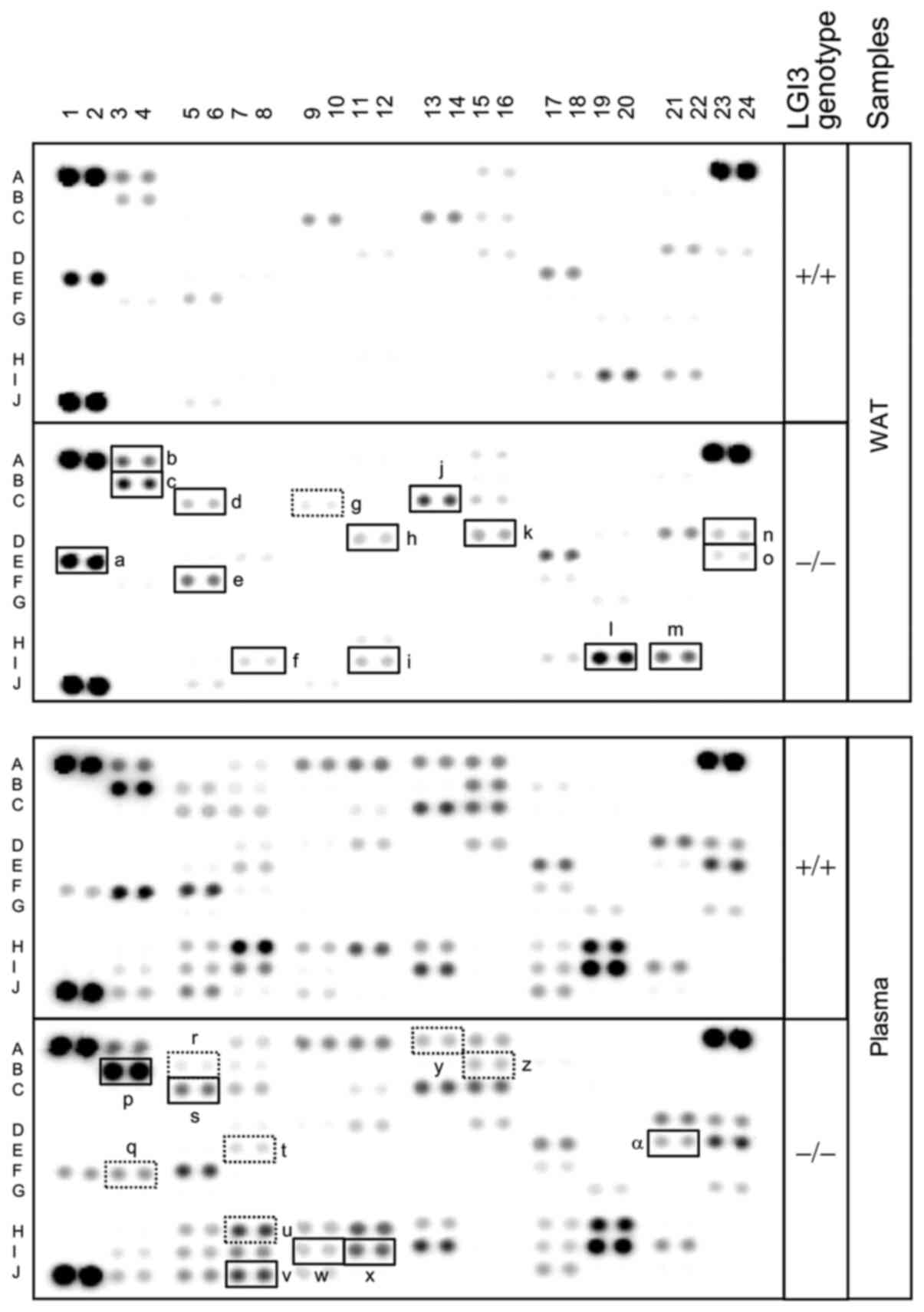
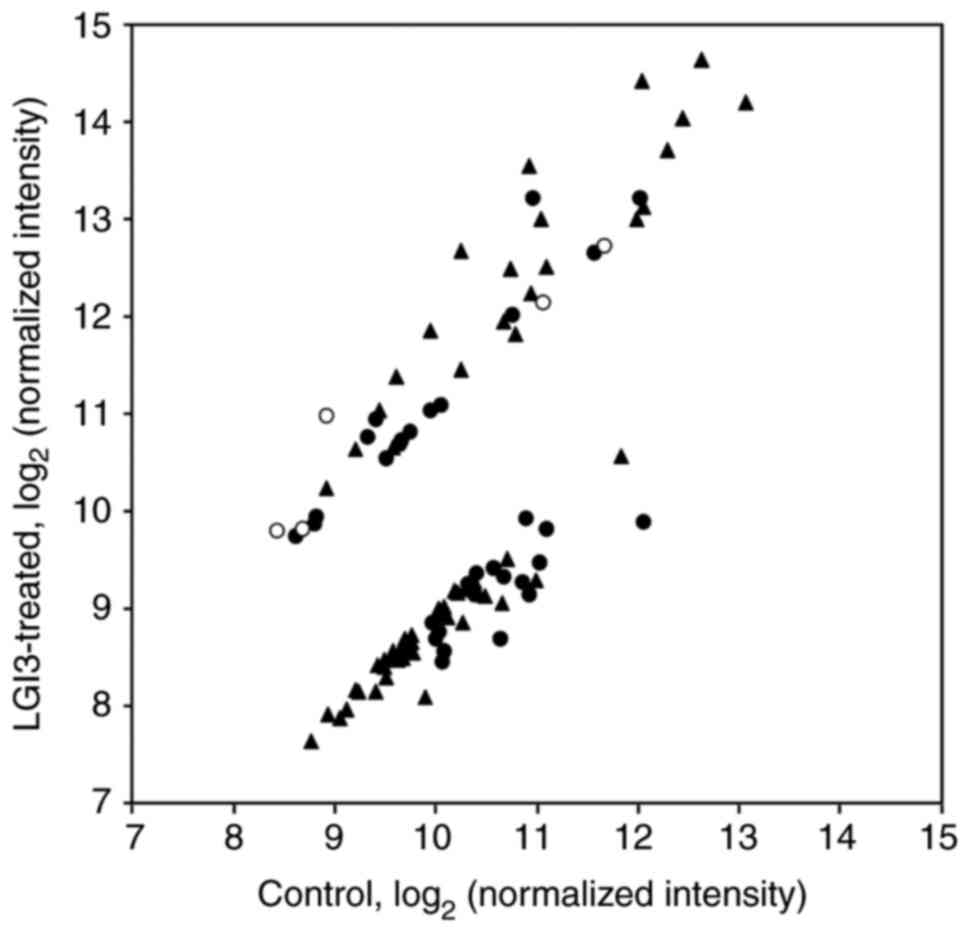
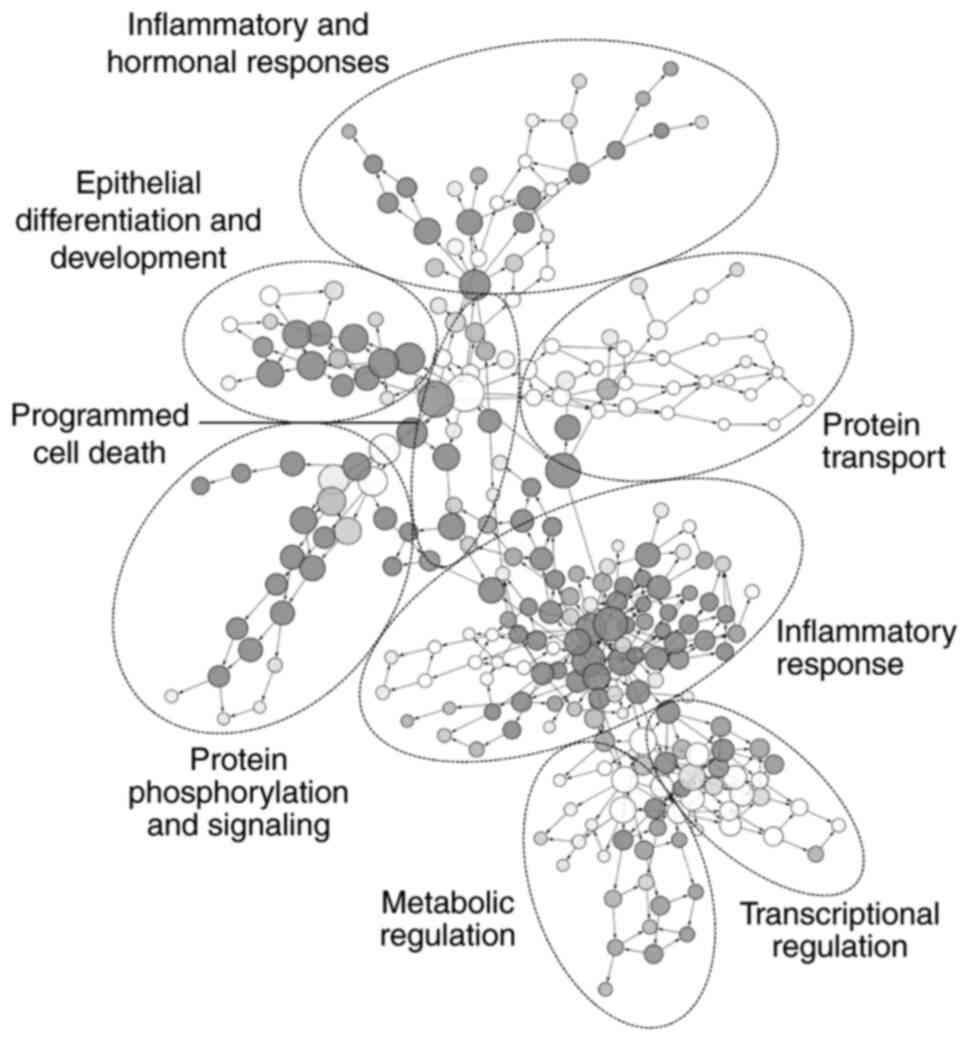
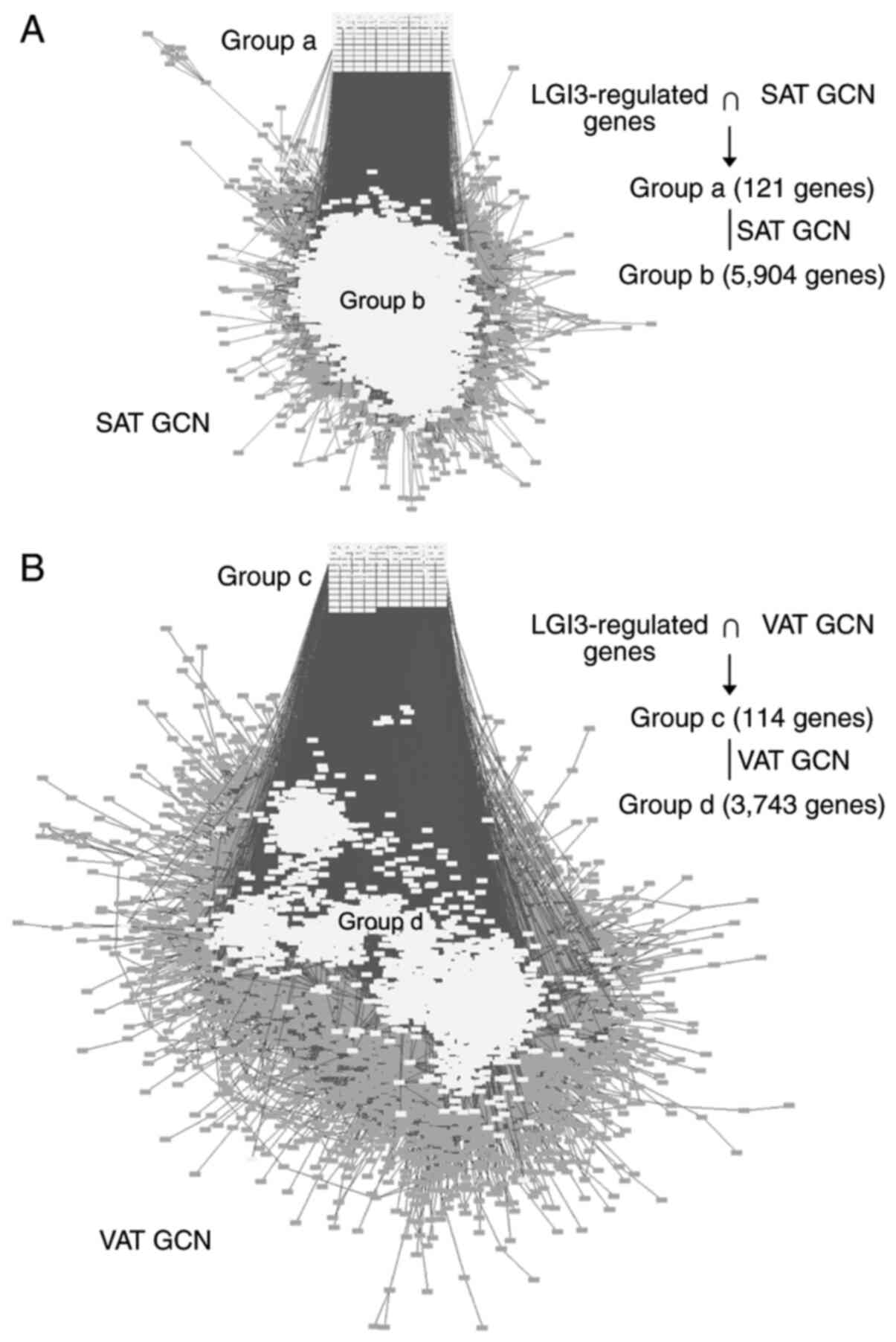
