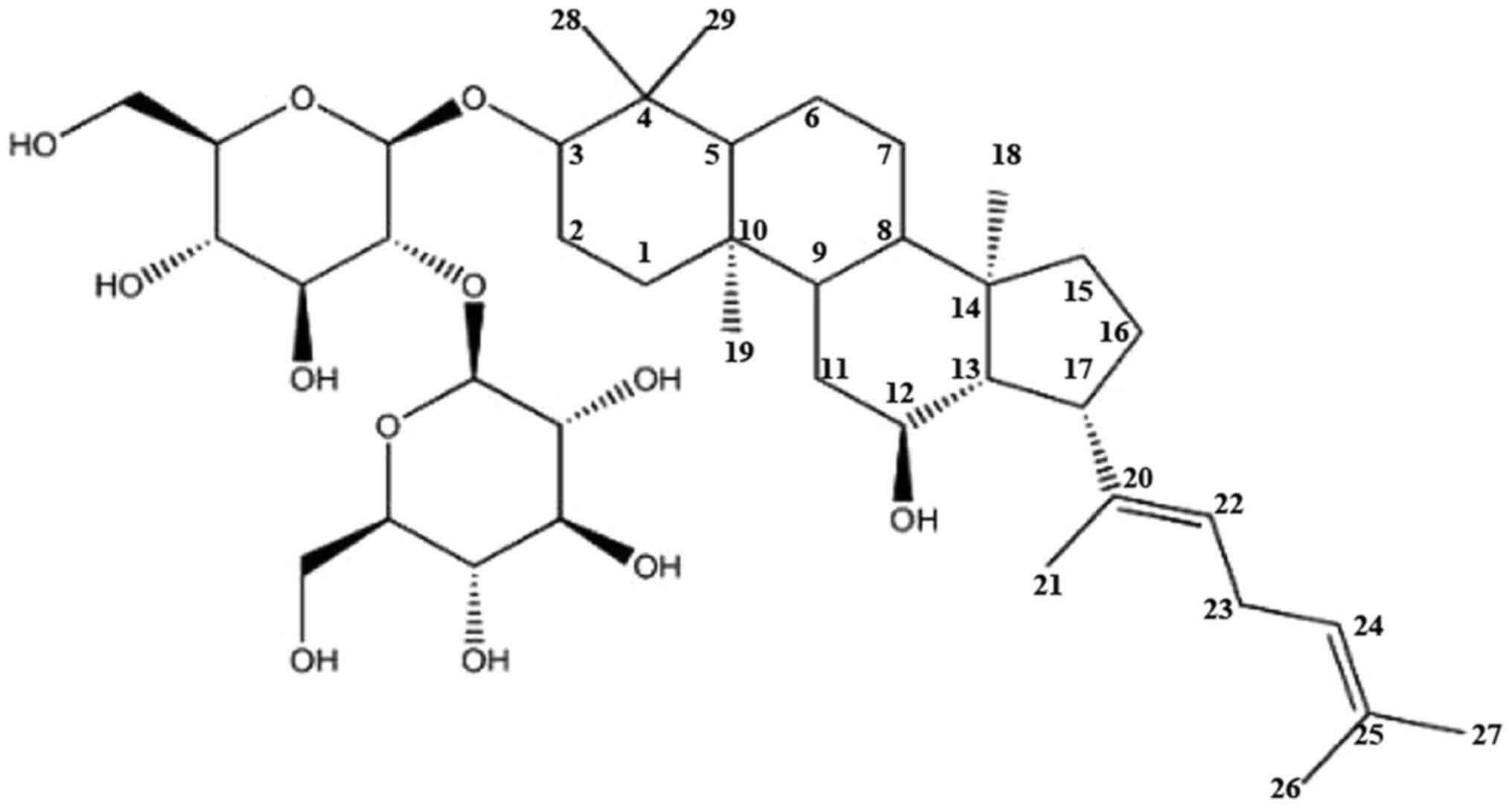
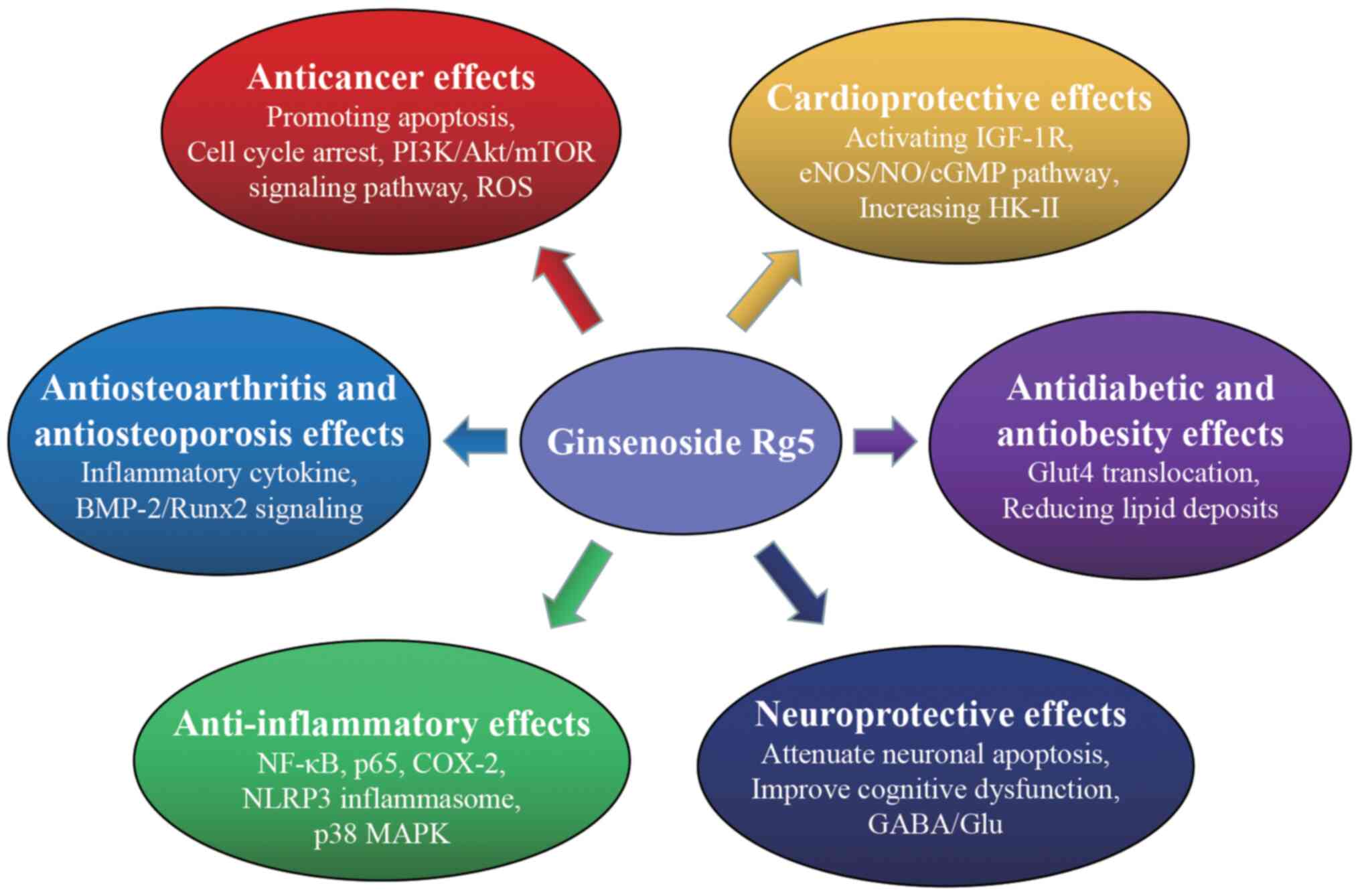
|
1
|
De Souza LR, Jenkins AL, Sievenpiper JL,
Jovanovski E, Rahelić D and Vuksan V: Korean red ginseng (Panax
ginseng C.A. Meyer) root fractions: Differential effects on
postprandial glycemia in healthy individuals. J Ethnopharmacol.
