renal cell
carcinoma progression via downregulating miR-126. Med Sci Monit.
24:7340–7347. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sun M, Nie FQ, Zang C, Wang Y, Hou J, Wei
C, Li W, He X and Lu KH: The pseudogene DUXAP8 promotes
non-small-cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion by
epigenetically silencing EGR1 and RHOB. Mol Ther. 25:739–751.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Afonso-Grunz F and Muller S: Principles of
miRNA-mRNA interactions: Beyond sequence complementarity. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 72:3127–3141. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zha Z, Jia F, Hu P, Mai E and Lei T:
MicroRNA-574-3p inhibits the malignant behavior of liver cancer
cells by targeting ADAM28. Oncol Lett. 20:3015–3023.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu CH, Jing XN, Liu XL, Qin SY, Liu MW
and Hou CH: Tumor-suppressor miRNA-27b-5p regulates the growth and
metastatic behaviors of ovarian carcinoma cells by targeting CXCL1.
J Ovarian Res. 13(92)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fang F, Chang RM, Yu L, Lei X, Xiao S,
Yang H and Yang LY: MicroRNA-188-5p suppresses tumor cell
proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting FGF5 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 63:874–885. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen Y, Zhao ZX, Huang F, Yuan XW, Deng L
and Tang D: MicroRNA-1271 functions as a potential tumor suppressor
in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through
the AMPK signaling pathway by binding to CCNA1. J Cell Physiol.
234:3555–3569. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Higashi T, Hayashi H, Ishimoto T, Takeyama
H, Kaida T, Arima K, Taki K, Sakamoto K, Kuroki H, Okabe H, et al:
MiR-9-3p plays a tumour-suppressor role by targeting TAZ (WWTR1) in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 113:252–258.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Erickson KE and Rukhlenko OS: Modeling
cell line-specific recruitment of signaling proteins to the
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. PLoS Comput Biol.
15(e1006706)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lin JF, Tsai TF, Lin YC, Chen HE, Chou KY
and Hwang TI: Benzyl isothiocyanate suppresses IGF1R, FGFR3 and
mTOR expression by upregulation of miR-99a-5p in human bladder
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 54:2106–2116. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Huang S, Guo Y and Li L: MiR-1294
confers cisplatin resistance in ovarian Cancer cells by targeting
IGF1R. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:1357–1363. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Khalil A and Jameson MJ: Downregulation of
igf1r expression inhibits growth and enhances cisplatin sensitivity
of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells in vitro. Horm
Cancer. 10:11–23. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu W, Kang L, Han J, Wang Y, Shen C, Yan
Z, Tai Y and Zhao C: MiR-342-3p suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma
proliferation through inhibition of IGF-1R-mediated Warburg effect.
Onco Targets Ther. 11:1643–1653. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ren L, Yao Y, Wang Y and Wang S: MiR-505
suppressed the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via
targeting IGF-1R. Biosci Rep. 39(BSR20182442)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ye Y, Zhuang J, Wang G, He S, Zhang S,
Wang G, Ni J, Wang J and Xia W: MicroRNA-495 suppresses cell
proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by directly
targeting insulin-like growth factor receptor-1. Exp Ther Med.
15:1150–1158. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu MD, Wu H, Wang S, Pang P, Jin S, Sun
CF and Liu FY: MiR-1275 promotes cell migration, invasion and
proliferation in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck via
up-regulating IGF-1R and CCR7. Gene. 646:1–7. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhou Y, Zhang Z, Wang N, Chen J, Zhang X,
Guo M, John Zhong L and Wang Q: Suppressor of cytokine signalling-2
limits IGF1R-mediated regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis.
9(429)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
StarBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42 (Database Issue):D92–D97. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang JH, Li JH, Shao P, Zhou H, Chen YQ
and Qu LH: StarBase: A database for exploring microRNA-mRNA
interaction maps from Argonaute CLIP-Seq and Degradome-Seq data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39 (Database Issue):D202–D209. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li Y: MIR31HG exhibits oncogenic property
and acts as a sponge for miR-361-3p in cervical carcinoma. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 529:890–897. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sun F and Wu K: Long Noncoding RNA PVT1
promotes prostate cancer metastasis by increasing NOP2 expression
via targeting tumor suppressor MicroRNAs. Onco Targets Ther.
13:6755–6765. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shi X, Huo J, Gao X, Cai H and Zhu W: A
newly identified lncRNA H1FX-AS1 targets DACT1 to inhibit cervical
cancer via sponging miR-324-3p. Cancer Cell Int.
