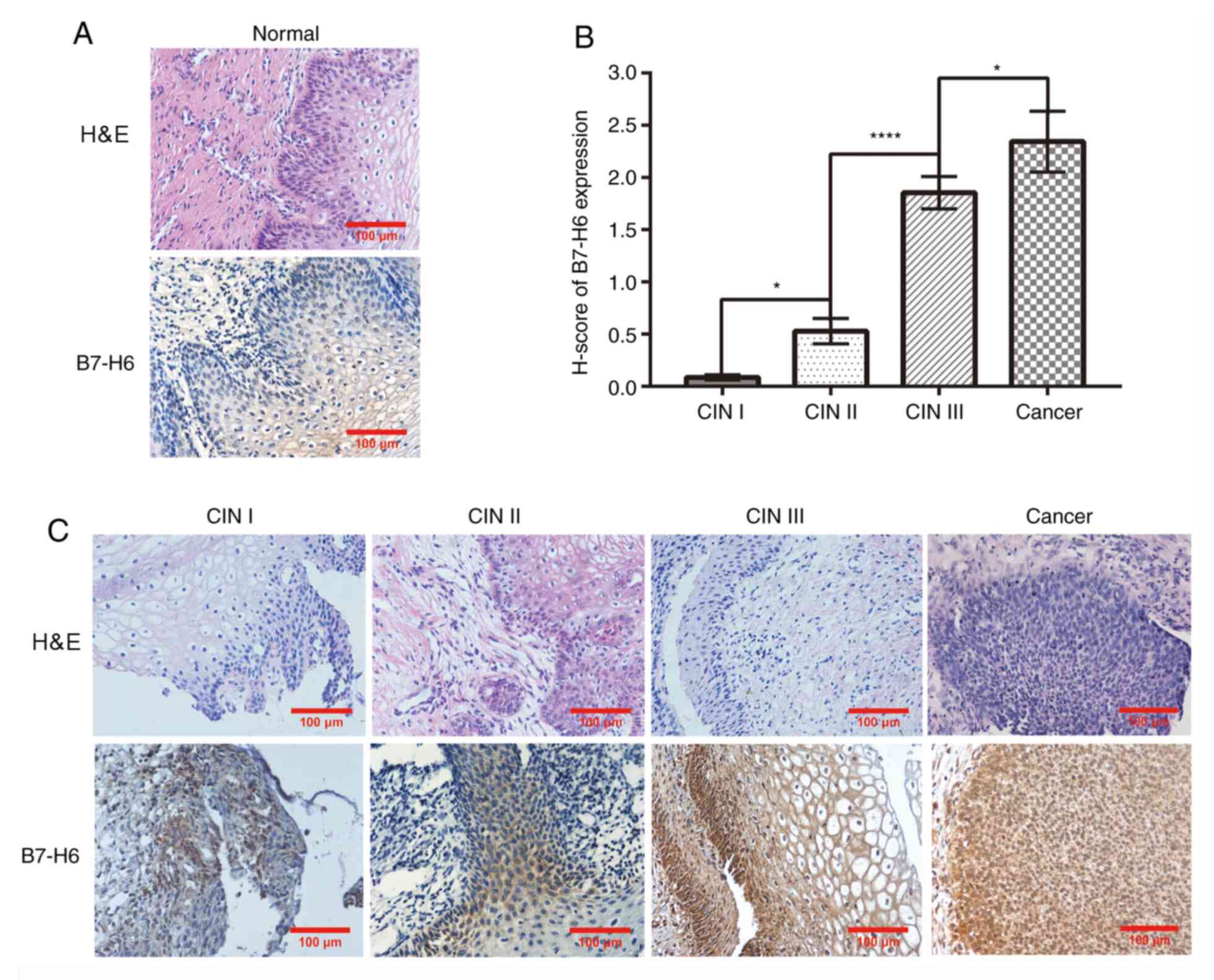
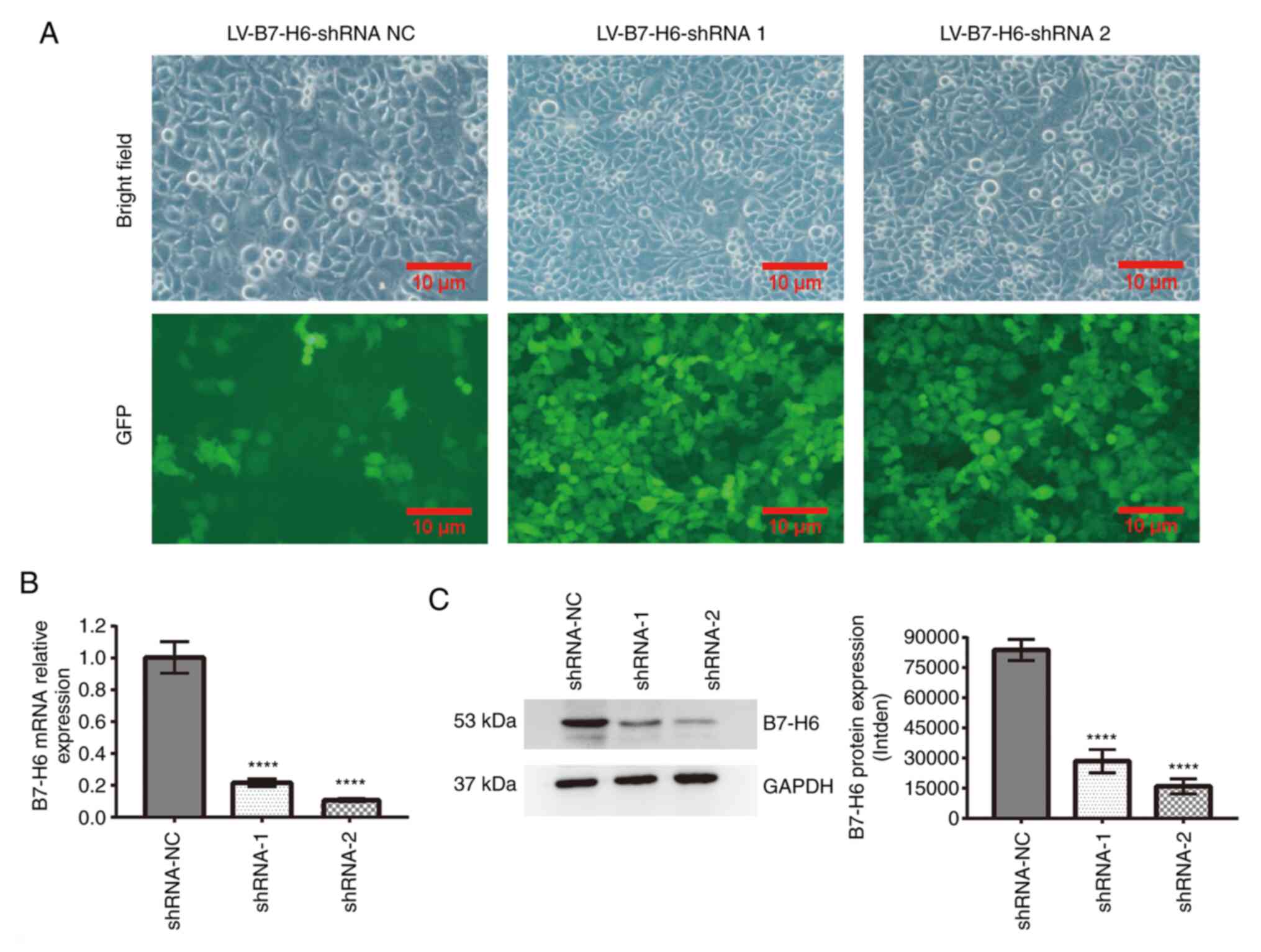
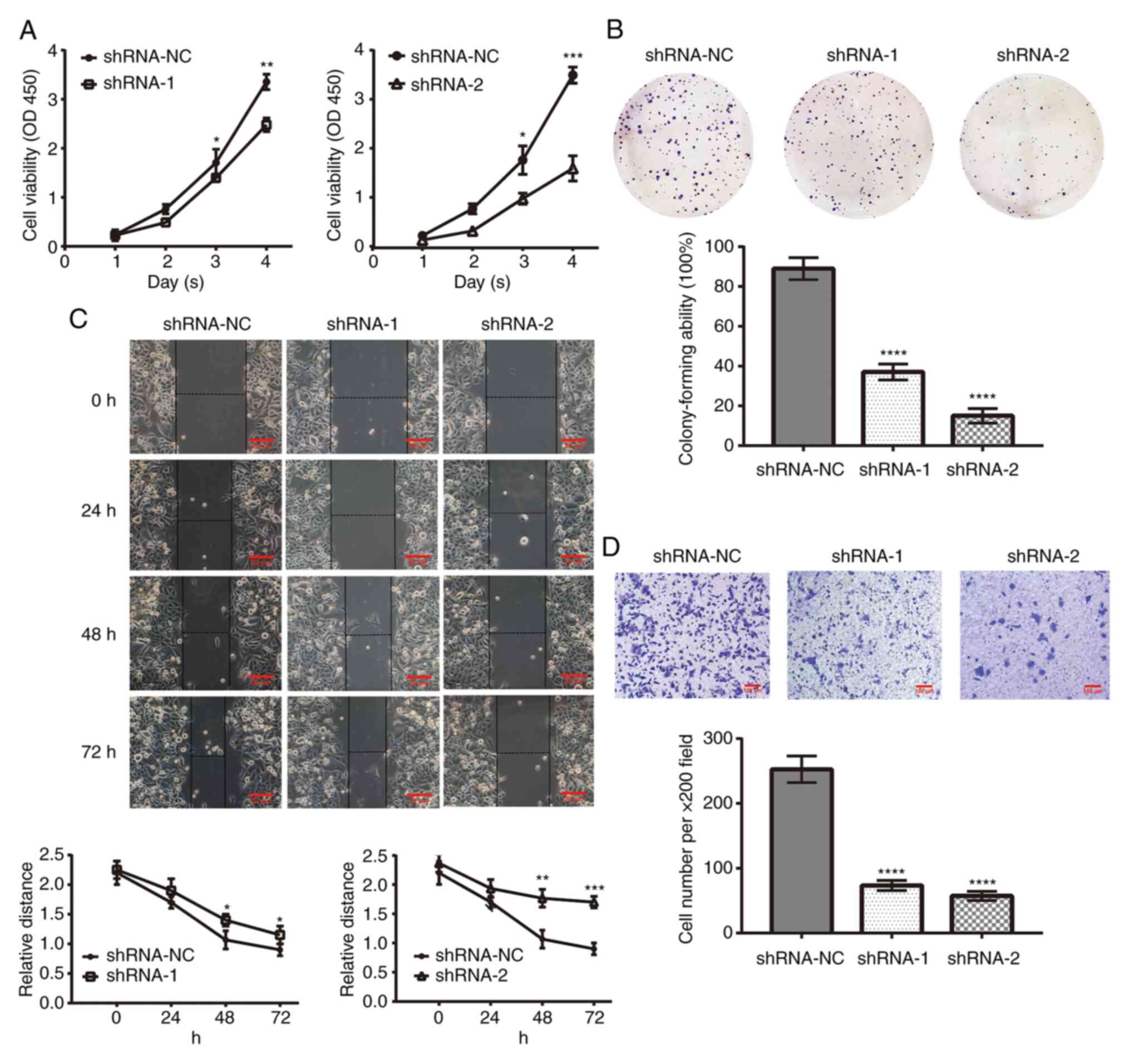
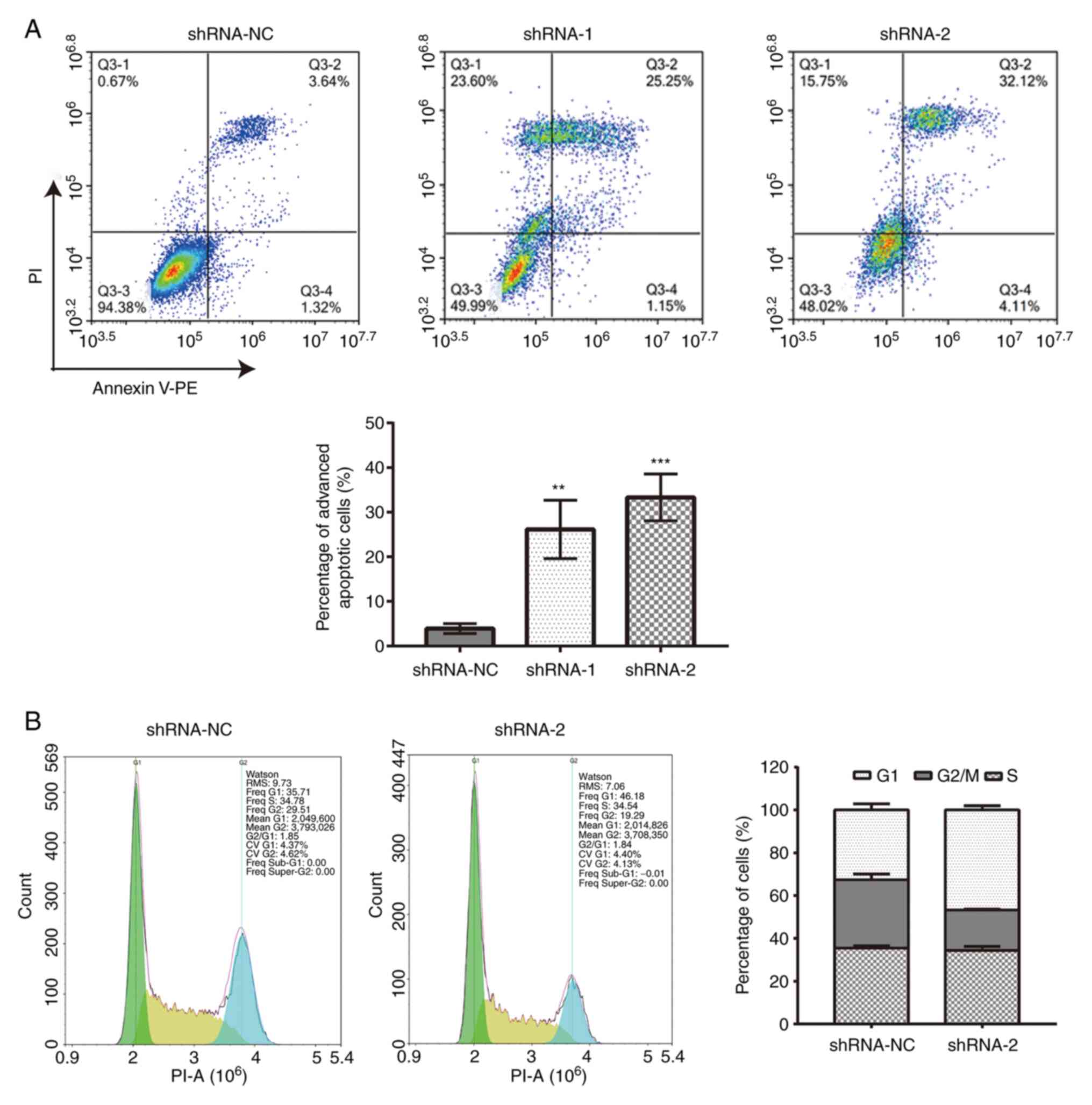
|
1
|
Stelzle D, Tanaka LF, Lee KK, Ibrahim
Khalil A, Baussano I, Shah ASV, McAllister DA, Gottlieb SL, Klug
SJ, et al: Estimates of the global burden of cervical cancer
associated with HIV. Lancet Glob Health. 2:e161–e169.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : Erratum in: Lancet
Glob Health 2, e119, 2021.
|
|
2
|
Abu Rustum NR, Yashar CM, Bradley K,
Campos SM, Chon HS, Chu C, Clinton L, Cohn D, Crispens MA, et al:
NCCN Guidelines Version 1.2021 Cervical Cancer. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 6:660–666. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chitsike L and Duerksen-Hughes P: The
potential of immune checkpoint blockade in cervical cancer: Can
combinatorial regimens maximize response? A review of the
literature. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 21(95)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ni L and Dong C: New B7 family checkpoints
in human cancers. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:1203–1211. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hu Y, Zeng T, Xiao Z, Hu Q, Li Y, Tan X,
Yue H, Wang W, Tan H and Zou J: Immunological role and underlying
mechanisms of B7-H6 in tumorigenesis. Clin Chim Acta. 502:191–198.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Wang Q and Mariuzza RA: Structure of
the human activating natural cytotoxicity receptor NKp30 bound to
its tumor cell ligand B7-H6. J Exp Med. 208:703–714.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Barrow AD, Martin CJ and Colonna M: The
Natural cytotoxicity receptors in health and disease. Front
Immunol. 10:909–913. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Joyce MG, Tran P, Zhuravleva MA, Jaw J,
Colonna M and Sun PD: Crystal structure of human natural
cytotoxicity receptor NKp30 and identification of its ligand
binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:6223–6228.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fiegler N, Textor S, Arnold A, Rölle A,
Oehme I, Breuhahn K, Moldenhauer G, Witzens-Harig M and Cerwenka A:
Downregulation of the activating NKp30 ligand B7-H6 by HDAC
inhibitors impairs tumor cell recognition by NK cells. Blood.
122:684–693. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pesce S, Tabellini G, Cantoni C, Patrizi
O, Coltrini D, Rampinelli F, Matta J, Vivier E, Moretta A, Parolini
S, et al: B7-H6-mediated downregulation of NKp30 in NK cells
contributes to ovarian carcinoma immune escape. OncoImmunology.