137:245–250. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhou QL, Zhu DN, Yang YF, Xu W and Yang
XW: Simultaneous quantification of twenty-one ginsenosides and
their three aglycones in rat plasma by a developed UFLC-MS/MS
assay: Application to a pharmacokinetic study of red ginseng. J
Pharm Biomed Anal. 137:1–12. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Christensen LP: Ginsenosides chemistry,
biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects. Adv Food Nutr
Res. 55:1–99. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shi W, Wang Y, Li J, Zhang H and Ding L:
Investigation of ginsenosides in different parts and ages of
Panax ginseng. Food Chem. 102:664–668. 2007.
|
|
5
|
Chen RJ, Chung TY, Li FY, Lin NH and Tzen
JTC: Effect of sugar positions in ginsenosides and their inhibitory
potency on Na+/K+-ATPase activity. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:61–69.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shin BK, Kwon SW and Park JH: Chemical
diversity of ginseng saponins from Panax ginseng. J Ginseng
Res. 39:287–298. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shin KC and Oh DK: Classification of
glycosidases that hydrolyze the specific positions and types of
sugar moieties in ginsenosides. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 36:1036–1049.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jin S, Jeon JH, Lee S, Kang WY, Seong SJ,
Yoon YR, Choi MK and Song IS: Detection of 13 ginsenosides (Rb1,
Rb2, Rc, Rd, Re, Rf, Rg1, Rg3, Rh2, F1, compound K,
20(S)-protopanaxadiol, and 20(S)-protopanaxatriol) in human plasma
and application of the analytical method to human pharmacokinetic
studies following two week-repeated administration of red ginseng
extract. Molecules. 24(2618)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cui CH, Jeon BM, Fu Y, Im WT and Kim SC:
High-density immobilization of a ginsenoside-transforming
β-glucosidase for enhanced food-grade production of minor
ginsenosides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 103:7003–7015.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Noh KH and Oh DK: Production of the rare
ginsenosides compound K, compound Y, and compound Mc by a
thermostable beta-glycosidase from sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Biol
Pharm Bull. 32:1830–1835. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liang LD, He T, Du TW, Fan YG, Chen DS and
Wang Y: Ginsenoside-Rg5 induces apoptosis and DNA damage in human
cervical cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:940–946. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Qi LW, Wang CZ and Yuan CS: Ginsenosides
from American ginseng: Chemical and pharmacological diversity.
Phytochemistry. 72:689–699. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim JH, Yi YS, Kim MY and Cho JY: Role of
ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng,
in inflammatory responses and diseases. J Ginseng Res. 41:435–443.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu Y and Fan D: The preparation of
ginsenoside Rg5, its antitumor activity against breast cancer cells
and its targeting of PI3K. Nutrients. 12(246)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim SJ and Kim AK: Anti-breast cancer
activity of fine black ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) and
ginsenoside Rg5. J Ginseng Res. 39:125–134. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zou Y and Liu P: Ginsenoside-Rg5 inhibits
proliferation of the breast carcinoma cells through promotion of
the proteins involved in AMP kinase pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med.
9:17664–17669. 2016.
|
|
17
|
Liu Y and Fan D: Ginsenoside Rg5 induces
apoptosis and autophagy via the inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway
against breast cancer in a mouse model. Food Funct. 9:5513–5527.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu Y and Fan D: Ginsenoside Rg5 induces
G2/M phase arrest, apoptosis and autophagy via regulating
ROS-mediated MAPK pathways against human gastric cancer. Biochem
Pharmacol. 168:285–304. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jin HS, Suh HW, Kim SJ and Jo EK:
Mitochondrial control of innate immunity and inflammation. Immune
Netw. 17:77–88. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Medzhitov R: Origin and physiological
roles of inflammation. Nature. 454:428–435. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Harrison DJ, Geller DS, Gill JD, Lewis VO
and Gorlick R: Current and future therapeutic approaches for
osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 18:39–50. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Akram M, Iqbal M, Daniyal M and Khan AU:
Awareness and current knowledge of breast cancer. Biol Res.