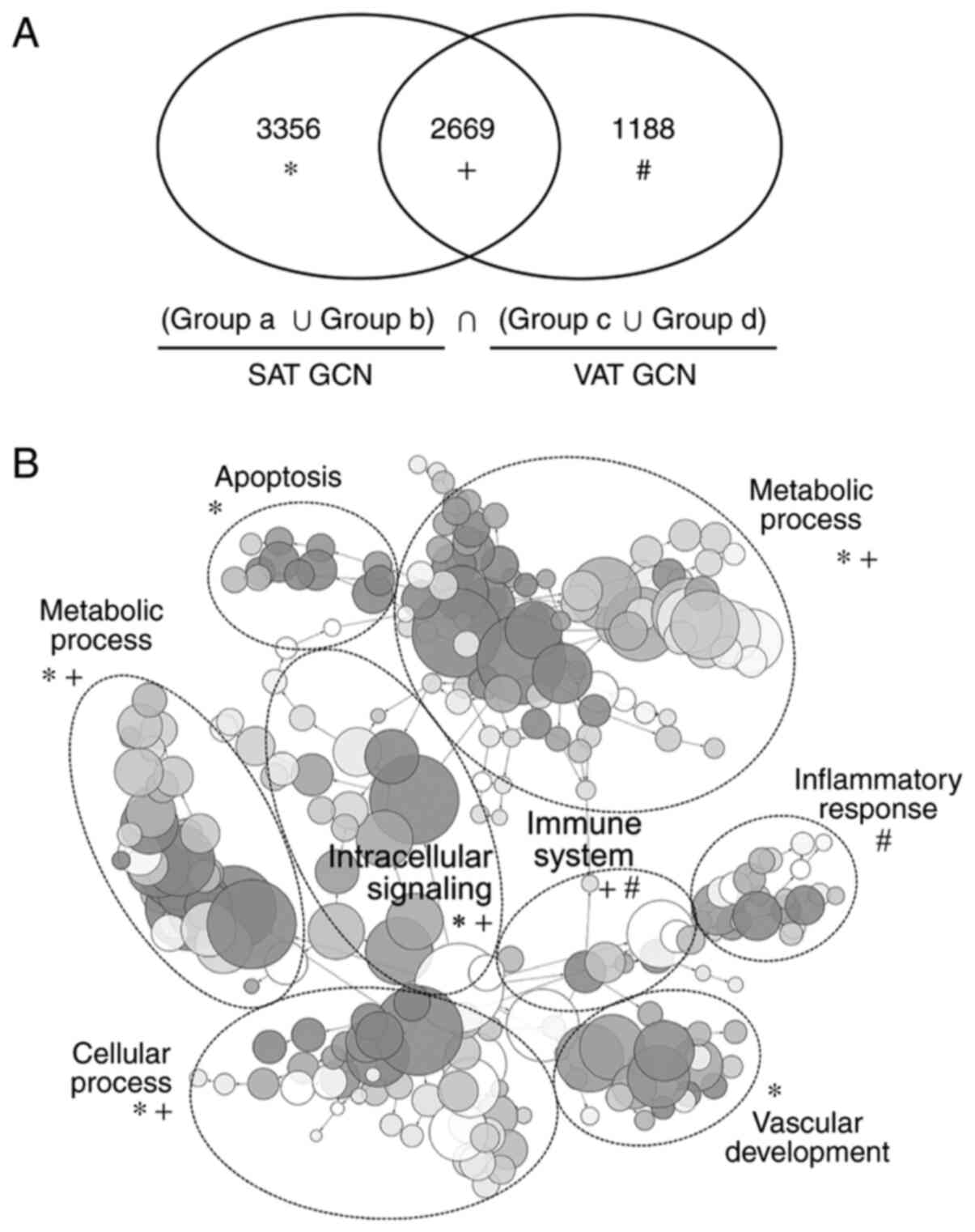
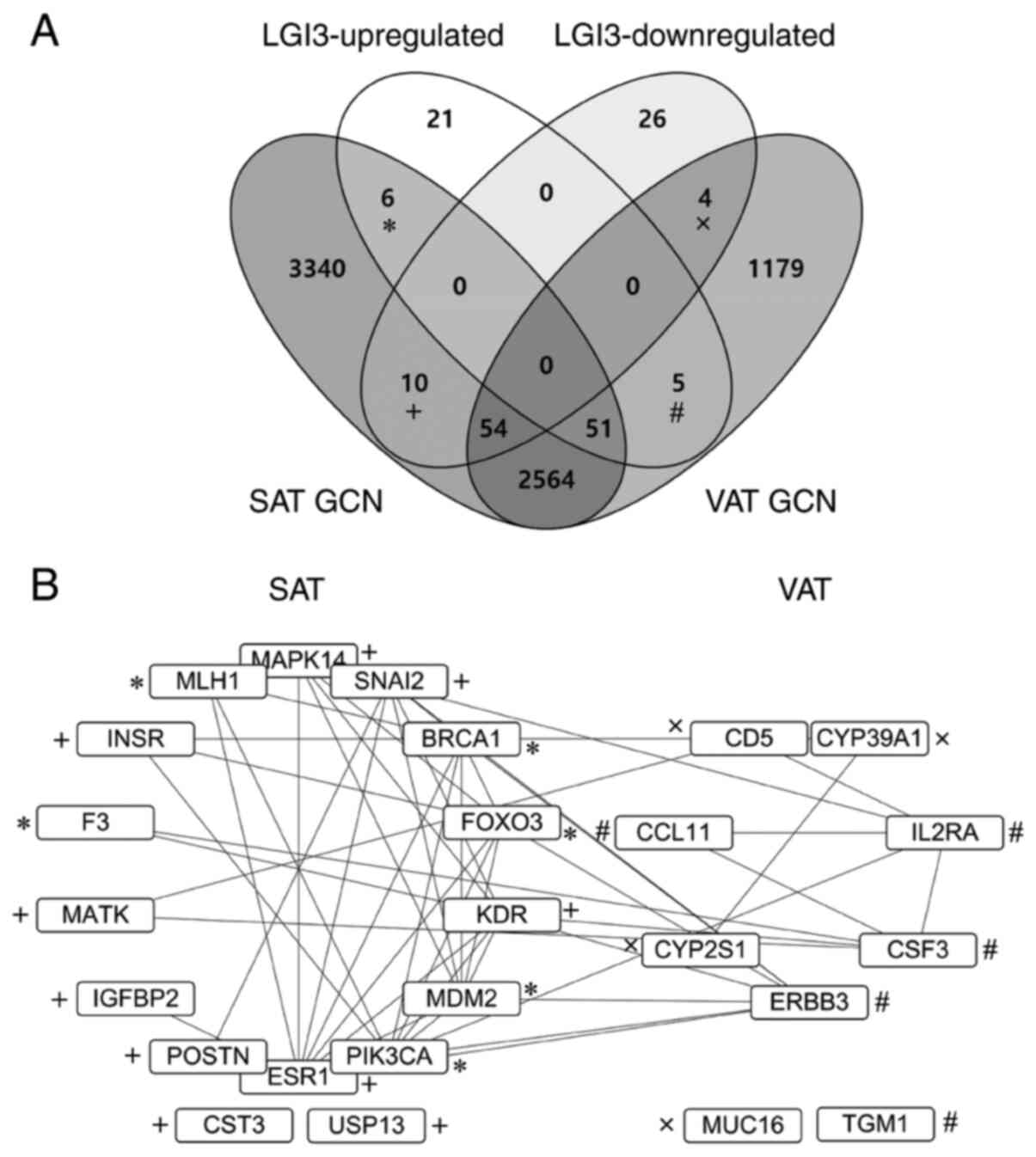
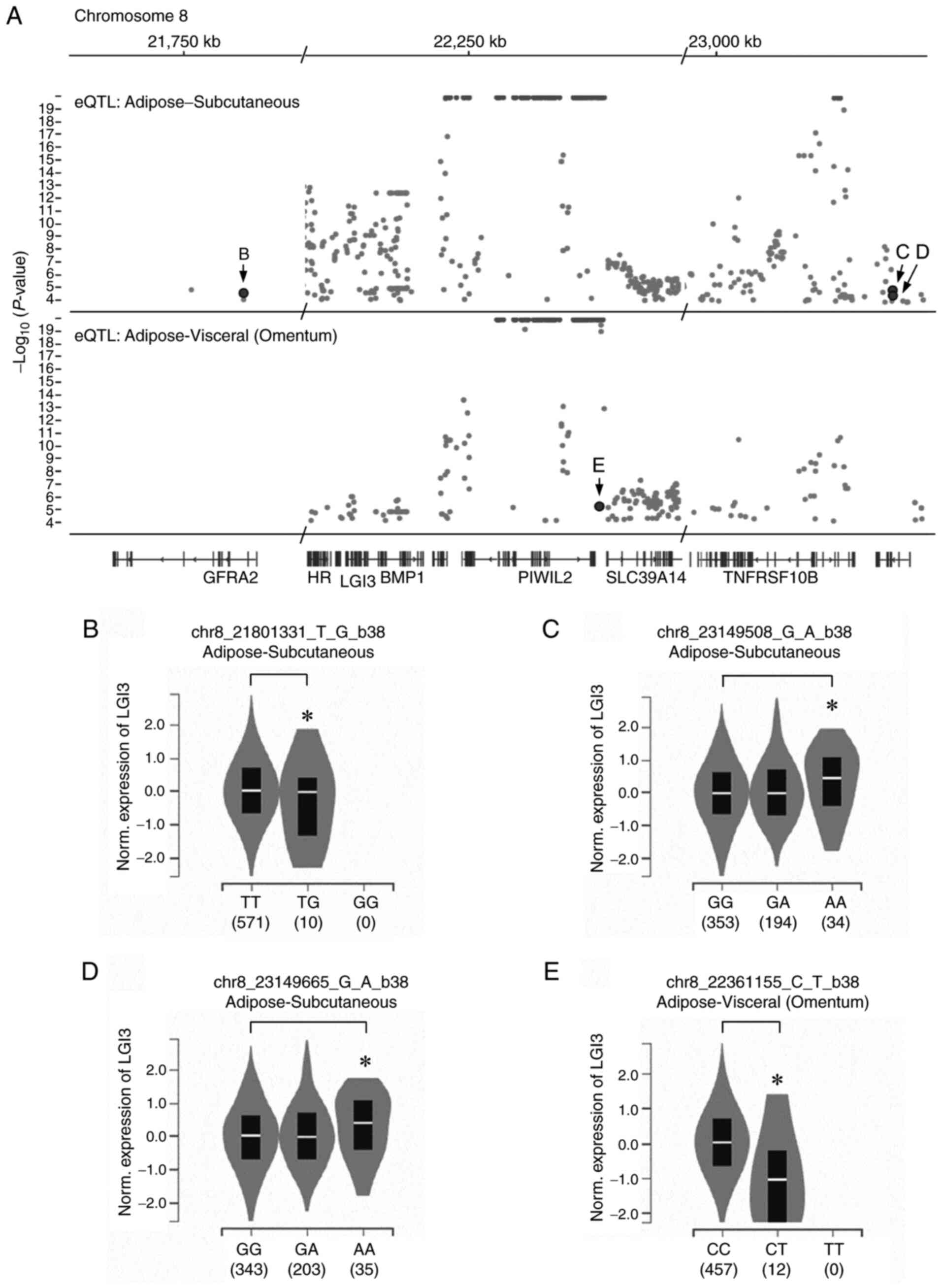
|
1
|
Lee SE, Lee AY, Park WJ, Jun DH, Kwon NS,
Baek KJ, Kim YG and Yun HY: Mouse LGI3 gene: Expression in brain
and promoter analysis. Gene. 372:8–17. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Park WJ, Lee SE, Kwon NS, Baek KJ, Kim DS
and Yun HY: Leucine-rich glioma inactivated 3 associates with
syntaxin 1. Neurosci Lett. 444:240–244. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Park WJ, Lim YY, Kwon NS, Baek KJ, Kim DS
and Yun HY: Leucine-rich glioma inactivated 3 induces neurite
outgrowth through Akt and focal adhesion kinase. Neurochem Res.