4(e1001224)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Schlecker E, Fiegler N, Arnold A, Altevogt
P, Rose-John S, Moldenhauer G, Sucker A, Paschen A, von Strandmann
EP, Textor S, et al: Metalloprotease-mediated tumor cell shedding
of B7-H6, the ligand of the natural killer cell-activating receptor
NKp30. Cancer Res. 74:3429–3440. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Phillips M, Romeo F, Bitsaktsis C and
Sabatino D: B7H6-derived peptides trigger TNF-α-dependent
immunostimulatory activity of lymphocytic NK92-MI cells.
Biopolymers. 106:658–672. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cao G, Wang J, Zheng X, Wei H, Tian Z and
Sun R: Tumor therapeutics work as stress inducers to enhance tumor
sensitivity to natural killer (NK) cell cytolysis by up-regulating
NKp30 ligand B7-H6. J Biol Chem. 290:29964–29973. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Textor S, Bossler F, Henrich KO,
Gartlgruber M, Pollmann J, Fiegler N, Arnold A, Westermann F,
Waldburger N, Breuhahn K, et al: The proto-oncogene Myc drives
expression of the NK cell-activating NKp30 ligand B7-H6 in tumor
cells. Oncoimmunology. 5(e1116674)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhou H, Dong J, Guo L, Wang X, Wang K, Cai
X and Yang S: The prognostic value of B7-H6 in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 9:18122–18130. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sun J, Tao H, Li X, Wang L, Yang J, Wu P,
Zhang Y and Guo Y: Clinical significance of novel costimulatory
molecule B7-H6 in human breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:2405–2409.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Jin X, Liu J, Zhao K, Xu H, Wen J,
Jiang L, Zeng X, Li J and Chen Q: The prognostic value of B7-H6
protein expression in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral
Pathol Med. 46:766–772. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Waxman AG, Chelmow D, Darragh TM, Lawson H
and Moscicki AB: Revised terminology for cervical histopathology
and its implications for management of high-grade squamous
intraepithelial lesions of the cervix. Obstet Gynecol.
120:1465–1471. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li D, Xiang S, Shen J, Xiao M, Zhao Y, Wu
X, Du F, Ji H, Li M, Zhao Q, et al: Comprehensive understanding of
B7 family in gastric cancer: Expression profile, association with
clinicopathological parameters and downstream targets. Int J Biol
Sci. 16:568–582. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen Y, Mo J, Jia X and He Y: The B7
Family Member B7-H6: A new bane of tumor. Pathol Oncol Res.
24:717–721. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen L, Feng J, Xu B, Zhou Y, Zheng X, Wu
C and Jiang J: B7-H6 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma
and its clinical significance [corrected]. Cancer Cell Int.
18:126–136. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : Erratum in: Cancer
Cell Int 18, 134 2018.
|
|
23
|
Jiang T, Wu W, Zhang H, Zhang X, Zhang D,
Wang Q, Huang L, Wang Y and Hang C: High expression of B7-H6 in
human glioma tissues promotes tumor progression. Oncotarget.
8:37435–37447. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu MR, Zhang T, Gacerez AT, Coupet TA,
DeMars LR and Sentman CL: B7H6-specific bispecific T cell engagers
lead to tumor elimination and host antitumor immunity. J Immunol.
194:5305–5311. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen XJ, Shen J, Zhang GB and Chen WC:
B7-H6 protein expression has no prognostic significance in human
gastric carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 20:203–207. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xu Z, Shen J, Wang MH, Yi T, Yu Y, Zhu Y,
Chen B, Chen J, Li L, Li M, et al: Comprehensive molecular
profiling of the B7 family of immune-regulatory ligands in breast
cancer. OncoImmunology. 5(e1207841)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Che F, Xie X, Wang L, Su Q, Jia F, Ye Y,
Zang L, Wang J, Li H, Quan Y, et al: B7-H6 expression is induced by
lipopolysaccharide and facilitates cancer invasion and metastasis
in human gliomas. Int Immunopharmacol. 59:318–327. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li YM, Liu ZY, Li ZC, Wang JC, Yu JM, Yang
HJ, Chen ZN and Tang J: Alterations of the immunologic
co-stimulator B7 and TNFR families correlate with hepatocellular
carcinoma prognosis and metastasis by inactivating STAT3. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:156–174. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wu F, Wang J and Ke X: Knockdown of B7-H6
inhibits tumor progression and enhances chemosensitivity in B-cell
non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Int J Oncol. 48:1561–1570. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|