50(33)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sun M, Ye Y, Xiao L, Duan X, Zhang Y and
Zhang H: Anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg3 (Review). Int J Mol
Med. 39:507–518. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Baldo BA and Pham NH: Adverse reactions to
targeted and non-targeted chemotherapeutic drugs with emphasis on
hypersensitivity responses and the invasive metastatic switch.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 32:723–761. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Majeed F, Malik FZ, Ahmed Z, Afreen A,
Afzal MN and Khalid N: Ginseng phytochemicals as therapeutics in
oncology: Recent perspectives. Biomed Pharmacother. 100:52–63.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Nakhjavani M, Hardingham JE, Palethorpe
HM, Tomita Y, Smith E, Price TJ and Townsend AR: Ginsenoside Rg3:
Potential molecular targets and therapeutic indication in
metastatic breast cancer. Medicines (Basel). 6(17)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang D, Wang A, Feng J, Zhang Q, Liu L
and Ren H: Ginsenoside Rg5 induces apoptosis in human esophageal
cancer cells through the phosphoinositide-3 kinase/protein kinase B
signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 19:4019–4026. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang YS, Li H, Li Y, Zhu H and Jin YH:
Identification of natural compounds targeting annexin A2 with an
anti-cancer effect. Protein Cell. 9:568–579. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lee KH, Lee YH, Kim SI, Park JH and Lee
SK: Ginsenoside-Rg5 suppresses cyclin E-dependent protein kinase
activity via up-regulating p21Cip/WAF1 and down-regulating cyclin E
in SK-HEP-1 cells. Anticancer Res. 17:1067–1072. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cui Y, Su Y, Deng L and Wang W:
Ginsenoside-Rg5 inhibits retinoblastoma proliferation and induces
apoptosis through suppressing BCL2 expression. Chemotherapy.
63:293–300. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Feng SL, Luo HB, Cai L, Zhang J, Wang D,
Chen YJ, Zhan HX, Jiang ZH and Xie Y: Ginsenoside Rg5 overcomes
chemotherapeutic multidrug resistance mediated by ABCB1
transporter: In vitro and in vivo study. J Ginseng Res. 44:247–257.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Dong Y, Fu R, Yang J, Ma P, Liang L, Mi Y
and Fan D: Folic acid-modified ginsenoside Rg5-loaded bovine serum
albumin nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy in vitro and in
vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 14:6971–6988. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bortolotti P, Faure E and Kipnis E:
Inflammasomes in tissue damages and immune disorders after trauma.
Front Immunol. 9(1900)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yi YS: Roles of ginsenosides in
inflammasome activation. J Ginseng Res. 43:172–178. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kim TW, Joh EH, Kim B and Kim DH:
Ginsenoside Rg5 ameliorates lung inflammation in mice by inhibiting
the binding of LPS to toll-like receptor-4 on macrophages. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:110–116. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Park JY, Choi P, Kim T, Ko H, Kim HK, Kang
KS and Ham J: Protective effects of processed ginseng and its
active ginsenosides on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: In vitro
and in vivo studies. J Agric Food Chem. 63:5964–5969.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li W, Yan M, Liu Y, Liu Z, Wang Z, Chen C,
Zhang J and Sun YS: Ginsenoside Rg5 ameliorates cisplatin-induced
nephrotoxicity in mice through inhibition of inflammation,
oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Nutrients. 8(566)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lee SM: Anti-inflammatory effects of
ginsenosides Rg5, Rz1, and Rk1: Inhibition of TNF-α-induced NF-κB,
COX-2, and iNOS transcriptional expression. Phytother Res.
28:1893–1896. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang Z, Hu JN, Yan MH, Xing JJ, Liu WC and
Li W: Caspase-mediated anti-apoptotic effect of ginsenoside Rg5, a
main rare ginsenoside, on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in
mice. J Agric Food Chem. 65:9226–9236. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhu Y, Zhu C, Yang H, Deng J and Fan D:
Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg5 against kidney injury via
inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and the MAPK signaling
pathway in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.
Pharmacol Res. 155(104746)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M and Rhodes A:
Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet. 392:75–87. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Andersson U, Wang H, Palmblad K, Aveberger
AC, Bloom O, Erlandsson-Harris H, Janson A, Kokkola R, Zhang M,
Yang H and Tracey KJ: High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1)
stimulates proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in human monocytes. J
Exp Med. 192:565–570. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Bae JS: Role of high mobility group box 1
in inflammatory disease: Focus on sepsis. Arch Pharm Res.