35:789–796. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lee SH, Jeong YM, Kim SY, Jeong HS, Park
KC, Baek KJ, Kwon NS, Yun HY and Kim DS: Ultraviolet B-induced LGI3
secretion protects human keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 21:716–718.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jeong YM, Park WJ, Kim MK, Baek KJ, Kwon
NS, Yun HY and Kim DS: Leucine-rich glioma inactivated 3 promotes
HaCaT keratinocyte migration. Wound Repair Regen. 21:634–640.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kim IW, Jeong HS, Kwon NS, Baek KJ, Yun HY
and Kim DS: LGI3 promotes human keratinocyte differentiation via
the Akt pathway. Exp Dermatol. 27:1224–1229. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kim US, Park JW, Park ES, Bang JS, Jung
TW, Kim DS, Abd El-Aty AM, Lee JH and Jeong JH: The suppressive
effect of leucine-rich glioma inactivated 3 (LGI3) peptide on
impaired skin barrier function in a murine model atopic dermatitis.
Pharmaceutics. 12(750)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee SH, Kwon NS, Baek KJ, Yun HY and Kim
DS: LGI3 is secreted and binds to ADAM22 via TRIF-dependent NF-κB
pathway in response to LPS in human keratinocytes. Cytokine.
126(154872)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jeong HS, Jeong YM, Kim J, Lee SH, Choi
HR, Park KC, Kim BJ, Baek KJ, Kwon NS, Yun HY and Kim DS:
Leucine-rich glioma inactivated 3 is a melanogenic cytokine in
human skin. Exp Dermatol. 23:600–602. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kwon NS, Baek KJ, Kim DS and Yun HY:
Leucine-rich glioma inactivated 3: Integrative analyses reveal its
potential prognostic role in cancer. Mol Med Rep. 17:3993–4002.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kwon NS, Kim DS and Yun HY: Leucine-rich
glioma inactivated 3: Integrative analyses support its prognostic
role in glioma. Onco Targets Ther. 10:2721–2728. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kim HA, Kwon NS, Baek KJ, Kim DS and Yun
HY: Leucine-rich glioma inactivated 3: Integrative analyses support
its role in the cytokine network. Int J Mol Med. 40:251–259.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim DS, Kwon NS and Yun HY: Leucine rich
repeat LGI family member 3: Integrative analyses reveal its
prognostic association with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett.
18:3388–3398. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kim HA, Park WJ, Jeong HS, Lee HE, Lee SH,
Kwon NS, Baek KJ, Kim DS and Yun HY: Leucine-rich glioma
inactivated 3 regulates adipogenesis through ADAM23. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1821:914–922. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim HA, Kwon NS, Baek KJ, Kim DS and Yun
HY: Leucine-rich glioma inactivated 3 associates negatively with
adiponectin. Cytokine. 62:206–209. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim HA, Kwon NS, Baek KJ, Kim DS and Yun
HY: Leucine-rich glioma inactivated 3 and tumor necrosis factor-α
regulate mutually through NF-κB. Cytokine. 72:220–223.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Animal research: Reporting of in vivo
experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines. Available from: https://arriveguidelines.org.
|
|
18
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lopes CT, Franz M, Kazi F, Donaldson SL,
Morris Q and Bader GD: Cytoscape web: An interactive web-based
network browser. Bioinformatics. 26:2347–2348. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Alvarez-Ponce D, Feyertag F and
Chakraborty S: Position matters: Network centrality considerably
impacts rates of protein evolution in the human protein-protein
interaction network. Genome Biol Evol. 9:1742–1756. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang dW, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lee S, Zhang C, Liu Z, Klevstig M,
Mukhopadhyay B, Bergentall M, Cinar R, Stahlman M, Sikanic N, Park
JK, et al: Network analyses identify liver-specific targets for
treating liver diseases. Mol Syst Biol. 13(938)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pratt D, Chen J, Welker D, Rivas R,
Pillich R, Rynkov V, Ono K, Miello C, Hicks L, Szalma S, et al:
NDEx, the network data exchange. Cell Syst. 1:302–305.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Maere S, Heymans K and Kuiper M: BiNGO: A
cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology
categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics. 21:3448–3449.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Thomas-Chollier M, Hufton A, Heinig M,
O'Keeffe S, Masri NE, Roider HG, Manke T and Vingron M:
Transcription factor binding predictions using TRAP for the
analysis of ChIP-seq data and regulatory SNPs. Nat Protoc.