20(358)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wu R, Zhao B, Ren X, Wu S, Liu M, Wang Z
and Liu W: MiR-27a-3p targeting GSK3β promotes triple-negative
breast cancer proliferation and migration through Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Cancer Manag Res. 12:6241–6249. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li G, Qi HW, Dong HG, Bai P, Sun M and Liu
HY: Targeting deubiquitinating enzyme USP26 by microRNA-203
regulates Snail1's pro-metastatic functions in esophageal cancer.
Cancer Cell Int. 20(355)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ma HF, Lv GX and Zhang DH: miR-381
mediates the development of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
via targeting STC2. Onco Targets Ther. 13:4485–4493.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Huo X, Han S, Wu G, Latchoumanin O, Zhou
G, Hebbard L, George J and Qiao L: Dysregulated long noncoding RNAs
(lncRNAs) in hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications for
tumorigenesis, disease progression, and liver cancer stem cells.
Mol Cancer. 16(165)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhang H, Xu HB, Kurban E and Luo HW:
LncRNA SNHG14 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via
H3K27 acetylation activated PABPC1 by PTEN signaling. Cell Death
Dis. 11(646)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
He H, Wang Y, Ye P, Yi D, Cheng Y, Tang H,
Zhu Z, Wang X and Jin S: Long noncoding RNA ZFPM2-AS1 acts as a
miRNA sponge and promotes cell invasion through regulation of
miR-139/GDF10 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
39(159)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yin D, Hua L, Wang J and Liu Y: Long
non-coding RNA DUXAP8 facilitates cell viability, migration, and
glycolysis in non-small-cell lung cancer via regulating HK2 and
LDHA by inhibition of miR-409-3p. Onco Targets Ther. 13:7111–7123.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Meng Q, Li Z, Pan J and Sun X: Long
noncoding RNA DUXAP8 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of
ovarian cancer cells via targeting miR-590-5p. Hum Cell.
33:1240–1251. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xu LJ, Yu XJ, Wei B, Hui HX, Sun Y, Dai J
and Chen XF: Long non-coding RNA DUXAP8 regulates proliferation and
invasion of esophageal squamous cell cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 22:2646–2652. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lin MG, Hong YK, Zhang Y, Lin BB and He
XJ: Mechanism of lncRNA DUXAP8 in promoting proliferation of
bladder cancer cells by regulating PTEN. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:3370–3377. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yang L, Mu Y, Cui H, Liang Y and Su X:
MiR-9-3p augments apoptosis induced by H2O2 through down regulation
of Herpud1 in glioma. PLoS One. 12(e0174839)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ding Y, Pan Y, Liu S, Jiang F and Jiao J:
Elevation of MiR-9-3p suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via down-regulating
FN1, ITGB1 and ITGAV. Cancer Biol Ther. 18:414–424. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Cai H, Yang X, Gao Y, Xu Z, Yu B, Xu T, Li
X, Xu W, Wang X and Hua L: Exosomal MicroRNA-9-3p secreted from
BMSCs downregulates ESM1 to suppress the development of bladder
cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 18:787–800. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Yang S, Cai H, Hu B and Tu J: LncRNA
SAMMSON negatively regulates miR-9-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells and has prognostic values. Biosci Rep.
39(BSR20190615)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Tang J, Li Y, Liu K, Zhu Q, Yang WH, Xiong
LK and Guo DL: Exosomal miR-9-3p suppresses HBGF-5 expression and
is a functional biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Minerva Med.
109:15–23. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Militello G, Weirick T, John D, Döring C,
Dimmeler S and Uchida S: Screening and validation of lncRNAs and
circRNAs as miRNA sponges. Brief Bioinform. 18:780–788.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Olgun G, Sahin O and Tastan O: Discovering
lncRNA mediated sponge interactions in breast cancer molecular
subtypes. BMC Genomics. 19(650)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M:
Functional interactions among microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 34:9–14. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Li DS, Ainiwaer JL, Sheyhiding I, Zhang Z
and Zhang LW: Identification of key long non-coding RNAs as
competing endogenous RNAs for miRNA-mRNA in lung adenocarcinoma.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:2285–2295. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lin P, Wen DY, Li Q, He Y, Yang H and Chen
G: Genome-wide analysis of prognostic lncRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs
forming a competing endogenous RNA Network in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1953–1967. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Schwartz MA and Ginsberg MH: Networks and
crosstalk: Integrin signalling spreads. Nat Cell Biol. 4:E65–E68.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Han X, Wang X, Zhao B, Chen G, Sheng Y,
Wang W and Teng M: MicroRNA-187 inhibits tumor growth and
metastasis via targeting of IGF-1R in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol
Med Rep. 16:2241–2246. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|