35:1511–1523. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kim JE, Lee W, Yang S, Cho SH, Baek MC,
Song GY and Bae JS: Suppressive effects of rare ginsenosides, Rk1
and Rg5, on HMGB1-mediated septic responses. Food Chem Toxicol.
124:45–53. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Shin YW, Bae EA and Kim DH: Inhibitory
effect of ginsenoside Rg5 and its metabolite ginsenoside Rh3 in an
oxazolone-induced mouse chronic dermatitis model. Arch Pharm Res.
29:685–690. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ahn S, Siddiqi MH, Aceituno VC, Simu SY,
Zhang J, Jimenez Perez ZE, Kim YJ and Yang DC: Ginsenoside Rg5:Rk1
attenuates TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced production of thymus- and
activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17) and LPS-induced NO
production via downregulation of NF-κB/p38 MAPK/STAT1 signaling in
human keratinocytes and macrophages. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
52:287–295. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chu S, Gu J, Feng L, Liu J, Zhang M, Jia
X, Liu M and Yang D: Ginsenoside Rg5 improves cognitive dysfunction
and beta-amyloid deposition in STZ-induced memory impaired rats via
attenuating neuroinflammatory responses. Int Immunopharmacol.
19:317–326. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Cheng Z, Zhang M, Ling C, Zhu Y, Ren H,
Hong C, Qin J, Liu T and Wang J: Neuroprotective effects of
ginsenosides against cerebral ischemia. Molecules.
24(1102)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lee YY, Park JS, Jung JS, Kim DH and Kim
HS: Anti-inflammatory effect of ginsenoside Rg5 in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Int J Mol Sci.
14:9820–9833. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Liu FF, Zhang Z, Chen W, Gu HY and Yan QJ:
Regulatory mechanism of microRNA-377 on CDH13 expression in the
cell model of Alzheimer's disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:2801–2808. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Bolognin S, Blanchard J, Wang X,
Basurto-Islas G, Tung YC, Kohlbrenner E, Grundke-Iqbal I and Iqbal
K: An experimental rat model of sporadic Alzheimer's disease and
rescue of cognitive impairment with a neurotrophic peptide. Acta
Neuropathol. 123:133–151. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Tao X, Finkbeiner S, Arnold D, Shaywitz A
and Greenberg M: Ca2+ influx regulates BDNF
transcription by a CREB family transcription factor-dependent
mechanism. Neuron. 20:709–726. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Bourtchuladze R, Frenguelli B, Blendy J,
Cioffi D, Schutz G and Silva A: Deficient long-term memory in mice
with a targeted mutation of the cAMP-responsive element-binding
protein. Cell. 79:59–68. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kim EJ, Jung IH, Van Le TK, Jeong JJ, Kim
NJ and Kim DH: Ginsenosides Rg5 and Rh3 protect scopolamine-induced
memory deficits in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 146:294–299.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Choi SY, Kim KJ, Song JH and Lee BY:
Ginsenoside Rg5 prevents apoptosis by modulating
heme-oxygenase-1/nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 signaling and
alters the expression of cognitive impairment-associated genes in
thermal stress-exposed HT22 cells. J Ginseng Res. 42:225–228.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wu J, Jeong HK, Bulin SE, Kwon SW, Park JH
and Bezprozvanny I: Ginsenosides protect striatal neurons in a
cellular model of Huntington's disease. J Neurosci Res.
87:1904–1912. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Shao J, Zheng X, Qu L, Zhang H, Yuan H,
Hui J, Mi Y, Ma P and Fan D: Ginsenoside Rg5/Rk1 ameliorated sleep
via regulating the GABAergic/serotoninergic signaling pathway in a
rodent model. Food Funct. 11:1245–1257. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Yuan CS, Attele AS, Wu JA and Liu D:
Modulation of American ginseng on brainstem GABAergic effects in
rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 62:215–222. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Sattler R and Tymianski M: Molecular
mechanisms of glutamate receptor-mediated excitotoxic neuronal cell
death. Mol Neurobiol. 24:107–129. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Yuan Q, Joiner WJ and Sehgal A: A
sleep-promoting role for the Drosophila serotonin receptor 1A. Curr
Biol. 16:1051–1062. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Cho YL, Hur SM, Kim JY, Kim JH, Lee DK,
Choe J, Won MH, Ha KS, Jeoung D, Han S, et al: Specific activation
of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor by ginsenoside Rg5
promotes angiogenesis and vasorelaxation. J Biol Chem. 290:467–477.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Yang YL, Li J, Liu K, Zhang L, Liu Q, Liu
B and Qi LW: Ginsenoside Rg5 increases cardiomyocyte resistance to
ischemic injury through regulation of mitochondrial hexokinase-II
and dynamin-related protein 1. Cell Death Dis.