6:1860–1869. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
GTEx Consortium: The genotype-tissue
expression (GTEx) project. Nat Genet. 45:580–585. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Stuart JM, Segal E, Koller D and Kim SK: A
gene-coexpression network for global discovery of conserved genetic
modules. Science. 302:249–255. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang Q, Lenardo MJ and Baltimore D: 30
years of NF-κB: A blossoming of relevance to human pathobiology.
Cell. 168:37–57. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sabir JS, El Omri A, Shaik NA,
Banaganapalli B, Al-Shaeri MA, Alkenani NA, Hajrah NH, Awan ZA,
Zrelli H, Elango R and Khan M: Identification of key regulatory
genes connected to NF-κB family of proteins in visceral adipose
tissues using gene expression and weighted protein interaction
network. PLoS One. 14(e0214337)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Verbisck NV, Costa ET, Costa FF, Cavalher
FP, Costa MD, Muras A, Paixão VA, Moura R, Granato MF, Ierardi DF,
et al: ADAM23 negatively modulates alpha(v)beta(3) integrin
activation during metastasis. Cancer Res. 69:5546–5552.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Antonov AS, Antonova GN, Munn DH, Mivechi
N, Lucas R, Catravas JD and Verin AD: αVβ3 integrin regulates
macrophage inflammatory responses via PI3 kinase/Akt-dependent
NF-κB activation. J Cell Physiol. 226:469–476. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Huang XF and Chen JZ: Obesity, the
PI3K/Akt signal pathway and colon cancer. Obes Rev. 10:610–616.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mauer J, Chaurasia B, Goldau J, Vogt MC,
Ruud J, Nguyen KD, Theurich S, Hausen AC, Schmitz J, Brönneke HS,
et al: Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of
macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance
to insulin. Nat Immunol. 15:423–430. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yokoyama M, Okada S, Nakagomi A, Moriya J,
Shimizu I, Nojima A, Yoshida Y, Ichimiya H, Kamimura N, Kobayashi
Y, et al: Inhibition of endothelial p53 improves metabolic
abnormalities related to dietary obesity. Cell Rep. 7:1691–1703.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Adachi H, Kurachi H, Homma H, Adachi K,
Imai T, Sakata M, Matsuzawa Y and Miyake A: Involvement of
epidermal growth factor in inducing adiposity of age female mice. J
Endocrinol. 146:381–393. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS and
Spiegelman BM: Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha:
Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science.
259:87–91. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lukjanenko L, Jung MJ, Hegde N,
Perruisseau-Carrier C, Migliavacca E, Rozo M, Karaz S, Jacot G,
Schmidt M, Li L, et al: Loss of fibronectin from the aged stem cell
niche affects the regenerative capacity of skeletal muscle in mice.
Nat Med. 22:897–905. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Jager J, Corcelle V, Grémeaux T, Laurent
K, Waget A, Pagès G, Binétruy B, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Burcelin R,
Bost F and Tanti JF: Deficiency in the extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) protects leptin-deficient mice
from insulin resistance without affecting obesity. Diabetologia.
54:180–189. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Donohoe F, Wilkinson M, Baxter E and
Brennan DJ: Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and
obesity-related cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21(1241)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pal A, Barber TM, Van de Bunt M, Rudge SA,
Zhang Q, Lachlan KL, Cooper NS, Linden H, Levy JC, Wakelam MJ, et
al: PTEN mutations as a cause of constitutive insulin sensitivity
and obesity. N Engl J Med. 367:1002–1011. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Berryman DE, Glad CA, List EO and
Johannsson G: The GH/IGF-1 axis in obesity: Pathophysiology and
therapeutic considerations. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 9:346–356.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zhang X, Xu A, Chung SK, Cresser JH,
Sweeney G, Wong RL, Lin A and Lam KS: Selective inactivation of
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase in adipose tissue protects against
diet-induced obesity and improves insulin sensitivity in both liver
and skeletal muscle in mice. Diabetes. 60:486–495. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Rull A, Camps J, Alonso-Villaverde C and
Joven J: Insulin resistance, inflammation, and obesity: Role of
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (or CCL2) in the regulation of
metabolism. Mediators Inflamm. 2010(326580)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cai H, Dong LQ and Liu F: Recent advances
in adipose mTOR signaling and function: Therapeutic prospects.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 37:303–317. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chen M, Lu P, Ma Q, Cao Y, Chen N, Li W,
Zhao S, Chen B, Shi J, Sun Y, et al: CTNNB1/β-catenin dysfunction
contributes to adiposity by regulating the cross-talk of mature
adipocytes and preadipocytes. Sci Adv. 6(eaax9605)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Matesanz N, Nikolic I, Leiva M,
Pulgarin-Alfaro M, Santamans AM, Bernardo E, Mora A, Herrera-Melle
L, Rodriguez E, Beiroa D, et al: p38α blocks brown adipose tissue
thermogenesis through p38δ inhibition. PLoS Biol.