8(e2625)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski Ł and
Szukiewicz D: The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory
cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm.
2014(561459)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Cheng W, Jing J, Wang Z, Wu D and Huang Y:
Chondroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 in human
osteoarthritis chondrocytes and a rat model of anterior cruciate
ligament transection. Nutrients. 9(263)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Chen Y, Lin S, Sun Y, Pan X, Xiao L, Zou
L, Ho KW and Li G: Translational potential of ginsenoside Rb1 in
managing progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 6:27–33.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Zhang P: Ginsenoside-Rg5 treatment
inhibits apoptosis of chondrocytes and degradation of cartilage
matrix in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Oncol Rep. 37:1497–1502.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Wang T, Liu Q, Tjhioe W, Zhao J, Lu A,
Zhang G, Tan RX, Zhou M, Xu J and Feng HT: Therapeutic potential
and outlook of alternative medicine for osteoporosis. Current Drug
Targets. 18:1051–1068. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Siddiqi MH, Siddiqi MZ, Ahn S, Kang S, Kim
YJ, Veerappan K, Yang DU and Yang DC: Stimulative effect of
ginsenosides Rg5:Rk1 on murine osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells.
Phytother Res. 28:1447–1455. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Ponnuraj SP, Siraj F, Kang S, Noh HY, Min
JW, Kim YJ and Yang DC: Amelioration of insulin resistance by Rk1 +
Rg5 complex under endoplasmic reticulum stress conditions.
Pharmacognosy Res. 6:292–296. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Xiao N, Lou MD, Lu YT, Yang LL, Liu Q, Liu
B, Qi LW and Li P: Ginsenoside Rg5 attenuates hepatic glucagon
response via suppression of succinate-associated HIF-1α induction
in HFD-fed mice. Diabetologia. 60:1084–1093. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Xiao N, Yang LL, Yang YL, Liu LW, Li J,
Liu B, Liu K, Qi LW and Li P: Ginsenoside Rg5 inhibits
succinate-associated lipolysis in adipose tissue and prevents
muscle insulin resistance. Front Pharmacol. 8(43)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Bai L, Gao J, Wei F, Zhao J, Wang D and
Wei J: Therapeutic potential of ginsenosides as an adjuvant
treatment for diabetes. Front Pharmacol. 9(423)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Park HJ, Kim JH and Shim I: Anti-obesity
effects of ginsenosides in high-fat diet-fed rats. Chin J Integr
Med. 25:895–901. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Liu H, Liu M, Jin Z, Yaqoob S, Zheng M,
Cai D, Liu J and Guo S: Ginsenoside Rg2 inhibits adipogenesis in
3T3-L1 preadipocytes and suppresses obesity in
high-fat-diet-induced obese mice through the AMPK pathway. Food
Funct. 10:3603–3614. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Liu H, Wang J, Liu M, Zhao H, Yaqoob S,
Zheng M, Cai D and Liu J: Antiobesity effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on
3T3-L1 preadipocytes and high fat diet-induced obese mice mediated
by AMPK. Nutrients. 10(830)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Zhang L, Zhang L, Wang X and Si H:
Anti-adipogenic effects and mechanisms of ginsenoside Rg3 in
pre-adipocytes and obese mice. Front Pharmacol.
8(113)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Yesmin Simu S, Ahn S, Castro-Aceituno V
and Yang DC: Ginsenoside Rg5: Rk1 exerts an anti-obesity effect on
3T3-L1 Cell Line by the downregulation of PPARγ and CEBPα. Iran J
Biotechnol. 15:252–259. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|