16(e2004455)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Fatima LA, Campello RS, Santos RS, Freitas
HS, Frank AP, Machado UF and Clegg DJ: Estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1)
regulates VEGFA in adipose tissue. Sci Rep. 7(16716)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kubota T, Kubota N and Kadowaki T:
Imbalanced insulin actions in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Key
mouse models of insulin signaling pathway. Cell Metab. 25:797–810.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ray A: Tumor-linked HER2 expression:
Association with obesity and lipid-related microenvironment. Horm
Mol Biol Clin Investig. 32:2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Huang X, Liu G, Guo J and Su Z: The
PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Biol Sci.
14:1483–1496. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lefterova MI, Haakonsson AK, Lazar MA and
Mandrup S: PPARγ and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 25:293–302. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Antonopoulos AS, Margaritis M, Coutinho P,
Shirodaria C, Psarros C, Herdman L, Sanna F, De Silva R, Petrou M,
Sayeed R, et al: Adiponectin as a link between type 2 diabetes and
vascular NADPH oxidase activity in the human arterial wall: The
regulatory role of perivascular adipose tissue. Diabetes.
64:2207–2219. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Du J, Fan LM, Mai A and Li JM: Crucial
roles of Nox2-derived oxidative stress in deteriorating the
function of insulin receptors and endothelium in dietary obesity of
middle-aged mice. Br J Pharmacol. 170:1064–1077. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Fernandez-Twinn DS, Blackmore HL, Siggens
L, Giussani DA, Cross CM, Foo R and Ozanne SE: The programming of
cardiac hypertrophy in the offspring by maternal obesity is
associated with hyperinsulinemia, AKT, ERK, and mTOR activation.
Endocrinology. 153:5961–5971. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K,
Hiasa K, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Miyachi H, Maeda S, Egashira K and
Kasuga M: MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose
tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J
Clin Invest. 116:1494–1505. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kapur S, Marcotte B and Marette A:
Mechanism of adipose tissue iNOS induction in endotoxemia. Am J
Physiol. 276:E635–E641. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Pietiläinen KH, Kannisto K,
Korsheninnikova E, Rissanen A, Kaprio J, Ehrenborg E, Hamsten A and
Yki-Järvinen H: Acquired obesity increases CD68 and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha and decreases adiponectin gene expression in adipose
tissue: A study in monozygotic twins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
91:2776–2781. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Ronis MJ, Sharma N, Vantrease J,
Borengasser SJ, Ferguson M, Mercer KE, Cleves MA, Gomez-Acevedo H
and Badger TM: Female mice lacking p47phox have altered adipose
tissue gene expression and are protected against high fat-induced
obesity. Physiol Genomics. 45:351–366. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Sindhu S, Thomas R, Shihab P, Sriraman D,
Behbehani K and Ahmad R: Obesity is a positive modulator of IL-6R
and IL-6 expression in the subcutaneous adipose tissue:
Significance for metabolic inflammation. PLoS One.
10(e0133494)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Uchida K, Satoh M, Inoue G, Onuma K,
Miyagi M, Iwabuchi K and Takaso M: CD11c(+) macrophages and levels
of TNF-α and MMP-3 are increased in synovial and adipose tissues of
osteoarthritic mice with hyperlipidaemia. Clin Exp Immunol.
180:551–559. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum
M, Leibel RL and Ferrante AW Jr: Obesity is associated with
macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest.
112:1796–1808. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Min JL, Nicholson G, Halgrimsdottir I,
Almstrup K, Petri A, Barrett A, Travers M, Rayner NW, Mägi R,
Pettersson FH, et al: Coexpression network analysis in abdominal
and gluteal adipose tissue reveals regulatory genetic loci for
metabolic syndrome and related phenotypes. PLoS Genet.
8(e1002505)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Skinkyte-Juskiene R, Kogelman LJ and
Kadarmideen HN: Transcription factor co-expression networks of
adipose RNA-seq data reveal regulatory mechanisms of obesity. Curr
Genomics. 19:289–299. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Lumeng CN, DelProposto JB, Westcott DJ and
Saltiel AR: Phenotypic switching of adipose tissue macrophages with
obesity is generated by spatiotemporal differences in macrophage
subtypes. Diabetes. 57:3239–3246. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Appari M, Channon KM and McNeill E:
Metabolic regulation of adipose tissue macrophage function in
obesity and diabetes. Antioxid Redox Signal. 29:297–312.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Morris DL, Singer K and Lumeng CN: Adipose
tissue macrophages: Phenotypic plasticity and diversity in lean and
obese states. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 14:341–346.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Mathis D: Immunological goings-on in
visceral adipose tissue. Cell Metab. 17:851–859. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|